Biome share sheet rbh2
advertisement

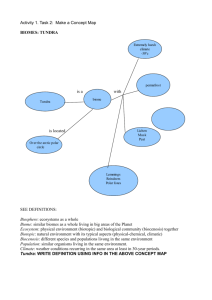
Name: Ryan Biome Basics Biome 3 plant examples and adaptations 3 animal examples and adaptations Climate Human Influences Location Tropical Rainforest Bengal Bamboo: This plant learned how to grow taller quickly, so it can get very much rain and sunlight. Coconut tree: They grow near some source of water, so the roots can find more moisture. Kapok Tree: This tree has learned to grow taller quickly. Bengal Tiger: This animal has camouflage to help it catch its prey in the tall grass. Toucan: This animal has a large beak to pick up prey. Macaw: This bird has gripping toes to hold on to tree’s bark. The weather in tropical rainforests is warm and damp. The average temperature of the year is about 80.5F. The temperature barely goes above 93F or below 68F. These rainforests are in the Tropical Wet Climate group. Farmers: If farmers run out of room to plant, they cut down trees so they can plant more. Construction: People started building a highway in the rainforest. Luckily, it was never finished. Tourism: Once people see what is happening to the rainforests, they want to help so they will donate money. Mining and Drilling: They are many valuable things under tropical rainforests, and miners want to find them. Almost are of these rainforests are near the equator. These rainforests are in Central America, South America, Southeast Asia, The middle of Africa, and a small part of Australia. Name: Ryan Biome Basics Temperate Deciduous Forest Tundra Ginkgo leaf tree: This plant learned how to tolerate heat and poor soil. Lady Fern: This plant can survive in very cold climates. Northern Arrowwood shrub: This plant can grow well in almost any soil. White-Tailed Deer: This animal has camouflage to hide from predators. The American Black Bear: This bear hibernates so it does not have to find food in the winter. American Bald Eagle: The eyesight of these animals is 4 to 8 times better and further than humans. 3 Plant Examples 3 Animal Examples Bearberry: This plant can survive in cold weather. Diamond-Leaf Willow: This plant reproduces fast Arctic Moss: This plant can live in very cold water temperatures. Arctic Fox: This animal grows thick fur in the winter and loses it in the summer. Caribou: It’s large hooves support the animal in snow (for the winter) and in marshy tundra (In the summer). Grizzly Bear: This animal hibernates in the winter, living off of fat stored in its The average annual temperature ranges from 80F to 15F. Precipitation goes from 50 cm. a year to 200 cm. a year. The precipitation comes from late fall, winter, spring, and early summer. This means that it is dry in late summer and early fall. Logging: People have done this because they can make paper with them. Urbanization: People have made houses in these forests because many people want to work in might want to work in the places where temperate deciduous forests are. Farming: If farmers don’t have room anywhere else to plant crops, they will cut down trees to clear an area. This type of forest is found in the east side of the USA, very little in south America; found at the very south tip of this continent. It is also found in a big part of Europe, in Japan, on the east side of Asia, and there is a smidge in Australia. Michigan is completely covered with temperate deciduous forests. Climate Human Influences Location The average winter temperature of the tundra is about -30F. In the summer the average temperature is about 45F. The tundra gets 6-10 inches of rain every year. This is less water than in major deserts! Climate Change: This is melting some of the tundra’s natural habitat. Overfishing and Overhunting: This makes there be very little animals. Development: Building roads and oil pipelines hurts the natural habitat. The tundra biome is located at the top of the world. It is near the north pole and it is called the arctic tundra. There is also the alpine tundra which is located on the top of tall mountains. Name: Ryan Biome Basics body. It occasionally goes out of hibernation for a little while. Desert Barrel Cactus Chain-fruit Cholla Jumping Cholla Thorny Devil Cactus Wren Jevelina All of these plants adapt by having roots that can take soil from the top of the ground. They have these because water evaporates quickly in the desert; and the plants have to get water before it evaporates. All of these animals adapted because they can get all of their water from plants. In the winter, cold desert temperatures are from -2C-4C. The average summer temperature is 2126C. The average temperature of the hot desert is 43.549C. Minimum temperature sometimes drop to 18C. The desert receives about 15 cm. of rainfall each year. Military