1D Motion Schedule
advertisement
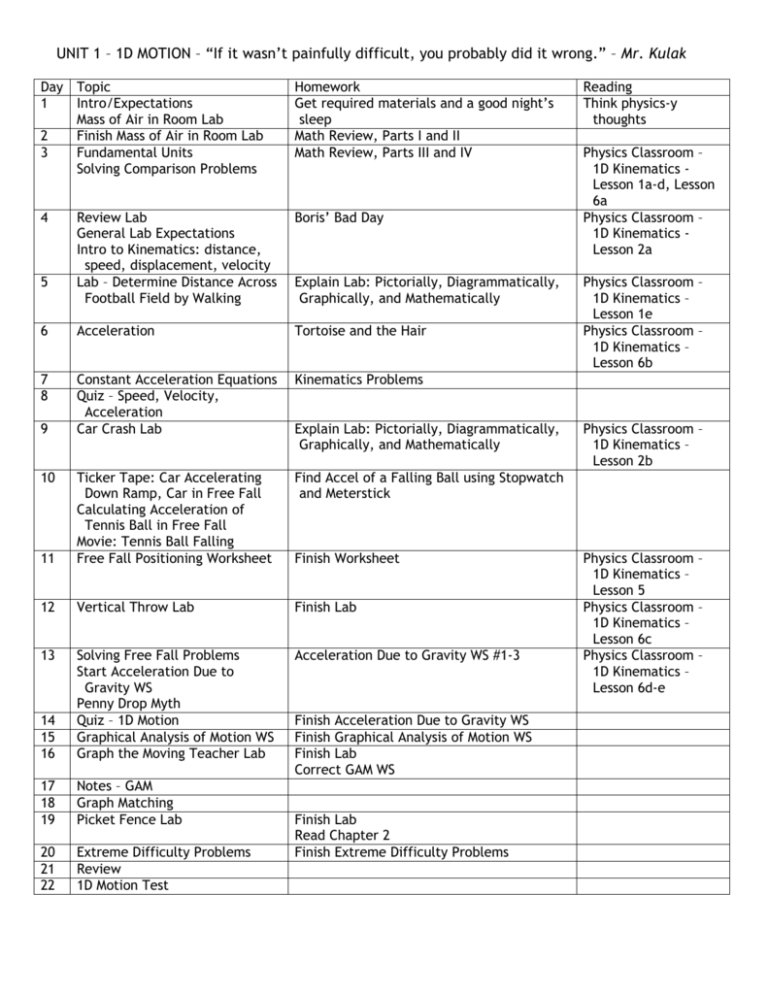
UNIT 1 – 1D MOTION – “If it wasn’t painfully difficult, you probably did it wrong.” – Mr. Kulak Day Topic 1 Intro/Expectations Mass of Air in Room Lab 2 Finish Mass of Air in Room Lab 3 Fundamental Units Solving Comparison Problems Homework Get required materials and a good night’s sleep Math Review, Parts I and II Math Review, Parts III and IV 4 Review Lab General Lab Expectations Intro to Kinematics: distance, speed, displacement, velocity Lab – Determine Distance Across Football Field by Walking Boris’ Bad Day 6 Acceleration Tortoise and the Hair 7 8 Constant Acceleration Equations Quiz – Speed, Velocity, Acceleration Car Crash Lab Kinematics Problems Find Accel of a Falling Ball using Stopwatch and Meterstick 11 Ticker Tape: Car Accelerating Down Ramp, Car in Free Fall Calculating Acceleration of Tennis Ball in Free Fall Movie: Tennis Ball Falling Free Fall Positioning Worksheet 12 Vertical Throw Lab Finish Lab 13 Acceleration Due to Gravity WS #1-3 14 15 16 Solving Free Fall Problems Start Acceleration Due to Gravity WS Penny Drop Myth Quiz – 1D Motion Graphical Analysis of Motion WS Graph the Moving Teacher Lab 17 18 19 Notes – GAM Graph Matching Picket Fence Lab 20 21 22 Extreme Difficulty Problems Review 1D Motion Test 5 9 10 Explain Lab: Pictorially, Diagrammatically, Graphically, and Mathematically Explain Lab: Pictorially, Diagrammatically, Graphically, and Mathematically Finish Worksheet Finish Acceleration Due to Gravity WS Finish Graphical Analysis of Motion WS Finish Lab Correct GAM WS Finish Lab Read Chapter 2 Finish Extreme Difficulty Problems Reading Think physics-y thoughts Physics Classroom – 1D Kinematics Lesson 1a-d, Lesson 6a Physics Classroom – 1D Kinematics Lesson 2a Physics Classroom – 1D Kinematics – Lesson 1e Physics Classroom – 1D Kinematics – Lesson 6b Physics Classroom – 1D Kinematics – Lesson 2b Physics Classroom – 1D Kinematics – Lesson 5 Physics Classroom – 1D Kinematics – Lesson 6c Physics Classroom – 1D Kinematics – Lesson 6d-e Big Ideas: Kinematics Quantities Scalar Position (x) Where you are [meters] = [m] Speed (S) How fast you are going S = distance/time [meters/second] = [m/s] Vector Displacement (d or ∆x or ∆y ) Your change in position ∆x = (xf – xi) -or- ∆y = (yf – yi) [meters] = [m] Velocity (v) How fast you are going in a direction v = ∆x/∆t [meters/second] = [m/s] Acceleration (a) How fast you are changing your velocity a = ∆v/∆t [meters/second/second] = [m/s2] Constant Acceleration Equations d = vit + 1/2at2 vf2 = vi2 + 2ad vf = vi + at Free Fall Acceleration is always down at 10 m/s2 Graphs velocity = slope of x vs t graph acceleration = slope of v vs t graph displacement = area under vs vs t graph velocity = area under a vs t graph