Lenses Virtual Lab using PhET Geometric Optics
advertisement

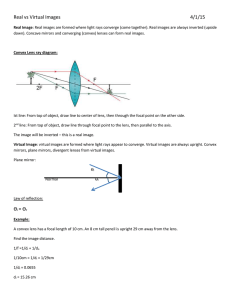
Geometric Optics Virtual Lab Name____________________________ Date ______ Objectives: To demonstrate the formation of images from convex and concave lenses. To identify the type of image formed by convex and concave lenses. To confirm the lens equations. Procedure: 1. Go to http://www.geogebratube.org/student/m6005 2. Take some time to play with the simulation to get familiar with how it works. 3. Position the focus at 4. This will create a convex lens. 4. Fill out the rest of Table 1. Keep the ho constant for the rest of the experiment. 5. Reposition the object and fill out the rest of Table 2. 6. Move the focus to -4. This will create a convex lens. 7. Fill out the rest of Table 2. Data: Table 1 Focal length, f 2f Height of object, ho 4 Position of Object Beyond 2f (cm) Table 2 At 2f Between 2f (cm) and f (cm) At f (cm) Between f and lens (cm) do di hi M Type of image: real, none, or virtual Direction of image: inverted or upright Table 3 Trial 1 f (cm) do(cm) di(cm) M Type of image: real, none, or virtual Direction of image: inverted or upright Trial 2 Questions and Conclusions: 1. For each of the real images you observed, calculate the focal length of the convex lens, using the lens/mirror equation. Show your calculations. Does your calculated value agree with the observed value? a. Beyond 2f b. At 2f c. Between 2f and f d. Between f and lens 2. Calculate the magnification for each image. Show your calculations. Does your calculated value agree with the observed value? a. Beyond 2f b. At 2f c. Between 2f and f d. Between f and lens e. Concave Trial 1 f. Concave Trial 2 3. When does a convex lens act like a magnifying glass? 4. Describe the conditions for forming a virtual image with lenses. 5. How does the image of a concave lens always appear? Where is it located with respect the lens and the object? 6. Research the two basic types of vision problems, farsightedness and nearsightedness, and describe the lens prescription for each. Use diagrams of the eye to show the light paths before and after remediation.