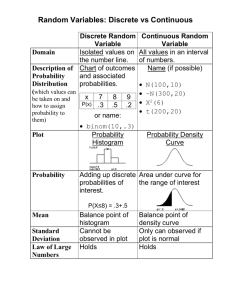
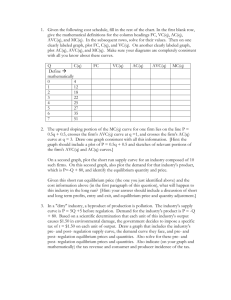
Prelim Guide - Materials Science & Engineering
advertisement

Tired of -illegible scribbles? -tenth-generation photocopies? -depressing 2-inch stack of old Prelim questions? Just try Prelim Guide The Concise Treatise by Chris Walton & Chris Olsen But first, read this: + This contains all the questions from my prelim file, which was as thick as anyone's, but I mostly entered repeated questions only once. If you want to see which questions were repeated most, or you just feel like going through the whole stack for some reason, go ahead, and please let me know if any questions were missed. + I typed in the questions and edited as best I could to put them in context and have them make sense, but understand that they were often incomplete. I can't guarantee that these represent the real prelim sessions. + + DO YOUR PART TOO - on prelim day, write down your questions right away. Write the questions, not just the topics, and be detailed. Then send them to Sam Nicols by e-mail at SPNICOLS@LBL.GOV. This list exists because other graduate students were kind enough to write it down for you. Do the same for future generations! Four out of five grad students agree - half the battle in the prelim is thinking and anwering questions on your feet. Don't let this guide be a substitute for mock exams with your friends. Grill each other, enlist older grad 1 students to grill you, but don't stay home reading whole time. textbooks and questions the (Updated Apr 98) I. THERMODYNAMICS A. Glaeser (Spring 85) Is the diagram at right correct? Why not? What is the change of energy for the path shown? A. Glaeser (Spring 86) Define a thermodynamic component. Draw G vs. T and G vs. P diagrams for one component. Is G vs. T a straight line? Why not? Draw P-T diagram for aone-component system. How is the slope for part A determined? What is point B called? Why? A. Searcy (Fall 86) Draw the phase diagram for you research material. How does thermodynamics relate to your research? Is the enthalpy positive or negative for a peritectic reaction? Write the reaction equation. What is the equation for DG? What is DG at the transformation temperature? Is DG for the reaction positive or negative below the transformation temperature? Above the transformation temperature? Sketch DG vs. T. Is DS positive or negative? Is DG positive or negative? What is the First Law of Thermodynamics? The Second Law of Thermodynamics? J. W. Morris (Fall 87) State the First and Second laws of Thermodynamics. Why must DG be negative for a reaction to occur? Are dislocations equilibrium defects? What is their equilibrium concentration? What about point defects? Draw a eutectic phase diagram. Suppose C0 is a concentration in the solid solution region at left. What will happen if a sample at C0 is rapidly cooled? Why does the phase diagram change in this way? Draw the probable microstructure. Could you ever get the eutectic composition by cooling C0? A. Glaeser (Spring 88) What is your research material? What is a component? Draw a 1-component phase diagram. Describe what happens as the system moves from A to B, and from B to C. Draw free energy curves corresponding to the system from A to B (const P) and from B to C (const T) What do the slopes of the curves represent? Why? What do the curvatures represent? Why? (Know dG = -SdT + VdP) D. de Fontaine (Fall 89) 2 State the First and Second Laws. Draw the Gibbs free energy curves for a two-component system. What is the condition for equilibrium? Define the heat capacity. Draw the P vs. T diagram for a 1-component system. Why does the l-g boundary end at Tcrit? State the Clausius-Clapeyron equation. (Possible question - can you derive it?) T. Devine (Spring 91) What is the chemical potential mathematically, and what does it mean? For an atom of A entering a mass of pure B, what happens atomistically to this chemical potential? (Explain DH and DS in this reaction). What is the surface free energy? (Not mathematically - phenomenologically, how would you measure it?) Suppose you have cooled at composition C, and reached a state where the volume fraction of B in a will not change further. Could anything else still happen? Why?(The b particles could still agglomerate) How would one b particle "know" of another's presence? Consider the iron fcc-bcc or titanium hcp-bcc transitions with rising temperature. Since these are temperature-dependent, what free energy terms might you expect to be responsible? (TdS term) Why would this be? (more room for disorder). A. Glaeser (?) State the First Law of Thermodynamics in words only. On what principle is it based? Write it in differential form. Write it in another way (more specific about the differential quantities from before) What are intensive and extensive variables? Identify the intensive and extensive variables in the First Law. What are state functions? Why is dU a state function, but not dq or dw? (Draws a closed path in PV space) Is the work for this curve positive or negative? Is the heat positive or negative? What are the two ways of finding the answer to those questions? A. Searcy (?) What is your research thesis? Draw the phase diagram for your system. What is a peritectic point? A eutectic point? Draw a phase diagram with the following characteristics: a peritectic at T1 and a congruent point at T2 > T1. Draw a phase diagram with 2 eutectics and a line compound. Are dislocations equilibrium defects? Are vacancies equilibrium defects? What is their concentration? What is this reaction? What is DG at Te? How to H and S change during the transformation? A. Searcy (?) What is your research topic? 3 Can you draw a T vs. composition binary phase diagram of your research materials? (Be prepared to explain it in terms of free energy curves and common tangents, and explain any unusual features it has.) Draw a 1-component P vs. T phase diagram. What form will the material take near 0K and why? (Explain in terms of the Third Law.) A. Glaeser (?) Draw the G vs. X curves at T1 and T2 Draw Gs and Gl at T1 and explain. What are the slopes of these curves at X = 0 and X = 1? Why? What does the common tangent at T2 mean? What is the other criterion of equilibrium at T2? In the second diagram, why is G vs. X very different from in the previous diagram? A. Glaeser (?) What is the name of the equation relating the number of phases, degrees of freedom and components in a system at equilibrium? State it. Draw a eutectic phase diagram. Draw G vs. XB at T1 and at T2. What do points 1, 2 and 3 represent? What does the length P represent? Explain why the curves shift as they do from T2 to T1. Draw G vs. T for the liquid and solid phases. A. Searcy (?) (With a student working on Al-Li) Is d' a metastable or a stable phase? Draw the metastable and stable equilibrium lines denoting the phase field d' ordering reaction. A. Glaeser (?) Given the reactions A(g) + B(g) = AB(s) and A(g) + B(s) = AB(s), explain in terms of DG, Kp, X, P and a: For the first reaction, what is the equilibrium constant? What happens if the temperature is raised? If more of one gas is added? What is the equilibrium constant for the second reaction? Relate it to the activities. Mock Prelim Prep Sheet (Marcel Sluiter) Name kinds of equilibrium, and the meaning of thermodynamic equilibrium. What is a thermodynamic phase? Can a surface be a phase? If a material contains two kinds of magnetic domains, which differ only in direction of magnetization, how many phases does it have if placed in a magnetic field? If removed from said field? G. Evans (Fall 91)* [Professor Evans gave students a list of questions and 3 minutes to think about them . Some questions came from the sheet; others followed from those based on the students' answers.] (Gives you a table of the relative partial pressures of water at selected temperatures.) How would you determine the heat of vaporization from this table? Does water have a vapor pressure at any temperature above 0K? If so, why don't satellites evaporate in space? 4 If a curve of partial pressure vs. 1/T changes slope, what does it mean? (Gives you an Ellingham diagram) Why do the slopes of the reaction lines change? Does DH change with the slope? Why are partial pressures of oxygen indicated instead of moles of oxide? Why is -DG plotted on the y-axis? (Gives the following reaction: CH3SiCl3 <----> SiC + HCl ) Balance this equation. Write down the equilibrium constant in terms of activities. What changes could you make to make things more convenient? (What is easier to measure than activities? i.e. activities of pure solids are one; activities of gases can sometimes be written as partial pressures). What equation relates the equilibrium constant to thermodynamic data? How would you obtain DG for the reaction? What must be true for the reaction to go forward? Evans (Spring 93)- (different questions for each person) Si+3HCl -> SiHCl3 +H2 T=800K Total P=P equilibrium constant=1E7. Si is a solid. Ratio of atomic conc of Cl to H is .02 How can we determine partial pressures of HCl and H2? K=3N(HCl) 3N(SiHCl3)/ 3N(HCl) 2N(H2)NSiHCl3) Gives 3 minutes to look at before solving at the board. A+2B->AB2 G=Ko +K1 nA + K2 nA2+K3nB+K4nB2+K5nAB2+K6nAB22 nA=# of moles of A nB=# of moles of B, nAB2=# of moles of AB2 You initially start with m moles of A and m moles of B and no AB2. Find equations to determine amounts of species. Sands (Fall 93) When can you apply E-TS? What assumptions are made? Draw G vs. X for 2 components A,B that have AA and BB bonds stronger than AB bonds. a) at high temperature. b) at low temperature. Using the Ni-Al phase diagram (given) show relative positions of each phase that develops as a function of distance from the interface when a semi-infinite slab of Ni is pressed against a semi-infinite slab of Al, and you wait long enough for significant diffusion to occur. (Assume no barriers to nucleation) Ternary diagram Ni-Al-As (given) A piece of Ni is pressed against a piece of AlAs. Do you have enough information to map the results of diffusion? [No, need to know the diffusivity of each component through each phase.] A. Glaser (Spring 94) Familiarize yourself with the Ni-Al phase diagram.(shows you the phase diagram) What are the first 3 invariant reactions on this phase diagram, starting from the Al side? What types of reactions are they? Why are these reactions termed invariant? For the Al-NiAl3 eutectic, draw free energy curves at T=Tc=640˚C. What does the common tangent represent? What is the curvature of NiAl3 curve? What name would you use to describe the NiAl3 portion of the phase diagram.