Exercises: The military of different countries will have practices on the desert because it is barren from humans. This can cause damage to the desert. Off-Roading: People do this for fun because they think it is cool and they want to show it off to friends. Doing this causes people running over plants and animals. Underground Pipes: Pipes carrying oil and other materials can cause the earth’s crust to become unstable. Some hot deserts are found in Australia, the USA, Mexico, Iran and Argentina. Some cold deserts are found in Antarctica, Argentina, China, Peru, and Chile. Some deserts that can be hot and cold (not at the same time) are in Afghanistan, Pakistan, Mongolia, China, and Iran. Name: Ryan Biome Basics This may lead to either earthquakes or sinkholes. Grasslands Savanna 3 Plant Examples 3 Animal Examples Whistling Thorn: It has tiny leaflets that can either absorb sunlight, or avoid it and reduce transpiration (plant evaporation). Baobab: In the wet months this tree stores water in its thick; fire resistant trunk for the nine dry months that are up ahead. Elephant Grass: This grass reproduces Ostrich: This bird can run as fast as 45 mph with its long legs. Cheetah: A cheetah’s top speed is 70 mph. It can keep up this speed for about 220330 yards. African Elephant: This animal has a long flexible trunk which it uses to grab different things. Climate Human Influences Location The savannah has a wet and dry climate. In the winter, this biome has a dry season. In the summer, it is wet. This biome gets all of its rain in the summer. During the dry months the plants usually die and some rivers and streams can go dry. This biome has an average of 20-50 inches of rain each year. Timber harvesting and seed harvesting: People have been doing this for domestic uses. They are doing it for mammals such as cows and goats. It has created a drop in tree growth. Eco Tourism: This allows the animals and the people to interact, but does not hurt either one. This biome is mostly in Africa; with about half of Africa covered (not in reality. In reality, they are spread out). They are in the southeastern tip of India, north central of Australia, the north part of South America (Venezuela and Columbia), and in the east part of Brazil. Name: Ryan Biome Basics through rhizomes. Rhizomes are root-like underground stems that make roots below and shoot up grass to the surface. Grasslands Prairies Blue Grama Grass Prairie Cord Grass Scribner’s Panic Grass These grasses have adapted to droughts, fire, and grazing animals. Temperatures: Summer: 80F or above Winter: 65-70F Spring: 70-75F Fall: 75F Prairie Dog: This animal burrows underground most of the time because it is close to the bottom of the food chain Buffalo: This animal has a special stomach so it can digest grass. Pronghorn: This animal can run up to 60 mph It is cold in the winter and warm in the summer. The average precipitation is 10-30 inches a year. The average temperature ranges from -40-70F. About every thirty years, there is a drought that lasts for years. Invasive Species: Humans have brought invasive plant species into this biome and they are doing bad things. Urbanization: People have built homes and have taken over the animal’s homes. Lakes: People have formed lakes; this has changed the grasslands greatly. This biome fills up about half of Africa, the central part of USA going from north to south, the central part of Asia going from east to west, and in the north-eastern part of south America. Name: Ryan Biome Basics Taiga 3 Plant Examples 3 Animal Examples Balsam Fir: Balsam fir trees’ roots grab water from the surface of the ground when it is really cold. Black Spruce: The black spruce tree reproduces very quickly after a fire burns. Eastern Red Cedar: The eastern red cedar can survive in -45 F and can go with less precipitation than in southern countries. Moose: Its feet are used as natural snowshoes in the winter. Wolverine: This animal can take on animals bigger than its size. Lynx: This animal is a skilled hunter with very good hearing. Climate Human Influences Location The average temperature in the winter is -50F. In the summer, the average is 50F. The taiga is very cold. The average precipitation is 12-33 inches. People Caused Forest Fires: Sometimes people set off forest fires either accidentally, or on purpose. Logging: People want to log to make paper and that is why trees are being cut down. Pollution: This is a problem all over the world. Pollution is bad wherever it is. Mining: People want to mine in these forests because they have a lot of oil. Overhunting: This is a big problem because it is killing many animals. The Taiga is located in the northern part of Asia, Europe and North America.