Clinical Trial
advertisement

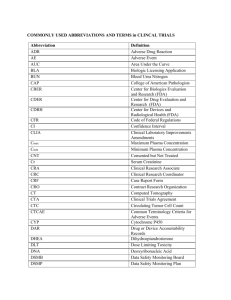
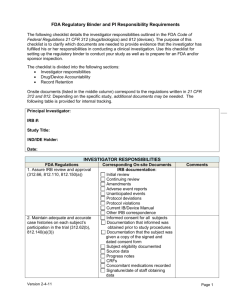
GLOSSARY OF CLINICAL RESEARCH TERMS 1572 FDA form which identifies the Principal Investigator, CoInvestigator, Sub-Investigators, and staff of a study. This can be computer-generated document. The sponsor requires a copy singed by the PI. Accepted CRF Case Report Form, which is accepted as complete by the sponsor (study monitor). A CRF may have been submitted and had requests for corrections or additional material before it was accepted. Adverse Event (AE) An undesirable and unintended, although not necessarily unexpected, result of therapy or other intervention. Case Report Form (CRF) Documents used to record protocol data. This is an extraction from the source documents (medical record and additional documents, i.e. subject diaries, coordinator notes) that the coordinator prepares, and the PI confirms. Case Report Forms are carefully monitored by the sponsor in regard to constancy with the source documents. ALL DATA RECORDED ON A CRF MUST BE VERIFIABLE ON SOURCE DOCUMENTATION. Confidential Disclosure Agreement (CDA) Document which we sign prior to receiving confidential information, such as a research protocol, promising not to disclose confidential and proprietary information about the trial or sponsor. Clinical Trial A carefully designed investigation of the effects of drug, medical treatment, or device on a group of patients. Clinical Investigator A medical researcher in charge of carrying out a clinical trial's protocol. Researchers are usually doctors, nurses, pharmacists or other health care professionals. Coordinator The person who brings together all aspects of the study. Usually this person is in charge of all documentation, and acts as a liaison between the sponsor and the Principal Investigator in the day-to-day activities of the clinical trial. Device, Class I Least regulated category of devices. The regulations address device registration, record keeping, labeling, adverse event reporting, and premarket notification. These guidelines provide reasonable assurances for device safety and efficacy Device, Class II Additional controls are necessary to assure safety and effectiveness. Until special controls are enacted, general control measures of Class I devices apply. Device, Class III Most regulated category of devices. This class is represented to be life sustaining or supporting, implantable or carry an unreasonable risk of illness or injury. Food and Drug Administration A government agency that enforces laws on the manufacture, testing, and use of drugs and medical devices. The FDA must approve all drugs and medical devices before the general public can use them. Form FDA 1571 First page of an Investigation New Drug Application (IND) that provides the basic information about the new drug and its sponsor. Form FDA 1572 Document(s) filed with an IND that provides FDA with a list of investigators and subinvestigators, their credentials, site(s) where the study is being conducted, laboratories used for tests, and assurance of RB review. Form FDA 482 Document that provides a "Notice of Inspection" to the investigator prior to a FDA audit. This form serves to identify the FDA inspector conducting the audit, along with the authority to review study related documents. Form FDA 483 Document that may be presented to the investigator by the FDA inspector at the conclusion of the FDA audit. This form lists the objectionable practices found during the FDA inspection of the clinical site. Good Clinical Practice (GCP) Describes the actions and responsibilities of the sponsor, investigator, and monitors to assure quality data from scientifically sound and safe clinical investigations. Investigation New Drug Application (IND) Application mandated by the Kefauver-Harris Amendment requiring that sponsors submit to FDA a detailed protocol, preclinical data, and investigator credentials prior to initiating phase I clinical trials. Informed Consent A discussion of all procedures, benefits, risks, and expectations of a clinical trial between clinical investigators and potential patients. The FDA requires all patients to sign an informed consent form before participating in a trial. Institutional Review Board (IRB) A board consisting of health care professionals from the institution where the clinical trial takes place, as well as members of the local community. The board scrutinizes all trial activities including recruitment, advertising, and potential risks. The IRB also makes sure that FDA regulations are being followed in a particular trial. Institutional Review