Class Summary Katia Schenhals H Block 10-01
advertisement

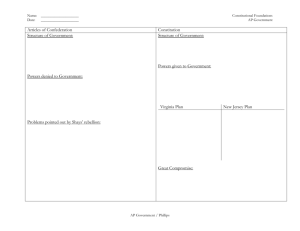
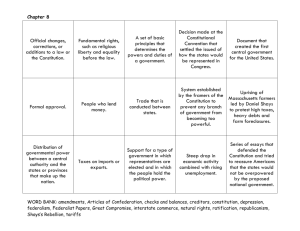
Class Summary Katia Schenhals H Block 10-01-09 Beginning with 5 minutes of connection, we then moved into the discussion of sources and why they’re important in our lives. Although they may mostly serve us in providing evidence for our opinions (theses) for now, they will prove useful in the future as our careers develop; researching material for ourselves, seeing if it is reliable and letting us become more aware of how there are sources all around us. This immediately led us into Zinn’s and Roche’s discussion about whether the “founding fathers were democratic reformers” and the evidence to prove their point. As Roche stated that the founding fathers were not only reformers but also democratic as the people had agreed with them, Zinn declared that the “reformers” were only an elite group who created a central government and were interested in providing security for themselves and those who belonged to their social status. Some sources that proved their theories were first shown in Roche’s argument as he primarily used James Madison’s convention notes (who had written the Constitution) and the Constitution itself, which were a series of compromises for the states and the nation. He used these documents to state his ideology that even though it wasn’t a piece of cake, all the states compromised on having equal rights among themselves (even though it excluded slaves and females). Zinn on the other hand, received his sources from court documents (pg 129), Shays’ Rebellion (Maj. Probs. Pgs 133-134), the Constitution itself, and the Federalist Papers (pg 131)-written by Alexander Hamilton, James Madison and John Jay (they who used this as propaganda for the persuasion of the public). Zinn declared his theory by indicating how the elite had controlled the constitution, how Shays’ Rebellion was an excuse to create a central government, and how there was the exclusion of certain classes even though the constitution was supposed to be directed to “the people”. This thus shows how evidence and sources developed the assertion of each person and the contraposition against each other. After reviewing the dates of presidency starting with George Washington, up to Thomas Jefferson, there was a separation between the federalists and the Jeffersonian/ Republicans as the presidents began to change their opinions about an idealized government. Beginning with GW (George Washington), JA (John Adams) and AH (Alexander Hamilton) as federalists, central banks and government were created, national debt was introduced, the unified monetary system developed, it became industrialized, and the elite controlled the majority of the people’s actions. In contrary to them, Thomas Jefferson focused on the agrarian ideal, small central gout, states rights, self-sufficiency among individuals, and the Declaration of Independence. In between the years of 1796 and 1800, John Adams became the president of the U.S. (a federalist) and the diplomatic relations with the French broke as the U.S. allied with the British after the French had helped the U.S. but were left behind. As we discussed some documents of “The Alien and Sedition Acts” as well as “Nullification”, Adams was critiqued for his specific rules applied to the people living in the U.S. at that time. These acts represented the bills passed by the federalists from Congress in 1798, trying to protect their citizens from the French, as they were afraid their enemies might attack them. These acts stated that in time of war, any suspicious aliens would be deported out of the country and in the Sedition Act of 1798, any malicious publication against the president would result in punishment (no freedom of speech). During the Kentucky and Virginia Resolutions of 1798, Jefferson and his people argued that the federal laws were unconstitutional, as they had no reason to overpower state laws and therefore began to revolt against the federalists. As we finished wrapping up class with this subject, next class we’ll be discussing a little bit more in depth these acts and how they ended. Review: Time: 1777-1787 Articles of Confederation Time: 1787 Shays’ Rebellion Time: 1787 Const. Convention Presidents from this time: Time: 1788-1796- 2 terms in gov. Time: 1796-1800- 1 term in gov. Time: 1800-1808- 2 terms in gov. The first constitution established Independent states created States had power over all gov. functions not affecting the central government. Congress of Confederation was created An uprising in Massachusetts Farmer Daniel Shays leads 700 poor, angry farmers on a revolution to lower taxes Source: Taking Sides Pg 129 and Maj. Probs. Pgs 133-134 Founding Fathers were introduced in Constitution. Republicanism Independence of states they had own governor elected by state legislature Legislature was elected by popular vote George Washington John Adams Thomas Jefferson