week
advertisement
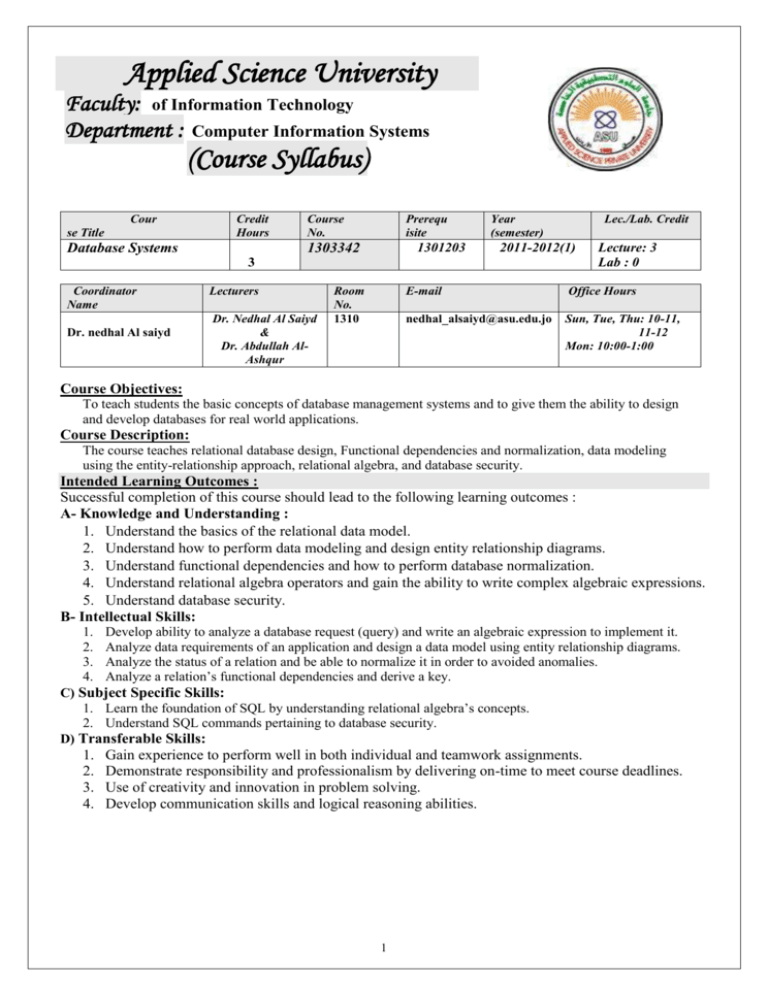
[ Applied Science University Faculty: of Information Technology Department : Computer Information Systems (Course Syllabus) Cour se Title Credit Hours Database Systems Course No. Prerequ isite 1301203 1303342 Year (semester) 2011-2012(1) 3 Coordinator Name Dr. nedhal Al saiyd Lecturers Dr. Nedhal Al Saiyd & Dr. Abdullah AlAshqur Room No. 1310 Lec./Lab. Credit Lecture: 3 Lab : 0 E-mail Office Hours nedhal_alsaiyd@asu.edu.jo Sun, Tue, Thu: 10-11, 11-12 Mon: 10:00-1:00 Course Objectives: To teach students the basic concepts of database management systems and to give them the ability to design and develop databases for real world applications. Course Description: The course teaches relational database design, Functional dependencies and normalization, data modeling using the entity-relationship approach, relational algebra, and database security. Intended Learning Outcomes : Successful completion of this course should lead to the following learning outcomes : A- Knowledge and Understanding : Understand the basics of the relational data model. Understand how to perform data modeling and design entity relationship diagrams. Understand functional dependencies and how to perform database normalization. Understand relational algebra operators and gain the ability to write complex algebraic expressions. Understand database security. B- Intellectual Skills: 1. 2. 3. 4. Develop ability to analyze a database request (query) and write an algebraic expression to implement it. Analyze data requirements of an application and design a data model using entity relationship diagrams. Analyze the status of a relation and be able to normalize it in order to avoided anomalies. Analyze a relation’s functional dependencies and derive a key. C) Subject Specific Skills: 1. Learn the foundation of SQL by understanding relational algebra’s concepts. 2. Understand SQL commands pertaining to database security. D) Transferable Skills: 1. 2. 3. 4. Gain experience to perform well in both individual and teamwork assignments. Demonstrate responsibility and professionalism by delivering on-time to meet course deadlines. Use of creativity and innovation in problem solving. Develop communication skills and logical reasoning abilities. 1 Course Contents : w e e k 1 2 3 Topics Reference (chapter) Database and Database Users. Introduction The Database approach Actors on the scene and actors behind the scene Advantages and disadvantages of the DB approach Ch. 1 Database System Concepts and Architecture Database System Concepts and Architecture Terminology (Data Model, Schema and Instance). 