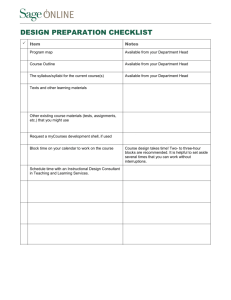
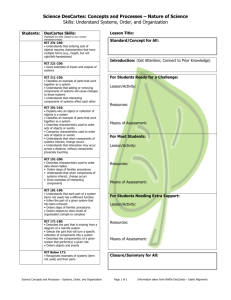
Language Arts Curriculum Guide Template
advertisement

1 Idaho State Curriculum Guide Pre-Algebra Number Sense Estimation/Accurate Computation Reasoning/Problem Solving Measurement ©State of Idaho 2003 Algebra, Functions, & Mathematical Models Geometry Data Analysis, Probability, & Statistics McRel Alignment—8th ISAT Cut Scores State Standards Sample Test Items New Vocabulary Number Sense State Standard and Benchmark Estimation/Accurate Computation Local Curriculum Number Sense 337.01a Place Value, Expanded and Standard Notation Learning Continuum and other Performance Objectives Reasoning/Problem Solving Measurement Sample Assessment and Sample Quizzes Algebra, Functions, & Mathematical Models Sample Sequence Minimum Hours Allotted Geometry Data Analysis, Probability, & Statistics Sample Teaching Strategy Return to Top Learning Continuum DMA Benchmark Teacher Observable ISAT For Learning: Have students choose an amount they’d like to win in the lottery and write that number in expanded form from standard notation. Then exchange expanded forms with a partner to see if they could convert to standard form and get the amount their partner wished for. Of Learning: RIT 221-230 RIT 231-240 Use this opportunity to compare and contrast as to why we may use standard notation instead of expanded form, possibly as a partner activity. Sample Resources 2 Idaho State Curriculum Guide Pre-Algebra State Standard and Benchmark 337.01a Ordering, Equalities, and Inequalities 337.01a 337.02b Fractions / Ratio / Proportion 337.01b Understand and use rational and irrational numbers Local Curriculum Learning Continuum and other Performance Objectives Learning Continuum DMA Benchmark Teacher Observable ISAT Learning Continuum DMA Benchmark Teacher Observable ISAT Teacher Observable DMA Sample Assessment and Sample Quizzes For Learning: Have students list the common simple fractions as a decimal, and as a percent. Arrange a list of numbers that are written as fractions, decimals or percents in order. Make chart of common fractions with decimal equivalents. Look for and explain the patterns. Of Learning: RIT 211-220 RIT 221-230 For Learning: Use fraction strips to show the meaning of a fraction. List the eye color of each student in the class. Use the data to write the ratio of blue eyes to brown eyes etc. Sample Sequence ©State of Idaho 2003 Minimum Hours Allotted Sample Teaching Strategy This may be a good time research the stock market, noting that shares recently went to decimal representation (In 2001 I believe) from fractional notation. Possibly integrate with history and research the crash of 1928 converting some stocks of that era as decimals used today, and visa-versa. Throw in percent of change from 1928 to today. There are many M&M activities that could be developed to show the concept of ratio and proportion. Of Learning: RIT 211-220 RIT 221-230 RIT 231-240 For Learning: Calculate square roots of 2, 3, 4, and 5 to the nearest ten-thousandth. Note which are rational and hypothesize which is the larger set. Sample Resources Identify the differences between rational and irrational numbers. Give examples of each. M&M activity http://www.isbe. state.il.us/ils/cla ssassess/math/st ageE/math6A6C 6D10AE.pdf Real number charts 3 Idaho State Curriculum Guide Pre-Algebra State Standard and Benchmark 337.01d Factorization / Divisibility 337.01a 337.01c Decimals 337.02b Percents 337.01c Exponents and Scientific Notation Local Curriculum Learning Continuum and other Performance Objectives Learning Continuum DMA Benchmark Teacher Observable ISAT Learning Continuum DMA Benchmark Teacher Observable ISAT Learning Continuum DMA Benchmark Teacher Observable ISAT Learning Continuum DMA Benchmark Teacher Observable ISAT Sample Assessment and Sample Quizzes For Learning: Have students define and give examples of prime numbers, composite numbers, and prime factorization. For Learning: On grid paper have students make a 10X10 decimal model. Have the students then show .3 or .8 on the grid model. Of Learning: RIT 211-220 RIT 221-230 RIT 231-240 For Learning: Have students fill in a chart like this including the decimal and the percent for each fraction. Of Learning: RIT 211-220 RIT 221-230 For Learning: Express the national debt in scientific notation. Calculate how many miles long it would be if we laid that many dollar bills end to end. Of Learning: RIT 211-220 RIT 221-230 RIT 231-240 Sample Sequence ©State of Idaho 2003 Minimum Hours Allotted Sample Teaching Strategy Sample Resources Have the students write a paragraph describing the differences between the two given examples, so that the students can get a feeling for the difference between LCM and GCF Create a mnemonic device for each. Lesson? Power Point LCM GCF Use models to demonstrate concept. In pairs or groups, have students discuss and record situations where decimals, percents, or fractions are most appropriate to use. Research instances of each making equivalent substitutions to see if info makes sense. Create a real world situation, such as an unmanned mission to mars, calculating distances using scientific notation. 4 Idaho State Curriculum Guide Pre-Algebra State Standard and Benchmark 337.01b Integers 337.01b Square Roots 337.01a Absolute Value 337.01e Position real numbers on a number line Local Curriculum Learning Continuum and other Performance Objectives Learning Continuum DMA Benchmark Teacher Observable ISAT Learning Continuum DMA Benchmark Teacher Observable ISAT Learning Continuum Teacher Observable DMA Sample Assessment and Sample Quizzes For Learning: Write two inequalities involving -3 and -1 State which number is smaller -3 and -1 Sample Sequence ©State of Idaho 2003 Minimum Hours Allotted Sample Teaching Strategy Create number lines to use with counters to demonstrate that the number that is further right is the larger value. Of Learning: RIT 221-230 For Learning: List all the perfect squares between 1 and 625 Estimate 79 Draw a square that has an area of 49 square centimeters Of Learning: RIT 221-230 RIT 231-240 For Learning: Determine between a set of numbers which has the greater absolute value: -7, 4, 0, 5. Drill and practice to memorize perfect squares between 1 and 625. Compare absolute value to distance. Going to grandma’s is 12 miles and 12 miles back. Neither is a negative number. For Learning: Locate a given set of numbers on a number line. DMA Benchmark Teacher Observable ISAT Of Learning: RIT 211-220 Create number lines in math journals for future reference. Sample Resources 5 Idaho State Curriculum Guide Pre-Algebra State Standard and Benchmark Local Curriculum Learning Continuum and other Performance Objectives Sample Assessment and Sample Quizzes Estimation and Computation 337.02a Rational Numbers 337.02a Decimals Learning Continuum DMA Benchmark Teacher Observable Learning Continuum DMA Benchmark Teacher Observable ISAT Sample Sequence ©State of Idaho 2003 Minimum Hours Allotted Sample Teaching Strategy Return to Top For Learning Evaluate the following expressions: ½ + 2/3 -5 x 7 12 – 5 7/8 Of Learning: RIT 211-220 RIT 221-230 RIT 231-240 For Learning: Compute batting averages for a given player or team. Teacher made assessment covering the four operations. Create a travel log taking a fictitious trip across the U.S. or integrate with Geography and countries they’re studying. Show the meaning of .3 times .8 with a 10x10 grid model. Of Learning: RIT 211-220 RIT 221-230 RIT 231-240 RIT 211-220 (Money) RIT 231-240 (Money) 337.02a Fractions Learning Continuum DMA Benchmark Teacher Observable ISAT For Learning: Using fraction bars, demonstrate through presentation or illustration a series of teacher chosen problems with all 4 operations. Of Learning: RIT 211-220 RIT 221-230 RIT 231-240 Using the stock market, give the kids $100,000 to “invest” for a month or so. The students should tabulate losses and gains each day – a chance to use Excel in a technology lesson. Sample Resources 6 Idaho State Curriculum Guide Pre-Algebra State Standard and Benchmark 337.02b recall common equivalent fractions decimals percents 337.01a 337.01c Percents 337.01c Integers 337.01b 337.02d Squares and Square Roots Local Curriculum Learning Continuum and other Performance Objectives Teacher Observable DMA Learning Continuum DMA Benchmark Teacher Observable ISAT Learning Continuum Sample Assessment and Sample Quizzes For Learning: Use of “Mad Minute” type exercises. For Learning: Students should be able to solve all 3 types of percentage problems: a) 30% of 60 is what number? b) 12 is 25% of what number? c) 18 is what % of 72? Of Learning: RIT 221-230 RIT 231-240 For Learning: Use counters to model Addition and subtraction of integers. DMA Benchmark Teacher Observable ISAT Of Learning: RIT 211-220 RIT 221-230 RIT 231-240 Teacher Observable DMA For Learning: Mad Minute type exercises. Calculate the square root to the hundredth position. Sample Sequence ©State of Idaho 2003 Minimum Hours Allotted Sample Teaching Strategy Drill and practice of common equivalencies such as 25%, 1/3, 0.5, ¾, etc. Sample Resources Common fractions chart? Take a class created survey and find the percentages of each answer. Using percentages of answers to a survey, have students figure out how many peers answered in a particular way. Create a manipulative system of green and orange counters to model positive and negative numbers to be used to model addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division. Drill and practice. Use real-world situation showing how carpenters use Pythagorean Theorem to make sure walls and floors are square -- straight. Power Point adding integers Power Point subtracting integers Page 82, 88 Pre-Algebra, Glencoe 1999. 