AP Statistics Syllabus - Course Outline & Expectations
advertisement

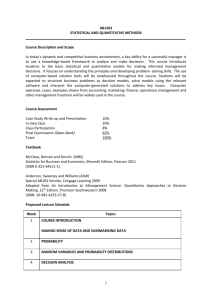
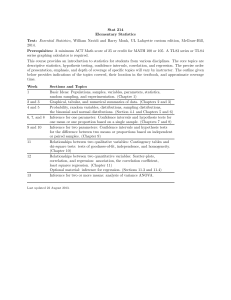
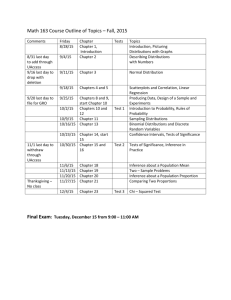
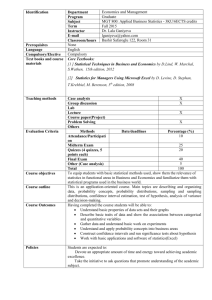
AP Statistics Syllabus Instructor: Mrs. Keerthi E-mail: Hkeerthi.rutlandhs@bibb.k12.ga.us Website: http://apcentral.collegeboard.com/ Use this site to see sample questions,answers and scoring commentary from the AP exam graders. COURSE DESCRIPTION: AP Statistics is the high school equivalent of a one semester, introductory college Statistics course. It is a two-semester, non-calculus based course, in the formal study of basic principles of statistical thinking and scientific investigation. Students will be exposed to four broad conceptual themes: Exploring Data, Sampling and experimentation, Anticipating Patterns and Statistical Inferences. Activities will require students to produce oral and written statistical arguments using appropriate terminology in a variety of applied settings. Activities will often require students to produce data, analyze data, model data and draw conclusions from data. Primary Textbook: Daniel S. Yates, David S. Moore, and Daren S. Starnes. The Practice of Statistics, 3rd Edition. (TI-83/84/89 Graphing Calculator Enhanced) W. H. Freeman & Co., 2007. Technology: - All students have or will borrow from the Math Department a TI-83/TI-83+/TI-84 for use in class . Class Expectations: • All students will come to class prepared, bringing each day their textbook, notebook and calculator. It is highly recommended that each student have his/her own TI-84 graphing calculator. This calculator provides several built in functions for statistics. • It is essential that each student have a 3-ring binder exclusively for this class divided into sections for homework, formula sheet, tables, special assignments, tests and quizzes. This will be especially helpful because some of the tests and quizzes may be open notebook. Attendance: • Regular attendance is essential to success in this class. Much of the curriculum requires individual participation in activities; hence, attendance is critical. Homework: • Homework will be assigned regularly throughout the school year. No late homework will be accepted unless it is late because of an excused absence. • Students are expected to read each section of the textbook carefully studying the examples, real-life applications and background information. Class Participation and Behavior: • Students are expected to participate actively in each class. Class activities will include both individual and group work. • Students are expected to show respect for other individuals, including fellow students and the teacher. Grading Policy: The Course grade is calculated using the following percentages for each type of assessment: Tests/ projects Quiz Class work Home work Finals 30% 20% 35% 15% -------100% 15% . The course syllabus is a general plan for the course; all information contained in the course syllabus/calendar is subject to change. Any changes will be announced in class and a revised syllabus distributed to students to be shared with their parents/guardians. Course Outline : (organized by chapters in the primary textbook) NOTE: All time periods are in days which are 85 minute periods on alternating school days. Preliminary Chapter “What is Statistics?” (1 day) - Activity: “Pepsi Challenge” Part I Analyzing Data: looking for patterns and departures from patterns Chapter 1 “Exploring Data” (4 days) - Displaying Distributions with Graphs: Dotplots, histograms, stemplots, timeplots, boxplots. - Describing Distributions with Numbers: Center (mean, median), Spread (IQR, variance, standard deviation, Shape (uniform, symmetric, skewed), quartiles, quintiles, percentiles, gaps and outliers. - Using the TI-83 for calculations and plots. - Activity: “Data Gathering and Presentation” Chapter 2 “Statistical Models for Distributions” (5 days) - Measures of Relative Standing and Density Curves: Density curve versus histogram, are equals density equals proportion of data. - Normal Distributions: The empirical rule, standardized scores, normal probability plot, percentiles again. Chapter 3 “Examining Relationships” (6 days) - Scatterplots and Correlation: Explanatory and response variables; form, direction and strength of a relationship. - Least-Squares Regression: Pearson Product Moment, meaning of slope and intercept, residuals. - Correlation and Regression Wisdom: influential points, outliers, meaning of rsquared. - Using the TI-84 for regression equations, r values, and residual plots. - Project: “Finding a Relationship” Chapter 4 “More about Relationships between Two Variables” (5 days) - Transforming to Achieve Linearity: Logarithm review, antilog exercises, transforming only the response variable, transforming both variables, appropriate exponential and power situations. - Relationships between Categorical Variables: Two way tables, marginal distributions, conditional distributions, Simpson’s paradox - UC Berkley Women’s Suit over admissions. - Establishing causation: Residual plots, lurking, confounding variables, extrapolation. - Using the TI-83 for residual plots and transforming data in lists. Part II Producing Data: surveys, observational studies, and experiments Chapter 5 “Producing Data” (6 days) - Decisions Through Data videos 15 - 18 - Designing Samples: SRS, stratification, representation, sampling biases. - Designing Experiments: Treatment, control, randomization, replication vs