(answer: line compound) If the temperature is lowered to 630C what happens to the liquidus curve?the solid curve? Why does the liquid curve move up further then the solid curves?Why are the curves drawn this way?Given a container with pure Ni and pure Al , what will take place in the container at T=1100C, at short, intermediate, and long times?Draw activity profile for Ni at that temperature. Along constant activity line, why is there a driving force for diffusion? How would pressure affect the phase diagram?What is the general eutectoid reaction?Describe congruent melting? What is the Gibbs phase rule?How many degrees of freedom are there at the eutectic point? Glaeser - Fall 94 5 What is you research Material (Nb/Nb3Al) Can you draw the phase diagram for Nb-Al? Say I have two pure chunks of Nb and Al in intimate contact in a closed container at some temperature below the solidus of any phase? What happens. Looking only at the Nb(ss)-Nb3Al region of the phase diagram, draw the G vs X for this region. Why do you get a two phase region? How does it come about? Assume the common tangent between the two curves is not horizontal. Isn't the chemical potential of each component in either phase different? After all the tangent hits the axis at points of different levels! How can there be equilibrium here? Why is it okay for the tangent to be non-horizontal, but still have equilibrium? What is your research? (fatigue of TiAl) Can you draw the titanium-aluminum phase diagram? If I fill a container half way with Al and the rest of the way with Ti and heat at 830 C, what happens at short times? At long times what will be the ordering of the phases in the container? Draw the relavent free energy curves (G vs. composition) if you have a composition in the TiAl3 + liquid phase field. Why are the equilibrium compositions associated with a common tangent? Assume the TiAl3 has a range of solubility (not a line compound) and that I have compositions of the "TiAl3" and liquid phases which are not the equilibrium compositions. What causes these phases to evolve to the equilibrium compositions? (Ans. diffusion down a chemical potential gradient) Evans - Spring 95 Write an equation for entropy. (dS=dQ/T) What assumptions are made in determining the entropy according to the equation S=So+int(Cp/T dT)? How can the equation be changed to make it more general? (addition of phase change values) What is So? Some people suggest that it would be better to determine S according to the equation S=So+int(Cp d(lnT)). What is wrong with this approach? Glaeser - Fall 95 Given a graph of a solid solution in T(temperature) vs. x(concentration).What happens as T decreases? Draw g(Gibbs free energy) vs. x for the same system. Why is there a two-phase equilibrium? What is the difference between a common tangent and two points with the same slope? Evans - Fall 96 Consider the Siemens process for making poycrystalline silicon: H2 + HSiCl3 -> Si + 3HCl Write the equilibrium constant in terms of the activities. Write the activities of the gases in terms of the partial pressure and change that of the pure solid Si. If K=10^-7 , the total pressure is one atmosphere and the pressure of HCl is fixed at 0.2 atm, what is the composition of the gas at equilibrium? How is mole fraction determined from partial pressure? Derive an expression for the equilibrium constant as a function of the total pressure given that: d(deltaGo)/dP = deltaVo Evans - Spring '99 Two Champers are seperated by a porous partition so that the gas can flow through it. Suppose initially you have pressure P0 at left side and empty at right side, prove that when the pressure of right side is equal to the left side at equilibrium, the free energy is minimum. Glaeser - Fall ‘99 6 What is your research? What is your background? (showing Ellingham diagram) Are you familiar with this diagram? (No). Then consider this 1-component phase diagram for water (shows L and several solid phases). (Drawing const P line through several phases) Draw the chemical potential vs pressure. Why did you plot g vs p when I asked for chemical potential? (Drawing a const T line through several phases) Now draw chemical potential versus T. Explain the slopes of the curves. Ellingham Diagram: what does this chart represent, why are the slopes all positive, why is there a slope change in some of them, at what point does the slope change occur? Evans - Spring ‘00 A pure salt in the solid phase dissolves in pure water. Write down the equilibrium constant and relate it to delta G. Plot log(concentration) vs. 1/T. What is the slope? If the concentration decreases with increasing temperature, is the reaction endo or exothermic? Evans – Fall ‘00 Gives an Ellingham diagram for chlorides. Can you say if TiCl4 can be reduced by Cr and Fe at 1000K and at room temp? Support your answer numerically. How is this diagram different from that for oxidation? (C-CO line has reverse slope) Can you tell me what that difference implies for processing? What min. G is needed for reaction to go fully forward? ---------------------------XXXXXXXXXXXXXX--------------------------II. ELECTRICAL AND MAGNETIC PROPERTIES E. Haller (Spring 85) Plot E vs. x for a semiconductor acceptor, and for a donor. Draw a p-n junction. What happens when it is joined and why? With a bias applied, how do diffusion current and voltage current vary? How does this explain the rectifying property of the junction? Plot s vs. T for a metal and for a semiconductor. Why are the curves different? E. Weber (Fall 85) Plot resistivity vs. T for a metal. What is the cause of residual resistivity at 0K? Why does the slope change, and how? Plot resistivity vs. T for a superconductor. Explain the dependence of conductivity on temp for an insulator. How can an ionic material conduct electricity? Plot conductivity vs. temp for a semiconductor. What are the slopes? Why is there a factor of 1/2 in them? If you know only one point on this graph, how can you find the Fermi energy? Explain dia-, para- and ferromagnetism. What happens to a diamagnetic material if no field is applied? What is an example of a paramagnetic material? Can calcium be paramagnetic? Why does ferromagnetism become paramagnetism at high temperature? How is this called thermodynamically? E.Weber (Spring 86) Draw resistivity vs. temperature for a metal. What is responsible for permanent resistivity at 0K? What is the main factor determining the slope of the part for T>0K? Draw resistivity vs. T for a superconductor. Describe the mechanism for superconductivity. 7 Draw s vs 1/T for a semiconductor. What is responsible for the slope of the initial region? Describe the Hall effect. How do electrons and holes move in this situation? How can you measure the band gap of an ionic material, optically? Draw a schematic of the measuring system. E. Haller (Fall 86) Describe some types of magnetism. Why are some materials ferromagnetic while others are not? How do the electrons line up in a ferromagnetic material? What happens if a magnetic field is applied? Do the spins change spontaneously? Draw a B vs. H curve. What is this called? What does the area correspond to? What happens if we continue the curve instead of making H periodic? What do you call materials with large/small hysterisis areas? Which would you use for a computer? Which would you use for a transformer? Draw E vs. x for a semiconductor. Why does a semiconductor look metallic? What if you looked under infrared light? Draw the band diagram for a p-n junction. What are the charges from (mobile and immobile)? What does the donor level refer to? What happens when the two regions are initially brought into contact? Why does this stop? What are the different currents? Apply now a reverse bias. Why is there still a current? What is the effect of temperature? Are there any holes in the n-region? How many? How does this depend on T? How many electrons are there in the n-region? Know also the Hall effect. E. Haller (Spring 87) Pick a topic from the board (semiconductors picked) Explain band gap theory, density of states for metals, semiconductors, insulators, p and n doping. (Misc. Haller question - Explain the Meissner effect) E. Weber (Fall 87) Plot resistivity vs. T for a metal, a semiconductor and an insulator. Why doesn't resistivity drop to zero for metals at low T? What is the (currently believed) mechanism for superconductivity? For a semiconductor, plot lnN vs. 1/T. Explain the reasons for the different slopes. Briefly explain the difference between paramagnetism and diamagnetism. E. Haller (Spring 88) Draw the band structure (E vs. x) of a heterojunction p-n junction. What accounts for the contact potential? Draw a schematic plot of charge density vs. position. From this, draw electric field and potential vs. position. Why is the potential vs. position curve different from that of the band diagram? Draw r vs. T for a superconductor. To what value does r drop? How can you tell? What experiment can you perform to demonstrate that superconductivity is not just the disappearance of electrical resistivity? Show this on a H-T diagram. What is the difference between types I and II superconductors? Can you make a type I into a type II? How? Assume you solidify molten iron and cool it to room temperature in the absence of magnetic fields. Is it magnetized? In what way? Show the domains. What happens to the domains as you increase an applied field? E. Haller (Spring 88) What material do you work with? What happens if it is put in a magnetic field? What if you put BaTiO3 in an electric field? 8 What is the capacitance of the parallel plate capacitor with and without a dielectric between the plates? Write an equation relating q, C and V. Change the voltage to V0. Remove the battery and insert a dielectric. What happens? Suppose you do the same thing with the battery attached? What happens if you apply an AC current to the capacitor? How is the dielectric affected? What types of polarizations are there? What are their cutoff frequencies? Can a microwave heat perfectly solid ice? E. Haller (Spring 89) (Choose a topic from the board) Describe the Hall effect in detail. How could you determine the Hall coefficient experimentally? How could you determine the mobility from Hall effect measurements? Draw the m vs. T plot for an n-type semiconductor. Describe a p-n junction. Show a reverse-biased p-n junction and show the driving force for electron movement across the junction. E. Weber (Fall 89) Why does the resistivity of a metal increase with temperature? Why doesn't it reach 0 at 0K? What is the mechanism of superconductivity, as we understand it now? What is the difference between direct and indirect band gaps? Show an Arrhenius plot of conduction in ionic solids What are para- and diamagnetism? What are their temperature dependences? At very low temperatures, paramagnetic materials become ferromagnetic - why? E. Haller (Spring 91) Pick one: dielectrics, semiconductors, magnetic materials, optical materials. On semiconductors: What is the crystal structure of semiconductors? What is the coordination? How can the four outer electrons form 4 equivalent bonds when 2 are "s" and two are "p"? Draw a [100] projection of silicon. Where are the electrons in this picture? Can you go from here to an energy-band diagram? Where are the electrons at 0K? Is the valence band completely full? Down to the last electron? Write and graph the fraction of filled states as a function of energy, both at 0K and at some elevated temperature. What if you wanted more electrons present - what would you do? What were the populations of electrons and holes before? What are they now? What is this law called? E. Haller (?) Explain the phenomenon of superconductivity. Draw the current-field curve for superconductivity. Explain the mechanisms of the superconducting transition from A to C and from B to C. What are "hard" and "soft" superconductors? Draw a schematic of the energy-level diagram of a p-n junction What is the physical origin of the small current in a reverse biased p-n junction? E. Haller (?) What are you working on? (if your answer contains the work "magnetic":) Draw domain configuration of a macroscopic magnet and explain why it is magnetic. How does this change in an applied field? Why would you want to add Si to Fe magnets? E. Weber (?) Plot resistivity vs. T for: 9 i) a metal. Explain the effects of impurities. What determines the residual resistivity at low T? ii) a