Acid-Base Properties of Amino Acids
advertisement

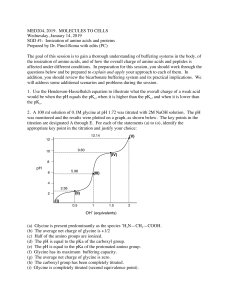
Acid-Base Properties of Amino Acids All of the amino acids are _____________ (they are ampholytes). They can act as either an ______________. Recall groups present. ____ pH - fully ____________________ ________ pH - _____________ as pH __________ at a group’s pKa half of the molecules will be protonated and half deprotonated (an equilibrium) _______ pH - fully ________________________ Example: Glycine pKaCOOH = 2.4 pKaNH2 = 9.8 Example: Lysine pKaCOOH = 2.2 pKaNH2 = 9.1 pKaR = 10.5 Forms of lysine present from low to high pH – circle the zwitterion Example: Aspartate pKaCOOH = 2.0 pKaNH2 = 9.9 pKaR = 3.9 Forms of aspartate present from low to high pH – circle the zwitterion ________________ – pH where zwitterion predominates (on average the amino acid is neutral here;charge = 0). Symbol:____________ pI is important in isoelectric focusing. For amino acids with non-ionizable side chains (Rgroups) pI is the average of the pKa’s of the amino and carboxylic groups Example: Glycine pI = For amino acids with ionizable side chains (R-groups) pI is the average of the two closest pKa’s Example: Lysine pI = Example: Aspartate pI = Look back at the species present at pH = 9.8 to see why this is the isoelectric point.