INTRODUCTION
advertisement
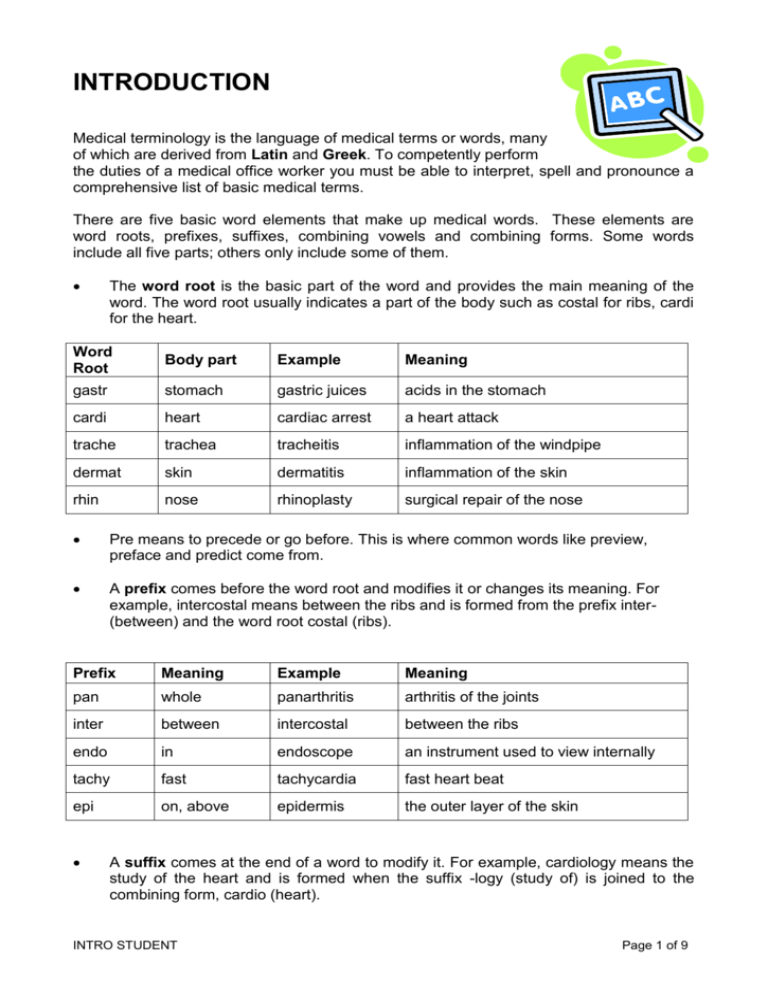
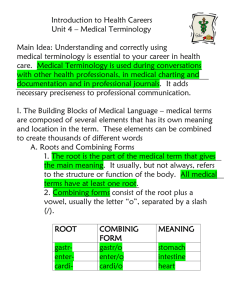
INTRODUCTION Medical terminology is the language of medical terms or words, many of which are derived from Latin and Greek. To competently perform the duties of a medical office worker you must be able to interpret, spell and pronounce a comprehensive list of basic medical terms. There are five basic word elements that make up medical words. These elements are word roots, prefixes, suffixes, combining vowels and combining forms. Some words include all five parts; others only include some of them. The word root is the basic part of the word and provides the main meaning of the word. The word root usually indicates a part of the body such as costal for ribs, cardi for the heart. Word Root Body part Example Meaning gastr stomach gastric juices acids in the stomach cardi heart cardiac arrest a heart attack trache trachea tracheitis inflammation of the windpipe dermat skin dermatitis inflammation of the skin rhin nose rhinoplasty surgical repair of the nose Pre means to precede or go before. This is where common words like preview, preface and predict come from. A prefix comes before the word root and modifies it or changes its meaning. For example, intercostal means between the ribs and is formed from the prefix inter(between) and the word root costal (ribs). Prefix Meaning Example Meaning pan whole panarthritis arthritis of the joints inter between intercostal between the ribs endo in endoscope an instrument used to view internally tachy fast tachycardia fast heart beat epi on, above epidermis the outer layer of the skin A suffix comes at the end of a word to modify it. For example, cardiology means the study of the heart and is formed when the suffix -logy (study of) is joined to the combining form, cardio (heart). INTRO STUDENT Page 1 of 9 Suffix Meaning Example Meaning itis inflammation appendicitis inflammation of the appendix algia pharyngalgia pain of the throat mastectomy removal of a breast plasty pain surgical removal of surgical repair of logy the study of oncology ectomy mammoplasty surgical repair of a breast study of cancer Suffixes that mean ‘relating to’ There is a group of suffixes that all mean relating to, pertaining to or connected with, the word root. Some of these are: ac cardiac al skeletal ar muscular ary urinary ic epigastric ive infective ous nervous relating to the heart The combining vowels (a, e, i, o, and u) are used to join together various parts of the word to make it easier to analyse and pronounce. The combining vowels (a, e, i, o, u ) are used to join root words to suffixes and root words to other root words. A combining vowel acts like a plus sign in maths. In most cases the combining vowel is ‘o’ For example, a cardiologist is a specialist who studies the heart. The combining vowel, ‘o’, is used to join the word root, cardi, to the suffix -logist. Word root Combining vowel gastr O rhin O rhin Suffix Word ic Gastroenteric eal rhinopharyngeal O -plasty Rhinoplasty Surgical repair of the nose gastr O logy Gastrology Study of the stomach cardi o logist cardiologist Specialist who studies the heart Word root Enter (intestine) Pharyng (throat) Meaning Relating to the stomach and intestines Relating to the nose and throat The combining form is simply a word root together with a combining vowel. ‘Gastr’ is the root for stomach but ‘gastro’ is the combining form of stomach. The combining INTRO STUDENT Page 2 of 9 form “gastro” is now ready to be joined to another root word or suffix. Turning the word root into the combining form makes it easier to pronounce. Body part Word root Combining form stomach gastr gastro intestine enter entero heart cardi cardio nose rhin rhino skin dermat dermato PRONUNCIATION OF MEDICAL TERMS Pronouncing medical words can be hard at times especially if you are not familiar with the words. Breaking medical words down into their parts makes them easier to pronounce. Look for the combining form(s), prefix and suffix, and pause between each one. For example, gastroenteritis becomes gastro-enter-itis. Most medical words are pronounced with a light emphasis on the first syllable. Listen attentively when experts use medical terminology to learn how words are pronounced and ask your supervisor if you are unsure of the correct pronunciation of medical words. You will often have to identify and speak medical terms within