superconductor. Explain superconductivity (better than BN&T explanation, please) iii) an ionic crystal. Explain the slopes. iv) a semiconductor. Explain the slopes. Suppose there is a shallow dopant? v) why is there a fourth slope for an extrinsic semiconductor at low temperatures? Explain freeze-out and compensation. Draw a Fermi level vs. T plot showing the shallow donor freezing out and compensation. Write an equation relating carrier concentration to conductivity. E.Weber (?) Draw r vs. T for a metal and for a semiconductor. How is r affected by defects in a superconducting metal? Draw s vs. 1/T for a semiconductor. What happens at low temp? Explain the slopes. How would you measure the carrier concentration in a semiconductor? What happens to the voltage gradient if the charge carriers are holes rather than electrons? How would you measure the band gap of a semiconductor? How would you measure the resistivity of a metal? How is the carrier concentration in a metal affected by an increase in temperature? E. Weber (Fall 91)* What is the difference between diamagnetism, paramagnetism and ferromagnetism? What happens atomistically (to the individual electrons) to give these properties? Explain the temperature dependence of the mobility. Why does resistivity increase with temperature in a metal? Why is the curve linear at high temperatures? Weber (Spring 93) - (same questions for each person) How does the resistance vary with temperature from a metal to a semiconductor to an insulator? Draw a curve for each. What is causing the increase in resistance for a metal? Do you know any numbers of conductivities for materials? How would the resistance of a metallic alloy that forms an ordered compound vary above and below the ordering temperature? Describe paramagnetism, diamagnetism, and ferromagnetism. Why are some materials paramagnetic, while others are diamagnetic? Why are some para and some ferromagnetic? What are the two competing thermodynamic forces? What’s antiferromagnetism? Illustrate ionic conductivity in a solid. What are the slopes of s vs. 1/T? What determine the vacancy concentration in the low T region. Plot n vs. 1/T for a semiconductor. Why do the slopes change? Draw E vs. x. How does the Fermi level change with T? How would you determine the Fermi level from the concentration? write the equation. experimentally how would you determine carrier concentration? (4pt probe, Hall effect) In GaAs, midgap donors of 1E18 and shallow acceptors of 1E16 cm^-3. Where is the fermi level? Haller (Fall 93) Choose a topic. (Semiconductors) What type of elements are intrinsic semiconductors? Donors? Acceptors? Draw E vs. k diagram for Si, for a direct band gap material. Where are electrons and holes? Describe the various means by which electronic transitions can occur. Then at very low temperatures. Draw the band diagram for a pn junction. 10 Give an expression for the number of electron and holes in each region. Where are the space charges located? What is the region near the interface called? Is it possible to widen this depletion zone, how? For the topic of capacitors, main question: How does the capacitance change when you increase the reverse voltage? Haller(Spring 94) What types of magnetism exist?Give examples of materials with each type. How does magnetism come about?How come Fe does not display magnetic properties?Why does it form domains?What are the boundaries of the domains called?Draw a detailed sketch of a Bloch Wall.How thick is it?How could your original sketch of the 2 domains reduce their energy?How could we change the domain structure?Does it take energy?Draw what happens as we apply a magnetic field to your iron sample?Why would you use Fe in a 60 Hz transformer?What would you use at 1 MHz?What is minimized when you cool ferromagnetic? Is iron magnetized when you cool it from melt?Discuss three types of magnetism. Draw hysteresis curve identify important points on the curve. What limits maximum B? Compare max B for Fe and Co. Discuss hard and soft magnets. A typical magnet has a field of about what? What types of magnet in a transformer, why? Draw band diagram for Si in E vs k and E vs x space. What's the band gap?Draw band diagram for GaAs. What's the difference between GaAs and Si?What happens with GaAs at high E?(answer: decreases mobility because mass gets heavier)With no doping why do you have electrons in the conduction band and holes in the valence band? Weber- Fall 94 How do you MEASURE if a material is paramagnetic or diamagnetic? (Use inhomogeneous B field) Draw metal resistivity curve vs. T. At zero kelvin will an ideal, pure metal be a superconductor? How does impurity affect the curve? Draw Ionic (insulator) conductivity vs. T. Describe the different regions. Draw a general curve for metal resistivity again. Say the metal is niobium which has a superconducting transition. Draw on the same curve what the resistivity curve for niobium would look like. What is the mechanism for superconductivity? Draw a simple band diagram for a semiconductor (intrinsic). (shows periodic table). Say I add phosphorus (assume this is silicon) how does the band diagram change? What if I add boron? What about Zn? What about sulfur? What are the typical values for energy difference between shallow sites and the conduction or valence band? Say this band diagram is for GaAs. What would it look like if I had an As on a Ga site? What is this called? Why is the electron on the Phosphorus atom delocalized in a Si semiconductor? Is it a property of the Si or the P? (Dielectric constant of Si) How does the Fermi energy vary with temperature for an n-type semiconductor? Haller - Spring 95 Draw a p-n junction. Are all of the carriers mobile on both sides? What would be the motion of the minority carriers? What type of current is that? Draw the I-V characteristics of a pn diode. Does it have a linear relationship in the lower region? (no, exponential) What happens at the breakdown voltage? Are there different types of breakdown voltages? Why is it beneficial to operate a zener diode in the range of 11 50% zener breakdown? (thermal effects of zener and avalanche breakdown cancel each other) Draw a transistor (npn). Which region is the base, emittor, collector? How would you create a gain from it? Weber - Fall 95 How can one find the energy of formation of a vacancy? What doping level is needed to find the effect of solubility of Fe in Si? Explain the difference between diamagnetism and paramagnetism. What is the lowest energy state for a ferromagnet which is first raised to a high T and then slowly cooled? Weber -Fall 96 Describe the mechanisms of conductivity for insulators, metals, and semiconductors? Explain the slope of conductivity vs. Temp. for an ionic compound. What is the charge of a Na vacancy in NaCl? Explain conductivity vs. T for a metal? How does the number of carriers vary with T for a metal? Haller - Spring 98 Choice of 2 out of four: magnetic materials, semiconductors, dielectrics and optics, superconductors. Magnetics: draw a hysterysis curve for soft and hard magnet. How does BvsH and MvsH go as they saturate? What kind of applications use hard and soft magnets? What material is a typical magnet made of? Why does a magnet form domains and what are the boundaries between domains called? Sketch the domain wall. Haller - Spring '99 Superconductor: PLot how the resistivity change with temperature for supreconductor (Nb) How to prove that reisitivity is zero for superconductor What happen if we applied field on superconductor. Why? Who found induction current? (Faradey) What you know about BCS theory? How long the Cooper Pair is? Is there any other electron in between? How long a Cooper Pair can exist? How large bonding energy between this Cooper Pair is. Just below Tc, how many fraction of electron can form Cooper Pairs? What is Type I and Type II superconductor and how can you make it. Pure Nb is Type I or II? How about YBCO? Sands - Fall ‘99 We are discussing electrical properties today. (Gives a log conductivity vs 1/T plot with A,B,C,D curves overlaid). Take a minute to review this and then discuss each curve. (There is an extrinsic seminconductor w/o compensation, superconductor, pure metal and dirty metal. The pure metal has a slight dependence on T, the dirty metal is constant w/ T). What are the various regimes and slopes of the semiconductor curve? Explain the temperature dependence of the pure metal curve. What is the source of resistivity here? What about for this curve (dirty metal)? Do you know a typical resistivity for a good conducting metal? (Draws M-H loop). What is the significance of this point (coercivity)? Explain the rectifying behavior of either a pn junction or a Schottky diode. (chose pn junction) What happens in forward bias? E. Haller - Spring ‘00 Draw in E vs. k space the difference between a direct band gap and an indirect gap semiconductor. How would you determine if a semicond. is direct or indirect? Plot abosorption vs. energy. What is the linear absorption coefficient? How do the plots for direct and indirect semicond. differ and why? Describe in the E vs. k diagram the mechanism by which a direct and indirect semicond. absorbs. Why is the indirect absorption process less likely? 12 Why do photons create a vertical transition while phonons a horizontal one? What’s the band gap of Si? What’s the “direct” gap of Si? How much energy does a phonon carry? Based on this information, what can you say about the two peaks in an indirect semicond. absorption? What about the heights of the peaks. Are they the same? What’s the difference in engery between the two peaks? If this measurement was done at low T, there are very few phonons. Why does the indirect transition still occur? If you have diode made of indirect semicond material, can electrons and holes recombine? The answer is yes to some degree. How do they recombine if conservation of momentum still needs to be satisfied and there are no phonons in your crystal? What about absorption in semi-insulating GaAs? If you have a recombination event at a deep trap or level, where does the energy go? The energy that is then absorbed is about 20 times more than that of a phonon. So can phonons still be generated? Weber – Fall ‘00 How does no. of carriers vary with temp. in metals? What is a typical value? Give / vs T for metals, semiconductors and insulators. Explain the mechanisms in each. In ioninc condutivity, why does the number of vacancies in extrinsinc regime exceed the equilibrium number? Can you name and explain main types of magnetism. Also, explain why a paramagnetic material turns ferromagnetic? What happens above Curie Temp.? ---------------------------XXXXXXXXXXXXXX--------------------------III. MECHANICAL PROPERTIES J. W. Morris (Fall 86) Draw a stress strain curve (suggests various materials) Why is there a UTS? When does it occur? If the material fractures past the UTS, what does the fracture surface look like? How does this occur? What happens (atomistically) in the elastic region? What happens in the plastic region? Describe some hardening mechanisms. Plot yield strength vs. T. Why does the material get softer at high T? T. Devine (Spring 87) How do the dislocations shown at right (A) interact? Over what range? Give the strength of the structure at right (B) as a function of t. Explain. Of the structures at right (C), is one ductile and one brittle or are both the same? Why? R. Ritchie (Fall 87) Name ways dislocations can harden a material. What is a Burger's vector? Plot strain vs. time for constant stress. What is the name for this slow strain? What causes the various regimes? Give the constitutive law for creep. Do you know a typical value for n? Can you suggest a different creep mechanism effective above 0.9 Tm? 13 How would you increase creep resistance above 0.9 Tm? What materials resist creep well? T. Devine (Spring 88) Suppose you have three metal bars, each 1 inch in diameter, and you want to make wire out of them by rolling and drawing. The stress-strain curves for each are as shown.