Cell Struct. notes

Biology 12
Notes – Cell Structure
Cell Biology
Cell Structures
A. Cells
Cells are units which are both structural and functional
Cells make up all living organisms
A cell is the smallest unit that contains all the processes necessary for life
Animal (human) cells have three basic parts:
Cell (or plasma) membrane: the outside barrier (*see unit G)
Nucleus: the control centre of the cell (contains DNA)
Cytoplasm: everything between the cell membrane and the nucleus; includes the organelles and the cytosol (the semiliquid “gel” organelles are in)
B. Organelles
structures found in the cytoplasm of the cell
generally membrane bound
perform a specific function for the cell
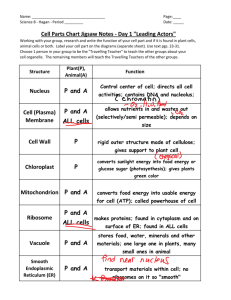
1. Nucleus
generally, the easiest part to identify in a cell: relatively large and round, generally found in the centre, appears dark on an electron micrographs
contains most of the genetic material (i.e. DNA) that controls the cell’s activities (*see more on this in unit D and
E)
composed of: the nuclear envelope, chromosomes, and the nucleolus a. Nuclear Envelope/Nuclear Membrane
the membrane which compartmentalizes the genetic material; separates it from the cytoplasm
inner membrane has a protein layer that helps the nucleus to maintain its shape and helps organize the chromatin
(genetic material plus proteins)
has pores in the membrane that control the movement of molecules in and out of the cell b. Chromatin
long threads of DNA plus proteins
cannot see individual DNA molecules; just a dark mass
exists when cell is not dividing
2005, Wedel 1
Biology 12
Notes – Cell Structure c. Chromosomes
long threads of DNA plus proteins
occurs when cell divides
chromatin coils up and forms rod-like structures that are individual visible under a microscope
humans have 46 chromosomes (2 copies of each type) d. Nucleolus
sphere-ish region in the nucleus; a darker mass
produces ribosomal RNA (rRNA) which join with proteins to form ribosomes which then leave the nucleus for the cytoplasm
can be more then one (plural: nucleoli)
2. Ribosomes
found in the cytoplasm
involved in protein synthesis (*see more in unit E)
composed of a large subunit and a small subunit made from rRNA, RNA, and proteins in the nucleolus
not membrane bound
in the cytoplasm, can be free or attached
free/cytoplasmic ribosomes: suspended in the cytosol, individual or in groups; make proteins that will be used in the cell (i.e. for the mitochondria)
bound ribosomes: attached to the rough endoplasmic reticulum; make proteins that will be exported (used outside the cell/secreted) or that will be incorporated to the cell membrane
cells which produce a large number of proteins will have a large number of ribosomes (and have prominent nucleolus) i.e. liver cells have millions
3. Endomembrane System
membranes and membrane-bound organelles that are related
directly by physical contact
indirectly through vesicles
sections off portions of the cell to restrict reactions to specific parts of the cell a. Vesicles
membrane-bound spheres/containers
formed by pinching off from membranes
can move throughout the cell and be incorporated into other membranes
2005, Wedel 2
Biology 12
Notes – Cell Structure b. Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
-
“endo” – within; “reticulum” – network
large network of membranes which makes tubes/tubules and sacs
continuous (attached to/part of) with the plasma/cell membrane
smooth and rough ER differ in function i. Smooth ER
doesn’t have ribosomes attached
synthesizes lipids, phospholipids, and steroids
involved in the first step of the hydrolysis of glycogen
has enzymes (especially in the liver) attached to it that can detoxifies drugs and poisons (i.e. alcohol)
stores calcium ions (Ca 2+ ) for use in muscle contraction
can form vesicles that transport proteins to the Golgi body ii. Rough ER
has ribosomes attached to the cytoplasm side of the
ER membrane
makes proteins that are for secretion (export) or that will become part of the membrane
makes the plasma/cell membrane
vesicles may pinch off and transport proteins and/or phospholipids to another part of the ER or cell membrane c. Golgi Apparatus/Body
organelle made of flattened membrane sacs/saccules; looks like a stack of slightly bent pancakes
one side of the stack faces the ER (where vesicles arrive) and the other faces the cell membrane (where vesicles depart)
vesicles carrying products from the ER are
processed/modified (i.e. changes the oligosaccharide on glycoproteins; alters phospholipids)
stored
packaged (forms vesicles)
re-routed (molecular tags on vesicles tell the cell where the vesicle, and its contents, should go
secreted (vesicles come off and attach to the plasma membrane, discharging their products outside the cell)
makes lysosomes
2005, Wedel 3
Biology 12
Notes – Cell Structure d. Lysosomes
membrane-bound organelles created by the Golgi body
contains hydrolytic digestive enzymes (enzymes that do hydrolysis) that work in an acidic environment (pH 5) inside the lysosome
breakdown
large molecules and cells that are taken into the cell
(by a process called phagocytosis) i.e. white bl. cells defend the body from bacteria by engulfing bacteria and using lysosomes to break them down
organelles and recycle the molecules
- specific diseases are the result of not being able to breakdown certain molecules i.e. Tay-Sachs: build up of lipids in the brain
Pompe’s: build up of glycogen which damages the liver
programmed cell death: destroy the cell they’re in i.e. breakdown the skin cells between the fingers of a fetus e. Vacuoles
membrane-bound sac
bigger than a lysosome or a vesicle
play a larger role in simple organisms like protozoa (stores and digests food and gets rid of excess water) and plants
(stores water and other substances and helps give plant structural support)
storage container f. Relationship between Membranes: Summary
2005, Wedel 4
Biology 12
Notes – Cell Structure
4. Mitochondria
a double membrane organelle: inner membrane is folded
(folds are called cristae and the space in the middle is the matrix)
not part of the endomembrane system
besides the membranes, they are also composed of their own DNA, RNA, and enzymes made from this DNA that are involved in the hydrolysis of glucose
C
6
H
12
O
6
+ 6 O
2
6 CO
2
+ 6 H
2
O + ENERGY
energy from the breakdown of glucose is coupled with the synthesis of ATP from ADP + P
[drawing of cell]
5. Other Structures i. peroxisomes: membrane-bound vesicle contains enzymes involved in the synthesis and hydrolysis; result of the enzymes action is the production of ii. hydrogen peroxide (H
2
O
2
) which is then broken down into water and oxygen cytoskeleton: a network of fibres throughout the cytoplasm involved in structural support and movement iii. centrioles: short, paired structures involved in cell division iv. cilia and flagella: hair-like projections on the outside of the cell membrane; involved in movement; cilia are shorter and numerous (i.e. cells in the respiratory tract); flagella are long, singular or paired (i.e. sperm
“tail”)
2005, Wedel 5
Biology 12
Notes – Cell Structure
6. Cell membrane (*see unit G)
made from: o phospholipids but also contains o proteins, o glycoproteins (proteins with a carbohydrate chain attached), o carbohydrates, o glycolipids (lipids with a carbohydrate chain attached) o cholesterol
semi-permeable: only allows certain molecules in and out of the cell
outside layer on an animal cell
{ONLY IN PLANTS}
7. Cell Wall
found outside the cell membrane on plant cells
made from long chains of cellulose
gives the plant its structural support
8. Chloroplasts
organelle found inside plant cytoplasm
contains chlorophyll (a green molecule)
chlorophyll molecules facilitate the photosynthetic reaction:
ENERGY (sunlight) + 6 CO
2
+ 6 H
2
O
C
6
H
12
O
6
+ 6 O
2
2005, Wedel 6