3-level Architecture and Data Independence. Database Languages and Utilities. Centralized and Client/Server architecture Classifications of Database Management Systems. Ch. 2 Data Modeling using the ER model Data Modeling using the ER model Conceptual Models for Database Design. Entities and Attributes. Entity Types. Entity Sets. Keys. Relationship Types, sets and Attributes. Mappings (1:N, N:M, 1:1). [Not to include MIN,MAX] Relational Model Concepts Characteristics of Relations Relational Model Constraints. Relational Model Operations. Operations that cause constraint violations Examples and review. ER-To-Relational Mapping The 7 mapping steps [Not to include step 8, 9 for EER]. Review for First Exam Queries in SQL. SELECT-FROM-WHERE structure. Aliasing and tuple variables. Optionally of WHERE. Using SELECT *. DISTINCT. Pattern Matching and Arithmetic Operators. Nested Queries. Correlated Nested Queries. EXISTS, NOT EXIST, LIKE, ANY, ALL. Joins. Aggregate Functions. Group by and Having. Order By. Examples. Why normalize? Redundant Info & Anomalies. Null Values in Tuples. Functional dependencies Ch3 4 The Relational Data Model and Relational Constraints 5 The Relational Data Model and Relational Constraints 6 ER-to-Relational Mapping 7 SQL 8 SQL 9 SQL 10 Functional Dependencies and Normalization 11 Functional Dependencies and Normalization 12 Functional Dependencies and Normalization 13 Functional Dependencies and Normalization 14 15 16 Topic Details Ch. 2 Assessment HW1 Ch. 3 Ch5 HW2 Ch. 5 Quiz1 Ch. 7 Ch. 8 EXAM 1 Ch. 8 HW3 Ch. 8 HW4 Ch. 10 Quiz2 Inference Rules for Functional Dependencies. Closure of a functional dependency. Closure of an attribute. Examples of how to find attribute closure. Keys and super keys Using closure to determine super keys and keys. Un-normalized relations 1NF, 2NF, and 3NF BCNF Review of Normalization. Examples Ch.10 EXAM2 Ch 10 HW5 Ch10 HW6 Database Security Types of Security. Control Measures. Database Security and the DBA. Access Protection, User Accounts and Database Audit. Types of Discretionary privileges. Ch. 23 Database Security Specifying Privileges using Views. Revoking Privileges. Grant Option. Example SQL commands. Specifying limits on propagation of privileges. Review. Ch 23 Final Exam Quiz3 FINAL 2 Course quality improvement : From the market and new subjects in the field. From students’ feedback (Evaluation sheet). Grade Distribution : Assessment Grade - First Exam - Second Exam - Assignments ( Reports /Quizzes/ Seminar / Homeworks ….) - Final Examination Date 20% 20% 20% 40% Reading List: Text Book Elmasri R. and Navathe S., “Fundamentals of Database Systems”, 5 rd Edition Addison Wesley 2007. Other References [1] Thomas Connolly and Carolyn Brgg , “Database Systems. A Practical Approach to Design, Implementation and Management “, 4nd Edition , Addison Wesley 2005. [2] Date C.J., “ An Introduction to Database Systems” , Vol 1, 8 th Edition, Addison Wesley 2004. [3] M. Kifer, A. Bernsten, and P. Lewis, "Database Systems: An Application-Oriented Approach", Addison Wesley, 2nd Edition, 2006. [4] David M. Kroenke, “Database Processing” , Prentice Hall 2000. [5] Korth H. and Silberschatz , “Database System Concepts”, 3rd Edition., McGrow – Hill 1998. [6] Mc Fadden F. R., Hopper J. A. and Prescat M. B, “Modern Database Management ", 5th Edition. , Addison Wesley 1999. Last update date: 8 Oct 2011, by: Dr. Nedhal Al Saiyd 3