(A) Which would you pick? (Think whether it is more important that the wire be strong or that it be easy to draw) Why? How may slip systems exist in fcc? In bcc? Consider fatigue. Plot Ds vs. N, the number of cycles to failure.(B) Most materials have curves like 1, but some fcc metals have curves like 2. Can you explain why? In which part of the graph is crack initiation important? Crack propagation? T. Devine (Spring 88) Suppose you pull an fcc and a bcc metal as shown(A). Explain the differences in their behavior. Do fcc and bcc metals show a ductile-brittle transition? Why does this occur? Why is there a fatigue limit in some steels? For the fatigue curve shown(B), are there regions where crack initiation and crack propagation are controlling? R. Cannon (Spring 89) What is your research material? (answered SiC - Si3N4) Draw engineering stress-strain curves for Al-SiC and Si3N4-SiC composites. Elaborate on them. What happens on loading? Why would one reinforce one brittle material (Si3N4) with another (SiC)? R. Cannon (Spring 89) Draw the stress-strain curve for your material. What determines Young's modulus? Compare these with the stress-strain curve and modulus for a metal, and for a polymer such as polyethylene. How is the yield point determined from these curves? Has any plastic deformation occurred at this point? Why is this point used as the yield point? Compare the modulus of various types of materials (ceramics, metals, polymers) and explain why they are different. R. Ritchie (Fall 89) Explain the forms of deformation at different temperatures. What forms of strain hardening exist? How does sy depend on the distance between precipitates? On the grain size? Derive an equation for the onset of necking, using the engineering stress-strain curve shown. R. Ritchie (Spring 91) What sorts of inelastic deformation exist? (3) Starting at low temp and moving up, which would come into play when? Are there any other mechanisms for T > 0.8 Tm? 14 What might happen to a material under load at constant temperature? Draw the strain as a function of time. Explain the different regimes. Can you write a constitutive law for the middle region? What is contained in the proportionality constant k? What is the order of magnitude of n? What happens to n in tertiary creep? What is a ductile-brittle transition temperature? Why does it happen? Can you explain why low-carbon steel has one, while aluminum doesn't? Draw toughness vs. T. Draw sy vs. T. What is the DBTT of the type of steel bridges are sometimes made from? R. Ritchie (?) What is an edge dislocation? A screw? Draw an edge dislocation. Where is its glide plane? Show how the edge glides and climbs. Why doesn't a screw dislocation climb? What mechanisms of deformation are important at high temperatures? Suppose an edge and a screw meet at right angles. What happens? What character are the jogs? How do the jogs impede motion of the dislocations? How does fracture toughness vary with thickness for a metal? For a ceramic? J. W. Morris (?) Draw a typical stress-strain curve for a ductile material, for a work hardenable material, and for a brittle ceramic material. What is the difference between elastic and plastic deformation? What causes necking? What are the differences in fracture surfaces for brittle and ductile failure? Where in the material are voids likely to occur? What is the yield strength depression with temperature when we have a work-hardened material with a solute? Explain the regimes shown. Name some methods of strengthening materials. ???????????? Draw a stress (engineering) vs. strain for polycrystalline iron in tension. Draw the same curve for true stress. Explain the differences between the curves. What does the fracture surface look like? Why? Define the critical stress-intensity factor KIC. What is the effect of a notch in the specimen? Explain what plane strain means. Define the ductile-brittle transition. J. W. Morris (?) Draw the various stress-strain curves typical of engineering materials. List the various methods of strengthening materials. Are dislocation present at 0K? Do they vibrate at this temperature? What do you know of the Considere criterion? T. Devine (?) Assume the material shown is purely elastic. Draw the stress intensity factor at the crack tip if the applied stress is very small. Suppose there is plasticity and the applied stress is larger - then what? The specimens shown are of the same material and have the same thickness and same plastic zone size, yet the one on the left is brittle and the other is ductile.Why? Suppose a Cu single crystal is being pulled as shown. Plot strain t vs. shear stress g.The material on the left is purely plastic, the other purely elastic. If they are pulled will their final shapes be the same or not? R. Ritchie (?) 15 Enumerate the different mechanisms for plastic deformation. Explain the two mechanisms by which dislocations move. Draw a creep curve (strain vs. log t). Explain each regime. Give a function which describes the central linear regime. Suggest a material to make each of the following objects and explain your choices: 1) a light bulb filament 2) a strong pressure vessel 3) a turbine blade R. Ritchie (?) (On plastic deformation) What mechanisms of plastic deformation are there? Draw the Burger's vector and line direction for an edge and a screw dislocation. Describe the movement of dislocations at low and high temperatures. If a screw dislocation and an edge dislocation meet, what effect does each have on the other? (On fracture toughness) Describe how the fracture toughness value of metals and ceramics vary with specimen thickness. A few other questions... What is a typical value for Poisson's ration u for a metal? Write Hooke's law in terms of stress and strain, for tension and for shear. Is the elastic modulus greatly affected by small alloying additions? By the presence of vacancies, dislocations, grain boundaries? How does the modulus vary with composition for a system showing complete solid solubility? ( Ans: By rule of mixing.) G. Cooper (Fall 91)* Draw an engineering stress-strain curve for a typical engineering alloy. What begins to happen at the point where the curve deviates from its initial linear behavior? What is this point called? Suppose it is not well-defined? What is the maximum of this curve called? What happens at the end? After fracture, what would you measure on the specimen? Where in the graph does work hardening occur? Why does work hardening occur? What types of dislocations are there? In what combinations can they interact? Draw diagrams of their interactions, labelling kinks and jogs and giving the direction of the Burger's vectors. Do all such interactions create obstacles for dislocation movement? What is the mechanism for climb? Plot strain vs. time for a metal undergoing creep. What happens in the three regions? How does fracture behavior change with temperature for a bcc alloy? (you should plot toughness vs. temp.) What is the reason for the ductile-to-brittle transition? Draw the curves for yield strength and twinning as a function of temperature.What other variable influences fracture behavior? Plot yield strength vs. T and cleavage strength vs. T on the same graph. Ferrari (Spring 93)- (same questions for each person) Shows BCC cell. Gives s direction and slip plane & direction. Find the t critical resolved shear stress. Under strain control, draw the stress strain curve of the elastic region. What happens when you heat to 200C(instantaneously) at that point? What happens if you continue to elongate? What does the stress vs. time look like? Repeat the above question under stress control. Strain vs time. We deposit a film on a material and it curves up. What are the stresses in the material, both shear and normal? Is the film in tension or compression? Plot stress vs depth into the thin film and material. How would you determine the stresses. Ritchie (Fall 93) 16 What are the mechanisms of plastic deformation of metals? Describe them. At what fraction of the absolute melting point does each apply? What is the constitutive relation between strain rate and stress? What value should the exponent have for the different deformation mechanisms? What happens to fracture toughness of a metal specimen as a function of thickness? Why? What happens to the strength of ceramic tensile test specimens as a function of size? Compare the results for ceramics in 3 point bending vs. straight tension.What are the mechanisms for creep? At what temperatures do they take place? What are typical values for n in the constituative law for creep? Why is Coble creep prefered over Nabarro-Herring creep at lower temperatures? How does the stress intensity factor vary with thickness: for a metal? for a ceramic? What is the lower plateau for a plot of Kc versus thickness called? Ferrari(Spring 94) Describe moment profile in a 4 point bend test.What is the shear stress diagram for the 4 point bend test?Where is smax?What is it?What are the boundary conditions for a plate with a void?What are the field equations for the plate?Whats the stress distribution at the crack. What is KI?How is it derived?Validity?Discuss viscoelasticity.Write governing equations.What is creep?Write equation for creep in the steady state. Draw s vs e for creep and viscoelasticity. Cooper - Fall 94 What is the Griffith Criteria? What are the competing energy terms? Can you write an equation for this relationship? Why does the term for the release of elastic strain energy have the form it does? What is stress concentration factor? Is it geometry dependent? Can you write a general form of the expression? What is it dependent on? What do you think a typical critical crack length is for (a) glass, (b) Aluminum (c) steel? What is plane stress and plane strain? We know that the concepts of plane stress and plane strain govern why we get a ductile ridge around the outside of a tensile rod, but how do predict the depth of the the ductile ligament? (There is no rigorous method that will do this) Derive the equation for the fracture Ritchie -Spring 95 Describe the deformation mechanisms in single crystal Cu (over various temperature ranges). Describe difference between hard and soft orientation. Draw stress-strain curve for polycrystaline Cu. Can you derive the conditions for necking from this? (not just ds/de=0) What deformation mechanisms are there in ceramics? for what temperatures? What defromation mechanisms are there for polymers? Cooper - Fall 95 Derive equations for the total stress in a fiber reinforced material in two scenarios: continuous fibers and fiber strips.How does sigma change with l for a material with length l=infinity and l=lo(finite length)? How does fracture change for l=lo and the two types of reinforcement?Draw graphs of sigma vs. l in both scenarios.Draw graphs of fracture strength vs. l in both scenarios. Ritchie - Fall 96 What are the mechanisms of dilcoation glide at high and low Temp.? What is hight T disloc. motion called? Why is dislocation motion lower at low T (near 0K) compared