Content and course structure core Heidelberg
advertisement

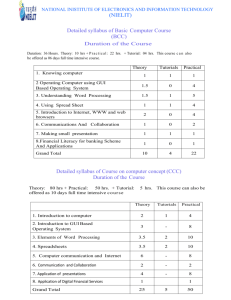
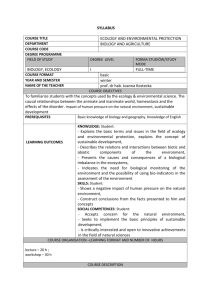
Content and course structure- Core course Heidelberg Content Introduction and orientation 45 Contact hours SIT (in hours) “Creating a Learning Community (Module 1)” 45 45 Selected topics from “Determinants of Health (Module 3)” 36 40 149 185 40 65 56 70 7 15 30 39 52 70 0,5 ECTS Concepts and research methods 225 7,5 ECTS - Concepts and definitions of health Introduction to environmental factors affecting health Fundamentals of medical anthropology Gender: Concepts and issues Introduction to societal and cultural influences on health and health disparities Poverty and equity in health “Research Foundations in International Health (Module 4)” Content see table 2 Health problems and responses Selected topics from “Introduction to International Health and Health Systems (Module 2)” - 150 - 5 ECTS - Introduction to major endemic diseases: viral and bacterial, parasitic, non-communicable Disease examples: STDs, HIV/AIDS, TB, leprosy, malaria, schistosomiasis, toxoplasma, hydatid disease, intestinal nematodes, filariae, smoking-related diseases, obesity, diabetes mellitus and cardiovascular disease Poisoning and accidental injury Violence Surgery and anaesthetics Diagnosis and essential laboratory Selected topics from “Determinants of Health (Module 3)” - Burden of disease Reproductive health and safe motherhood Neonatal and infant morbidity and mortality Principles and strategies for disease control and health promotion Concepts and principles of primary health care Global trends in health Nutrition Integrated management of childhood illness Physical, mental and social health of adults Urban health Air, water and noise pollution Toxic chemicals and health Risk management in environmental health Methods of environmental impact assessment Case Studies used in “Research Foundations in International Health (Module 4)” Health systems, management and communication 210 SIT Selected topics from “Introduction to International Health and Health Systems (Module 2)” - Introduction to International Health and health systems Stakeholders in International Health Health systems in low and middle income countries Comparison and rankings of health systems globally “Health Policy, Health Economics & Evaluation” (Module 5) 7 ECTS Content see table 2 “Health Planning and Management (Module 6)” 68 101 483 630 Content see table 2 Total Table 2: Note: c = contact hrs; s = self-study hrs Building blocks of Contents the core course Creating a Learning Community (Module 1) Introduction to International Health and Health Systems (Module 2) - Orientation to the programme Orientation to the facilities and services of the University of Heidelberg Introduction to University computing and library resources Orientation to living in Germany Teambuilding workshop 45 c/hrs - 70 c/hrs 34 s/hrs - International Health and health systems Stakeholders in International Health Health systems in low and middle income countries Major endemic diseases: viral and bacterial, parasitic, noncommunicable Disease examples: STDs, HIV/AIDS, TB, leprosy, malaria, schistosomiasis, toxoplasma, hydatid disease, intestinal nematodes, filariae, smoking-related diseases, obesity, diabetes mellitus and cardiovascular disease Poisoning and accidental injury Diagnosis and essential laboratory Violence Surgery and anaesthetics - Concepts and definitions of health Burden of disease Reproductive health and safe motherhood Neonatal and infant morbidity and mortality Principles and strategies for disease control and health promotion Concepts and principles of primary health care Global trends in health Nutrition Integrated management of childhood illness Physical, mental and social health of adults Urban health Environmental factors affecting health Air, water and noise pollution Toxic chemicals and health Risk management in environmental health Methods of environmental impact assessment Fundamentals of medical anthropology Gender: Concepts and issues Societal and cultural influences on health and health disparities 92 c/hrs 18 s/hrs - Health Problems and Determinants of Health (Module 3) Hours (SIT) 45 SIT 104 SIT 110 SIT Research Foundations in International Health (Module 4) - Poverty and equity in health - Research methods in International Health Ethical principles for research in International Health Formulating a research project Introduction to proposal writing Introduction to qualitative research Observation: Types and techniques Interviewing: Types and techniques Types of Qualitative Research: (e.g. Observation, Interview, sampling, focus group discussion) Developing guidelines for focus group discussions Qualitative data analysis Presenting qualitative data Foundations and scope of epidemiology in International Health Demography Measures of disease occurrence Screening and diagnostic testing Infectious disease epidemiology Measures of association and causality Confounding, interaction and stratified analysis Introduction to biostatistics: Types of variables, summarising data, tables & graphs, measures of location and variation The Normal distribution, sampling variation, standard errors and confidence intervals Principles of statistical testing Significance tests and confidence intervals for qualitative variables Significance tests and confidence intervals for quantitative variables Sampling and sample size calculations Correlation and regression Overview of advanced regression methods Design of survey instruments Reliability and validity in survey-based studies Methods of survey administration: data collection and management Analysis of survey results Observational study designs Randomized clinical trials Introduction to health services research methods Tutorials in the use of Epi-Info software 156 c/hrs 44 s/hrs Health policy and evaluation What is health policy and how does health policy develop? Health policy and health systems design Introduction to health economics Consumer, firm and social choice Burden / cost of illness, cost benefit analysis and cost effectiveness / utility analysis Financing of health systems 52 c/hrs 18 s/hrs Health Policy, Health economics and Evaluation (Module 5) - 200 SIT 70 SIT Health Planning and Management (Module 6) - Health planning and management Organisational behaviour and development Leadership and management styles Communication, negotiation and conflict resolution The financial management cycle Budgeting basics Budget control and cash flow analysis Financial statements Physical asset management Quality improvement in health care Managing for quality Health planning: Methods and tools of assessment, monitoring and evaluation The Health and Management Information System (HMIS) Application of Project Cycle Management (PCM) to health planning Application of LogFrame methods to health planning Health planning workshop 68 c/hrs 33 s/hrs 101 SIT