Multiple Choice Questions Testbank – Chapter 20 Go to memo
advertisement
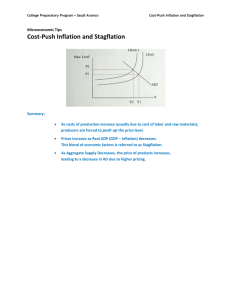
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS TESTBANK – CHAPTER 20 Go to memorandum Answer the following questions by selecting the appropriate answer from the list below. Question 1 Which one of the following statements about inflation is true? Inflation refers to: A. a sudden and self-contained increase in prices. B. a small increase in prices. C. “too much money chasing too few goods”. D. a sustained increase in the general price level. E. an increase in the purchasing power of money. Question 2 If the consumer price index at the end of 2011 was 100 and at the end of 2012 was 120, then the rate of inflation for 2012 was: A. 25%. B. 20%. C. 16,66%. D. 1,5%. E. –16,66%. Question 3 Use the table below to answer the question. Year GDP at current prices GDP at constant 2012 prices GDP deflator 2011 400 000 600 000 A 2012 500 000 B C In the table above, A, B and C are respectively equal: A. 66,67, 500 000 and 100. B. 80, 900 000 and 100. C. 133,33, 600 000 and 66,67. D. 66,67, 600 000 and 1. E. 133,33, 500 000 and 100. © VAN SCHAIK PUBLISHERS Question 4 If inflation was 10% in a particular year and you received a 20% increase in income during the same year, then over the year your: A. real and nominal income both fell. B. real and nominal income both rose. C. real income fell, but nominal income rose. D. real income rose, but nominal income fell. E. nominal income rose, but real income was unchanged. Question 5 Bracket creep would be eliminated if tax rates were based on: A. nominal income. B. real income. C. per capita income. D. real disposable income. E. nominal disposable income. Question 6 If the real interest rate is negative, then: A. the inflation rate is larger than the nominal interest rate. B. the inflation rate is smaller than the real interest rate. C. the inflation rate is smaller than the nominal interest rate. D. lenders will gain. E. the real value of a loan will increase. Question 7 Simon borrowed R10 000 from the bank at the end of 2011 at a fixed interest rate of 20%. At the end of 2012, the inflation rate was 25%. Inflation has been ________ to Simon; the real value of his loan plus interest payments changed to ________. A. B. C. D. E. beneficial; R9 600 beneficial; R4 800 beneficial; R8 000 costly; R12 500 costly; R10 500 © VAN SCHAIK PUBLISHERS Question 8 A depreciation of the rand may have inflationary consequences in South Africa because it: A. increases the costs of exports. B. discourages savings. C. decreases the international competitiveness of South African producers. D. increases the costs of imported goods. E. discourages exports. Question 9 Which of the following statements is/are correct? i. One way to combat demand-pull inflation is if the Reserve Bank raises the interest rates. ii. Demand-pull inflation usually leads to increased prices and increased unemployment. iii. Demand-pull inflation can be initiated by a cut in the marginal tax rate. A. B. C. D. E. i and ii i and iii ii and iii All three statements are correct Only statement iii is correct Question 10 Which of the following statements is incorrect? A. Cost-push inflation is associated with rising prices and declining unemployment. B. Attempts to decrease cost-push inflation by restrictive monetary or fiscal policy are likely to produce even greater unemployment. C. Cost-push inflation may result from firms increasing their profit margins. D. Cost-push inflation may follow from a depreciation of the domestic currency against the currencies of the country’s major trading partners. Question 11 Which one of the following can be regarded as a neutral definition of inflation? A. Inflation is too much money chasing too few goods. B. Inflation is an excessive increase in the money supply C. Inflation is a persistent increase in the cost of production. D. Inflation is a continuous and considerable rise in the price level. © VAN SCHAIK PUBLISHERS Question 12 Which one of the following statements is true? A. The consumer price index (CPI) measures the cost of all consumer goods and services. B. A 10% rate of inflation means that inflation is 10% per month. C. The inflation rate is calculated from a set of CPI figures. Question 13 The producer price index (PPI): A. measures the cost of a representative basket of goods and services to the consumers. B. includes the cost of manufactured goods to the consumers. C. includes the cost of capital and intermediate goods. D. excludes the price of imported goods. Question 14 Inflation is: A. B. C. D. E. an increase in certain important prices in the economy. a once-off increase in prices in general. a rapid increase in the quantity of money. a sustained increase in prices in general. too much money chasing too few goods. Question 15 Which one of the following is not an important statement about the definition of inflation? A. B. C. D. E. The definition should be neutral, which means that it should not refer to specific causes of inflation. The definition should emphasise that inflation is a process. The definition should emphasise that inflation pertains to the general level of prices. The definition should emphasise that price increases have to be considerable to be classified as inflation. The definition should make it clear what the causes of inflation are. © VAN