reproducibility, scope of inference, blocking. Part III Probability and Random Variables: foundations for inference [C2c] [C5] Chapter 6 “Probability and Simulation: The Study of Randomness” (7 days) - Simulation: Random digits, TI-83, proportion being simulated. - Probability Models: Sample space, events, tree diagrams, Venn diagrams, two-way tables. - General Probability Rules: Conditional, joint, independence, disjoint, union, intersection. Chapter 7 “Random Variables” (6 days) - Discrete and Continuous Random Variables - Probability distributions: Adding constants, multiplying values. - Means and Variances of Random Variables: Combining variables. Chapter 8 “The Binomial and Geometric Distributions (6 days) - Fly-Mating Simulation - Bumpers and Balls - The Binomial Distributions: Binomial Coefficient, Probability per “way”, Characteristics of the setting. - The Geometric Distributions: Difference in setting, Probability calculation. Chapter 9 “Sampling Distributions” (5 days) - German Tank Problem – to illustrate sampling variability can be used to judge quality of a method for estimating a population parameter. - Simulation of coin flipping to generate sampling distribution. - Sampling Distributions: vs Population Distribution, variability of samples, mean of sampling distribution and population parameter - Sample Proportions: Connection to binomial distribution, normal distribution, mean, standard deviation. - Sample Means: CLT, normal distribution, mean, standard deviation. - Probability of a randomly drawn value from the population vs the average of a sample of n values. Part IV Inference: conclusions with confidence Chapter 10 “Estimating with Confidence” (8 days) - Confidence Intervals: Voter surveys, plus or minus what? - Simulating Multiple Confidence Intervals: What is confidence? - Estimating a Population Mean: Standard deviation, sample size and confidence level. - Estimating a Population Proportion: estimated proportion, margin of error and sample size. Chapter 11 “Testing a Claim” (5 days) - Pick a Card: When is a claim refuted/weakened/made unbelieveable by the probability of an actual result? - Significance Tests: the Basics: Hypotheses, alpha level, probability of a result, rejecting or failing to reject, upper tail, lower tail or two tail. - Carrying Out Significance Tests: Format of setup and statement of conclusion. - Use and Abuse of Tests: Sampling until test is positive, practical significance. - Using Inference to Make Decisions: Level of significance. Chapter 12 “Significance Tests in Practice” (4 days) - Tests About a Population Mean: t-distribution; sample size requirements/population distribution requirements, Type I and Type II errors, power. - Tests About a Population Proportion: rules of thumb, power. Chapter 13 “Comparing Two Population Parameters” (4 days) - Comparing Two Means: Distribution requirements; independence; one and two tailed tests; matched pairs, confidence intervals - Comparing Two Proportions: requirements, independence; confidence intervals - Using the TI-83 for tests. Chapter 14 “Inference for Tables: Chi-Square Procedures” (5 days) - Goodness of Fit: M & M’s - Inference for Two-Way Tables: test of independence, test of homogeneity. Chapter 15 “Inference for Regression” (2 days) - The Regression Model: review residuals, least squares regression line; confidence interval for slope, hypothesis test for slope. - Using the TI-83. Review for the AP Exam Post Exam Topics (5 days) (vary to fit time remaining.) - “Analysis of Variance” - “Multiple Regression” Final project . Parents may monitor their student’s progress by signing up for Parent Connect in the guidance office. Parent Connect is updated weekly to show your student’s grades and attendance for each class. I am available before and after school, and I will gladly provide extra help and attention any time you feel it is needed. I am looking forward to a great year at RHS! : Please complete the attached questionnaire, along with your parents, and return to me. I look forward to working with you in AP Statistics. I have read the information in Ms Keerthi’s AP Statistics Syllabus and understand all grading policies, teacher expectations and classroom rules. Student’s Name (print)________________________________________________ Student’s Signature__________________________________________________ Address___________________________________________________________ Home Phone_____________________ Student’s E-mail address______________________________________________ Parent’s Name______________________________________________________ Parent’s Signature___________________________________________________ Parent’s E-mail address________________________________________________ Best telephone number to contact parent___________________________________ (please specify if this is home, work or cell) ********************************************************************** *** Please answer the following. The last math class I took was ________________ and my grade was ___________. (an approximation of grade is okay) 1. I am prepared to enhance my learning experience by doing the following things each day. (List at least two things).________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ 2. Outside of school, I spend most of my time doing….. (i.e. Working, studying, sports, etc)___________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________ 3. Is there anything else that you would like me to know about you? ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________