to room temp? (Peirl's stress) Why is the yield stress of 17 aluminum lower than steel? (stacking fault energy) How can two partial screw dislocations cross slip? How does the fracture toughness of steel (for a bridge) vary with T? Why? How do two screw dislocations look after they have intersected? What is the new segment called? (jog) What is it's slip plane ? If a shear stress is applied to a jogged screw dislocation, what will happen? How does fracutre toughness vary with thickness for a notched specimen? Why? Represent plane-stress on a Moore's circle. Why is the tensile strength greater for two steel bars soldered together compared to the tensile strength of a bar of the solder material? Ritchie - Spring 98 What are the mechnisms of plastic deformation? What is the Schmidt relation? Draw slip in a single crystal, define easy and hard directions. Explain fatigue. Draw an S-N curve. Fatigue limit - what is it qualitatively and quantitatively? What happens if you change the mean stress in cyclic loading? Ritchie - Spring '99 List Mechanisms of Plastic Deformation. Derive the condition for necking. List the ways for hardening materials. Discuss the grain size effect on both metal and ceramics. Cooper - Fall ‘99 Draw a stress strain curve for a typical engineering alloy (drew ~Al-2024). What is the highest point called? Identify points of interest on this curve. Where does yielding occur? Show the yield point (0.2% offset) on this curve. Now draw stress-strain for a steel alloy (drew 1020 mild steel). Identify the yield point on this curve (UYS,LYS). What explains this behavior? (Referring to point in middle of Luders band) What happens if you unload the specimen at this point (in tensile test)? What do you expect the surface to look like? ("Orange-Peel" appearance). Have you heard of "Orange peeling?". (Explaining this is a big problem in painting cars) What would you do to avoid this problem? (cold roll before painting). What happens if you cold roll a long time prior to painting? What do you know about fracture? What is the Griffith crack criterion? Why does the strain energy release term have the form shown? Do you know a typical crack length in glass? (~1 micron) Derive the griffith crack criteria What are typical critical crack lengths for steel, aluminum Ritchie - Spring 00 Describe various strengthening mechanisms for metals. How does solid solution work? What two ways can a dislocation intereact with a precipitate? Under what conditions do each occur? What about strengthening of a ceramic? (Not toughening.) What types of strengthening would be applicable at high temperatures? Low temperatures? Draw a stress/strain curve? At what strain is the yield? At what strain does failure occur? What is the condition for necking? Why doesn’t necking start to occur right after the yield point? Derive the condition for necking. Ritchie – Fall ‘00 Draw stress-strain curve for Cu. Explain the parameters that decide strength and ductility. Why does necking start suddenly and not from the very beginning? Draw curve for DBTT? Explain what the axes actually are. How will you test it? What is the essential difference between crack propagation in the case of elastic and plastic deformation? ---------------------------XXXXXXXXXXXXXX--------------------------18 IV. MATERIALS CHARACTERIZATION R. Gronsky (Spring 86) What is diffraction? Is there a limit to the source used for diffraction? How do you detect x-rays? How does a scintillator work? How do you produce x-rays? What is the difference between Ka and Kb x-rays? What is the mechanism for absorption? Why do metals glow when heated? What do you need for microscopy? What is coherence? What is contrast? How can you improve contrast? What is noise? How can you differentiate between noise and signal? R. Gronsky (Spring 86) (Shows you a steel bar) How would you characterize this material? How would you find the lattice parameter precisely? In powder diffraction, what effect does a very small particle size have on the diffraction pattern? What effect do dislocations have? If both effects were possibly present, how could you distinguish between them? How could you characterize defects in a metal? R. Gronsky (Spring 87) Describe absorption and emission. (Gives you his pen) How could you characterize this pen? What is it made of? Define chromatic aberration. Why might we use a green filter on an optical microscope? R. Gronsky (Spring 87) List ways in which absorption phenomena are used to characterize materials. When are these applicable? For the bulk? For the surface? What physical phenomena are occurring? Define diffraction. State Bragg's law. For a bcc crystal, explain the presence of an (004) reflection. How does it appear? Why does it actually represent the (002) plane? Why is it not for the (004) plane? Explain what we mean by spectroscopy. Give an example. Is Auger a bulk technique? Why? G. Thomas (Fall 87) What is your research material? How do/would you characterize it? (for Al-SiC composites) How would you find the volume fraction of fibers by x-ray diffraction? Where would the diffraction lines for SiC and Al be? R. Gronsky (Spring 88) How would you determine the density of a material? How would you find its crystal structure? What does the diffraction pattern tell you? (not only the geometry but the intensities) How can you determine the grain structure of a material? Suppose it is resistant to chemical etching? How do light polarizing filters work? R. Gronsky (Spring 89) Describe to a teenager the meaning of "diffraction". State Bragg's law. Draw the (200) plane in bcc, and show Bragg's law graphically. What is the meaning of (400) diffraction? (is it the 4th order of (100) diffraction?) How could you determine the chemical composition of a material (besides diffraction)? Describe in detail the physical mechanisms involved. 19 G. Thomas (Fall 89) Describe the basics of x-ray diffraction in bulk and in powders. Define the structure factor. Is it different for different elements? How can we measure very low dislocation densities? Explain how characteristic x-rays can be used for chemical analysis. J. Washburn (Spring 91) (Shows a piece of steel, heavily cold-worked, with a crack. Says it was found near a car at a crash scene, and you are an expert witness and are to decide if it came from a larger piece in the car) How would you determine if this piece has the same structure as the larger piece? If it had the same alloying additions? The same carbon content? How do these techniques you mention work? (Shows a lump of brass, machined as some mechanical part.) How could you tell if this piece was machined from a casting or from a forged billet? G. Thomas (?) Draw an orthorhombic unit cell. What are its slip systems? How could we characterize a slip system? How could we find the surface orientation of a bulk sample? What information can we obtain from powder diffraction? How can we learn chemical composition from diffraction methods? R. Gronsky (?) (Hands you a copper crucible) How would you find the crystal structure of this? How would you learn its chemical identity? Suppose it is an alloy, and thus not included in the ASTM card file. How would you obtain its lattice parameter? Why is Debye-Scherrer diffraction used to find lattice parameters? This specimen has been cold-worked. How would you find its dislocation density? How would a high dislocation density affect Debye-Scherrer results? If the material had very fine grains (i. e. about 1 micron), how would this affect the Debye-Scherrer results? If the specimen is Cu - 4%Al, how would you determine which atoms sit on which sites using a diffractometer? R. Gronsky (?) What are the most important parts of a microscope? What are the various characteristic radiations used to characterize materials and what are their physical origins? How can you improve the contrast of an image? How can you distinguish noise from the useful signal? G. Thomas (?) Describe Auger spectroscopy. What physical effect is at work? What sorts of results are obtained? What can a TEM diffraction pattern tell you about the sample? Explain what we mean by characterization. What method would you use to find the crystal structure of a material? Why is x-ray diffraction more accurate than electron diffraction? Write down the expression for the structure factor. Explain the physical significance of the exponent. Explain how the atomic scattering factor differs for x-rays and electrons. What are the scattering mechanisms for each case? Plot f vs. sinq/l. Explain. Plot intensity vs. distance for a typical powder diffraction result. 20 ?????????????? State Bragg's law. Draw the bcc structure. Draw an (004) plane in it. What atoms are in this plane? If there are no atoms in it, how can it give a reflection in diffraction? What is the diffraction condition in bcc? Define the structure factor. Can you calculate it? Is it different for x-rays, electrons, neutrons? (Shows a powder diffraction pattern on a film strip.) Explain this pattern. How was it obtained? Why are the bands curved? (Shows a Laue pattern) Explain this pattern. How was it obtained? Why does it have spots? (Shows an x-ray diffraction plot and a neutron diffraction pattern.) What is the main purpose of neutron diffraction? Is the Bragg condition the same as for x-rays? G. Thomas (Fall 91)* (Gives you a small abacus on a marble base.) How would you learn what this is made of? How would you find out if the beads are homogeneous or plated? Why would it be difficult to use EDS or x-ray diffraction to find this out, if the beads are made of brass? (Ans. structure factors of Zn and Cu are similar) What technique would be better and why? (Ans. neutron diffraction) Draw an fcc unit cell. How many atoms are in the cell? How many terms are in the structure factor equation? If this were Cu3Au, where could the copper atoms be? What is the primitive cell? Who is your advisor? What is your research material? (Gives you a chunk of light metal with very pronounced grains.) How would you determine if this is a metal? How would you get more information on the structure? Draw the hexagonal close-packed and face-centered tetragonal unit cells. Derive the structure factor for both. If you have materials A (a single element) and BC (a compound) with the same structure and same lattice parameter, how would you distinguish them? Would the structure factors be the same? Gronsky (Spring 93)- (same questions for each person) Describe diffraction. How do the intensities vary generally with q? What can diffraction tell you about defects? What information does diffraction give you about a material? How can we use visible light for characterization? Why can’t we use visible light for diffraction? Is there diffraction from the window blinds? If you have vacancies what does it do to the diffraction peaks? What about an ordered compund like b-brass? How does deformation change the peaks? Which side of the peak corresponds to compressed planes? Asked about inelastic scattering processes. What are the differences between x-ray and electron diffraction? What kind of patterns can we get? Suppose you had a lump of metal dug out of the earth, how would you characterize it? (powder diffraction) How would you assess the crystal quality of a crystal? Why would we use neutron diffraction? How will the Advanced Light source, a source of soft x-rays be useful for materials characterization? Gronsky (Fall 93) What test would you do to see if a material is BCC or FCC? What test would you do to see if a material is a semiconductor or an insulator? How would you use x-ray diffraction to locate the exact mole fraction at which the solvus line occurs between a phase and a+b phase region for a solid solution? What is spectroscopy? Name and describe on type of spectroscopy. He hands you a chunk of material that looks like Si or Ge. 21 What can you tell me about the material properties of this material? Start with optical properties, then go on from there. If you mention electron diffraction, be prepared to discuss the significance of the structure factor. How would you determine the solidus line for a binary alloy? Tim Sands(Spring 94) Gives you 3 materials: metal, semiconductor and ceramic. Asks you to select one.How would you characterize this material (given almost no lab budget)?