Section Summary 11.1
advertisement

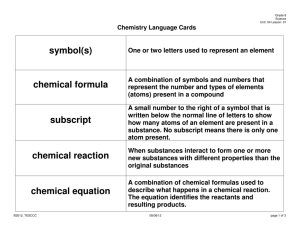
SECTION SUMMARY 11.1 Describing Chemical Reactions Summary: A chemical reaction can be concisely represented by a chemical equation. The substances that undergo a chemical change are the reactants. The new substances formed in a chemical reaction are the products. In accordance with the law of conservation of mass, a chemical equation must be balanced. When balancing an equation, you place coefficients in fro t of reactants and products so that the same number of atoms of each element are on each side of the equation. An equation must never be balanced by changing the subscripts in the chemical formula of a substance. Special symbols are used to show the physical state of a substance in a reaction. The symbol for a liquid is (l); for a solid, (s); and for a gas (g). A substance dissolved in water is designated (aq). If a catalyst is used to increase the rate of a chemical reaction, its formula is written above the arrow. To write a word equation, write the names of the reactants to the left of the arrow separated by plus signs; write the names of the products to the right of the arrow, also separated by plus signs. To write a skeleton equation, write the formulas for the rattans to the left of the yields sign and the formulas of the products to the right. After writing the skeleton equation, use coefficients to balance the equation so that it obeys the law of conservation of mass. 11.1 Describing Chemical Reactions Vocabulary Terms: Chemical Equation: a representation of a chemical reaction; the formulas of the reactants (on the left) are connected by an arrow with the formulas of the products (on the right.) Skeleton equation: a chemical equation that does not indicate the relative amounts of the reactants and products Catalyst: substance that speeds up the reaction but is not used up in the reaction Coefficient small whole numbers that are placed in front of the formulas in an equation in order to balance it Balanced equation: a chemical equation in which each side of the equation has the same number of atoms of each element and mass is conserved Reactants: substances that undergo chemical change Products: new substance that is formed in a chemical reaction The End of the Summary