7 Idaho State Curriculum Guide Pre-Algebra State Standard and Benchmark 337.02c Order of operations Local Curriculum Learning Continuum and other Performance Objectives Teacher Observable DMA 337.02e Select method of computation Teacher Observable DMA 337.03a predict computation results Teacher Observable DMA 337.03b recognize when estimation is appropriate Teacher Observable DMA Sample Assessment and Sample Quizzes For Learning: Evaluate: 2(16 – 4) ÷ 4 + 6 x 3 = For Learning: Given a story problem, describe how you would solve the problem. Include all computations and how you would use the four operations. For Learning: Estimate total price for 5 shirts costing $18. 67 each. (5 x $20) For Learning: Explain when/not and why/not doctors and builders should use estimation. Sample Sequence ©State of Idaho 2003 Minimum Hours Allotted Sample Teaching Strategy Create a game using three number cubes. Have one of the number cubes 4 – 9, while the other two are 1 – 6. Make a board with 64 - 100 chosen numbers that the object is to get three or four in a row by using order of operations to “land” on a spot. In groups or pairs, have the students discuss how they would handle each situation: a) Going to the grocery store and having a fixed amount to spend. b) Taking a test in school with all technology available. c) Describe situations where pencil and paper is better than mental math. Going to the grocery store and having a fixed amount to spend, give the kids a list and ask if they have enough money. Have students interview adults to find out when they use estimation and when they would never use estimation. Sample Resources 8 Idaho State Curriculum Guide Pre-Algebra State Standard and Benchmark Local Curriculum Learning Continuum and other Performance Objectives 337.03c Determine if estimate is an overestimate or underestimate Teacher Observable DMA Sample Assessment and Sample Quizzes For Learning: Johnny has $30 for his date with Sally. He wants to take her to a movie, $7.50 each, dinner at Pizza Hut, $13.58 pizzas, and Dairy Queen for $0.99 Blizzards. He thinks he has enough. Is his estimate of $30 low, or high, or just right? Mathematical Reasoning and Problem Solving 338.01a Use strategies for real world situations 338.01b Recognize pertinent information 338.01c Make predictions and decisions Sample Sequence ©State of Idaho 2003 Minimum Hours Allotted Sample Teaching Strategy Use a real world dealing with an estimate of travel time to a location you/ they are heading. Record the actual time it took to arrive and indicate whether the estimate was low, high or just right. Return to Top For Learning: If paint costs $15 a gallon and covers 300 square feet, how much will it cost to paint your classroom (give measurements). As a group, have kids plan a class party with a set amount of money. DMA For Learning: Given a problem, identify which information you need to complete the problem. Teacher Observable For Learning: Using a graph, predict what the future numbers will be. Tell the kids you have a problem such as you locked your keys in the car. Explain it’s your mother’s birthday and your cat is having kittens, your spare key is at home, your daughter dyed her hair green and so on. Have kids solve your problem and state which info was pertinent. Using research provided by fish and game, have students work in groups to predict the salmon run for the next two years. Teacher Observable DMA Teacher Observable DMA Sample Resources 9 Idaho State Curriculum Guide Pre-Algebra State Standard and Benchmark 338.02a 338.02b 338.02c Use reasoning skills to recognize problems and Local Curriculum Learning Continuum and other Performance Objectives Learning Continuum DMA Benchmark Teacher Observable ISAT Sample Assessment and Sample Quizzes For Learning: Knowing how to find the area of a square, have the students find the surface area of a cube. DMA Teacher Observable DMA Sample Teaching Strategy Of Learning: RIT 211-220 RIT 221-230 RIT 231-240 For Learning: Use technology to find the square root of 15,025. Use Excel to collect data and select the best way to graphically show results. Many M&M projects work here. mathematically. Teacher Observable Minimum Hours Allotted Integrate a unit with Reading and English where the students write a proposal/report for a fictitious company. Maybe a car dealership is opening a new lot in town and wants to know what type of cars to place on the lot. After giving students a variety of info, have them explain the concepts used as well as their reasoning to solve the situation for which they formulated their conjecture and plan of attack and came up with their conclusions. express them 338.03a 338.03b 338.03c Apply appropriate technology and models to find solutions to problems. 338.04a 338.04b 338.04c Communicate results using appropriate terminology and methods. Sample Sequence ©State of Idaho 2003 For Learning: Present report using graphs, models, tables, and a written portion including proper terminology to show how they arrived at their conclusion. Great opportunity for an interdisciplinary unit between Math, English, Reading, Science, and Geography. Maybe a study on endangered species and solutions to get them off the endangered list. Sample Resources 10 Idaho State Curriculum Guide Pre-Algebra State Standard and Benchmark Local Curriculum Learning Continuum and other Performance Objectives Sample Assessment and Sample Quizzes Concepts and Principles of Measurement 339.01a-f 339.01d Understand and use U.S. customary and metric measurements. Learning Continuum (Length, Weight, Volume) Learning Continuum (Time, Temp) Learning Continuum (Area, Perim., Circumference) DMA Benchmark Teacher Observable ISAT 339.02a Use rates to make indirect measurements Teacher Observable DMA Sample Sequence ©State of Idaho 2003 Minimum Hours Allotted Sample Teaching Strategy Return to Top For Learning: Teacher made application test where students must find area, perimeter, volume, in multiple converted units, i.e., meters and centimeters. Keep vocabulary up to date in math journals. Select and use appropriate units and tools to make formal measurements as well as estimates in standard and metric measures. Of Learning: RIT 211-220 (Angle Measure) RIT 211-220 (Length, Weight, Volume) RIT 221-230 (Length, Weight, Volume) RIT 231-240 (Length, Weight, Volume) As a group project, design and determine how much lumber would be needed to build a doghouse. Include an estimate of costs and materials. Maybe have the students include some measures in both standard and metric. Place containers in room with labels of what size they are, i.e. e., liter, gallon, quarts, pints, and cups. Create a poster with standard formulas for area, perimeter, volumes, distance, and circumference. RIT 231-240 (Time, Temperature) RIT 211-220 (Area, Perim, Circum) RIT 221-230 (Area, Perim, Circum) RIT 231-240 (Area, Perim, Circum) For Learning: If five gallons of ice cream costs $4.50, how much does 1 quart cost? Given the weight of a certain item in the classroom, estimate the weight of other items. Sample Resources 11 Idaho State Curriculum Guide Pre-Algebra State Standard and Benchmark 339.03a Use proportions, ratios and scales 339.04a Understand units and relations to one another Local Curriculum Learning Continuum and other Performance Objectives Teacher Observable DMA Teacher Observable DMA Sample Assessment and Sample Quizzes 343.01a 343.01b 343.01c Patterns, Sequences, Functions DMA Benchmark Teacher Observable ISAT Minimum Hours Allotted For Learning: If 2 inches on the map represents 300 km, how many kilometers is 75. inches? For Learning: Extend the first five numbers in the Fibonacci sequence and explain the pattern. Using what we know about the distance formula, how might we estimate our travel time if we need to go 465 miles? Vocabulary quiz. Of Learning: RIT 211-220 RIT 221-230 RIT 231-240 Sample Teaching Strategy Use nutritional info on the back of items brought in by students to find total calories, fat, sugar, etc. contained in package as well as cost per ounce, gram, or whatever measure chosen. Use map scale to determine distances. Enlarge a cartoon to a given scale. Determine the reading hours of an entire class if everyone reads for twenty minutes. For Learning: If you are traveling 60 mph for 4.5 hours, how far did you travel? Algebra, Functions, and Mathematical Models Learning Continuum Sample Sequence ©State of Idaho 2003 Return to Top Discovery of patterns is fun for most kids. Give them some sequences to extend. Have them explain the pattern. Demonstrate what we know about the Pythagorean theorem, see if one of the classroom wall is square. Continue to keep adding vocabulary to math journals, continuously correcting improper terminology usage. Sample Resources 12 Idaho State Curriculum Guide Pre-Algebra State Standard and Benchmark 343.02a Represent data as graph, table & mathematical relationship 343.03a Local Curriculum Learning Continuum and other Performance Objectives Teacher Observable DMA Use patterns and functions to solve problems Teacher Observable DMA 340.03a Learning Continuum Solving Equations and Inequalities DMA Benchmark Teacher Observable ISAT Sample Assessment and Sample Quizzes For Learning: Given a set of data, organize it in a table and as a graph. Show the mathematical relationship that exists. For Learning: Illustrate a line graph showing distance traveled at a constant speed of 60 mph. For Learning: Solve x + 6 > 5 and 3y – 9 = 24 Of Learning: RIT 211-220 RIT 221-230 RIT 231-240 Sample Sequence ©State of Idaho 2003 Minimum Hours Allotted Sample Teaching Strategy Sample Resources Find an article from the paper or recent magazine, and while the students are taking notes, hold a class discussion about what is being represented and any mathematical relationship that exists. Also show an example of no mathematical relationship. Use temperature as an example. Let the x-axis represent time, while the y-axis represents temperature. Start at ay time and temp, assuming constant increase. If given 6:00 a.m. and 9:30 a.m. predict the temperature at noon. Have the students compare and contrast inequalities with equality. Have the students make a journal entry describing an instance where they would equality and inequalities. Power Point presentation one step equations with addition and subtraction-? 