Chapter 4 Study Guide
advertisement
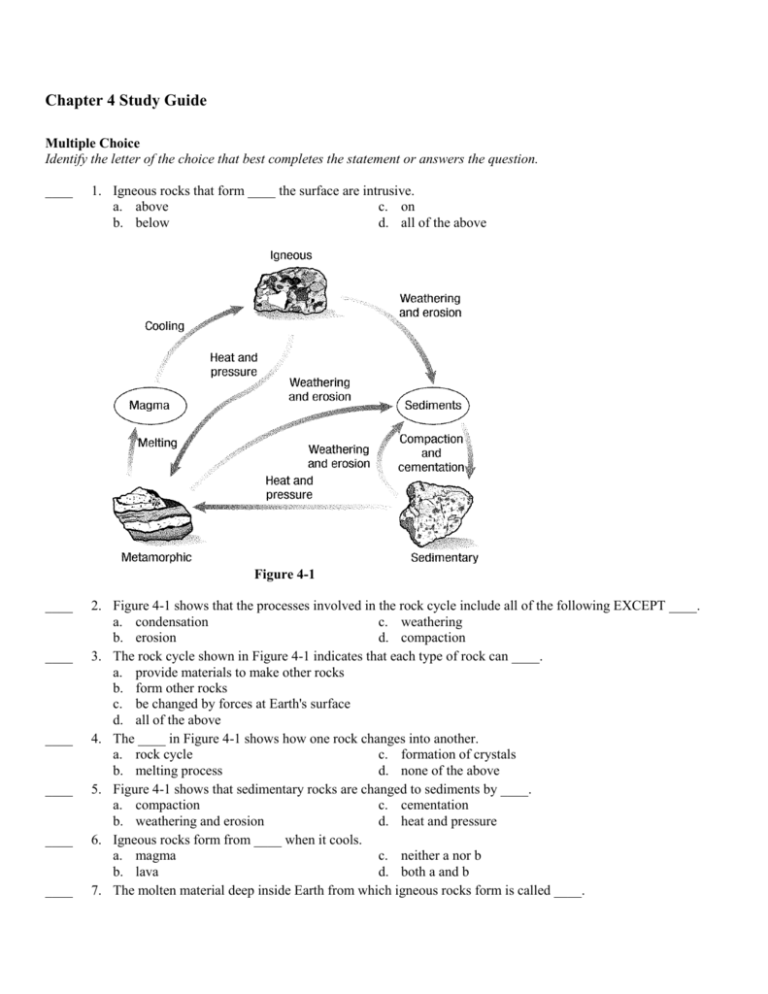
Chapter 4 Study Guide Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. ____ 1. Igneous rocks that form ____ the surface are intrusive. a. above c. on b. below d. all of the above Figure 4-1 ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ 2. Figure 4-1 shows that the processes involved in the rock cycle include all of the following EXCEPT ____. a. condensation c. weathering b. erosion d. compaction 3. The rock cycle shown in Figure 4-1 indicates that each type of rock can ____. a. provide materials to make other rocks b. form other rocks c. be changed by forces at Earth's surface d. all of the above 4. The ____ in Figure 4-1 shows how one rock changes into another. a. rock cycle c. formation of crystals b. melting process d. none of the above 5. Figure 4-1 shows that sedimentary rocks are changed to sediments by ____. a. compaction c. cementation b. weathering and erosion d. heat and pressure 6. Igneous rocks form from ____ when it cools. a. magma c. neither a nor b b. lava d. both a and b 7. The molten material deep inside Earth from which igneous rocks form is called ____. ____ 8. ____ 9. ____ 10. ____ 11. ____ 12. ____ 13. ____ 14. ____ 15. ____ 16. ____ 17. ____ 18. ____ 19. a. magma c. neither a nor b b. lava d. both a and b Foliated rocks are distinguished by ____. a. layers c. large mineral grains b. lack of layers d. air holes Lava that cools quickly forms ____ rocks. a. extrusive metamorphic c. intrusive metamorphic b. extrusive igneous d. intrusive igneous All of the following conditions in Earth can cause metamorphic rocks to form EXCEPT ____. a. exposure to air c. heat b. the presence of hot, watery fluids d. pressure Quartz is a mineral; granite is ____. a. also a mineral c. a gem b. a rock d. an ore A classification of metamorphic rocks would include whether they are ____. a. chemical or organic c. foliated or nonfoliated b. intrusive or extrusive d. basaltic or granite Sedimentary rocks are ____. a. formed from magma b. a type of foliated igneous rock c. formed because of changes in temperature and pressure, or the presence of hot watery fluids d. formed when loose materials become pressed or cemented together or when minerals form from solutions The pressure and heat that produce magma are caused in part by ____. a. gravity c. radioactive elements b. magnetic fields d. lava Metamorphic rocks can undergo all of the following changes EXCEPT ____. a. an exchange of atoms between minerals b. melting c. the formation of new, bigger minerals d. the flattening of mineral grains Detrital rocks are ____. a. made from broken fragments of other rocks b. formed from magma c. deposited from solution d. all of the above Fine-grained, extrusive rocks include all of the following EXCEPT ____. a. granite c. basalt b. scoria d. pumice A rock is always ____. a. made of molten material b. a mixture of minerals, organic matter, volcanic glass, or other materials c. formed by heat and pressure d. either igneous or sedimentary The crystals that form in