Marketing Plan EVALUATION
advertisement

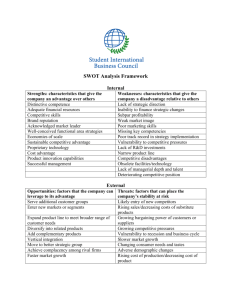
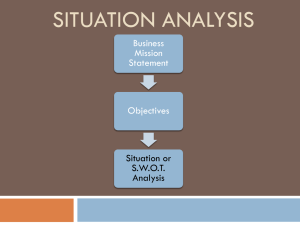
MARKETING PLAN EVALUATION COMPANY NAME _____________________________________ TEAM MEMBERS NAMES _________________ _________________ _________________ _________________ EVALUATORS NAME __________________________________ MET I. EXECUTIVE SUMMARY: A high level summary of the marketing plan. II. THE CHALLENGE - Brief description of the product to be marketed and associated goals, such as sales figures and strategic goals. III. SITUATION ANALYSIS A. Company Analysis: Goals, Focus, Culture, Strengths, Weaknesses, Market share B. Customer Analysis: Number, Type, Value drivers, Decision process, Concentration of customer base for particular products. C. Competitor Analysis: Market position, Strengths, Weaknesses, Market shares D. Collaborators: Subsidiaries, Joint ventures, Distributors, etc. E. Climate: Political and legal environment a. PEST analysis (macro-environmental) i. Political Factors – government regulations and legal issues and define both formal and informal rules under which the firm must operate. 1. Tax Policy 2. Employment Laws 3. Environmental regulations 4. Trade restrictions and tariffs 5. Political stability ii. Economic Factors – affect the purchasing power of potential customers and the firm’s cost of capital. Factors of the macro economy include: 1. Economic Growth CRITERIA EVALUATION 2. Interest Rates 3. Exchange Rates 4. Inflation Rates iii. Social Factors – the demographic and cultural aspects of the external macro environment. These factors affect customer needs and the size of potential markets. 1. Health Consciousness 2. Population Growth Rate 3. Age Distribution 4. Career Attitudes 5. Emphasis on Safety iv. Technological Factors-can lower barriers to entry, reduce minimum efficient production levels, and influence outsourcing decisions. 1. R&D Activity 2. Automation 3. Technology Incentives 4. Rate of Technological Change v. External Opportunities and Threats – PEST factors with external micro environmental factors can be classified as opportunities and threats in a SWOT Analysis. F. SWOT Analysis a. The firm’s internal attributes can be classified as strengths and weaknesses. b. The external environment presents opportunities and threats (see E-Climate above). IV. MARKET SEGMENTATION A. Describe the market segment – demographics, psychographics, geographics. B. Behavioral segmentation – usage rate patterns (of a product), percent of sales (they contribute to), what they want, how they use a product, support requirements, how to reach them, price sensitivity, brand loyalty, benefits sought. V. ALTERNATIVE MARKETING STRATEGIES – List and discuss the alternatives that were considered before arriving at the recommended strategy. Alternatives might include discontinuing a product, re-branding, positioning as a premium or value product, etc. VI. SELECTED MARKETING STRATEGY – Discuss why the strategy was selected then the marketing mix decisions (4 P’s). A. Product – The product decisions should consider the product’s advantages and how they will be leveraged. Product decisions should include the following: Brand Name, Quality, Scope of Product Line, Warranty, Packaging B. Price – Discuss pricing strategy, expected volume, and decisions for the following pricing variables: List Price, Discounts, Bundling, Payment Terms and Financing Options, Leasing Options C. Distribution (Place) a. Distribution channels – direct and indirect (using intermediaries) b. Motivating the Channel – think of “trade promotions” i. Slotting Allowances – manufacturer pays (cash premiums) retail chain for the costs involved in placing a new product on its shelves. ii. Buying Allowances – manufacturer offers a price discount to the wholesalers/retailers to encourage the purchase of a product. Sometimes used to encourage the purchase of larger quantities. iii. Trade Shows & Conventions iv. Sales Incentives c. Criteria for Evaluating Distributors d. Locations e. Logistics, including transportation, warehousing, and order fulfillment D. Promotion – think of the promotional mix a. Advertising – how much and which mediums b. Public Relations c. Consumer Sales Promotions i. Premiums - coupons, factory packs, traffic builders, coupon plans ii. Incentives – contests, sweepstakes, rebates iii. Product Samples – trial sizes through direct mail or door-to-door iv. Promotional Tie-Ins – Sales promotional arrangements between one or more retailers or manufacturers. v. Product Placement – Develop product/brand recognition through special events, on TV, movies. vi. Visual Merchandising– Projecting the right image to customers through coordination of the physical elements in a place of business. vii. Displays - Coordinating the visual & artistic aspects of presenting a product to a target group of customers. viii. Loyalty Marketing Programs – frequent buyer programs, reward customers for multiple purchases. d. Personal Selling VII. SHORT AND LONG TERM PROJECTIONS – The selected strategy’s immediate effects, expected long-term results, and any special actions required to achieve them. This section may include forecasts of revenues and expenses as well as the results of a break-even analysis. VIII. CONCLUSION – Summary of everything above. IX. APPENDIX: List any exhibits here - calculations of market size, commissions, profit margins, break-even analysis, etc.