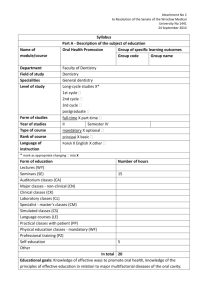
4 th year course specification 2013
advertisement

Mansoura University Faculty of Dentistry Department of Conservative Dentistry COURSE SPECIFICATION 4th Year Clinical Operative Dentistry Professor Dr Salah Hasab Mahmoud, Chairman of Conservative Dentistry Department 2012/2013 1 Mansoura University Faculty of Dentistry Conservative Dentistry Department Division of Operative Dentistry Academic Year 2012/2013 Year 3 Course Purpose The overall purpose of the course is to facilitate the transition of students from the pre-clinic laboratory to the clinic setting. Students are expected to demonstrate competency in the surgical treatment of dental caries prior to being certified ready for patient treatment. Treatment planning in Operative Dentistry will be discussed, which includes the diagnosis of dental caries and other dental abnormalities; and the understanding of different treatment options relating to the diagnosis Aim To achieve competency in the clinical skills of conservative dentistry: the diagnosis, management, treatment planning and treatment of caries by amalgam restorations. Objectives in years 3 I. Treatment planning in Dentistry a. To introduce to the student the current status of treatment planning in private practice. b. To provide the student with reasons for the variation in treatment planning among general dentists. c. To introduce to the student the concept of utilizing evidence based dentistry in treatment planning. d. To introduce to the student the problem oriented model in treatment planning. e. To introduce to the student the importance of 2 other factors (patient’s preference and caries risk assessment) in formulating treatment options. II. Diagnosis of dental caries and treatment options 2 a. To introduce to the students the current method in diagnosing pits and fissures caries lesions; and the available treatment options. b. To introduce to the students the current method in diagnosing smooth surface caries lesions; and the available treatment options. c. To introduce to the students the current method in diagnosing proximal surface caries lesions; and the available treatment options. d. To introduce to the students the current method in diagnosing root surface caries lesions; and the available treatment options. e. To introduce to the students the current method in diagnosing secondary caries lesions; and the available treatment options. IV. Competency in the surgical treatment of dental caries in a simulated clinical setting a. To test for student competency in Class I amalgam preparation and restoration. b. To test for student competency in Class II amalgam preparation and restoration. d. To introduce to the student various matrixing methods used. VI. Introduction to Operative Dentistry Clinic a. To introduce to the student rules and regulations in the Operative Dentistry Clinic b. To introduce to the student the evaluation system used in the Operative Dentistry Clinic c. To introduce to the student the proper operator and patient positioning in the dental chair. Clinical course, progress and development Activity Sunday, Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday 3 Names of Demonstrators Mohamed Samer Weahm Abd El-Latef Nashat Magdy Tamer El-shahwy Radwaa Elmorsy Rabab Elaraby Huda Abed El-haliem Eman Sobh The aim of year 3 is to ensure that you have completed most of the requirements for finals which are: (a) Number of Class I amalgam restorations 15 (b) Number of Class II amalgam restorations 10 Competency test By the end of year 3 you will be expected to complete a competency test in operative dentistry. The assessment will be undertaken by the Professors of the filed on the clinic not your usual timetabled teacher. Failure to pass the test by the end of year 3 may hinder your progression into year 4. Attendance You are expected to attend all clinical sessions. When patients fail to attend or you cannot get a chair booked you are still expected to attend. A register will be kept of student attendance. During the following periods your demonstrator will assess your progress. There will be no patient treatment during this period. Student assessment of staff Towards the end of the year 3 you will have the opportunity to comment confidentially on various aspects of your demonstrator’s teaching. The demonstrator and the departmental year co-ordinator will review this. These forms are anonymous. If there are major difficulties then students will be invited to speak directly to the departmental co-ordinator or the head of division to attempt to resolve them. Do not feel inhibited to ask for help and guidance at any time. Please do not be afraid to ask for help as this is much better than ignoring a problem that can multiply and become much more difficult to sort out later. Lecture programme year 3 and Intended learning Outcome Assessment of Dental Patient This lecture addresses the rationale and method for gathering relevant medical and dental information (including the examination of the patient) and the use of this information for dental treatment. After the lecture a student should be able to: 4 Perform and document patient assessment procedures which are vital to the practice of dental hygiene—a complete and accurate assessment is the starting point to providing thorough patient care. Caries Diagnosis Diagnosis, prevention, and treatment of dental caries must be the foremost objectives of operative dentistry. As the aim of this lecture is to develop scientifically based recommendations that can be applied by dentists, it is important that the “everyday” fundamentals of clinical caries diagnosis are addressed clearly and objectively. Clinical caries diagnosis represents the foundation on which the answers to most of the consensus questions will be based, either through providing information on caries detection (or acting as the benchmark from which other methods must be judged), being part of risk assessments, being used in the assessment of both primary and secondary preventive strategies, or playing a key role in informing clinical decision making. After completing the lecture, you'll be able to: 1. 