telephone conversations where you won’t have the benefit of being able to study the written word. You will certainly have to recognise words when you create medical documents from audio dictation. The accurate spelling of medical terminology is critically important in medical office work. Just one letter missing, or out of place, can change the entire meaning of a word. You need to be aware that the English spellings may differ from the American spellings in which words are spelt the way they sound with any silent vowels omitted. THE IMPORTANCE OF SPELLING MEDICAL TERMS CORRECTLY Misspelling a medical word, even by adding or leaving out one letter, can entirely change its meaning. For instance: Abduction Adduction carrying away from carrying toward Arteritis Arthritis inflammation of an artery inflammation of a joint Ileum Ilium lower part of small intestine hip bone There are some rules that make it easier to spell and check medical words and to understand their meaning. They include: INTRO STUDENT Page 3 of 9 reading the word backwards dropping a vowel when joining word parts adding s or ies to for plurals Be aware that there are some exceptions to the general rules, particularly with regard to reading the word backwards. Plurals Like common words, most medical words are made into plurals just by adding s or by replacing y with ies. However, because there are many Latin words involved in medical terminology, there are a few unusual plural rules you have to be aware of Singular ending -a Plural ending -ae -is -es -um -a -us -i -ix, -ex -ces Singular example Vertebra Hernia Diagnosis Testis Ovum Bacterium Bronchus Bacillus Cervix Appendix Plural example Vertebrae Herniae Diagnoses Testes Ova Bacteria Bronchi Bacilli Cervices Appendices Meaning Part of the spine Protrusion of an organ Identification of a disease Male sexual organ Female egg cell Microscopic organism Small airway Type of bacterium Part of the uterus Part of the large intestine American versus English spelling One of the major difficulties with spelling medical words is that there are two ways of spelling many words – the English way and the American way. In the past most Australian doctors have used English spelling of medical terms. These days, however, American spelling is increasingly common. English American Pronunciation Meaning diarrhoea diarrhea di-a-rear Watery motion foetal fetal fee-tal Child in the womb haematologist hematologist hema-tol-ogist Blood specialist leucocyte leukocyte lew-ko-site White blood cell oedema edema e-deema Swelling paediatrics pediatrics peedi-atrics Area of child health Medical language appears intimidating at first but with regular practice you will soon come to understand its principles and to have at your fingertips one of the medical office worker’s most essential tools – a working knowledge of medical terminology. Refer to a medical dictionary for assistance if necessary, but always check with your supervisor if you are still unsure of how to spell a medical term. Revision INTRO STUDENT Page 4 of 9 From which languages are most medical terms derived What are the five medical word parts Where will a prefix appear Where will a suffix appear What is the function of the combining form What word part is logist What word part is cardi What word part is inter What word part is o What word part is cardio What word part is al Which syllable is generally stressed in medical terms What is the difference between intermuscular and intramuscular How do American medical words differ from the English version What are three rules that assist in understanding medical words Diseases and disorders When a person becomes ill or suffers an injury they want to know three things: 1. What is wrong with me? 2. Am I going to get better or am I going to die? 3. How long will it take before I recover or die? These are simple enough questions and we have all asked one or more of them in our lives. However the answers are not always simple and the doctor may have to do a great deal of work before answering them. Imagine that a man comes to see the doctor. You ask him what is wrong and he tells you he has cut his finger and it may need stitches. This sounds simple enough, it’s not a very deep cut, he may or may not need stitches, and the finger will be better in about two weeks. Now see it from the doctor’s point of view. What did the patient cut his finger on? Was it a deep or superficial cut? Is there