(answer:density measurements) Discuss characterization techniques used on your research topic (compositional,structural, and mechanical) If have a surface reaction ( a material in an unknown environment) how would you characterize it?How would a diffraction pattern differ from a random sample and a textrured sample. Shows a Si ingot, what orientation is it?(answer (100) because of the four fold symmetry)What would you use to find effective number of carriers?What would you use to find impurities? Gronsky - Fall 94 How can you determine if a material is BCC or BCT? (peak splitting) How do you determine if a material you suspect to be heavily deformed has dislocations? (TEM-g*b, or etch pits) How would you determine the tie line compositions in a Ternary alloy? You can assume it has been cooled under equilibrium conditions. (EDS/WDS) Explain what EDS and WDS measure. Explain how both work. Sands - Spring 95 Derive the Bragg condition for refraction. Does the Bragg equation give any info about intensity of peaks? Why would a BCC lattice have no refraction using a purely kinematic model? (Gives unknown material) What can you tell about this materials from inspection? Given the equipment in a typical high school lab, how would you characterize it? How would you characterize its chemical make up, using any equipment? Gronsky - Fall 95 How does residual stress affect x-ray line widths?What determines the resolution of a microscope?Describe one type of spectroscopy. What is Bragg's Law? When measuring lattice constants using x-ray diffraction, how does the accuracy change with theta? Gronsky - Fall ‘96 Describe diffraction. How is diffraction used to study materials? What information does one get from x-ray diffraction? What is the structure factor? Shows a wafer of material. If I have already determined the crystal structure of the wafer to be diamond cubic, how can I determine whether it is silicon or GaAs? What is the mechanism for the production of characteristic x-rays? What energy is required to expel core shell electrons? Weber - Spring '99 How can you determine the dislocation density? Which one is good for high densith, which is for low density? Why there is a contrast for dislocation under TEM? What does g.b=0 mean? What about structure factor for simple cubic and BCC. How it will change if you have ordering-disordering phase transformation. How can you determine the thickness of multiple thin film. How it works? Draw the typical curve for RBS. Gronsky - Fall ‘99 Your research budget is small; you can only do x-ray diffraction experiments on a Co-Ni alloy. Prove your worth by telling me how you would extract the maximum information with your limited equipment. You can assume complete solubility. 22 Are you using Laue or Debye-Scherrer technique? Since Co and Ni are neighbors on the periodic table, could you really get information about motif from the intensities (structure factor)? Could you tell determine degree of crystallinity? Instead of an alloy, you have a mixture of pure Co and Ni powders. What does your d.p. (powder method) look like now? How could you tell composition now? Does it matter what angles you consider...now a series of questions requiring knowledge of how the intensity of diffraction peaks changes with various parameters. Under what conditions can one see the 100 reflection in fcc? (first order 200 = second order 100 reflection; ie, n=2 in Bragg law). Sands - Spring ‘00 Shows you a shiny multi-colored material with many facets. What can you tell from visual inspection? Why is it multicolored? What can you determine with x-ray diffraction? Why can’t you see a 100 relfection from a BCC crystal? What can you determine by using: alpha particles, low and high energy electrons, neutrons, and low evergy ions. What about XPS and Auger? The wavelength of you incident particle/radiation determines the minimum feature size you can see. You can accelerate electrons to modify its wavelength or you can also use hard x-rays that have comparable wavelengths. Which would be better to use? Gronsky – Fall ‘00 Give a I vs 2 plot with 5 peaks roughly equispaced. You know that this is obtained from a powder of one of these elements – Ag, Ni, and 2 others. Can you tell me which? (you can eliminate the FCC materials owing to the uniform spacing, then talk about how to use Bragg’s law, indexing etc- talk about ratio of d-spacing). --------------------------XXXXXXXXXXXXXX--------------------------V. PHASE TRANSFORMATIONS D. de Fontaine (Spring 86) Explain classical nucleation theory: Write the fundamental equation in terms of volume free energy and surface energy, assuming a spherical nucleus. Derive the size of the critical nucleus. How can the nucleus attain the critical size? Explain the mechanism. Explain nucleation behavior just below the melting point. Draw a eutectic phase diagram: At temperature T1, plot the molar free energy vs. composition for a and b. How can you explain the equilibrium condition of the two phases? What is the driving force for precipitation at C1? How can you determine the maximum driving force? T. Devine (Fall 86) In the phase diagram at right, how could you determine the fraction of b present at Cx, at equilibrium at temperature T1? Draw the free energy curves (G vs. X) for this 23 temperature. What happens to the curve at x = 0? Why? Suppose you bring Cx up to T0 and hold until homogenized. Then cool to T1. Draw the microstructure. What will the microstructure look like after a long time? Suppose you cooled from T0 to T1. Draw the microstructure. Is it easier to undercool gas to liquid, liquid to solid, or Sa to Sb (assuming a solidstate transition a to b)? Why? What does nucleation depend on? J. W. Morris (Spring 87) What is a phase transformation? What properties may be involved? What two categories of phase transformation are there? Describe them. In which category does spinodal decomposition fall? A. Searcy (Spring 87) Define a thermodynamic phase. What is a first-order phase transformation? How would you distinguish between two phases in your sample? (could use hardness, TEM, light microscopy) Which of these methods is most reliable and accurate? Explain the freezing of water in terms of kinetics. Name a phase transformation in which there is no nucleation. What is the key feature that allows this type of transformation? Describe the nucleation and growth phenomena in the cooling of a material that has congruent melting behavior. D. de Fontaine (Fall 87) Explain nucleation. What is the probability to nucleate a particle? Plot G vs. T. At Tm, what is DG and what is the probability to nucleate? What is the critical nucleus radius at Tm? Why do we need undercooling to nucleate? D. de Fontaine (Spring 88) Draw a typical T-T-T diagram. Label the axes and indicate the phases present. Why does the curve have the shape it does? How can you apply a curve like this to the solidification of liquid Si? What happens if you miss the nose of the curve? By drawing a 2-dimensional M2O2 crystal (M a metal) describe how an oxygen vacancy can have electrical activity. What "chemical reactions" can you write for this process? (equations of vacancies, interstitials, electrons, etc.) J. W. Morris (Spring 91) Name the two principal types of phase transformations. Give an example of each. What is the fundamental difference between them, on an atomistic level? (The answer he sought is that a spinodal stems from a chemical instability, while a martensitic transformation is caused by a mechanical instability.) J. W. Morris (?) Draw a eutectic phase diagram. If we cool rapidly at C0 (between c=0 and max. solid solubility) what happens? Show this as an effective solidus on the diagram. **** Draw the microstructure. Is it possible to get the eutectic composition by solidifying at C0? (Shows the Nb-Al phase diagram - very complex) If we cool very rapidly at C0 (in the Nb-rich solid solution region) What is the phase with the greatest Al content? (Returning to the eutectic diagram) 24 At what temperature would you homogenize? Explain heterogeneous nucleation in this system. What is the main cause of heterogeneous nucleation? In the diagram at right, what is the name of the zone **** at the arrow? Would you prefer that these zones be large or small? Explain homogeneous nucleation in this system. T. Devine (?) What are the critical radii for nucleation in gases, liquids, solids? Draw a phase diagram showing a spinodal. Draw the accompanying free energy curves for T > Tc, T = Tc, T < Tc. (Possible question - explain from these curves the regions of stability in the spinodal.) ??????????????? State Fick's first and second laws. What effects might dislocations have on a phase transformation? D. de Fontaine (?) Explain nucleation: Write an equation for nucleation (energy to form a nucleus) and graph it. Explain what DGv and gs are. What is the critical nucleus size? What are the preferred nucleation sites? T. Devine (?) From the phase diagram at right, draw the free energy of the liquid and solid at the temperature shown. What is the reason for the asymptotic behavior of these curves near x = 0 and x = 1? Qualitatively explain the concept of the critical nucleus in nucleation and growth solidification. Is this critical nucleus small or larger in a liquid to solid transformation than in a solid-solid transformation? Explain why. D. de Fontaine (?) What is your research material? (answered TiO2) What is its crystal structure? Draw a phase diagram for Ti and O. What could you do to TiO2 to make it an offstoichiometric compound with the same crystal structure? If the off-stoichiometry were due to vacancies on a sublattice, could you treat the problem theoretically? If so can you name a model to use? In the regular solution model what term is important in determining ordering? State Fick's 2nd Law. What is D? What does it contain? What is Q in the expression for D (D = D0exp (-Q/RT))? What terms make up Q? What is Q for interstitial diffusion? What else is in D? How does entropy enter into D? L. DeJonghe (Fall 91)* Draw a eutectic phase diagram (be neat). What happens during equilibrium cooling of a hypo-eutectic solid? What is the likely structure of the matrix? Draw an arbitrary isotherm below Te. Draw the corresponding G vs. comp. diagram. What points on the phase diagram correspond to the common tangent points? What is the significance of these points, in terms of the chemical potential? Write down the equation for the energy of formation of a classical nucleus. Plot the surface and volume free energy vs. the radius. How can you find the critical nucleus size from these? 