13 Idaho State Curriculum Guide Pre-Algebra State Standard and Benchmark 340.03b Graph representation of linear equations Local Curriculum Learning Continuum and other Performance Objectives Teacher Observable DMA Benchmark Teacher Observable ISAT DMA Benchmark Teacher Observable ISAT Learning Continuum 340.02a Properties For Learning: Simplify the expression 4a + 3b – 7 – b + 2a. For Learning: Simplify 2(3a + 2c) + a – 4c. 340.02b Order of Operations For Learning: Graph the equation y = 2x – 4. DMA 340.02c Simplifying Expressions Sample Assessment and Sample Quizzes DMA Benchmark Teacher Observable ISAT For Learning: Identify through matching the expression and the property it is an instance of. Sample Sequence ©State of Idaho 2003 Minimum Hours Allotted Sample Teaching Strategy Sample Resources While students take notes, write an equation on the board. Demonstrate that to complete the graph you pick a point for x and see what y equals thus creating an ordered pair. Try to get the students to realize this is nothing more than substituting for one value to find the other. Note that no matter what substitutions are made, the ordered pairs are always on the line. Now we only need two points to make a line. Relate this to stocking shelves in a grocery store; we still sort by item. A review activity recalling order of operations works here. Ask “Why would we not use order of operations here when we use it every other time”. Create another game as we did the first time we encountered order of operations. This is a great jigsaw activity. Also, you can set up a scavenger hunt in the classroom where you have left notes on and demonstrations of that the kids have to find and write down in their journals. Power Point Presentation properties 14 Idaho State Curriculum Guide Pre-Algebra State Standard and Benchmark 340.01a 340.01c Use Variables and math symbols in expressions, equations and inequalities 340.01b Translate word problems into an algebraic expression Local Curriculum Learning Continuum and other Performance Objectives Sample Assessment and Sample Quizzes Teacher Observable DMA For Learning: As a quiz, given a word phrase, translate into an algebraic expression and visaversa. Teacher Observable DMA For Learning: As a quiz, given a word phrase, translate into an algebraic expression and visaversa. Concepts and Principles of Geometry 341.01a Shapes and Figures, 2- & 3dimensional Learning Continuum DMA Benchmark Teacher Observable ISAT Minimum Hours Allotted Sample Teaching Strategy Let a represent apples, b represent bananas, c represent cantaloupe, and g represent grapes. Ask the students how these items are sorted at the store. Reinforce that we keep apples together and so on, in reference to addition and subtraction. I like to refer to multiplication as a blender. Next, have them write an expression for 2 apples, 4 bananas, 6 cantaloupes, and 9 grapes. While the students take notes demonstrate that Sara baby-sits for different periods of time and wants to write an algebraic expression to represent how much she will make if she charges $4.50 an hour. Have students write in their math journals how they could use algebra like Sara from above did. Return to Top For Learning: Quiz matching pictures and defining properties to the correct to the correct two- and three- dimensional object. Of Learning: RIT 211-220 RIT 221-230 Sample Sequence ©State of Idaho 2003 Create a chart listing the types of one- and two- dimensional objects. Then classify the objects using their defining properties. Finally, draw a picture of the shapes. Sample Resources 15 Idaho State Curriculum Guide Pre-Algebra State Standard and Benchmark 341.01b Construct and measure geometric shapes 341.01d Congruency and Similarity 341.01d 341.01g Symmetry and Transformations 341.01c 341.01h Geometric Properties and Terminology Local Curriculum Learning Continuum and other Performance Objectives Teacher Observable Sample Assessment and Sample Quizzes DMA Benchmark Teacher Observable ISAT Learning Continuum DMA Benchmark Teacher Observable ISAT Learning Continuum DMA Benchmark Teacher Observable ISAT Minimum Hours Allotted Sample Teaching Strategy For Learning: Use appropriate tools to measure shapes and angles. Use rulers, compasses, and protractors to measure geometric shapes and angles in the classroom. For Learning: Identify through matching which figures are congruent and which are similar. Have students take notes as you go over similarities and differences in concepts of congruence, and symmetry of shapes. Have students identify items in the room that are congruent, similar and/or symmetric. Through your demonstration while students take notes, go over symmetry and the transformations rotation, translation and reflection. DMA Learning Continuum Sample Sequence ©State of Idaho 2003 Of Learning: RIT 211-220 RIT 221-230 For Learning: Identify which figures share symmetries and construct their lines of symmetry. Identify type of transformation. Of Learning: RIT 211-220 RIT 231-240 For Learning: Vocabulary quiz over geometry terms. Match the description with the figure, i.e., a quadrilateral that has only one pair of opposite sides that are parallel matches with a trapezoid. Of Learning: RIT 211-220 RIT 221-230 RIT 231-240 Have students take notes on geometry vocabulary. Use vocabulary to play bingo or concentration. Use pinwheel or jigsaw to learn/teach groups vocabulary and properties. Sample Resources 16 Idaho State Curriculum Guide Pre-Algebra State Standard and Benchmark 341.03a Coordinate 341.01e 341.02a Apply formulas for perimeter, circumference, area, and Pythagorean theorem 341.01f Surface area and volume Local Curriculum Learning Continuum and other Performance Objectives Learning Continuum DMA Benchmark Teacher Observable ISAT Teacher Observable DMA Teacher Observable DMA Sample Assessment and Sample Quizzes For Learning: Using a city map, have students locate buildings or intersections using streets as coordinates. Of Learning: RIT 211-220 (Graphing) RIT 221-230 (Graphing) RIT 231-240 (Graphing) For Learning: Calculate the area and perimeter of a basketball court and it’s center circle as well as it’s key. Using the Pythagorean theorem, calculate the missing side. For Learning: Given a figure with measurements given, calculate surface area and volume. Data Analysis, Probability, and Statistics 342.01a 342.01b Analyze and make conclusions drawn from tables charts and graphs Teacher Observable DMA Sample Sequence ©State of Idaho 2003 Minimum Hours Allotted Sample Teaching Strategy Create a game similar to “Battleship”. Relate to Geography and latitude and longitude (recall). Create a poster with standard formulas for area, perimeter, volumes, distance, the Pythagorean theorem, and circumference. Construct a cylinder, pyramid, rectangular prism, cube, etc., and calculate surface area and volume. Return to Top For Learning: Quiz over the interpretation of a graph, table, and a chart. Using graphs, charts, or tables found in the paper, hold a class discussion over what the info is trying to present as the students take notes. Sample Resources 17 Idaho State Curriculum Guide Pre-Algebra State Standard and Benchmark 342.02a Collect organize, and display data 342.04a Probability & Prediction 342.04b 342.05b Language of probability 342.04c 342.05c Recognize equally likely outcomes Local Curriculum Learning Continuum and other Performance Objectives Learning Continuum DMA Benchmark Teacher Observable ISAT Learning Continuum DMA Benchmark Teacher Observable ISAT Teacher Observable DMA Teacher Observable DMA Sample Assessment and Sample Quizzes For Learning: Have the students create a survey. They are to collect the results, organize and display the data as an individual project. For Learning: Quiz on basic simple probabilities such as: What is the probability that you will roll an even number on a six-sided number cube. Sample Sequence ©State of Idaho 2003 Minimum Hours Allotted Sample Teaching Strategy Have students collect and display data by surveying the actual number of chocolate chips in a cookie. There are many M&M activities that can be used here also. Find the probability of drawing a jack of hearts in a standard deck of cards. Of Learning: RIT 221-230 For Learning: Give a quiz over the vocabulary used in probability. For Learning: Quiz over probability of rolling a 5 on a number cube and the probability of a spinner landing on a certain number or set of numbers. Use vocabulary to play bingo or concentration. Have the students bring coins, or they can use two sided counters, and let each flip the coin 50 times recording each result. Then survey the class and see how many, if any, had 25 of each. Next, add all students’ results and see if overall heads and tails were even. Ask why or why not. Sample Resources 18 Idaho State Curriculum Guide Pre-Algebra State Standard and Benchmark 342.05a Combinations and Permutations 342.03a Statistics 342.03b Range, frequency and distribution Local Curriculum Learning Continuum and other Performance Objectives Learning Continuum DMA Benchmark Teacher Observable ISAT Learning Continuum DMA Benchmark Teacher Observable ISAT Teacher Observable DMA Sample Assessment and Sample Quizzes For Learning: Have students model the theoretical probability of rolling a 7 with two six sided number cubes. Of Learning: RIT 221-230 For Learning Have students compute an individual mean, median, mode, and range of grades in a particular course. Of Learning: RIT 221-230 RIT 231-240 For Learning: Given a set of data, create a frequency distribution chart. Sample Sequence ©State of Idaho 2003 Minimum Hours Allotted Sample Teaching Strategy Have five students volunteer and come to the front of the class. To demonstrate permutations, have 3 chairs and see how many ways the kids can be arranged where order matters. Using the same kids and chairs, demonstrate how many ways the kids can be grouped where order doesn’t matter, combinations. Survey