damage to any nerves or blood vessels? Will the man need antibiotics? Is his tetanus vaccination up to date? How long ago was the wound made? All these questions will need to be answered before the doctor tells the man how bad his wound is and, if and when he will recover. In the worst case scenario the man may have cut himself on a piece of rusty metal two weeks ago, the wound has become badly INTRO STUDENT Page 5 of 9 infected, and the finger has become gangrenous. Despite surgery and aggressive antibiotic therapy, the man’s immune system cannot recover and he dies. Because no two medical cases are the same, it is important for the doctor to spend time investigating and researching before answering the patient’s questions. There a number of special terms associated with determining diseases: Aetiology is the study of the cause of diseases and how the patient contracted them Signs are clinical evidence of diseases or disorders. Evidence can include seeing a red, inflamed throat, recording a high temperature. Symptoms are sensations of diseases experienced by the patient. The patient may feel her throat is very sore, or feels hot. Disease is a set of signs and symptoms that disrupts with the normal function of an organ or a body system. In the case of diabetes, a patient would have raised blood sugar levels, excessive thirst, a need to urinate frequently, and weight loss. The urinary system would have to work harder to try to eliminate the sugar from the blood stream and this could result in kidney damage. Diagnosis is when the doctor decides what the disease or disorder is causing the signs and symptoms. Prognosis is the possibility of the patient recovering from the disease. Morbidity means sickness Mortality means death Acute means something is quick to begin and probably quite severe Chronic refers to something lasting for a long time Terminal means that the disease will cause the patient to die Activity 1 Rewrite these questions using the medical terms you have just read. What is wrong with me? ___________________________________________________________________________ How long will it take before I recover or die? __________________________________________________________________ Is it severe or long lasting? INTRO STUDENT Page 6 of 9 ___________________________________________________________________________ Am I going to get better or am I going to die? __________________________________________________________________ Diseases and disorders of the major body systems There are many different types of disease and injuries that affect each body system. In this unit you will be introduced to some of the more common disease terms. Common name Medical term hayfever Allergic rhinitis baldness Alopecia stroke Cerebral vascular accident earwax Cerumen bruise Contusion scar Cicatrix pressure sore Decubitus ulcer nose bleed Epistaxis boil Furuncle piles Haemorrhoids bad breath Halitosis kissing disease Infectious mononucleosis change of life Menopause measles Morbilli heart attack Myocardial infarction mole Naevus lice Pediculosis afterbirth Placenta fever Pyrexia german measles Rubella blood poisoning Septicaemia snoring Stertorous breathing squint Strabismus INTRO STUDENT Page 7 of 9 fainting Syncope consumption Tuberculosis hives Urticaria chickenpox Varicella wart Verruca Disorder Prefixes Meaning a, an without brady slow dys difficult or painful hyper above hypo below oligo few poly many tachy fast Disorder Suffixes Meaning -ema swelling -trophy nourishment -ia condition of -iasis abnormal condition of -itis inflammation -megaly enlargement -oma tumour (a lump or mass, which may or may not be cancerous) -osis abnormal condition -ptysis spitting up -staxis dripping (blood) INTRO STUDENT Page 8 of 9 Policies and Procedures As a medical office worker you will be required to adhere to policies and procedures. These policies and procedures are usually contained in a manual and provide important information regarding how you are to perform your role. They are used as a guide in performing your job related tasks. Government Legislation As a medical office worker, you are legally bound and governed by law to maintain strist confidentiality, privacy and security in regards to patient information . Legislation includes 1. Freedom of Information Act 1982 2. Privacy and Personal Information Protection Act 1998 3. Occupational Health and Safety Act 2000. INTRO STUDENT Page 9 of 9