SCHAIK PUBLISHERS Question 16 Which one of the following statements is incorrect? A. B. C. D. E. The consumer price index (CPI) is simply another term for the inflation rate. The CPI is an index that reflects the cost of a representative basket of consumer goods and services. The inflation rate is usually expressed as an annual rate. The inflation rate is usually obtained by comparing the CPI for a particular month with the CPI for the same month of the previous year. The inflation rate is expressed as a percentage change (from one year to the next). Question 17 Which one of the following statements is correct? A. B. C. D. E. The PPI basket contains goods and services. The PPI basket excludes capital goods. The prices used to compile the PPI exclude value-added tax. The CPI basket includes capital goods. The CPI basket excludes services. Question 18 Which one of the following statements is incorrect? A. B. C. D. E. The CPI pertains to the cost of living. The PPI pertains to the cost of production. The CPI basket includes services. The PPI basket includes intermediate goods. The prices in the CPI basket exclude value-added tax. Question 19 Inflation tends to: A. B. C. D. E. benefit lenders at the expense of borrowers. benefit taxpayers at the expense of the government. benefit the young at the expense of the elderly. benefit creditors at the expense of debtors. benefit people with fixed nominal incomes. © VAN SCHAIK PUBLISHERS Question 20 Inflation tends to: A. B. C. D. E. discourage speculative practices. encourage saving. create balance of payments problems. redistribute income from the government to the private sector. benefit creditors at the expense of debtors. Question 21 Extremely high inflation is called: A. B. C. D. E. disinflation. deflation. stagflation. hyperinflation. bracket creep. Question 22 Which one of the following is not a possible cause of demand-pull inflation? A. B. C. D. E. An increase in government spending. An increase in the oil price. An increase in consumption spending. An increase in investment spending. An increase in export earnings. Question 23 Which one of the following statements about demand-pull inflation is incorrect? A. B. C. D. E. Demand-pull inflation tends to be accompanied by an increase in the level of production and income. Demand-pull inflation may be illustrated by a rightward shift of the AD curve. Demand-pull inflation may be caused by a greater availability of consumer credit. Demand-pull inflation may be caused by the availability of cheaper consumer credit. Demand-pull inflation tends to be accompanied by higher unemployment. © VAN SCHAIK PUBLISHERS Question 24 Which one of the following is not a possible cause of cost-push inflation? A. B. C. D. E. An increase in wages. An increase in profit margins. A decrease in interest rates. A decrease in productivity. An increase in the cost of imported capital and intermediate goods. Question 25 Which one of the following statements is incorrect? Cost-push inflation: A. B. C. D. E. can be illustrated by an upward shift of the AS curve. is also called stagflation. is associated with a decrease in production, income and employment. can be eliminated by appropriate monetary and fiscal policies. may be the result of a supply shock. Question 26 Which one of the following will not be appropriate in an attempt to combat demand-pull inflation? A. B. C. D. E. An increase in interest rates. An increase in taxes. A decrease in government spending. Stricter control of consumer credit. Measures to increase the productivity of labour. Question 27 Which one of the following statements is correct? A. B. C. D. E. Inflation is a problem and therefore has to be combated at all cost. Inflation has definite advantages and should therefore be stimulated. In deciding on anti-inflation policy, the costs of other economic problems, such as unemployment and a lack of economic growth, should also be considered. Inflation is such as serious problem that the possible side effects of anti-inflation policies should not even be considered. Unemployment, inflation, low economic growth and balance of payments problems are all serious macroeconomic problems and therefore there is no need to prioritise when economic policy has to be formulated and implemented – all these problems should be regarded as priority number one. © VAN SCHAIK PUBLISHERS Question 28 Which one of the following is not an essential feature of inflation targeting? A. B. C. D. E. The public announcement of quantitative inflation targets. The recognition that the primary aim of the central bank is to ensure rapid economic growth. A broad based approach to the analysis of inflation. A high degree of transparency A high degree of accountability. Question 29 Which one of the following statements is correct? A. B. C. D. E. Inflation targeting is based on the assumption that all elements of the inflation process are under control of the central bank. Under an inflation-targeting framework there is no limit to the discretionary powers of the central bank. Inflation targeting will only work if there is a strong and stable relationship between changes in the money stock and inflation. One of the key aspects of inflation targeting is the impact on inflation expectations. Under an inflation-targeting framework the governor of the central bank does not need to consult anyone before taking a