HW Packet for Chapter 2: Motion in One Dimension (50 pts) Name
advertisement

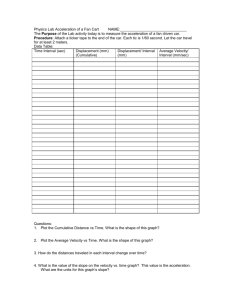
HW Packet for Chapter 2: Motion in One Dimension (50 pts) Name ________________________ Answer the following questions using your notes and Chapter 2 of your book. Use the correct units and show your work. Definitions: 1) Define frame of reference. 2) What is the difference between distance and displacement? 3) Explain how after your entire day you can have a displacement of zero. 4) What is average velocity? 5) What is the difference between average velocity and speed? 6) Define acceleration. 7) What three ways can velocity change? 8) Fill in the table below. Units for: Distance Displacement Time Speed Average velocity Average acceleration Example of units Direction (yes or no) Distance versus Time Graphs The graph below shows the motion of an object starting at 0 meters at time = 0 seconds. Distance versus Time 10 8 6 d (m) 4 2 0 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 time (s) 9) What is the average velocity of the object during the time interval from 0 to 2 seconds? 10) What is the average velocity at 1 second? 11) During which interval(s) is the velocity zero? How do you know? 12) At t = 8 s, what is the displacement of the object? 13) At t = 8 s, what is the distance traveled by the object? 14) During which time interval is the average velocity away from the FOR the greatest? How do you know? 15) During which time interval is the average velocity towards the FOR the smallest? How do you know? 16) If a car starts from rest and travels for 130 s with an average velocity of 1.3 m/s south, what is the displacement of the car? 17) If a bug moves at an average velocity of 90 cm/sec north, how long will it take to travel 3200 cm? 18) If you run at an average velocity of 3.0 m/s east for 600 m and then you slow down and run 2.0 m/s east for 300 m, what is the average velocity for your trip? (Find ∆t for each part of the trip first) Relative Motion Problems 19) You are in a car moving a constant velocity of 40 km/hr going east. Your best friend is in a car moving on the same straight road at 72 km/hr going west. Draw a picture of the cars. What is the relative velocity of your car to your friend’s car? If you start 60 km apart, how long will it take until you pass each other (or crash head on)? How far will your car have traveled when the cars meet? 20) A car is traveling east at a constant velocity of 50 km/hr. Another car on the same straight, level road is traveling east at a constant velocity of 65 km/hr. The slower car is 24 km in front of the faster car. Draw a picture of the cars. What is the relative velocity of the faster car to the slow car? How long will it take the faster car to catch up to the slower car? What distance will each car have traveled when the slower car catches the faster car? Acceleration Problems 21) A racing car moving at 10 m/s north increases its velocity to 16 m/s north in a time interval of 3 s. What is its average acceleration (including direction) during this time interval? 22) Your average accelerate is 2.35 m/s2 for a time of 22 seconds. If your starting velocity is 12 m/s east, what is your final velocity? 23) You travel in a car with a constant velocity of 50 m/s north. Your average deceleration is -4.5 m/s2. How much time will it take you to come to rest? 24) You are traveling with some constant initial velocity north. You accelerate to a final velocity of 42 m/s in a time of 3.8 seconds. If your average acceleration is 2.1 m/s2, what was your initial velocity? 25) What is your average deceleration if it takes you 3 seconds to change your velocity from 60 m/s south to 48 m/s south? 26) What was your initial velocity if you decelerate at a constant rate of 16.5 m/s2 east for 5.6 seconds to a stop sign? Velocity versus Time Graphs The graph below shows the motion of an object starting from rest at time = 0. Velocity vs. Time 6 5 4 3 2 1 v (m/s) 0 -1 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 -2 -3 -4 -5 -6 time (s) 27) What is the average acceleration from 0 to 2 seconds? 28) What is the speed at time equals 1 second? 29) What is the average acceleration from 3 to 4 seconds? 30) During which time interval(s) is the object at rest? How do you know? 31) During which time interval is the object moving with the greatest acceleration away from the FOR? Explain. 32) During which time interval is the object moving with the greatest acceleration towards the FOR? Explain. 33) What distance is traveled by the object from time equals 0 seconds to time equals 4 seconds? 34) During which time interval(s) is the object decelerating away from the FOR? Explain how you know this. 35) During which time interval(s) is the object decelerating towards the FOR? Explain how you know this. 36) The following graph shows the distance time graph of Fred’s movements up and down the aisle at a store. He starts at one end of the aisle. 6 5 4 d (m) 3 2 1 0 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 time (s) Write a story describing Fred’s movements at the store that would correspond to the motion represented by the graph. Use adjective like at rest, constant velocity, away from the FOR and towards the FOR. I am looking for 6 statements. 37) Transform the graph to a velocity versus time graph. You must find the correct velocities. 3 2 1 v (m /s) 0 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 -1 -2 -3 time (s) Show your work.