the students about their father’s age, moms don’t like us to know. Collect and organize the data to demonstrate finding the mean, median and mode. Maybe use a jigsaw method to have students discover and teach each other about mean, median and mode. Bring lists of professional sports teams or leagues and have the kids work in groups or individually to organize the data into a frequency distribution. While you’re demonstrating with one set of data, have the students working with another set. Sample Resources 19 Idaho State Curriculum Guide Pre-Algebra ©State of Idaho 2003 APPROVED ISAT PROFICIENCY SCORES Return to Top Approved by the State Board of Education March 6, 2003 READING Basic Proficient Advanced 2 174 182 193 3 185 193 204 4 192 200 211 5 198 206 217 6 203 211 222 7 207 215 226 8 210 218 229 9 213 221 232 10 216 224 235 LANGUAGE Basic Proficient Advanced 2 176 184 197 3 186 194 207 4 193 201 214 5 200 208 221 6 204 212 225 7 207 215 228 8 211 219 232 9 213 221 234 10 214 222 235 MATH Basic Proficient Advanced 2 174 185 201 3 185 196 212 4 194 205 221 5 202 213 229 6 208 219 235 7 214 225 241 8 222 233 249 9 229 240 256 10 231 242 258 PROFICIENCY LEVELS DEFINITIONS Approved by the State Board of Education March 6, 2003 ADVANCED: Exceeds Standards Back to Top The student demonstrates thorough knowledge and mastery of skills that allows him/her to function independently above their current educational level. The student demonstrates a comprehensive understanding of all relevant information relevant to the topic at level. The student demonstrates comprehension and understanding of knowledge and skills above his/her grade level. The student can perform skills or processes independently without any significant errors. 20 Idaho State Curriculum Guide Pre-Algebra PROFICIENT: Meets Standards ©State of Idaho 2003 Back to Top The student demonstrates mastery of knowledge and skills that allow them to function independently on all major concepts and skills related to their educational level. The student demonstrates a comprehensive understanding of all information relevant to the topic, at level. The student can perform skills or processes independently without any significant errors. BASIC: Below Standards Back to Top The student demonstrates basic knowledge and skills usage but cannot operate independently on concepts and skills related to his/her educational level. Requires remediation and assistance to complete tasks without significant errors. The student has an incomplete knowledge of the topic and/or misconceptions about some information. The student requires assistance and coaching to complete tasks without errors. BELOW BASIC: Critically Below Standards Back to Top The student demonstrates significant lack of skills and knowledge and is unable to complete basic skills or knowledge sets without significant remediation. The student has critical deficiencies of relevant knowledge of topic and/or misconceptions about some information. The student cannot complete any skill set without significant assistance and coaching. 21 Idaho State Curriculum Guide Pre-Algebra ©State of Idaho 2003 State Standards—8th Grade Math Return to Top 336. MATHEMATICS STANDARDS – GRADE 8, SECTIONS 337 THROUGH 343. The samples associated with the content standards are meant to illustrate meaning and to represent possible areas of application. They are not intended to be an exhaustive list, but are samples of applications that would demonstrate learning. 337. BASIC ARITHMETIC, ESTIMATION, AND ACCURATE COMPUTATIONS. Rationale: An understanding of numbers and how they are used is necessary in the everyday world. Computational skills and procedures should be developed in context so the learner perceives them as tools for solving problems. Standard – The student will: Understand and use numbers. 01. a. Return to Place Value Content Knowledge and Skills: Read, write, order, and compare real numbers (integers, fractions, decimals, percents, ratios) and absolute values. Return to Ordering Return to NS: Decimals Return to Fraction/ Ratio/ Proportions Return to Absolute Value Return to EC: Percents Return to Use Rational Numbers b. Understand and use real numbers, both rational and irrational. i. ii. iii. iv. v. vi. i. ii. Return to NS: Integers Samples of Applications: Interchange fractions, decimals, or percents, to determine pricing markup or markdown. Use fractions to increase or decrease recipes. Use percentages to computer taxes and commissions. Use decimals to computer interest problems. Use ratios to compute sports averages (batting averages). Which has greater absolute value, -5 or 2? Explain that irrational numbers neither terminate nor repeat when written in decimal form. Calculate the square root of a number to the thousandths. Return to NS: Square Roots Return to EC: Squares and Square Roots c. Return to NS: Decimals Return to Exponents Return to EC: Percents Show a sense of magnitudes and relative magnitudes of real numbers (integers, fractions, decimals) using scientific notation and exponential numbers. i. ii. Express distances in our solar system using scientific notation. Order a list of fractions, decimals, and exponential numbers. Return to EC: Integers Return to Factorization / Divisibility d. Develop and apply number theory concepts. i. Identify prime factorization, greatest common factors and least common multiples. Return to Position Numbers on Number Line e. Understand the position of real numbers on a number line. i. ii. Locate a given set of real numbers on a number line. Accurately identify positive and negative integers on a thermometer. 22 Idaho State Curriculum Guide Pre-Algebra 02. Perform computations accurately. a. Consistently and accurately add, subtract, multiply, and divide rational numbers. b. Instantly recall common equivalent fractions, decimals, and percents. c. ©State of Idaho 2003 i. Plan a road trip. Record and calculate gas mileage, food and lodging expenses. Evaluate numerical expressions using the order of operations. i. Find the surface area of a cylinder. d. Understand and use exponents. i. Solve problems using exponential growth, for instance, Sally tells 3 friends a secret. The next day those 3 friends tell 3 other friends. If this pattern continues for 5 days, how many friends will hear the secret? e. Select and use an appropriate method of computation from mental math, paper and pencil, calculator, or a combination of the three. f. Use appropriate vocabulary. a. Use estimation to predict computation results. b. Recognize when estimation is appropriate and understand the usefulness of an estimate as distinct from i. Estimate the population of people at the mall on any given date. Explain why or when exact answers might be necessary. Return to EC: Rational Numbers Return to EC: Decimals Return to EC: Fractions Return to Fraction/ Ratio/ Proportions Return to Recall Common Equivalents Return to NS: Percents Return to Order of Operations Return to EC: Squares and Square Roots Return to Select Method of Computation 03. Estimate and judge reasonableness of results. Return to Predict Computation Results Return to Recognize Appropriate Estimation ii. 23 Idaho State Curriculum Guide Pre-Algebra c. Return to Determine if Estimate is Over or Under d. 338. an exact answer. Determine whether a given estimate is an overestimate or underestimate. i. ©State of Idaho 2003 Estimate driving time to a given destination and compare to actual time (given particular miles per hour). Use appropriate vocabulary. MATHEMATICAL REASONING AND PROBLEM SOLVING. Rationale: These processes are essential to all mathematics and must be incorporated in all other mathematics standards. Standard – The student will: 01. Understand and use a variety of problem-solving skills. Content Knowledge and Skills: a. Samples of Applications: Use a variety of strategies, including common mathematical formulas to compute problems drawn from real-world situations. i. i. Given a problem, identify essential information. i. After finding the area of square, find the surface area of a cube. ii. iii. Return to Use Strategies in Real Life Return to Recognize Pertinent Information b. Recognize pertinent information for problem solving. Return to Make Predictions and Decisions c. Make predictions and decisions based on information. Use reasoning skills to recognize problems and express them mathematically. a. Use a variety of methods, such as words, numbers, symbols charts, graphs, tables, diagrams, and models, to explain mathematical reasoning and concepts. b. Apply solutions and strategies to new problem situations. 02. Return to Use Reasoning Skills Return to Use Reasoning Skills Determine amount of interest earned in a savings account. Compute amount of paint needed for a bedroom. Given $500 to plan a year-end class party using several committees, develop a budget for the party. 24 Idaho State Curriculum Guide Pre-Algebra Return to Use Reasoning Skills 03. Apply appropriate technology and models to find solutions to problems. c. Formulate conjectures and justify (short of formal proof) why they must be or seem to be true. i. a. Understand the purpose and capabilities of appropriate technology use as a tool to solve problems. i. Use technology to find the square root of 5,281. b. Use computer applications to display and manipulate data. i. Display and compare the frequency of various M&M colors using computer applications. c. Select appropriate models to represent mathematical ideas. a. Use a variety of methods, such as words, numbers, symbols, charts, graphs, tables, diagrams, and models, to communicate mathematical information. i. Write an explanation on how to solve a problem. Display results of a problem in graphic form. Return to Use Technology Return to Use Technology Return to Use Technology 04. Communicate results using appropriate terminology and methods. ©State of Idaho 2003 ii. ii. Debate the following: If people like cheese and mice like cheese, then people are mice. On a crisp autumn day, the 1st four students to class are wearing shorts. What will be the possible attire of the rest of the students in the class? Explain. Return to Communicate Results b. Use appropriate vocabulary to communicate mathematical information. c. Use appropriate notation. Return to Communicate Results Return to Communicate Results 339. CONCEPTS AND PRINCIPLES OF MEASUREMENT. Rationale: The first step in scientific investigation is understanding the measurable attributes of objects. Standard – The student will: Content Knowledge and Skills: Samples of Applications: 25 Idaho State Curriculum Guide Pre-Algebra 01. Understand and use U.S. customary and metric measurements. a. Select and use appropriate units and tools to make formal measurements using both systems. ii. Return to Measurement Return to Measurement 02. 