policy decision. © VAN SCHAIK PUBLISHERS MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS TESTBANK – CHAPTER 21 MEMORANDUM Go back to Multiple Choice Questions Answer the following questions by selecting the appropriate answer from the list below. Question 1 Which one of the following statements about inflation is true? Inflation refers to: A. a sudden and self-contained increase in prices. B. a small increase in prices. C. “too much money chasing too few goods”. D. a sustained increase in the general price level. E. an increase in the purchasing power of money. Question 2 If the consumer price index at the end of 2011 was 100 and at the end of 2012 was 120, then the rate of inflation for 2012 was: A. 25%. B. 20%. C. 16,66%. D. 1,5%. E. –16,66%. © VAN SCHAIK PUBLISHERS Question 3 Use the table below to answer the question. Year GDP at current prices GDP at constant 2012 prices GDP deflator 2011 400 000 600 000 A 2012 500 000 B C In the table above, A, B and C are respectively equal: A. 66,67, 500 000 and 100. B. 80, 900 000 and 100. C. 133,33, 600 000 and 66,67. D. 66,67, 600 000 and 1. E. 133,33, 500 000 and 100. Question 4 If inflation was 10% in a particular year and you received a 20% increase in income during the same year, then over the year your: A. real and nominal income both fell. B. real and nominal income both rose. C. real income fell, but nominal income rose. D. real income rose, but nominal income fell. E. nominal income rose, but real income was unchanged. Question 5 Bracket creep would be eliminated if tax rates were based on: A. nominal income. B. real income. C. per capita income. D. real disposable income. E. nominal disposable income. Question 6 If the real interest rate is negative, then: A. the inflation rate is larger than the nominal interest rate. B. the inflation rate is smaller than the real interest rate. C. the inflation rate is smaller than the nominal interest rate. D. lenders will gain. E. the real value of a loan will increase. © VAN SCHAIK PUBLISHERS Question 7 Simon borrowed R10 000 from the bank at the end of 2011 at a fixed interest rate of 20%. At the end of 2012, the inflation rate was 25%. Inflation has been ________ to Simon; the real value of his loan plus interest payments changed to ________. A. B. C. D. E. beneficial; R9 600 beneficial; R4 800 beneficial; R8 000 costly; R12 500 costly; R10 500 Question 8 A depreciation of the rand may have inflationary consequences in South Africa because it: A. increases the costs of exports. B. discourages savings. C. decreases the international competitiveness of South African producers. D. increases the costs of imported goods. E. discourages exports. Question 9 Which of the following statements is/are correct? i. One way to combat demand-pull inflation is if the Reserve Bank raises the interest rates. ii. Demand-pull inflation usually leads to increased prices and increased unemployment. iii. Demand-pull inflation can be initiated by a cut in the marginal tax rate. A. B. C. D. E. i and ii i and iii ii and iii All three statements are correct Only statement iii is correct Question 10 Which of the following statements is incorrect? A. Cost-push inflation is associated with rising prices and declining unemployment. B. Attempts to decrease cost-push inflation by restrictive monetary or fiscal policy are likely to produce even greater unemployment. C. Cost-push inflation may result from firms increasing their profit margins. D. Cost-push inflation may follow from a depreciation of the domestic currency against the currencies of the country’s major trading partners. © VAN SCHAIK PUBLISHERS Question 11 Which one of the following can be regarded as a neutral definition of inflation? A. Inflation is too much money chasing too few goods. B. Inflation is an excessive increase in the money supply C. Inflation is a persistent increase in the cost of production. D. Inflation is a continuous and considerable rise in the price level. Question 12 Which one of the following statements is true? A. The consumer price index (CPI) measures the cost of all consumer goods and services. B. A 10% rate of inflation means that inflation is 10% per month. C. The inflation rate is calculated from a set of CPI figures. Question 13 The producer price index (PPI): A. measures the cost of a representative basket of goods and services to the consumers. B. includes the cost of manufactured goods to the consumers. C. includes the cost of capital and intermediate goods. D. excludes the price of imported goods. Question 14 Inflation is: A. B. C. D. E. an increase in certain important prices in the economy. a once-off increase in prices in general. a rapid increase in the quantity of money. a sustained increase in prices in general. too much money chasing too few goods. Question 15 Which one of the following is not an important statement about the definition of inflation? A. The definition should be neutral, which means that it should not refer to specific causes of inflation. B. The definition should emphasise that inflation is a process. C. The definition should emphasise that inflation pertains to the general level of prices. D. The definition should emphasise that price increases have to be considerable to be classified as inflation. E. The definition should make it clear what the causes of inflation are. © VAN SCHAIK PUBLISHERS Question 16 Which one