Glossary: 1 tissue 2 dermal tissue 3 ground tissue 4 vascular tissue
advertisement

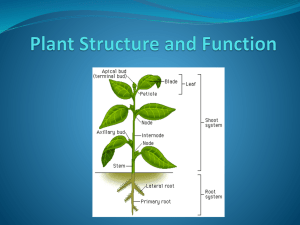
Glossary: 1 2 3 4 tissue dermal tissue ground tissue vascular tissue Tissues – groups of cells that are similar in appearance and function, for example: Structures (organs) – groups of tissues working together with a common function; e.g., roots, stems, leaves, flowers, fruits, and seeds. Plant – made up of a number of coordinated structures to form a working unit. Plant Tissue Systems The tissues of a plant are organized into three tissue systems: the dermal tissue system, the ground tissue system, and the vascular tissue system. Use information from the table to answer the questions below it. Tissue System Component Location of Tissue Systems and Its Tissues Functions Dermal Tissue Epidermis Periderm (in System • protection older stems • prevention of and roots) water loss Parenchyma Ground Tissue System tissue • Collenchyma photosynthesis tissue • food storage Sclerenchyma • regeneration tissue • support • protection Xylem tissue Vascular Tissue System Phloem tissue • transport of water and minerals • transport of food Plant Tissues Tissues are groups of cells with similar structures & functions Plants have 3 tissue systems --- ground, dermal, and vascular tissues Plant tissues make up the main organs of a plant --- root, stem, leaf, & flower Ground tissue makes up most of the plant's body, dermal tissue covers the outside of the plant, & vascular tissue conducts water & nutrients Plant cells are arranged into tissues and tissue systems A simple tissue is composed of only one type of cell; a complex tissue is composed of more than one cell type. Plants are composed of specialized cells and tissues In plants, the formation of new cells, tissues and organs is restricted almost entirely to regions known as meristems Dermal Tissue: Covers the plant body and consists of epidermis in young plants & non-woody plants that is replaced later by periderm in woody plant Epidermis is made of parenchyma cells in a single layer Epidermis on stem and leaves prevents water loss by transpiration & produces a waxy material called cuticle Epidermis Of a Leaf Epidermal cells on roots form extensions called root hairs to absorb H20 & nutrients Openings in the epidermis on the underside of a leaf where gases are exchanged are called stomata (stoma, singular) Sausage-shaped guard cells are found on each side of the stoma to help open and close the pore to prevent water loss Dead cork cells replace epidermis in woody stems & roots Ground Tissue: Ground tissue constitutes the majority of the plant body and contains parenchyma, collenchyma, and sclerenchyma cells Ground tissue of the leaf (called mesophyll) uses the energy in sunlight to synthesize sugars in a process known as photosynthesis Spongy Mesophyll of Leaf Ground tissue of the stem (called pith and cortex) develops support cells to hold the young plant upright Ground tissue of the root (also called cortex) often stores energy- rich carbohydrates Vascular Tissue: Vascular tissues transport water and dissolved substances inside the plant and helps support the stem The 2 types of vascular tissue are xylem & phloem Xylem carries water and dissolved ions from the roots to stems and leaves Phloem carries dissolved sugars from the leaves to all other parts of the plant Xylem has 2 kinds of conducting cells --- tracheids & vessel elements Xylem Cells Tracheids are long, narrow sclerenchyma cells with walls and pits for water to move between them Vessel elements are short, wide sclerenchyma cells without end walls stacked on top of each other Angiosperms (flowering plants) have tracheids & vessel elements, while gymnosperms (cone bearers) only have tracheids Phloem moves sap (dissolved sugars & minerals) from source (where they are made) to sink (where they will be used) Phloem Cells Phloem is made of cells called sieve tube members and companion cells sieve tube members are stacked to form tubes called sieve tubes with porous sieve plates between the cells for movement of sugars Companion cells are along each sieve tube member & help in loading sugar into the sieve tube CONCLUSION: Seed plants contain 2 types of vascular tissue (xylem & phloem) to help transport water, minerals, & food throughout the root & shoot systems Plant cells have several specialized structures including a central vacuole for storage, plastids for storage of pigments, and a thick cell wall of cellulose Plant cells are all box-shaped in appearance