03. 04. Select and use the appropriate tool to measure the length of a school building, the length of a classroom, the length of a thumbtack and the length of a student’s shoe. Measure the interior angles of a triangle. b. Apply estimation of measurement to real-world and content problems using actual measuring devices. c. Recognize the differences and relationships among measures of perimeter, area, and volume (capacity) in both systems. i. Model length, area, and volume using various manipulatives (string, tiles, and cubes). d. Solve problems involving length, perimeter, area, volume (capacity), weight, mass, and temperature. i. Design and determine how much lumber would be needed for an average size doghouse. Design a laser alarm system using numerous mirrors as reflection points. e. Convert unit of measurement within each system. f. Use appropriate vocabulary. Apply concepts of rates and other derived or indirect measurements. a. Use rates to make indirect measurements. Apply the concepts of ratios and proportions. a. Apply dimensional analysis. i. ©State of Idaho 2003 Return to Use Rates Understand and use proportions, ratios, and scales. Return to Use Proportions a. Understand units and their relationship to one another and to real-world ii. i. ii. i. ii. iii. i. Use formulas and appropriate procedures for solving measurement problems, for instance, distance equals rate * time. Given the weight of 1 gallon of water, calculate the weight of water in the swimming pool. Use proportions to find the height of a flagpole. Use map scale to determine distances. Enlarge a cartoon to a given scale. Determine the reading hours of an entire class if everyone reads 20 minutes. 26 Idaho State Curriculum Guide Pre-Algebra Return to Understand Units 340. ©State of Idaho 2003 applications. CONCEPTS AND LANGUAGE OF ALGEBRA. Rationale: Algebra is the language of mathematics and science. Through the use of variables and operations, algebra allows students to form abstract models from contextual information. Standard – The student will: 01. Use algebraic symbolism as a tool to represent mathematical relationships. Content Knowledge and Skills: Samples of Applications: a. Understand and use variables in expressions, equations, and inequalities. i. If B represents the number of boys in the class, and G represents the number of girls in the class, write an equation and solve it in the number of students in the classroom. b. Translate simple word statements and story problems into algebraic expressions and equations. i. Given that the price of gas is changing each week, write an algebraic expression to represent the cost of purchasing 10 gallons of gas. Return to Use Variables Return to Translate Word Problems c. Return to Use Variables 02. Evaluate algebraic expressions. a. Understand and use the following properties in evaluating algebraic expressions: commutative, associative, identity, zero, inverse, distributive, and substitution. i. Evaluate expressions such as 2x + y when given values for x and y. b. Understand and use the order of operations in evaluating basic algebraic expressions. i. Explain why order of operations is important when evaluating expression such as: 3 + 2 * 8. c. Simplify algebraic expressions. i. Simplify expressions such as: 3a + 4b – 5a + 6b –7. a. Solve one- and two-step equations and inequalities using inverse operations. i. Solve equation such as: 12x – 5 = 31. b. Explore graphical representation i. Use technology to create a graph of linear Return to Properties Return to Order of Operations Return to Simplify Expressions 03. Solve algebraic equations and inequalities. Use symbols (<, >, =, , , ) to express relationships. Return to Solving Equations 27 Idaho State Curriculum Guide Pre-Algebra Return to Graph Linear Equations 341. to show simple linear equations. ©State of Idaho 2003 relations. CONCEPTS AND PRINCIPLES OF GEOMETRY. Rationale: The study of geometry helps students represent and make sense of the world by discovering relationships and developing spatial sense. Standard – The student will: 01. Apply concepts of size, shape, and spatial relationships. Content Knowledge and Skills: a. Precisely describe, classify, and understand, relationships among types of one-, two-, and threedimensional objects using their defining properties. b. Construct and measure various angles and shapes using appropriate tools. Return to Geometric Properties/Terminology c. Understand and apply fundamental concepts, properties, and relationships among points, lines, planes, angles, and shapes. Return to Congruency/ Similarity d. Recognize and apply congruence, similarities, and symmetry of shapes. e. Return to Shapes and Figures Return to Construct / Measure Shapes i. Compare measurements of opposite and alternate angles in a parallelogram. Apply formulas for perimeter, circumference, and area to polygons and circles. i. Calculate the area of a center circle of a basketball court. f. Understand the concept of surface area and volume (capacity). i. Construct a cylinder and calculate its surface area and volume (capacity). g. Explore and model the effects of reflections, translations, and rotations on various shapes. i. Create a tessellation using a combination of reflection, translation or rotation showing movement on a plane. Return to Symmetry / Transformations Return to Apply Formulas Return to Surface Area Return to Symmetry / Transformations Samples of Applications: 28 Idaho State Curriculum Guide Pre-Algebra Return to Geometric Properties/Terminology 02. Apply the geometry of right triangles. h. Use appropriate vocabulary. a. Investigate right triangle geometry using the Pythagorean Theorem. i. ii. ©State of Idaho 2003 Investigate the relationships among the 3 sides of a right triangle of a Pythagorean triple. Determine the length of a handicap access ramp given the height and length of the incline. Return to Apply Formulas 03. Apply graphing in two dimensions. a. Use the coordinate plane as it relates to real-world applications. Return to Coordinate 342. DATA ANALYSIS, PROBABILITY AND STATISTICS. Rationale: With society’s expanding use of data for prediction and decision-making, it is important that students develop an understanding of the concepts and processes used in analyzing data. Standard – The student will: 01. Understand data analysis. Content Knowledge and Skills: a. Return to Analyze Charts Return to Analyze Charts 02. Collect, organize, and display data. Apply simple statistical measurements. Return to Statistics i. ii. b. Explain and justify conclusions drawn from tables, charts, and graphs. c. Understand and use appropriate vocabulary. a. Collect, organize, and display data with appropriate notation in tables, charts, and graphs (scatter plots, line graphs, bar graphs, pie charts). i. Choose and calculate the appropriate measure of central tendency – mean, median, and mode. i. Return to Use Data 03. Analyze and interpret tables, charts, and graphs (scatter plots, line graphs, bar graphs, pie charts). Samples of Applications: a. ii. iii. ii. iii. Analyze and interpret bar graphs and pie charts in magazines or newspapers. Given a scatter plot, choose a line of best fit. Collect and display data by surveying the actual number of chocolate chips in cookies. Survey and graphically display music preference categories. Identify the usefulness and/or limitations of surveys. Compute an individual mean grade in a particular course. Find the median student height in a classroom. Find the most common shoe size in your class. 29 Idaho State Curriculum Guide Pre-Algebra b. Return to Range, Frequency, Distribution 04. Understand basic concepts of probability. a. Explore the significance of range, frequency, and informal distribution. i. Model situations of probability using simulations. i. ii. ii. Return to Probability / Prediction Understand and use the language of probability. c. Recognize equally likely outcomes. i. Document frequency of heads and tails when flipping a coin 100 times. a. Make predictions based on experimental and theoretical probabilities. Understand and use appropriate vocabulary. i. Find the theoretical and experimental probability of throwing a pair of 6 sided number cubes and getting a sum of 7. Conduct statistical experiments and interpret results using tables, charts, or graphs. i. Graphically display the results of 40 spins of a 4-quadrant spinner; explain the results. or decisions based on data. Return to Language of Probability Calculate range and distribution of professional basketball salaries. Create a frequency distribution chart of professional basketball salaries. Find the probability of drawing a jack of hearts in a standard deck of cards. Use a spinner to represent the number of points scored by a 75% free throw shooter in a basketball game b. Return to Language of Probability Return to Recognize Outcomes 05. Make predictions ©State of Idaho 2003 b. Return to Combinations/ Permutations c. Return to Recognize Outcomes 343. FUNCTIONS AND MATHEMATICAL MODELS. Rationale: One of the central themes of mathematics is the study of patterns, relationships, and functions. Exploring patterns helps students develop mathematical power. Standard – The student will: 