Chondrichthyes
advertisement

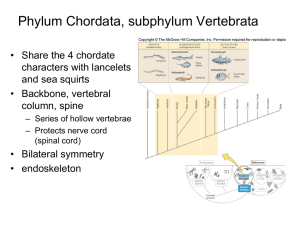
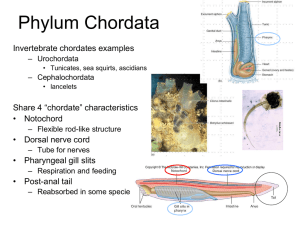
i. Chondrichthyes a. Cartilaginous fish b. Sharks, skates, rays c. 400 million years d. Sharks i. Anatomy 1. Heterocercal caudal fins 2. Teeth a. Multiple rows that constantly replace 3. No swim bladder a. Keep swimming b. Rigid pectoral fins c. Squalene oil 4. No operculum a. 5. Exposed gills Scales = denticles 6. Claspers a. Male reproductive structure ii. Hunt for food 1. Sound a. Sound travels 5x faster in water b. Low-pitched = splashing 2. Smell a. 3. Vision/sight a. 4. Blood Dilate their eyes Ampullae of lorenzini a. Detect weak electrical signals 5. Taste a. Exploratory bites, confirms whether they should eat it iii. Attacking humans 1. Mistake them for prey a. Surfer – looks like a seal b. Spearfisherman – stealing sharks food 2. Occur in a. Shallow water b. Summer iv. Reproduction 1. Internal fertilization – claspers 2. 3 types of birth a. Oviparous – egg laying b. Ovoviviparous – internal egg, live birth (sand tiger) c. Viviparous – live births (placenta/umbilical cord) lemon shark e. Skates vs rays i. Skates are smaller/ rays are larger ii. Skates no stinger/rays have a stinger iii. Skates have a fin on their tail/rays have a smooth tail iv. Similarities 1. Enlarged pectoral fins 2. Ventral gills