Exam 1
advertisement

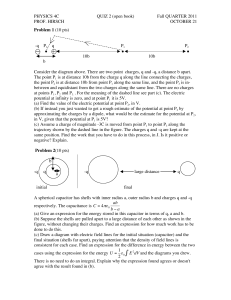
Exam 1 PHY 2140 Row: Seat: Date, 2003 Please type your name here Please type your student number here Instructions: The following procedure must be followed in order to correct any (unlikely) mistakes in the grading. 1. Do all the questions. Show your work for partial credit. I must be able to understand what you have done while I am reading the exam – not when you explain it to me after the exam is graded and returned. 2. For each problem: (a) write down any formula(s) used (b) justify why you used that particular formula(s) (c) copy the answer you have circled from the exam pages to the General Purpose Answer Sheet and fill in the ovals. (d) show your work! 3. The formula sheet is on the last page of the exam. You may detach it from the rest of the exam. NAME 1. Two identical conducting spheres are placed with their centers 0.30 m apart. Initially, the first sphere has a charge of 12 x 10-9 C and the second a charge of -18 x10-9 C. The spheres are then connected by a conducting wire. What is the magnitude of the electrostatic force between the two spheres when the charges are in equilibrium? a. b. c. d. e. 3.0 x 10-7 N 5.0 x 10-7 N 6.0 x 10-7 N 9.0 x 10-7 N not enough information 2. Three charges are arranged as shown, producing a net electric force on the charge at the origin. Find the angle made by this force with the positive x axis. yy a. b. c. d. e. 37 45 130 225 260 --22 C C 11 m m --88 C C xx ++22 C C 22 m m . 3. Determine the point nearest the charges where the total electric field is zero. Take the -2.50 C charge to be at the origin of the x axis. 11..0000 m m a. b. c. d. e. –1.80 m –1.27 m 0.27 m 0.39 m 1.27 m --22..5500 C C --66..0000 C C NAME 4. The potential difference across two charged parallel plates is 200 V. This potential difference causes a charged dust particle to move from one plate to another. If the dust particle has charge 2.00 C and mass 1.00 x 10-5 kg, find the speed of the dust particle as it reaches the second plate. a. b. c. d. e. 0.73 m/s 8.94 m/s 160 m/s 3.2 x 104 m/s Dust has no charge. 5. The plates of a parallel plate capacitor are separated by 1.00 x 10–4 m. If the material in between them is a jelly with a dielectric constant of 2.26, what is the plate area needed to provide a capacitance of 1.50 pF? a. b. c. d. e. 1.00 x 10-6 m2 4.35 x 10-6 m2 7.50 x 10-6 m2 9.00 x 10-6 m2 I don’t think I’m ready for that jelly. 6. Find the charge on the 2 F capacitor in the following circuit. a. b. c. d. e. 4 C 12 C 18 C 24 C not enough information 22 FF 44 FF 22 FF 1122 V V 7. A rectangular gold bar has two sides of length 0.04 m and one side of length 0.10 m. To prevent theft, the block can be connected to a 1.90 V source across any opposite faces of the block. Find the current that can flow through the block along its longer side. The resistivity of gold is 2.44 x 10-8 m. a. b. c. d. e. 1.23 x 106 A 3.17 x 106 A 7.78 x 106 A 1.46 x 107 A Resistance is futile. 8. The filament of a light bulb has a resistance of 20.0 at 20 C (when the light is off and the filament is at room temperature). When the light is on, the resistance is 160 . Find the temperature of the filament when it is hot. Take the temperature coefficient for resistivity to be 3.5 x 10-3 for the filament at 20 C. a. b. c. d. e. 939 C 1120 C 1440 C 2020 C 2310 C 9. If the size of the charge value is tripled for both of two point charges maintained at a constant separation, the mutual force between them will be changed by which factor? a. b. c. d. e. 9.0 3.0 1/3 1/9 Fear factor. 10. Consider a simple parallel-plate capacitor whose plates are given equal and opposite charges and are separated by a distance d. Suppose the plates are pulled apart until they are separated by a distance D>d. The electrostatic energy stored in the capacitor is a. greater than b. the same as c. smaller then before the plates were pulled apart. 11. A “free” electron and a “free” proton are placed in an identical electric field. After the particles are released, the acceleration of the proton will be a. greater then b. the same as c. smaller than the acceleration of the electron. 12. (bonus) Each of the protons in a particle beam has a kinetic energy of 3.25x10-15 J What are the magnitude and direction of the electric field that will stop these protons in a distance of 1.25 m? a. b. c. d. e. 5.12 x 104 N/C and opposite to the motion 1.63 x 104 N/C and opposite to the motion 5.12 x 104 N/C and along the motion 1.63 x 104 N/C and along the motion 2.16 x 104 N/C and perpendicular to the motion v A x f xi a t f ti Ax Ay 2 W ( F cos ) s KE q1 q 2 E 2 energy P I 2R 1 2 mv 2 F q0 q r 1 1 1 Ceq C1 C 2 A d 1 QV 2 R Ax V ke VB VA Ed C 0 Ay v v x 0 t 2 2 r t f ti tan 2 v 2 v0 2ax F ke v f vi A V 2 R energy Q2 2C Ax A cos x v0 t Fx = m ax Fy = m ay Wnet = KEf - KEi KEf +PEf = KEi + PEi E ke PE k e q r2 q1 q 2 r C eq C1 C 2 I Q t R R0 1 T T0 Req R1 R2 1 1 1 Req R1 R2 ke=8.99 x 109 Nm2/C2 1 kWh = 3.60 x 106 J 1 2 at 2 v v0 at 0 1 T T0 g = 9.8 m/s2 = 8.85 x 10-12 C2/Nm2 Ay A sin 1 eV = 1.6 x 10-19 J PE qVB VA Q CV energy 1 2 C V 2 V IR P IV