01. Understand the concept of functions. Content Knowledge and Skills: a. Samples of Applications: Extend patterns and identify a rule (function) that generates the pattern using real numbers. i. Use functional relationships to explain how a change in one quantity results in a change in another. i. ii. Extend the 1st five numbers in the Fibonacci sequence and explain the rule. Explain how the amount of sales tax depends on the cost of the item. Return to Pattern, Sequence, Function b. Return to Pattern, Sequence, Function ii. Find the number of pencils needed for a classroom if each student must have 3 pencils. Explain how the number of pencils needed will change as the number of students’ change. Using what we know about a 3, 4, 5, right triangle, prove a corner of a room is square or 30 Idaho State Curriculum Guide Pre-Algebra not square. c. Return to Pattern, Sequence, Function Understand and use appropriate vocabulary. ©State of Idaho 2003 31 Idaho State Curriculum Guide Pre-Algebra 02. Represent equations, inequalities, and functions in a variety of formats. Return to Represent Data 03. Apply functions to a variety of problems. Return to Use Patterns and Functions ©State of Idaho 2003 a. Represent a set of data in a table, as a graph, and as a mathematical relationship. i. Collect data on the temperature of hot water as it cools over time and organize and display the results in several forms, including tables and graphs. a. Use patterns and functions to represent and solve problems. i. Illustrate on a line graph distance traveled at a constant speed of 55 miles per hour. 33 Idaho State Curriculum Guide Pre-Algebra ©State of Idaho 2003 New Vocabulary () and Symbols () ISAT “SubGoal” RIT Below 150-160 Algebraic o for answer to equation (151-160) Concepts Return to Top RIT 161-170 o ( ) used in equations RIT 191-200 if-then, product, sum o variables, exponents (signs / symbols) inequality, if-then statement, term in sequence, square numbers, negative coefficient o I=pxrxt o <, > symbols RIT 201-210 input, output, table, associative, equation o , RIT 231-240 RIT 171-180 regression equation, varies inversely as the square, slope of parallel lines, solution to system, factor (used with equations) sign o – used as negative RIT 211-220 RIT 241-250 RIT 181-190 commutative, solve, square numbers, input, output, number sequence RIT 251-260 parabola, intercepts, number of solutions, simultaneous equations, counterexample, solution set, sin A, cosine, tangent, discriminant, imaginary solutions, difference of two squares, read solution set from graph, factor completely RIT 221-230 absolute value, evaluate, quotient o square root symbol, %, absolute value symbol RIT 261-300 34 Idaho State Curriculum Guide Pre-Algebra ©State of Idaho 2003 New Vocabulary () and Symbols () ISAT “SubGoal” RIT Below 150-160 Compu- (Below 150) and tation Return to Top RIT 161-170 o $, decimal point o +, =, (151-160) equals, facts o x (multiplication symbol) RIT 191-200 “Solve for n” estimate, round, closest to, sum, of (used as in “½ of 36”) o square root symbol RIT 211-220 smallest, tenth o – as a negative, + as a positive RIT 241-250 decimal fractions, opposite RIT 181-190 closest, how many o division symbol (both forms) RIT 201-210 difference, not true, power of 10, rounded, thousands o ¢, % RIT 231-240 RIT 171-180 RIT 251-260 sum of opposites RIT 221-230 product, divide, most, if – then, compute, lowest terms RIT 261-300 35 Idaho State Curriculum Guide Pre-Algebra ©State of Idaho 2003 New Vocabulary () and Symbols () ISAT “SubGoal” Geometry RIT Below 150-160 shape, circle, same as RIT 161-170 matches, triangle, square, corners, cone, closed, inside RIT 171-180 congruent, figure RIT 181-190 o Return to Top RIT 191-200 o symmetrical, parallel, intersecting, diagonal, pair, angle, cylinder, outside, inside, sphere, faces, corresponding, point, intersect, outside, axis of symmetry, line segment, pentagon symbol for parallel lines RIT 201-210 o RIT 231-240 intersection, quadrilaterals, octagon, parallelogram, pyramid, isosceles, right angle, diameter, right angle, geometric, perpendicular, plane for triangle, angle symbol RIT 241-250 RIT 211-220 o symmetrical, perpendicular, ray, vertex, rotation, triangular prism, corresponding parts, supplementary, acute angle, transformation - congruent symbol, - double o arrow symbol for similarity, - pi symbol, ABC – to label triangle RIT 251-260 symmetry, point, sides, rectangle, cube, straight, line segment, shortest line AB (with double arrow over AB), line segment AB (with segment line over AB) RIT 221-230 radius, polygon, circumference, trapezoid, rectangular box, equilateral, similar, obtuse angle, straight angle, slide angle symbol, label for line – L1 RIT 261-300 36 Idaho State Curriculum Guide Pre-Algebra transformation, hypotenuse, edge, isosceles, scalene triangle, similar trapezoids, alternate interior angles, sum of angles in triangle o symmetrical halves, diameter, radius, angle bisector, tangent, corresponding parts of congruent triangles, Pythagorean theorem, corresponding angles, complementary angles, construction sign for parallel lines ©State of Idaho 2003 slope, non-vertical and non horizontal, midpoint, endpoint, rotational symmetry, reflected, perpendicular bisector, similar triangles, similar trapezoids, similar cylinders, conditional, counterexample, conclusion of inthen statement, interior of angle, exterior angle of regular polygon, interior angle of regular polygon, sum of angles in triangle equals 180 degrees, congruent angles, adjacent angles, vertical angles postulate (261-270) HL (271-280) 37 Idaho State Curriculum Guide Pre-Algebra ©State of Idaho 2003 New Vocabulary () and Symbols () ISAT “SubGoal” Measurement Return to Top RIT Below 150-160 o longest, shortest, how tall, kilometer, meter, time (151-160) C for Celsius, cm for centimeter RIT 161-170 o RIT 191-200 o height, width, parallelogram, square, rectangle, triangle, year, ton, seconds, kilogram, distance, miles, liter mm = millimeter, a.m. and p.m., hr = hours, min = minutes o rectangular house, height and base, algebraic expression, rows and columns, checking account, car purchase, commission, simple interest F = 9/5 C + 32, formula for finding volume of a pyramid o RIT 201-210 o RIT 231-240 how long, names of days of week, next, names of months, pennies, centimeter, inches degree symbol, : for time – 1:00, face of quarter, dime, penny, and nickel RIT 171-180 right angle, circumference, minutes, decades, milligrams, gram, cubic feet, volume, liters, length, weight, kilometers, millimeters, mass ft for feet, mL = milliliters, right angle symbol, symbol for line segment, doubled and tripled, rectangular solid, cylindrical tank, algebra tiles, inscribed, time-and-a-half, sales tax, discount o RIT 211-220 o RIT 241-250 line segment, area, square units, perimeter, days, week, set, coins, thermometer, temperature, pounds, ounces, pints, quarts $, decimal point for cents, F = Fahrenheit, lb = pounds, sq = square units, cent sign, recognize back of penny, nickel, dime, and quarter RIT 181-190 yards, measure of angle, degrees, protractor, centuries, below zero, Celsius, rectangular solid, rectangular prism, decades, ounces ” = inches, yd = yards, b = base, h = height, r = radius, s = side, angle symbol, - for negative, + for positive, d = distance, tsp = teaspoon, pt = pint, gal = gallon, qt = quart, c = cup RIT 221-230 o RIT 251-260 o circumscribed, distance formula formula for finding volume of a cone, formula for volume of a cube, formula for finding volume of a rectangular solid about, length, estimate, perimeter, change, quarter, dollars, dozen, units, feet, yard, grams, meters, cups, gallons, nickel, pennies, dime, tablespoon, hours, minutes, degree m = meters, g = grams reasonable, formula, segment BC, pi, radius squared, diameter, metric units, quarts, gallons, rectangular box, base, rate oz = ounces, C = circumference RIT 261-300 rate of interest, successive discounts (271-280) 38 Idaho State Curriculum Guide Pre-Algebra ©State of Idaho 2003 New Vocabulary () and Symbols () ISAT “SubGoal” Number Sense RIT Below 150-160 how many o for answer RIT 161-170 Return to Top RIT 191-200 o thirds, fourths, rounded, thousands, exponential form, mixed number, improper fraction, lowest common denominator, percent, expanded form, prime, factor, proportion use of dot as a multiplication symbol ones, tens, hundreds, thousands, numeral, ordinal numbers through eleventh, counting RIT 171-180 even numbers, same as, fewest o < and > signs, = sign RIT 201-210 o RIT 231-240 missing number, pentagon, simplest fraction, biggest, hundredths, one less, decimal numeral, squared, divisible, inequality, expanded numeral, equivalent, point, standard numeral, sequence + used as positive symbol, used as negative symbol RIT 241-250 Base ten, prime factors RIT 181-190 first, second, third, etc., odd, one-fourth, one-half, reduce, fractions, order, divisible, round, smallest, largest, lowest terms, greatest common factor, least common multiple, closest, units, set, digit, greater than, greatest RIT 221-230 always true, proportion, multiply, between, tens digit, standard numeral, ratio RIT 211-220 o counting number, portion, fractional part, lowest terms, reciprocal, order, scientific notation, prime factorization, not prime, factor tree, common multiples, greatest common denominator, equivalent, nearest dollar square root symbol RIT 251-260 RIT 261-300 infinite non-repeating decimal (261-270) 39 Idaho State Curriculum Guide Pre-Algebra ©State of Idaho 2003 New Vocabulary () and Symbols () ISAT “SubGoal” RIT Below 150-160 RIT 161-170 Reasoning and Problem Solving how many, not, in all, altogether RIT 171-180 Return to Top RIT 191-200 o terms, meter, millimeters, kilogram, feet, yards, unit of measurement, height, thousands, hundreds, tens, table, graph, length, width, rectangular, area, square inches, exactly, coins, numeral, even, change, average, opposite, percent, subtrahend, addend, formula, circle, diameter, operation, total, fact, fraction, surfaces, cube, temperature, first – fifth (ordinal names), difference, equivalent tally marks, =, - as an integer sign, %, C, for answer RIT 201-210 equation, product, increased, number line, information not needed, division, estimate, odd, prime, cube, pattern, geometric patterns, extra information o rxt=d RIT 231-240 regression equation RIT 241-250 matrix product, number sentence, problem, how many more, multiples, greater than, left, how much, money, answer, about, outside, inside, shape, calendar, picture RIT 211-220 RIT 181-190 add, subtract, multiply, divide, rate, kilometers, hours, between, equals, cost, time, less than, closest to, equation, weigh, minutes, pieces, dozen, cups, inches, pounds, miles, sum, dime, nickel, pennies, quarter o +, $, decimal point for cents, ¢ RIT 221-230 decimals, fractions, what shape, hour, minutes, gallons, average, probability, graph, squares o % o RIT 251-260 mortality, odometer, magic square, deducted, less than twice, addends, less than sum, rectangle, diameter, radius, label (units), area, perimeter I = prt RIT 261-300 40 Idaho State Curriculum Guide Pre-Algebra ©State of Idaho 2003 New Vocabulary () and Symbols () ISAT “SubGoal” RIT Below 150-160 Data Analysis, Statistics and Probability Return to Top RIT 161-170 RIT 191-200 average, bar graph, percentage o % vertex, fractional part, amount of sales, translation, matrix, possibility, mean salary, coordinates of points RIT 201-210 RIT 231-240 probability RIT 171-180 least often, how many ways, ordered pairs, coordinates, distance formula RIT 241-250 coordinate, Venn diagram, greatest decrease, endpoints, midpoint chance RIT 181-190 RIT 211-220 dice, arranged, highest mean RIT 251-260 most often RIT 221-230 even numbers, mean, median, integer, intersection, table, frequency, origin, quadrant RIT 261-300 41 Idaho State Curriculum Guide Pre-Algebra ISAT “Sub-Goal” RIT 211-220 ©State of Idaho 2003 RIT 221-230 RIT 231-240 Algebra Solving Equations, Simplifying Expressions, Order of Operations Return to Guide Solve decimal equations (one step, addition and subtraction) Solve integer equations (one step, multiplication and division) Evaluate expressions using the order of operations (may include parentheses or exponents) Solve quadratic equations Solve for missing addends in an addition or subtraction sentence Use boxes or other symbols to stand for any number in expressions or equations Solve whole number equations with one variable (multiplication and division) Solve integer equations (one step, all four operations) Solve equations involving more than one operation Solve one-step linear equations in one variable using addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division with integer solutions Simplify numeric expressions by applying properties of rational numbers (e.g. identity, inverse, distributive, associative, commutative) Write an algebraic expression to model a situation Evaluate an algebraic expression for given values Explore equivalent ratios involving missing variables Use the correct order of operations to evaluate numeric and algebraic expressions Simplify and evaluate expressions that include positive and negative integral components Simplify polynomials by combining like terms Use the rules of exponents to multiply and divide monomials Solve simple linear equations and inequalities over the rational numbers Create a table of (x, y) values for the given linear equation and graph the function 42 Idaho State Curriculum Guide Pre-Algebra ISAT “Sub-Goal” Patterns, Sequences, Functions RIT 211-220 Use logic to solve a problem involving a function table Return to Guide Properties Return to Guide ©State of Idaho 2003 RIT 221-230 Complete a function table according to a rule Recognize and continue a number pattern and/or geometric representation (e.g. Fibonacci sequence, triangular numbers) State a rule to explain a number pattern, including arithmetic progression Investigate geometric patterns and relationships and describe them algebraically RIT 231-240 Using whole numbers, complete a function table based on a given rule Graph linear functions, noting that the vertical change (change in yvalue) per unit of horizontal change (change in x-value) is constant Identify linear equation for a straight line Understand the properties of integers: commutative, associative, identity, zero property of multiplication, distributive property of multiplication over addition, and inverse property of addition Data Analysis, Probability, and Statistics Solve problems involving arrangements Data Analysis Return to Guide Read and interpret information from a graph Interpret Venn Diagrams Make predictions from a graph Combinations and Permutations Use a tree diagram to determine the number of possible outcomes of an event Solve problems involving combinations and permutations Interpret data given in horizontal and vertical bar graphs to solve problems Read and interpret information in a table Read and interpret information from a graph Return to Guide 43 Idaho State Curriculum Guide Pre-Algebra ISAT “Sub-Goal” Probability and Prediction RIT 211-220 Investigate experimental probability of an event using a coin or spinner ©State of Idaho 2003 RIT 221-230 RIT 231-240 Investigate experimental probability Determine the number of possible outcomes of an event of an event using a coin or spinner Predict outcomes using probability Return to Guide Statistics Return to Guide Know the concepts of mode, median, and mean; compute and compare them in simple examples to demonstrate that these measures of central tendency may differ for a given set of data Calculate range, mode, median, and mean 44 Idaho State Curriculum Guide Pre-Algebra ISAT “Sub-Goal” RIT 211-220 ©State of Idaho 2003 RIT 221-230 RIT 231-240 Estimation and Computation Decimals Return to Guide Add decimals through hundredthousandths with a calculator Multiply a decimal by a decimal, factors to thousandths Divide a decimal by a whole number and vice versa Compute basic operations with monetary amounts up to and including $20.00 Subtract whole numbers and decimals to the hundredths place (same number of digits) Write a number sentence to solve one-step word problems involving the operations of addition, subtraction, and multiplication of fractions and decimals Subtract decimals through hundredthousandths with a calculator Multiply a decimal by multiples of 10, 100, or 1000 Divide a whole number (or decimal) by a decimal to thousandths Add whole numbers and decimals to the hundredths place (same number of digits) Subtract decimals to the hundredths place (not the same number of digits) Subtract decimals to thousandths, vertically and horizontally, with and without regrouping Subtract a decimal from a whole number Multiply a decimal by a decimal, factors to thousandths place Divide a decimal by a whole number and vice versa Divide a whole number (or decimal) by a decimal to thousandths place Compute and count change greater than $20.00 45 Idaho State Curriculum Guide Pre-Algebra ISAT “Sub-Goal” Fractions Return to Guide RIT 211-220 Add fractions with like denominators, answer in lowest terms Add mixed numbers with unlike denominators with regrouping Multiply a whole number by a fraction Divide a fraction by a fraction Divide a mixed number by a whole number or a fraction Integers Return to Guide Percents Return to Guide Add integers with like signs Add integers with unlike signs Add several integers Multiply integers with unlike signs Divide integers with unlike signs ©State of Idaho 2003 RIT 221-230 Add and subtract fractions with like denominators; change improper fractions to mixed numbers Subtract fractions having unlike denominators, answer in lowest terms Add and subtract whole numbers, fractions and mixed numbers Use estimation to solve problems involving mixed numbers Divide a whole number, fraction or mixed number by a mixed number Divide integers, like signs RIT 231-240 Add fractions having unlike denominators with answer reduced to lowest terms Subtract fractions having unlike denominators with answer reduced to lowest terms Add and subtract mixed numbers with like denominators with regrouping Add and subtract mixed numbers with unlike denominators with regrouping Add and subtract whole numbers, fractions, and mixed numbers Multiply a fraction by a fraction; answer in lowest terms Multiply mixed numbers Divide a fraction by a fraction Divide a mixed number by a whole number or a fraction Multiply three factors using fractions, mixed numbers, and whole numbers in any combination, answer in lowest terms Divide a whole number, fraction, or mixed number by a mixed number Find the percent one number is of another (20 is what % of 90) Find a number from a percent (4 is 9% of what number) Add integers with unlike signs Add several integers Multiply integers with like signs Divide integers with like signs Find the percent one number is of another (8 is what % of 20?) Find a number from a percent (20 is 45% of what number?) 