slowly cooled magma produce ____ mineral grains. a. tiny c. fine-grained b. invisible d. large ____ 20. A detrital rock is named according to ____. a. its age c. the shape and size of the sediments b. its location d. the color of the sediments ____ 21. Changes that take place in rocks never create or destroy ____. a. rocks c. matter b. crystals d. minerals ____ 22. ____ would be considered a rock. a. Quartz c. Granite b. Mica d. all of the above ____ 23. Magma from deep inside Earth rises toward the surface because ____. a. it is denser than surrounding solid rock b. it is less dense than surrounding solid rock c. it has the same density as surrounding solid rock d. none of the above ____ 24. When lava cools at Earth's surface, ____ igneous rocks are formed. a. extrusive c. intrusive b. metamorphic d. coarse-grained ____ 25. When magma cools deep inside Earth, ____ igneous rocks are formed. a. extrusive c. detrital b. fine-grained d. intrusive ____ 26. Basaltic igneous rocks are ____. a. light-colored c. rich in iron and magnesium b. lower in density than granitic rocks d. both a and b ____ 27. Granitic igneous rocks are all of the following EXCEPT ____. a. light-colored c. high in silica content b. lower in density than basaltic rocks d. high in iron content ____ 28. An igneous rock can form from ____ magma. a. basaltic c. granitic b. andesitic d. all of the above ____ 29. Metamorphic rocks that show layers of dark minerals alternating with layers of light minerals are classified as ____. a. nonfoliated c. foliated b. extrusive d. intrusive ____ 30. Metamorphic rocks with a non-foliated texture show metamorphic change that involves ____. a. mineral grains arranging into layers b. growth in the size of the mineral grains c. mineral grains flattening under pressure d. mineral grain melting ____ 31. Sedimentary rocks form because of all of the following EXCEPT ____. a. sediments becoming pressed or cemented together b. crystals solidifying from magma c. sediments forming from solution d. water evaporating, leaving crystals behind ____ 32. Sediments in sedimentary rocks are often ____. a. held together with natural cements b. formed when atoms of melted minerals rearrange themselves c. formed when lava erupts from a volcano d. formed by magma trapped below Earth's surface ____ 33. Sandstone is a(n) ____ sedimentary rock. a. chemical c. organic b. detrital d. none of the above ____ 34. Sedimentary rocks formed from the remains of once-living things are ____. a. metamorphic c. organic b. detrital d. none of the above ____ 35. Sedimentary rocks formed from broken fragments of other rocks are ____. a. chemical c. organic b. detrital d. none of the above Matching Match each statement with the correct item below. a. compaction e. b. cementation f. c. limestone g. d. coal h. ____ ____ ____ ____ 36. 37. 38. 39. ____ ____ ____ ____ 40. 41. 42. 