25 Draw a TTT diagram for steel. Why is there a knee in the curves for diffusioncontrolled tranformations? What do you know about martensitic transformations? DeFontaine (Spring 93)- (different questions for each person) Who do you work for? What is you research material? (answered compound semiconductors) How do you purify Ge? Why does it work? Show me on a phase diagram. What value determines how much impurity is divided between solid and liquid phases? (ko) What equation governs the impurity concentration? Say you plated a material and diffused. What governs this process? (dc/dt=d/dx(D dc/dx). Draw diffusion profiles. How can you determine activation energy and entropy terms? What is a first order transition? What is a second order transition? Can you draw it? What is a mutation? Can you explain what is going on? Basics of growth and nucleation. Is spinodal decomposition 1st or 2nd order?(1st) What about right at the top of the miscibility gap? (2nd). Why is a C curve C shaped? (not just balance between nucleation and growth). Who do you work for? (Morris) Where did you do your undergraduate work? (Yale) What is your research project? (Surface fatigue crack growth) Tell me what you know about diffusion. Write some equations on the board. Write an equation for D. How does it vary for intersitial and substitutional diffusion? Is there an entropy term? How can you determine Do and Q experimentally? What is the solution to this system? What is the equation? How do you fit you measured values to this curve? Morris (Fall 93) What do you work on? (CVD deposition of Si) Describe the phase transformation that occurs in that process. What gives rise to the energy barrier for nucleation? What thermodynamic potential applies? How do expitaxial films form? How do polygranular films form? How do you adjust conditions to form amorphous films? What do you need to do to make an amorphous metal? Who is your advisor? (DeJonghe) What material is your research on? (SiC) Can you draw a phase diagram for SiC? What kind of phase transformation is it? When you have a to transition, the grains can grow very fast, but not the grains, why? In ceramics processing, often additives are added to improve densification. What thermodynamic effect do additives have on your system? Defontaine(Spring 94) Are dislocations an equilibrium defects?Are vacancies?Derive classical nucleation theory. Why is this theory necessary?Are there barriers to nucleation in a second order transformation? Since you're a ceramist, what are the types of point defects in materials?Are these defects equilibrium defects?Why?Draw g vs c for vacancies.Draw g vs c for a lower T. What are the equilibrium concentration of defects at T1 and T2? For solid solution defects (B in A), say I have 3% B in at room temperature. Is that the equilibrium concentration of B in A?What is the equilibrium concentration of B in A?Can you vary [B] from 0 to 1 in A? What is the concentration of vacancies at Tm for materials?What is the order of magnitude of the concentration of vacancies at Tm?How many vacancies in Cu(cm3) at room temperature?divancies, will they form?nearTm?Give examples of vacancy clustering 26 Draw TTT diagram. How does it look as you approach Tm ?Explain the shape. What's the probability of having a nucleus of critical size. What does DG* term mean?How would you use a TTT?How does it apply to any other phase transformations?Why do you have the nucleation theory. Name some point defects. Are vacancies equilibrium defects?Give expression for equilibrium concentration of defects?Are dislocation equilibrium defects?Which concentration is higher at high temperatures single vancancy or divancies. Why?Write equilibrium equation for vacancies. Discuss types of vacancies. Write down vacancy reaction.(Asked a student working with Germanium)Write down the equation for normal freeze and melt zone. Discuss temperature dependence of diffusion.Plot. Give expression for D. What is the preexponential. In a real sample is D linear?What are the dimension of the diffusion coefficient? Morris (Fall 94) What is your research (fatigue of TiAl) What particular alloy are you using? What are the phases present? What are their structures? Can you draw the relevant portion of the phase diagram? How are these materials processed? What kind of structure does this produce? What happens if you heat treat at this temperature and the slowly cool? What kind of heat treatment could you use to refine grain size? Devine - Spring 95 Draw a one-component, P-T phase diagram. (goes through various transformations and asks about the slope of each line)Why is there undercooling but no overheating? (draws TTT diagram) Why does this curve have this shape? i.e. What are the controlling factors in the top and bottom of the curve? What is the equilibrium structure of an eutectic phase? Why does it have that structure? Morris - Fall 95 MBE vs. MOCVD: Explain each growth technique. Why does one produce "cleaner" material? How do dislocations form? List 3 ways. Devine - Fall 96 Draw a TTT curve. What governs the shape of this curve. How would the microstructure look if transforming at small undercooling compared to large undercooling for a two component system which has a eutectic phase diagram ( composition not the eutectic composition)? What is the microstructure when cooling through the eutectic point? Sometimes the eutectic composition microstructure is composed of fine beta phase needle-like particles. Why is this? Suppose we have (A) a Cu crucible full of water at -5C and (B) another one at +5C and begin to transform. For case A, the ice-water interface is jagged and for case B it is smooth. Why is this? Chrazn - Spring '99 Derive the nucleation theory for both homogeneous and heterogeneous nucleation Morris - Fall ‘99 What is your research? (magnetic media) If you take bcc iron, single crystal, and cool it through the Curie temperature how does the magnetization vary with temperature? When do you expect domains to form? Do you expect to see a few large domains or numerous small domains? Larger domains have less interface energy per unit volume..why do we observe small numerous domain structures? What happens in a paramagnetic-ferromagnetic phase transformation? There are relatively many paramagnetic elements compared to the number of ferromagnetic elements..Why? (usually more stable in antiferromagnetic alignment Morris - Spring 00 What’s your research? (PLD of Stainless Steel) Describe the PLD process. How is it possible to get high entropy phases upon thin filn deposition? For homogeneous nucleation, the critical activation engery is proportional to the cube of the surface energy over the square of the pressure or free energy per unit 27 volume. There is also a geometrical factor that takes the contact angle into consideration. If you have two phases, a low T and a high T phase, which would have the higher surface engery? How would that affect your activation energy? If your substrate is perfectly smooth and clean, what else other than surface energies can affect the deposited phase? How important is coherency for epitaxial type growth? Chrzan – Fall 00 What is diffusion? Can you give equations for Fick’s first and second laws? Derive them? Why is there a factor of 1/6in the first law? How will the equation change if the unit cell is changed? Does direction of planes being considered matter? Does the first law assume steady state? Is the assumption of linear variation of concentration with distance valid? I have a tank made of Pd, full of hydrogen. Can you give an expression for the time taken for steady state to be achieved, if it is? Can you give expression for diffusion length? Can you give a rough value for diffusivity of Hydrogen? ---------------------------XXXXXXXXXXXXXX--------------------------VI. BONDING AND CRYSTALLOGRAPHY G. Thomas (Fall 86) Draw an fcc unit cell. Can you put atoms anywhere else in this cell? Are there any restrictions on the number of atoms per unit cell? What are the translation vectors if the unit cell has 4 atoms? If it has one atom? (i. e. what is the primitive cell?) Draw an orthorhombic unit cell. How is it defined in terms of lengths and angles? Draw a face-centered orthorhombic unit cell. If you put an atom halfway along the c-axis, how would the unit cell change? How can you determine structure? What would happen if there were a lot of atoms in the unit cell? What determine when you see the lines? What kind of bonding does an element with an fcc structure have? Explain metallic bonding. Why are some metals fcc and some bcc? What kind of bonding is NaCl? Explain ionic bonding. L. de Jonghe (Spring 86) List and describe the types of bonds. Define a Bravais lattice. What is meant by electronegativity? What is the effect of adding Na+ to a silica glass? Where is the largest interstitial site in fcc? Draw this octahedron in the structure. (Selecting an arbitrary face of the octahedron) Write down the Miller indices of that plane. Plot the energy vs. position for one atom in the neighborhood of another. What is responsible for the repulsive force? How can you determine the elastic modulus from that diagram? Explain mathematically why this is true. G. Thomas (Fall 86) What is the simplest statement we can make about a structure? (ans. whether it is primitive or not) If it is not primitive is the unit cell larger or smaller? How does the diffraction pattern change? How can the diffraction pattern give us the structure factor? In a given row of the periodic table, why are the heavier atoms non-metallic? What crystal structure becomes more common? 28 In an element with configuration 1s2 2s2 2p1 how many atoms are available for bonding? How can more bonds be formed? What is the new configuration? L. de Jonghe (Spring 87) What are the main bond types? What is the force on a dislocation for an applied shear stress t? Draw the crystal structure of a silica glass. What happens when you add Na2O? Explain the equilibrium separation distance between atoms. Define the bulk modulus in one dimension. L. de Jonghe (Spring 87) Name the 14 Bravais lattices. Draw the rhombohedral and tetragonal lattices. Relate ionic, metallic and covalent bonding to electrical properties. A. Searcy (Spring 88) What are your research material and subject? Describe the bonding involved. Why does it bond in this way? Describe the different types of bonding. In GaAs what bond type occurs? What forms on the surface of cleaved Si crystal immediately after cleavage? Describe its structure. Why is it not crystalline? If you had two crystals, one a pure metal and one a silica-like material, and they both had the same enthalpy of sublimation, why would the metal crystallize more readily upon deposition from the vapor phase than the silica-like material? (i. e. what can you say about the directionality and coordination of the bonding?) L. de Jonghe (Spring 89) What is a lattice? How many different crystal systems/point lattices are there? Name them. What law is used in x-ray diffraction to determine the crystal structures? Write it. What other information can be obtained from x-ray diffraction in addition to the spot pattern? Describe the various bonding types in materials and relate them to the electrical conductivity, approximately. T. Devine (Fall 89) Name the 3 types of primary bonds. Give some characteristics of each and an example of each. Explain the potential well diagram for equilibrium separation of two atoms. Why is it so steep for r < r*? G. Thomas (Spring 91) Draw a phase diagram for two substances A and B that have complete solubility in each other. What does this tell you about their crystal structures? About their bond strengths with each other? Suppose A' and B' are neighbors on the periodic table. Would you expect them to behave like A and B? Draw a unit cell with two types of atoms in it (e. g. CsCl structure). Suppose A and B had electronic configurations 1s2 2s2 2p1 and 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p5. Would you expect a continuous solid-solution range as before? What sort of phase diagram would you expect? What would be the melting point of such a compound, compared with the pure-element melting points? How might you determine the structure of the reaction product? Suppose you weren't sure if it was tetragonal or orthorhombic - what you would you want to measure very closely to find out? Why would x-ray diffraction be better than electron diffraction? G. Thomas (?) 