2. 3. Understand the basics of cariology, specifically diagnose caries more effectively especially in its early stages Learn more about the new methods in caries diagnosis Distinguish between different types of dental caries Treatment Planning This lecture provides essential knowledge for creating treatment plans for adult dental patients. Treatment planning strategies are presented to help with balancing the ideal with the practical, with emphasis placed on the central role of the patient - whose needs should drive the treatment planning process. The focus is on planning of treatment, not on the comprehensive details of every treatment modality in dentistry Selection of Restorative Materials This lecture covers the followings: 5 Biological considerations of the tooth while selecting the restorative materials. Physical and clinical properties of the restorative materials. General factors considered while selecting restorative material After the lecture a student should be able to: select the restorative material appropriate for every patient. Biological Considerations of Operative Procedures This lecture covers the physical, chemical and thermal irritation of the restorative procedures on the soft and hard dental tissues. After the lecture a student should be able to: recognize the biological considerations during tooth cutting and restoration with different restorative material. Pain Control & Postoperative Sensitivity This lecture covers the causes of pain occurred during operative procedures and postoperative sensitivity (causes, theories, management). After the lecture a student should be able to: 1. Control of pain occurred during operative procedures. 2. Deal and mange the postoperative sensitivity. Temporary Restoration This lecture covers types and advantages of temporary fillings. After the lecture a student should be able to select and place the ideal temporary filling for each specific case. Management of Non- Carious Lesions This lecture covers the types of non-carious lesions which include abrasion, erosion and attrition of teeth. After the lecture a student should be able to diagnose and treat non-carious tooth defects. Management of Mild & Moderate Carious Lesions This lecture will address the followings: 1. Mild and moderate carious lesions. 2. Past, present, and future treatment modalities. After the lecture a student should be able to select non invasive strategies and new treatment modalities for treatment of these lesions. Operative Management of Deep Carious Lesions and Pulp Protection To understand the principles of when to treat deep dental caries. This lecture addresses the new developments in concepts behind the carious process and handling of the deep carious lesions. 6 After the lecture the student will be able to: 1. Describe the structure of carious dentin. 2. Differentiate between affected and infected dentin. 3. To give students a broad understanding of the alternative methods available for removing carious dentin, with advantages and disadvantages. Current concepts of adhesion to dental hard tissues Hard tissue anatomy, requirements for adhesion and different adhesive systems will be covered. After the lecture a student should be able to: 1. Explain the relevance of tooth structure for adhesion 2. Describe the effects of surface preparation prior to bonding 3. Describe the concepts of resin hybridization 4. Discuss the differences between resin based and glass ionomer adhesion 5. Explain the concept of shrinkage stress and its effect on bonding Direct Posterior Composite Restorations This lecture addresses the followings: 1. Indications for direct posterior composite 2. Choosing posterior composite 3. Clinical stages for restorations using direct posterior composite After the lecture a student should be able to prepare and restore a posterior tooth with direct posterior composite material. Reading list The reading list given in the second year should be consulted. Tutors may give students supplemental references relating to tutorial topics. It is expected that students will use the reading list as a basis for undertaking literature searches. The last editions of the following books are useful. Hugh Devlin, Operative Dentistry A Practical Guide to Recent Innovations, Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg B Kidd, EAM, Pickards Manual of Operative Dentistry. Oxford Medical Publications AJE Qualtrough, JD Satterthwaite, LA Morrow, PA Brunton, Principles of Operative Dentistry, Blackwell Publishing Robert G. Craig, John M. Powers, Restorative Dental Materials, Mosby, Inc. 7 James Summitt, J Williams Robbins, Richard Schwartz, Jose dos Santos, Fundamentals of Operative Dentistry A Contemporary Approach, Quintessence Publishing Co, Inc Theodore M. Robersons, Sturdevant's Art & Science of Operative Dentistry, Mosby, Inc. Course Director Course director: Dr. Nadia Zaghloul, Associate Professor of Operative Dentistry Chairman of the Department Dr. Salah Hasab Mahmoud, Professor of Operative Dentistry 8