Lecture Notes for Section 2.3

Trigonometry Lecture Notes Section 2.3 Page 1 of 7
Section 2.3: Finding Trigonometric Function Values Using a Calculator
Big Idea: If you need the value of a trigonometric function of an angle that is not 30
, 45
, or
60
, then you need a calculator to get the answer.
Big Skill: You should be able to use a calculator to find the value of any trig function at any given angle.
Evaluating Sine, Cosine, and Tangent on a Calculator
Make sure your calculator is in degree mode.
Enter the trig function followed by the angle in parentheses.
For angles in DMS, you can enter the angle using the DMS functionality of your calculator.
For angles in DMS, you also can enter the angle as the number of degrees plus fractions of a degree.
Trigonometry Lecture Notes Section 2.3
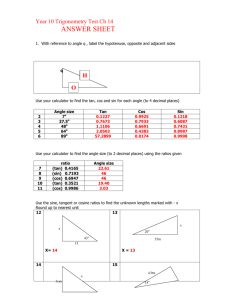
Practice:
1.
Compute sin(52
)
2.
Compute cos(187.48
)
3.
Compute tan(-2000
)
4.
Compute sin(187
44
)
5.
Compute cos(-225
32
11
)
6.
Compute tan(1500
22
38.95
)
Page 2 of 7
Trigonometry Lecture Notes Section 2.3 Page 3 of 7
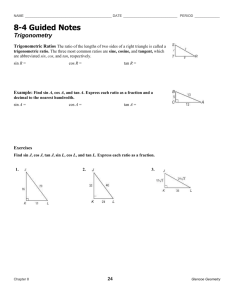
Evaluating Secant, Cosecant, and Cotangent on a Calculator
Calculators do not have buttons for these functions.
You have to use the reciprocal identities to evaluate these trig functions on a calculator.
The Reciprocal Identities (Section 1.4) sec
1 cos
csc
1 sin
cot
1 tan
To enter the reciprocal calculations correctly, you have to enter 1 divided by the correct trig function. DO NOT use the SIN -1 , COS -1 , or TAN -1 buttons for cosecant, secant, or cotangent; those are the inverse functions (not the reciprocals).
For angles in DMS, you can enter the angle using the DMS functionality of your calculator.
For angles in DMS, you also can enter the angle as the number of degrees plus fractions of a degree.
Trigonometry Lecture Notes Section 2.3
Practice:
7.
Compute sec(52
)
8.
Compute csc(187.48
)
9.
Compute cot(-2000
)
10.
Compute cot(187
44
)
11.
Compute csc(-225
32
11
)
12.
Compute sec(1500
22
38.95
)
Page 4 of 7
Trigonometry Lecture Notes Section 2.3 Page 5 of 7
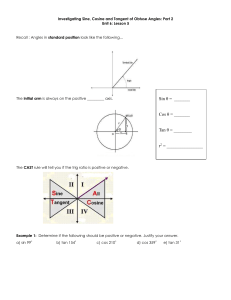
Finding Angle Measures on a Calculator
Recall the use of inverse functions from algebra: o The composition of a function and its inverse (and vice-versa) “cancel” o
2
2
16 ; 3
2
9
3 ; the square root and squaring functions are inverses of each other o We also say that the composition of a function and its inverse return the argument of the inner function. o This property can be used to solve equations by isolating a function and then applying the inverse function to both sides. x
2
15
15
2
k f
1
f
1
x
225 x
f
1
We can use this inverse function property notion to solve equations where a trig function of an unknown angle is equal to a constant. We then just take the inverse function of both sides of the equation to find the angle. o The inverse sine function is written as sin
-1
. o The inverse cosine function is written as cos -1 . o The inverse tangent function is written as tan
-1
. sin
0.5
sin
1
sin
sin
1
sin
1
cos cos
1
cos
0.5
cos
1
cos
1
tan tan
1
tan
0.5
tan
1
tan
1
26.565
Note that when you use the inverse trig functions on a calculator, o The sin
-1 o The cos
-1
function returns an angle in the interval 90
function returns an angle in the interval 0
90
180
.
. o The tan -1 function returns an angle in the interval 90
90 .
Trigonometry Lecture Notes Section 2.3 Page 6 of 7
To find an angle for the secant, cosecant, and cotangent functions, you have to use the reciprocal identities first to convert the equation so that it has cosine, sine, or tangent. csc
2.2
sec
19 sin
1
2.2
cos
1
19 sin sin
1
sin
1
2.2
sin
1
1 / 2.2
sin
1
1 / 2.2
27.036
cos cos
1
cos
1
19 cos
1
1 / 19
cos
1
1 / 19
93.017
cot
1 tan
1
1 tan tan
1
tan
1
tan
1
tan
1
Practice:
13.
Find an approximate numerical answer for a value of
that satisfies cos
0.87
.
14.
Find an approximate numerical answer for a value of
that satisfies sin
0.53
.
15.
Find an approximate numerical answer for a value of
that satisfies tan
1.115
.
Trigonometry Lecture Notes Section 2.3 Page 7 of 7
16.
Find an approximate numerical answer for a value of
that satisfies sec
2.54
.
17.
Find an approximate numerical answer for a value of
that satisfies csc
2.6
.
18.
Find an approximate numerical answer for a value of
that satisfies cot
12.5
.