Stagflation - Stephen Kinsella
advertisement
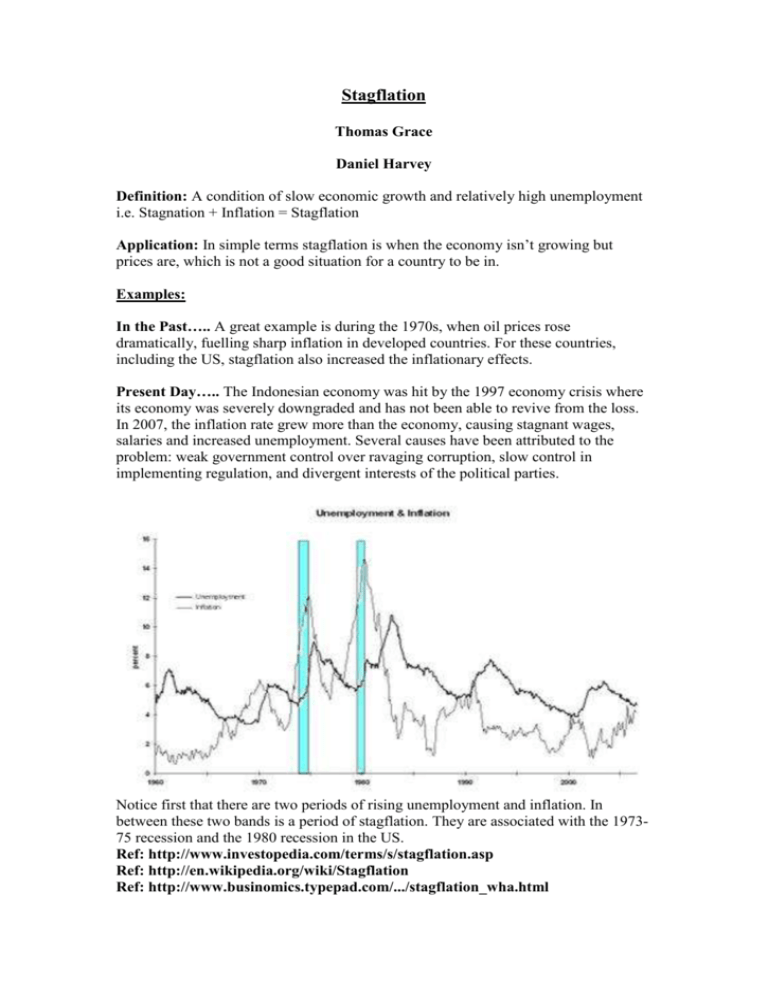
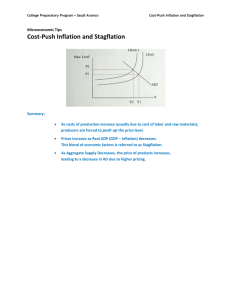
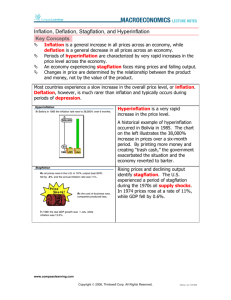
Stagflation Thomas Grace Daniel Harvey Definition: A condition of slow economic growth and relatively high unemployment i.e. Stagnation + Inflation = Stagflation Application: In simple terms stagflation is when the economy isn’t growing but prices are, which is not a good situation for a country to be in. Examples: In the Past….. A great example is during the 1970s, when oil prices rose dramatically, fuelling sharp inflation in developed countries. For these countries, including the US, stagflation also increased the inflationary effects. Present Day….. The Indonesian economy was hit by the 1997 economy crisis where its economy was severely downgraded and has not been able to revive from the loss. In 2007, the inflation rate grew more than the economy, causing stagnant wages, salaries and increased unemployment. Several causes have been attributed to the problem: weak government control over ravaging corruption, slow control in implementing regulation, and divergent interests of the political parties. Notice first that there are two periods of rising unemployment and inflation. In between these two bands is a period of stagflation. They are associated with the 197375 recession and the 1980 recession in the US. Ref: http://www.investopedia.com/terms/s/stagflation.asp Ref: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Stagflation Ref: http://www.businomics.typepad.com/.../stagflation_wha.html