AP United States History Manifest Destiny and Sectionalism
advertisement

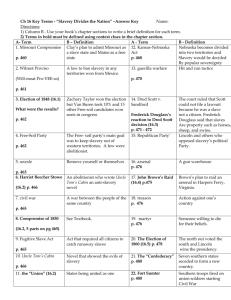
AP United States History Manifest Destiny and Sectionalism 1. Which is the correct chronological order to illustrate a cause-and-effect relationship among the following events leading to the Civil War? a) South Carolina secedes, election of Lincoln, Lincoln-Douglas debates, Dred Scott decision, Kansas-Nebraska Act b) Kansas-Nebraska Act, Dred Scott decision, South Carolina secedes, Lincoln-Douglas debates, election of Lincoln c) Dred Scott decision, Kansas-Nebraska Act, Lincoln-Douglas debates, election of Lincoln, South Carolina secedes d) Kansas-Nebraska Act, Dred Scott decision, Lincoln-Douglas debates, election of Lincoln, South Carolina secedes e) Dred Scott decision, Lincoln-Douglas debates, election of Lincoln, South Carolina secedes, Kansas-Nebraska Act 2. In the antebellum (pre-Civil War) years, the railroad’s most important impact on the economy was the: a) creation of a huge new market for railway equipment b) creation of the basis for greater cooperation between Southern planters and Northern textile manufacturers c) generation of new employment opportunities for unskilled urban workers d) participation of the federal government in the financing of a nationwide transportation network e) accessibility to Eastern urban markets provided to Midwestern farmers 3. “…the descendants of Africans who were imported into this country, and sold as slaves…are not included, under the word ‘citizens’ in the Constitution, and can therefore claim none of the rights and privileges which the instrument provides for and secures to the citizens of the United States.” This passage above is from which of the following? a) Marbury vs. Madison b) The Republican party platform of 1856 c) McCulloch vs. Maryland d) Dred Scott vs. Sandford e) the Freedmen’s Bureau Act of 1866 4. Which of the following most likely increased Mexican suspicion of United States territorial objectives in the 1830’s and 1840’s? a) abolitionist agitation in the North b) Jackson’s policy toward the annexation of Texas c) the Webster-Ashburton Treaty d) Clay’s speeches in the campaign of 1844 e) support for “manifest destiny” in the American press and by Americans in Mexico 5. In the Presidential campaign of 1860, which of the following positions was asserted by the Republican Party platform with respect to slavery? a) slavery should be abolished immediately by the federal government b) the extension of slavery to other countries should be prohibited c) the Missouri Compromise line should be extended to the Pacific Ocean, and slavery should be protected below that line d) the gradual emancipation of the slaves should begin, and the federal government should compensate slave owners for the loss of property e) the extension of slavery to United States territories should be prohibited, but slavery should be protected in the states where it already existed 6. In the 1850’s, the South differed from the North in that the South had: a) a better developed transportation system b) a better educated white population c) fewer European immigrants d) more cities e) less interest in religion 7. Which of the following statements about the Dred Scott decision is correct? a) it recognized the power of Congress to prohibit slavery in the territories, but refused on technical grounds to free Scott b) it stated that black people were not citizens of the United States c) it upheld the constitutionality of the Missouri Compromise d) it upheld the principle of popular sovereignty e) it freed Scott, but not other slaves in similar circumstances 8. Which of the following best describes the policy of the government of Mexico toward Texas? a) it tried to sell Texas to the United States at the time of the Louisiana Purchase b) it encouraged American settlement in Texas in the 1820’s and early 1830’s c) it governed Texas with stringent regulations in the 1820’s d) it encouraged the establishment of a strong local government in Texas in the mid-1830’s e) it favored the annexation of the Republic of Texas by the United States in the 1830’s and 1840’s 9. Which of the following was a plan to prohibit slavery in the territories gained after the Mexican-American War? a) the Compromise of 1850 b) the Kansas-Nebraska Act c) the Wilmot Proviso d) the Webster-Ashburton Treaty e) the Freeport Doctrine 10. Which two states did James K. Polk successfully annex into the United States during his Presidency? a) California and Oregon b) Utah and New Mexico c) Texas and California d) New Mexico and Arizona e) Oregon and Texas 11. All of the following are true about the Treaty of Guadalupe-Hidalgo except: a) that it was an agreement reached before Santa Anna’s victory at the Alamo b) that it ended the Mexican-American War c) that it resulted in Mexico ceding new lands to the United States d) that it required Mexico to recognize the Rio Grande as the Texas/Mexico boundary e) that it resulted in the increase of sectional arguments over slavery in the United States’ territories 12. Which of the following was not associated with the Bleeding Kansas period of the 1850’s? a) the transcontinental railroad issue b) the burning of Lawrence by Missouri border ruffians c) the Freeport Doctrine d) John Brown’s killing of 5 pro-slavery supporters e) the caning of Charles Sumner by Preston Brooks 13. A proposal to prevent the spread of slavery to the territories after the Dred Scott ruling was offered by: a) David Wilmot in the Wilmot Proviso b) Abraham Lincoln in the Emancipation Proclamation c) Stephen Douglas with the doctrine of popular sovereignty d) Stephen Douglas in the Freeport Doctrine e) James K. Polk in the Treaty of Guadalupe-Hidalgo 14. All of the following were results of the Kansas-Nebraska Act except: a) that antislavery northerners formed the Republican Party b) that it repealed the Missouri Compromise of 1820 c) that the question of slavery in the territories would be decided by popular sovereignty d) that it abolished the slave trade in Washington D.C. e) that it led to a population increase in both territories 15. The 1860 Republican Party platform favored all of the following except: a) construction of a transcontinental railroad b) protective tariffs c) the abolition of slavery d) free homesteads e) the supremacy of the federal government over the states 16. Which of the following was true about the Compromise of 1850? a) it allowed California to be admitted as a free state b) it was originally written by Stephen Douglas c) it shut out the possibility of slavery in the territories d) it overturned the Webster-Ashburton Treaty e) it ended slavery in Washington D.C. 17. Stephen A. Douglas argued in his Freeport Doctrine during the Lincoln-Douglas debates that: a) the Dred Scott decision was unconstitutional b) actions by territorial legislatures could keep slavery out of the territories c) popular sovereignty would guarantee slavery in all U.S. territories d) Congress should re-open the Atlantic slave trade e) Free soil settlers in the territories would successfully vote down the expansion of slavery 18. Advocates of Manifest Destiny claimed the motive for territorial expansion was to: a) achieve a political balance between north and south b) secure new resources and markets for the United States c) extend American liberty to new territories d) ensure that no foreign powers gained territory in North America e) begin again the importation of slaves to expand U.S. agricultural markets 19. People who favored the concept of nativism feared and opposed: a) slavery b) abolition c) immigration d) popular sovereignty e) secession 20. Which of the following was intended to spark a general slave uprising? a) the publication of Uncle Tom’s Cabin b) the raid on Harper’s Ferry c) the work of the Underground Railroad d) the secession of South Carolina from the United States e) the passage of the Fugitive Slave Act