Joint Structure and
advertisement

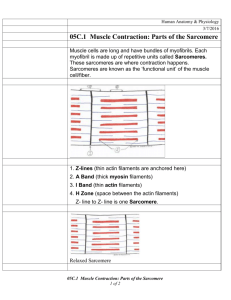
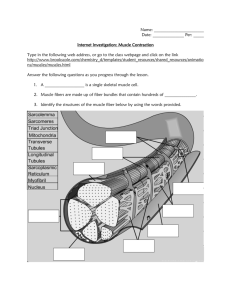
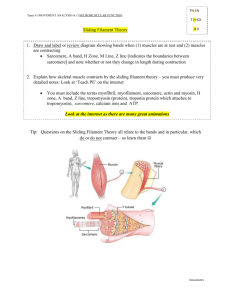
Joint Structure and Muscle Structure and Contraction Exam Questions Topic 7.1 45 Marks 1. Read through the following account of a human joint, then write on the dotted lines the most appropriate word or words to complete the account. The bones in a joint such as the elbow are protected from damage by friction in two ways. The ends of each bone are covered by ............................................ and the space between them is filled with ................................................which acts as a lubricant. Muscles are attached to the bones by.............................................. made of ......................................................tissue. Muscles can only move a bone when they ............................................ and so always work in ..................................................pairs. (Total 6 marks) 2. Distinguish between each of the following. (a) Tendons and ligaments ……………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………… (2) (Total 2 marks) Hull's School 1 3. The diagram show a section through a human synovial joint. (a) Describe one function for each of the structures labelled A and B. A ........................................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................................... B. .......................................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................................... (2) (Total 2 marks) 4. The diagram below shows the arrangement of tissues in a synovial joint. (a) Name the parts labelled A and B. A ......................................................................................................................................... B ......................................................................................................................................... (1) Hull's School 2 (b) Describe how the structure of a synovial joint allows smooth movement. …………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………… (1) (c) In athletes, articular cartilage thickens as a result of training. Explain the benefit of thicker cartilage in a knee joint. ……………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………… (2) (Total 4 marks) Hull's School 3 5. The diagrams below, (labelled 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5), show five possible states of a sarcomere from striated muscle. The relative positions of some actin and myosin filaments are shown. Z disk Myosin Z disk Actin 1 2 3 4 5 The graph below shows the relationship between sarcomere length and the amount of tension generated during the contraction. The letters A, B, C, D and E on the graph correspond to the different positions of the actin and myosin filaments, shown on the diagrams above, during the contraction. A C B D E 100 80 Tension 60 as % of maximum 40 20 0 1.0 (a) (i) 1.5 2.0 2.5 3.0 Sarcomere length / m 3.5 4.0 State the letter of the stage on the graph which corresponds to the greatest length of the sarcomere shown in the diagrams. (1) (ii) State the length of the sarcomere when the maximum tension is generated during contraction (1) Hull's School 4 (iii) Which diagram of the sarcomere shows the position of the actin and myosin filaments when the maximum tension is generated? (1) (b) (i) Describe two ways in which the positions of structures in the sarcomere you have identified in (a) (ii) differ from those in the sarcomere at its greatest length 1 ….…………………………………………………………………………. 2 ….…………………………………………………………………………. (2) (ii) Explain how a sarcomere in a contracting muscle would change between the state shown in diagram 1 and that in diagram 3 ……………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………… (4) (Total 9 marks) 6. Read through the following passage, which refers to the structure and function of striated muscle, then write on the dotted lines the most appropriate word or words to complete the account. A striated muscle fibre contains many strands, called …………………………………. , which run the length of each fibre. Within these strands there are thick filaments made of the protein ……………………………………. , and thin filaments which contain the protein …………………………………… When a muscle contracts, the two kinds of filament slide past each other. Energy to enable the sliding filaments to move is provided by molecules of …………………………….. ,attached to the head of each thick filament. (Total 4 marks) Hull's School 5 7. The diagram below shows part of a myofibril in a relaxed muscle. A (a) B Name the parts labelled A and B. A ............................................................................................................................ B ............................................................................................................................ (2) (b) In the space below, make a drawing to show this part of the myofibril when it is fully contracted. (3) (c) Describe the role of calcium ions in muscle contraction. ............................................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................................... (2) (Total 7 marks) Hull's School 6 8. The electron micrograph below shows a longitudinal section of a muscle fibre. Dr Don Fawcett/Science Photo Library (a) (i) State the number of myofibrils shown in the electron micrograph. ............................................................................................................................... (1) (ii) Name part A. ............................................................................................................................... (1) (b) Calculate the magnification if the section labelled B is actually 1.6 m wide. Show your working. Answer ...................................... (2) (Total 4 marks) Hull's School 7 9. The diagrams below show one sarcomere in its fully relaxed state and when it is partially contracted. H zone H zone actin myosin Fully relaxed sarcomere (a) Partially contracted sarcomere Calculate the percentage change in width of the H zone when the sarcomere is partially contracted. Show your working. Answer ................................................ % (3) (b) During the contraction of this sarcomere, the myosin filaments pull the actin filaments towards the centre of the sarcomere. Explain how this is brought about. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (4) (Total 7 marks) Hull's School 8