of the following statements is incorrect? A. The consumer price index (CPI) is simply another term for the inflation rate. B. The CPI is an index that reflects the cost of a representative basket of consumer goods and services. C. The inflation rate is usually expressed as an annual rate. D. The inflation rate is usually obtained by comparing the CPI for a particular month with the CPI for the same month of the previous year. E. The inflation rate is expressed as a percentage change (from one year to the next). Question 17 Which one of the following statements is correct? A. B. C. D. E. The PPI basket contains goods and services. The PPI basket excludes capital goods. The prices used to compile the PPI exclude value-added tax. The CPI basket includes capital goods. The CPI basket excludes services. Question 18 Which one of the following statements is incorrect? A. B. C. D. E. The CPI pertains to the cost of living. The PPI pertains to the cost of production. The CPI basket includes services. The PPI basket includes intermediate goods. The prices in the CPI basket exclude value-added tax. Question 19 Inflation tends to: A. B. C. D. E. benefit lenders at the expense of borrowers. benefit taxpayers at the expense of the government. benefit the young at the expense of the elderly. benefit creditors at the expense of debtors. benefit people with fixed nominal incomes. © VAN SCHAIK PUBLISHERS Question 20 Inflation tends to: A. B. C. D. E. discourage speculative practices. encourage saving. create balance of payments problems. redistribute income from the government to the private sector. benefit creditors at the expense of debtors. Question 21 Extremely high inflation is called: A. B. C. D. E. disinflation. deflation. stagflation. hyperinflation. bracket creep. Question 22 Which one of the following is not a possible cause of demand-pull inflation? A. B. C. D. E. An increase in government spending. An increase in the oil price. An increase in consumption spending. An increase in investment spending. An increase in export earnings. Question 23 Which one of the following statements about demand-pull inflation is incorrect? A. Demand-pull inflation tends to be accompanied by an increase in the level of production and income. B. Demand-pull inflation may be illustrated by a rightward shift of the AD curve. C. Demand-pull inflation may be caused by a greater availability of consumer credit. D. Demand-pull inflation may be caused by the availability of cheaper consumer credit. E. Demand-pull inflation tends to be accompanied by higher unemployment. © VAN SCHAIK PUBLISHERS Question 24 Which one of the following is not a possible cause of cost-push inflation? A. B. C. D. E. An increase in wages. An increase in profit margins. A decrease in interest rates. A decrease in productivity. An increase in the cost of imported capital and intermediate goods. Question 25 Which one of the following statements is incorrect? Cost-push inflation: A. B. C. D. E. can be illustrated by an upward shift of the AS curve. is also called stagflation. is associated with a decrease in production, income and employment. can be eliminated by appropriate monetary and fiscal policies. may be the result of a supply shock. Question 26 Which one of the following will not be appropriate in an attempt to combat demand-pull inflation? A. B. C. D. E. An increase in interest rates. An increase in taxes. A decrease in government spending. Stricter control of consumer credit. Measures to increase the productivity of labour. Question 27 Which one of the following statements is correct? A. Inflation is a problem and therefore has to be combated at all cost. B. Inflation has definite advantages and should therefore be stimulated. C. In deciding on anti-inflation policy, the costs of other economic problems, such as unemployment and a lack of economic growth, should also be considered. D. Inflation is such as serious problem that the possible side effects of anti-inflation policies should not even be considered. E. Unemployment, inflation, low economic growth and balance of payments problems are all serious macroeconomic problems and therefore there is no need to prioritise when economic policy has to be formulated and implemented – all these problems should be regarded as priority number one. © VAN SCHAIK PUBLISHERS Question 28 Which one of the following is not an essential feature of inflation targeting? A. The public announcement of quantitative inflation targets. B. The recognition that the primary aim of the central bank is to ensure rapid economic growth. C. A broad based approach to the analysis of inflation. D. A high degree of transparency E. A high degree of accountability. Question 29 Which one of the following statements is correct? A. Inflation targeting is based on the assumption that all elements of the inflation process are under control of the central bank. B. Under an inflation-targeting framework there is no limit to the discretionary powers of the central bank. C. Inflation targeting will only work if there is a strong and stable relationship between changes in the money stock and inflation. D. One of the key aspects of inflation targeting is the impact on inflation expectations. E. Under an inflation-targeting framework the governor of the central bank does not need to consult anyone before taking a policy decision. © VAN SCHAIK PUBLISHERS