43. weathering marble erosion slate a kind of organic sedimentary rock The process in which rock is exposed to air, water, or ice and breaks into pieces. a kind of chemical sedimentary rock The process in which pressure from the upper layers of sediment pushes down on the lower layers, causing the sediments to stick together and form solid rock. The process in which minerals hold sediment together, like glue, making a detrital sedimentary rock. the movement of weathered material a kind of foliated metamorphic rock a kind of nonfoliated metamorphic rock Completion Complete each sentence or statement. 44. Sandstone is a(n) ____________________ rock. 45. Granite is a(n) ____________________ rock. 46. Rock salt is a(n) ____________________ rock. 47. Obsidian is a(n) ____________________ rock. 48. Gneiss is a(n) ____________________ rock. 49. Slate is a(n) ____________________ rock. 50. Limestone is a(n) ____________________ rock. 51. Silica-rich, thick magma is ____________________ magma. 52. Dense, heavy, dark-colored igneous rocks form from ____________________ magma. 53. Light-colored rocks with lower density form from ____________________ magma. 54. Rocks that form from ____________________ magma have mineral compositions between those of granitic and basaltic magma. 55. Large-grained, light-colored rocks that form deep inside Earth are composed of ____________________ magma. 56. Lava flowing from volcanoes in Hawaii is ____________________ magma. Chapter 4 Study Guide Answer Section MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. 31. 32. 33. 34. 35. ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: B A D A B D A A B A B C D C B A A B D C C C B A D C D D C B B A B C B DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: A B A B B B B B B B B B B A B B A B B A A A B B B B B A B A A B B B B OBJ: OBJ: OBJ: OBJ: OBJ: OBJ: OBJ: OBJ: OBJ: OBJ: OBJ: OBJ: OBJ: OBJ: OBJ: OBJ: OBJ: OBJ: OBJ: OBJ: OBJ: OBJ: OBJ: OBJ: OBJ: OBJ: OBJ: OBJ: OBJ: OBJ: OBJ: OBJ: OBJ: OBJ: OBJ: 4/2 2/1 2/1 2/1 8/3 3/2 3/2 7/3 4/2 6/3 1/1 7/3 8/4 3/2 6/3 9/4 9/4 1/1 4/2 9/3 2/1 1/1 3/2 4/2 4/2 5/2 5/2 5/2 7/3 7/3 8/4 8/4 9/4 9/4 9/4 STO: STO: STO: STO: 3.5.7.A.2 3.5.7.A.4 3.5.7.A.4 3.5.7.A.4 STO: 3.5.7.A.2 STO: 3.5.7.A.2 STO: 3.5.7.A.2 STO: 3.5.7.A.2, 3.5.7.A.3 STO: 3.5.7.A.2 STO: 3.5.7.A.2, 3.5.7.A.3 STO: 3.5.7.A.2 STO: 3.5.7.A.4 STO: 3.5.7.A.2 STO: 3.5.7.A.2 STO: 3.5.7.A.2 MATCHING 36. ANS: D 37. ANS: E 38. ANS: C DIF: B DIF: B DIF: B OBJ: 9/4 OBJ: 2/1 OBJ: 9/4 STO: 3.5.7.A.4 39. 40. 41. 42. 43. ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: A B G H F DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: B B B B B OBJ: OBJ: OBJ: OBJ: OBJ: 9/4 9/4 2/1 7/3 7/3 STO: 3.5.7.A.4 COMPLETION 44. ANS: sedimentary 45. ANS: igneous STO: 3.5.7.A.2 46. ANS: sedimentary 47. ANS: igneous STO: 3.5.7.A.2 48. ANS: metamorphic STO: 3.5.7.A.2, 3.5.7.A.3 49. ANS: metamorphic STO: 3.5.7.A.2, 3.5.7.A.3 50. ANS: sedimentary 51. ANS: granitic 52. ANS: basaltic 53. ANS: granitic 54. ANS: andesitic 55. ANS: granitic 56. ANS: basaltic DIF: A DIF: A OBJ: 8/4 OBJ: 3/2 DIF: A DIF: A OBJ: 8/4 OBJ: 3/2 DIF: A OBJ: 6/3 DIF: A OBJ: 6/3 DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: OBJ: OBJ: OBJ: OBJ: OBJ: OBJ: OBJ: A A B B B A A 8/4 5/2 5/2 5/2 5/2 5/2 5/2