46 Idaho State Curriculum Guide Pre-Algebra ISAT “Sub-Goal” Squares RIT 211-220 Calculate the square of any number less than 100 ©State of Idaho 2003 RIT 221-230 Evaluate expressions using square roots Return to Guide Whole Numbers Divide a 3-digit or 4-digit number by a 1-digit number Use multiplication as a check for division Multiply by multiples of 10 and 100 with an emphasis on mental math Divide a 4-digit number by a 2-digit number Return to Guide Identify similar figures (same shape, may or may not be the same size) Identify congruent polygons and their corresponding sides and angles Identify congruent triangles according to corresponding parts (SSS, SAS, ASA) Graph ordered pairs in all four quadrants (coordinate geometry) Develop computational fluency with division facts Divide multi-digit numbers using a calculator Introduce the math strategy of compatible numbers in estimating for all four operations RIT 231-240 Identify perfect squares in a list of numbers and calculate the positive square root of a perfect square Divide a 2-digit number or a 3-digit number by a 1-digit number with remainder Divide multi-digit numbers using a calculator Geometry Congruency and Similarity Return to Guide Coordinate Return to Guide Find location of coordinates on a number line Locate the vertex on a coordinate grid 47 Idaho State Curriculum Guide Pre-Algebra ISAT “Sub-Goal” Geometric Properties and Terminology Return to Guide RIT 211-220 Identify points, lines, line segments, rays, and angles Identify angles: right, obtuse, and acute Identify when two intersecting lines are perpendicular Identify properties of similar figures Measure angles using a protractor Shapes and Figures, 2- and 3-Dimensional Return to Guide Identify faces, edges, and corners (vertices) on solid figures Contrast open and closed figures Identify polygons: triangle, quadrilateral, pentagon, hexagon, and octagon Identify quadrilaterals: square, rectangle, parallelogram, trapezoid, rhombus Analyze solid figures: triangular pyramid and rectangular pyramid (faces, edges, and vertices) ©State of Idaho 2003 RIT 221-230 Identify the center, radius and diameter of a circle Measure angles using a protractor Classify angles: supplementary and complementary Classify angles: adjacent, vertical, corresponding, and supplementary Find the missing angle measurement in a triangle when two angles are known Analyze circles: center, chord, diameter, radius, arc, semicircle, and circumference Analyze solid figures: rectangular prism, triangular prism, triangular pyramid, square, pyramid (faces, edges and vertices) Classify polygons by sides and angles RIT 231-240 Classify triangles by sides (equilateral, isosceles, and scalene) and angles (acute, obtuse, and right) Classify polygons by sides and angles Identify and discriminate between regular and irregular polygons Find the missing angle measurement in a triangle when two angles are known Solve word problems involving similar polygons Identify the base angles of a triangle Know the definition of the hypotenuse of a triangle Calculate the circumference of a circle using the formula 48 Idaho State Curriculum Guide Pre-Algebra ISAT “Sub-Goal” Symmetry and Transformations RIT 211-220 Identify types of transformations (rotation) ©State of Idaho 2003 RIT 221-230 RIT 231-240 Understand meaning and representation of a dilation Return to Guide Measurement Area, Perimeter, Circumference Return to Guide Length, Weight, Volume Calculate the area of irregular shapes Understand the effects of changing dimensions on perimeter and area Measure length to the nearest millimeter, centimeter, meter, and kilometer Return to Guide Time, Temperature Measure length with metric measures (centimeter) Measure length with customary measures (inch) Select the appropriate unit of measure for length, area, and volume Compute word problems with time and calendars Return to Guide Number Sense Absolute Value Return to Guide Find the perimeter of a square or rectangle using the formula Find the perimeter of polygons Calculate the area of a parallelogram and rectangle Calculate the area of a triangle Find the volume of a pyramid Definition and application of absolute value Convert from Celsius to Fahrenheit Subtract Fahrenheit temperatures 49 Idaho State Curriculum Guide Pre-Algebra ISAT “Sub-Goal” Decimals Return to Guide Exponents and Scientific Notation Return to Guide Factorization / Divisibility Return to Guide RIT 211-220 Round monetary amounts to the nearest single coin or bill which could be used to pay for a purchase up to and including $20.00 Write the decimal equivalent of a fraction and label as repeating or terminating Round decimals to nearest whole number, tenth, or hundredth Write a terminating decimal as a fraction or mixed number Round decimals to nearest whole number, tenth, hundredth, or thousandth Identify and order decimal and fractional coordinates on a number line Order of “powers” Write a whole number or a decimal in scientific notation Write a number expressed in scientific notation in standard form Understand and use rules of divisibility Identify the greatest common factor of two whole numbers: list the factors or prime factorization Identify the greatest common factor and least common multiple of two whole numbers ©State of Idaho 2003 RIT 221-230 Identify and order decimal and fractional coordinates on a number line Relate fractions to decimals Write a decimal or mixed decimal for a fraction (2/3=0.66) RIT 231-240 Write a decimal or mixed decimal for a fraction Write a whole number or a decimal in scientific notation (negative exponents) Identify and use powers of 10 Identify the least common denominator for 3 or more fractions: list the multiples or prime factorization Evaluate expressions using the order of operations that include exponents Find products by applying rules for exponents 50 Idaho State Curriculum Guide Pre-Algebra ISAT “Sub-Goal” Fractions, Ratio, and Proportions Return to Guide RIT 211-220 Write improper fractions from picture presentations Change a fractional numeral to its simplest form (lowest terms) Compare and order fractions and mixed numbers Identify and order decimal and fractional coordinates on a number line Integers Return to Guide Ordering Return to Guide Percents Return to Guide Identify the greater or lesser of 2 integers Order integers on a number line Compare and order fractions with the same denominator and with different denominators Order decimals to thousandths; identify the greater or lesser of two decimals to thousandths Express a fraction as a decimal and as a percent ©State of Idaho 2003 RIT 221-230 Model and write numerical fractions Change a fractional numeral to its simplest form (lowest terms) Understand the concept of ratio using concrete and pictorial models Determine if a pair of ratios is equal or not equal using the equivalent fractions method Write the missing number in 2 equivalent ratios Solve proportions using the cross product method Understand the meaning of integers Order a set of integers from least to greatest Place numbers in correct order on a number line Write a ratio (fraction) as a percent and a percent as a ratio (fraction): denominators of 100 RIT 231-240 Define ratio Write ratios in a variety of ways 51 Idaho State Curriculum Guide Pre-Algebra ISAT “Sub-Goal” Place Value Return to Guide RIT 211-220 Understand and identify the place value and value of each digit in numerals through the billions ©State of Idaho 2003 RIT 221-230 Match word names to numerals to the hundred thousands in decimals RIT 231-240 Write numerals in expanded form through the billions Understand and identify place value and value of each digit in numerals through the hundred billions Choose and use an appropriate problem solving strategy: Draw a picture, Make a model, Guess and test, Make a list, Make a table, Find a pattern, Work backwards, Solve a simpler problem, Draw a diagram, or Write an equation Write and solve an equation using ratios, given a word problem Write and solve an equation for a word problem Solve simple interest problems (amount x rate x time) Use estimation to determine if solutions to word problems are reasonable Use logic to predict outcomes Work backwards to solve problems Solve multi-step problems involving computation Find correct mathematical expressions to represent word problems Find simple interest earned Find commission and total pay Find missing numbers in a diagram by using patterns Use map scales to solve problems Solve if-then logic problems Solve complex word problems involving ratio, percent, discount, sale price, rounding and estimation, averaging, length, volume, rate, calendars, probability, money, and time Given the answer to a problem, determine the question Formulate expressions and equations to model problem solving situation Mathematical Reasoning and Problem Solving Mathematical Reasoning and Problem Solving Return to Guide Solve practical word problems involving perimeter and area of a square, rectangle or triangle Solve practical problems involving the mean (average) of a set of numbers Solve one- and two-step word problems involving any combination of basic operations on whole numbers, decimals, and fractions Determine the discount price and sale price Choose and use an appropriate problem solving strategy: Draw a picture, Make a model, Guess and test, Make a list, Make a table, Find a pattern, Work backwards, Solve a simpler problem, Draw a diagram, or Write an equation Calculate the cost of one item or the unit cost using a proportion 52 Idaho State Curriculum Guide Pre-Algebra ©State of Idaho 2003 53 Idaho State Curriculum Guide Pre-Algebra Sample Test Items Return to Top RIT 211-220: Algebraic Concepts Return Return RIT 221-230: Algebraic Concepts Return Return RIT 231-240: Algebraic Concepts Return Return RIT 211-220: Computation Return Return Return Return RIT 221-230: Computation Return Return Return Return Return ©State of Idaho 2003 54 Idaho State Curriculum Guide Pre-Algebra RIT 231-240: Computation Return Return Return Return RIT 211-220: Geometry Return Return Return Return RIT 221-230: Geometry Return Return Return RIT 231-240: Geometry Return Return RIT 211-220: Measurement Return Return Return Return Return ©State of Idaho 2003 55 Idaho State Curriculum Guide Pre-Algebra ©State of Idaho 2003 RIT 221-230: Measurement Return Return RIT 231-240: Measurement Return Return Return Return RIT 211-220: Number Sense and Numeration Return Return Return Return Return Return RIT 221-230: Number Sense and Numeration Return Return Return Return Return Return RIT 231-240: Number Sense and Numeration Return Return Return Return Return Return Return 56 Idaho State Curriculum Guide Pre-Algebra ©State of Idaho 2003 RIT 211-220: Problem Solving Return RIT 221-230: Problem Solving Return RIT 231-240: Problem Solving Return RIT 211-220: Statistics, Probability, & Graphing Return RIT 221-230: Statistics, Probability, & Graphing Return Return Return Return RIT 231-240: Statistics, Probability, & Graphing Return Return