Board submission (IRB) A form request, by the PI to the Institution Review Board, to review clinical protocol and approve its performance at the site. IRB submissions are usually submitted on standardized forms. These forms may be computerized. Investigational Treatment The drug or medical device that is tested during a clinical trial. New Drug Application (NDA) Marketing application mandated by the Food, Drug and Cosmetic Act that requires sponsors submit to FDA all clinical and laboratory data supporting a request for drug approval prior to marketing. Phases Drugs and medical devices must pass three segments or phases of testing before they can be eligible for FDA approval. Phase I/II Study Earliest phase of drug development in which a limited number of human subjects are exposed to the test article. The objective of this phase or a clinical trial is to establish a drug's safety and toxicity profile. Phase II studies expand the numbers of patients exposed to the drug, and begin to collect data suggesting efficacy. Phase III Study Phase of study designed to demonstrate drug efficacy in patient populations with specific disease indications and to collect additional safety data in a larger cohort of patients. These studies are usually multicentered, involving hundreds to thousands of patients. Phase IV Study Post-marketing studies may be requested by the FDA to provide additional data, or are intended to expand labeling to other populations or other indications, or simply to market the drug in a variety of clinical settings. Principle Investigator A medical professional who is overseeing the treatment of the patients in the clinical trial. Protocol A plan that sets guidelines for a trial and usually involves several different trial locations. A protocol is usually designed by the sponsor of a clinical trial. Record storage A secure locked cabinet in a locked room where records for the clinical study are stored. Long term record storage is also required for clinical trial REGULATORY DOCUMENTS Protocol, protocol amendments, investigator's confidentiality agreement and contract with sponsor, signed FDA 1572(s), CV (s) for all investigator's and sub-investigators, IRB Documents (letter of approval) informed consent (IRB approval required), lab certification and normal ranges, Serious Adverse Experience Reports ("Safety Reports"), sponsor correspondence, monitoring record, signature sheet, shipping forms for drug, drug log, dispensing logs, randomization sheets, Investigational Material Shipping (IMS) Forms, drug return form. Serious Adverse Event (SAE) Any untoward medical occurrence that at any dose: results in death; is life threatening; requires inpatient hospitalization or prolongation of existing hospitalization; results in persistent or significant disability or incapacity or is a congenital anomaly/birth defect. Screening chart A list of patients who have been screened but were not entered as subjects into a clinical study. Screening A process whereby potential subjects are reviewed to see if they meet the inclusion criteria of a study. Site The place of business where a clinical study is being conducted. A site may be a stand-alone place of business or part of a larger institution. The site/institution is usually the employer of the PI. Source documents Documents from which data is extracted to the CRF. Source documents include materials duplicated from the charts, subject diaries, laboratory reports, consent forms, coordinator's notes, etc. In large institutions where there are regulations that limit materials entered into medical charts, a separate file that duplicates and references all pertinent information is essential. Sponsor The pharmaceutical company, research institution, or other health organization that funds a clinical trial and designs its protocol. The organization that initiates (and ultimately pays for) the clinical trial. Standard Treatment A FDA-approved treatment currently in wide use. In trials involving new treatments, there may be no pre-existing treatment at all. In these cases, the lack of any treatment is considered the standard treatment. Generally, the goal of a clinical trial is to introduce an investigational treatment that is safer and more effective than the standard treatment. Unscheduled events Medical procedures/laboratories that are not budgeted items but occur because of the subject's participation in the clinical trial. These expenses are charged to the clinical trial account. The contract should describe the financial responsibility for these events. The consent form should reiterate the description that is in the contract.