29 Define a lattice. Why do materials bond together? Define 4 types of bonding and give examples. How is the bond type apparent in the material's mechanical properties? Prof. Bragg (?) What are the coordinates of the largest interstitial sites in fcc? How many are there per unit cell? What about in bcc? In an ionic material with the anions and cations the same size, why can we not have 12-fold coordination? What is the c/a ration of hcp? Calculate the density of BaO, which has the NaCl structure. (Given the two atomic weights and the lattice parameter) Thomas (?) What is the alloy system of your research? (answered Al-Li) What is the crystal structure of the ordered d' phase? What is the difference between a primitive cell and a unit cell? How would the diffraction pattern for a DNA molecule look? What is the type of bonding in Li? In He? What are the physical origins of these bonds? D. de Fontaine (?) Draw the energy levels for the hydrogen atom. Write an expression for the energy levels. What calculation must be done to find this expression? Now bring two hydrogen atoms together. What happens? What is the equilibrium separation? What happens at zero separation? Why? Bring 2 Na atoms together. Will they bond? Assume they do; plot energy vs. separation and explain. Could you calculate this the same way as for the hydrogen atom? Explain the difference between metallic and covalent bonding. Consider tin. What sort of bonding does it have? How many nearest neighbors? What is the structure of graphite? What is the bonding type between the sheets? What sort of lattice does GaAs have? Give appropriate coordinates for the basis, if Ga is at 000. What kind of void is occupied by As? How many of these voids are there in an fcc lattice and how man of them are occupied? A. Searcy (?) What is your research material? What is its crystal structure? Describe the structure of silicon. What type of bonding occurs? What is a possible structure for SiC? Where might the C atoms go? What is the structure of graphite? Would you expect it to conduct electricity? D. de Fontaine (Fall 91)* What is a Bravais lattice? How many are there? How many crystal systems are there? Does this mean that each crystal system has two Bravais lattices associated with it? How many rotational symmetries exist? Why can't 5-fold symmetry exist in a periodic lattice? Draw an fcc unit cell. Is this a Bravais lattice? How many atoms does it have? Where are the lattice points? If the structure you've drawn were Cu3Au, where would the copper atoms be? Explain why two hydrogen atoms will bond when put in close proximity. What happens if two chlorine atoms are brought together? What is this arrangement called? (Thompson octet) How does the number of atoms needed to create a stable molecule change with the group number on the periodic table? Explain the mechanism for metallic bonding. Explain the splitting of energies for bonding states. What is you research project? Draw the silicon unit cell. How many atoms does it have? What is the lattice structure? What sort of bonding does silicon have? Why can't aluminum have covalent bonding? Describe the GaAs structure. Why do Si and GaAs only occupy half the tetrahedral sites? What is the nature of the covalent bond? How would you determine the structure of the material? If you are using TEM, what is a diffraction pattern, and how do you use it? Explain possible differences between 30 measured intensities of diffraction patterns obtained by TEM and x-ray diffraction. What is the structure factor, and how is it used to determine structure? Explain why the elements fit into a periodic table. Why is it periodic? Why is the energy of the 4s state lower than that of the 3d state? Devine (Spring 93)- (same questions for each person) Lennard-Jones potential-What things can you determine about the material from it? Can you write the equation of potential vs. distances? Why are there these dependencies? What is n for the repulsive force? Inert gases-Melting points increases w/ atomic #. Why? Bring a dipole up to a perfect metal-is there an attraction? (Yes-you induce an opposite dipole in the metal-image force) Placing NaCl in water, we model the Na+ and Cl- with a spherical potential distribution, why can we not do this for metal ions in water? (concide their outer shell electron configuration and the shape of the s,p,d orbitals). Some transition metal have low temperature fcc and high temperature bcc configurations. Why? (something to do with the entropy of the structures) Some just have the fcc phase. Why? DeJonghe (Fall 93) Name the types of bonding, briefly describe, and give examples. Give the function for the potential between two oppositely charges ions as a function of distance and graph it. Can you use this function to predict crystal structure? What crystal structures can result from ionic bonding? What determines the structure for a given compound? How is the Madelung constant calculated? (Describe procedure) Devine(Spring 94) What are the crystal structure of metals?In Iron and Titanium we see phase transformations at low tempertures, what causes them?What is their character?We have 2 grains A and B separated by a boundary. We are at a temperature where the boundary will move. What direction will it move? Why?If we are going to group the elements in the periodic table, how would you suggest we do it?Differentiate Kr and Ge on basis of atomic number, crystal structure, and Tm. Along row 3 why does the Tm change?Along Period VII the Tm increases as you go down the column Why?Period IV the Tm decreases as you go down the column Why?Why do some crystal structures go from fcc to bcc at high T.Group the elements in the periodic table according to the type of bonding. Which way is the meniscus in a tube with Hg?Why? DeJonghe-Fall 94 Draw the atomic arrangement on the (120) in BCC. Draw the potential vs. distance curve for two ions coming together in space. Describe each section of the curve, and write the equation describing it Show the different contributions on the graph, indicating over what range they contribute, and why they act the way they do Can you get the Elastic modulus from this curve? How? What about bulk modulus? What is Valence? How does it relate to number of electrons and bonding in solids? When atoms come together, what happens to their atomic orbitals? Draw the diagram describing this for a metal, semiconductor (intrinsic), draw the Ef for each. Why doesn't the electron just spiral in to the nucleus? In ionic bonding, where does the change associated with each ion come from? Do ions in real materials have integral charge? Ferrari - Spring 95 In Column IV of the periodic table, the sublimation temperature decreases as you go down. Why is this?Why can there not be five-fold symmetry (derive math)? Draw the 31 pole plot for 6mm group. is there a horizontal mirror plane? What is the form? is it open or closed? Sands - Fall 95 Which structures are close packed? What type of bonding? What is the symmetry of the [100] direction in zinc-blende? 3-fold? Describe a method for obtaining the Miller indices of a plane. What is a primitive cell structure? What is a transition metal? Why are the usually BCC? Explain cohesion in metals. De Jonge - Fall 96 Describe the different bond types and why they occur. Why doesn't an orbiting electron simply fall into the nucleus. Draw the energy vs. distance curve for two ions. Explain the forces involved. How can you derive the bulk modulus from this curve? What is electronegativity? What can it be related to? Why is the NaCl bonding ionic in the solid state but not in the gaseous state? (Madelung energy) Devine - Spring 98 Describe the different types of bonding. Name some crystal structures with ionic bonds. What is the coordination number? Describe the zinc blende structure. what is zinc blende of only 1 component called? What is the coordination number in diamond? What kind of bonds are there in diamond structure? Name some materials with this structure. In vacuum if we cleave Si surface, what happens at the surface? How is it different from the bulk? What if you heat it up? If you heat it to Tm will the surface melt faster? What about cleaved Cu surface in vacuum? How does the surface differ from the bulk? Draw potential energy vs. r cuve. Why do noble gases form FCC rather than HCP if HCP < FCC by ~ 1%? You have 2 blocks of ice at 15 C, it is observed that they bond together, why? At -30 C the blocks of ice don't bond together, why? Devine - Spring '99 List the type of Bonding. Plot the potential curve vs.q r for two He, what is the attractive and repulsive forse? Why attractive force is r^(-6)? What about two H atoms? What is the difference? Why there is no He2 molecular? Why H2O and HF has irregular melting temperature (Hydrogen Bonding)? Why H2O has higher specific heat than any other liqiud. Why Mg is ductile and MgO is brittle? Why MgO is harder and his melting temperature is higher than NaCl? DeJonghe - Fall ‘99 Describe types of bonding. How could you tell the difference between an ionic \crystal and and covalent crystal? What is electronegativity? What determines whether Mg+2 sits in a tetrahedral or octahedral site in a certain ionic crystal? Why does NaCl bond ionically in the solid phase while bonding covalently in the gaseous state? Explain how metallic bonding can lead to high thermal conductivity, how is this different from thermal conductivity in insulators Devine - Spring 00 Define electronegativity. What type of bonding is most likely to occur in the molecule HF has a difference in electronegativity of about 1 or 1.5? (Given that F has the highest electronegativity of 4.) Gives you a plot of boiling temperatures for various molecules containing hydrogen. The trend is as you go down a column of the periodic table, the boiling point increases. Why? On the same plot you can see that water and HF have the highest boiling points of all. Why? Why does water have a higher boiling point than HF? 32 Draw a close packed plane. What are tetrahedral and octahedral voids? For closepacked crystals, the stacking goes as either ABAB or ABCABC. Is this a requirement for all types of cyrstals? What are the major types of bonding? What is the Madelung constant? Is it greater or less than 1? DeJonghe – Fall ‘00 Describe types of bonding. Explain the properties due to each bonding.In ionic bonding, where does the change associated with each ion come from? Do ions in real materials have integral charge? What kind of bonding do you see in SiC? Why? What factors effect crystal structure. What is electronegativity? Why does NaCl bond ionically in the solid phase while bonding covalently in the gaseous state? Explain how to get Madelung Energy. What kind of bonding do you observe in noble elements in solid form? 33