SELF-ASSESSMENT EXERCISE: WHAT KIND OF LEADER AM I?1
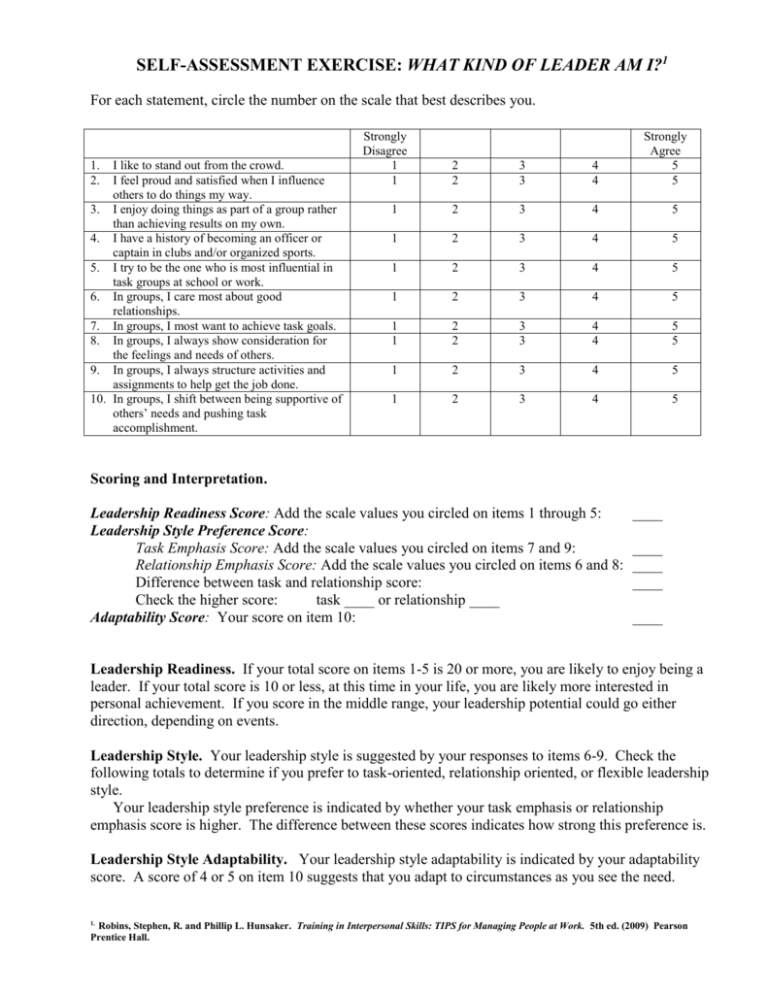
For each statement, circle the number on the scale that best describes you.
1.
2.
I like to stand out from the crowd.
I feel proud and satisfied when I influence
others to do things my way.
3. I enjoy doing things as part of a group rather
than achieving results on my own.
4. I have a history of becoming an officer or
captain in clubs and/or organized sports.
5. I try to be the one who is most influential in
task groups at school or work.
6. In groups, I care most about good
relationships.
7. In groups, I most want to achieve task goals.
8. In groups, I always show consideration for
the feelings and needs of others.
9. In groups, I always structure activities and
assignments to help get the job done.
10. In groups, I shift between being supportive of
others’ needs and pushing task
accomplishment.
Strongly
Disagree
1
1
Strongly
Agree
5
5
2
2
3
3
4
4
1
2
3
4
5
1
2
3
4
5
1
2
3
4
5
1
2
3
4
5
1
1
2
2
3
3
4
4
5
5
1
2
3
4
5
1
2
3
4
5
Scoring and Interpretation.
Leadership Readiness Score: Add the scale values you circled on items 1 through 5:
Leadership Style Preference Score:
Task Emphasis Score: Add the scale values you circled on items 7 and 9:
Relationship Emphasis Score: Add the scale values you circled on items 6 and 8:
Difference between task and relationship score:
Check the higher score:
task ____ or relationship ____
Adaptability Score: Your score on item 10:
____
____
____
____
____
Leadership Readiness. If your total score on items 1-5 is 20 or more, you are likely to enjoy being a
leader. If your total score is 10 or less, at this time in your life, you are likely more interested in
personal achievement. If you score in the middle range, your leadership potential could go either
direction, depending on events.
Leadership Style. Your leadership style is suggested by your responses to items 6-9. Check the
following totals to determine if you prefer to task-oriented, relationship oriented, or flexible leadership
style.
Your leadership style preference is indicated by whether your task emphasis or relationship
emphasis score is higher. The difference between these scores indicates how strong this preference is.
Leadership Style Adaptability. Your leadership style adaptability is indicated by your adaptability
score. A score of 4 or 5 on item 10 suggests that you adapt to circumstances as you see the need.
1.
Robins, Stephen, R. and Phillip L. Hunsaker. Training in Interpersonal Skills: TIPS for Managing People at Work. 5th ed. (2009) Pearson
Prentice Hall.
Situation R1: Low readiness. When followers are unable and unwilling, the leader should use the
directive and autocratic telling style that emphasizes task-oriented behavior.
Situation R2: Moderate readiness. When group members are unable but willing, the leader should
focus on being more relationship-oriented, using a selling style.
Situation R3: Moderate to high readiness. When group members are able but unwilling, the leader
needs to engage in a participative style that provides a high degree of relationship-oriented behavior
but a low degree of task behavior.
Situation R4: High readiness. When followers are able, willing, and confident, the leader should
grant these self-sufficient and competent followers considerable autonomy by using the delegating
style.
Style 1 (S1): High task and low relationship. The TELLING style is directive because the leader
produces a lot of input but a minimum amount of relationship behavior. The leader defines roles in an
autocratic manner and tells people what, how, when, and where to do tasks.
Style 2 (S2): High task and high relationship. The SELLING style is also directive, but in a more
persuasive, supportive, and guiding manner. The leader provides considerable input about task
accomplishment but also emphasizes human relations in a coaching style.
Style 3 (S3): High relationship and low task. In the PARTICIPATING leading style, less direction
and more collaboration exist between leader and group members. This is a consultative or consensus
type of leadership in which the leader concentrates on facilitating shared decision making.
Style 4 (S4): Low relationship and low task. In the DELEGATING leadership style, the leader
delegates responsibility for a task to group members but is kept informed of progress.
---------
i
When is each leadership style most effective?. The answer depends on many
factors. The challenge is to approach each situation from a fresh perspective, and
to accept that each situation—and perhaps even each individual—may require a
unique approach.