File - Human Development and Family Studies 290 & 413
advertisement
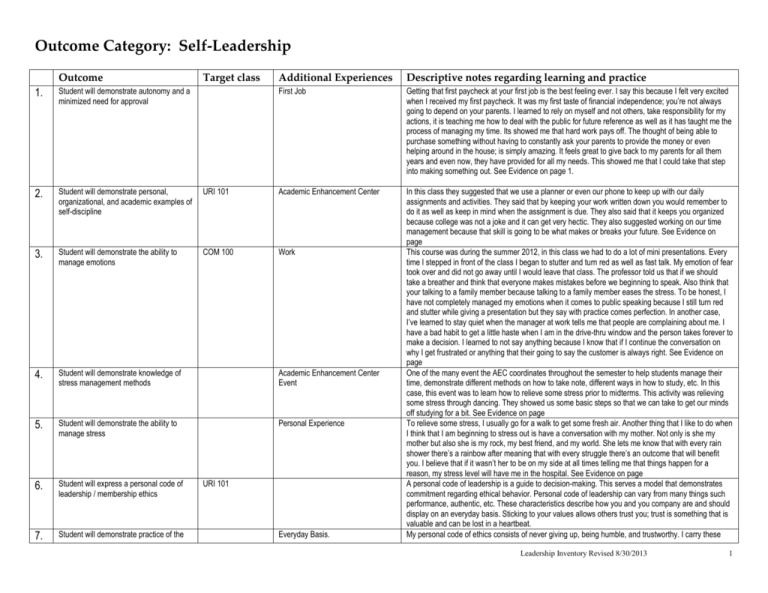
Outcome Category: Self-Leadership Outcome Target class Additional Experiences Descriptive notes regarding learning and practice First Job Getting that first paycheck at your first job is the best feeling ever. I say this because I felt very excited when I received my first paycheck. It was my first taste of financial independence; you’re not always going to depend on your parents. I learned to rely on myself and not others, take responsibility for my actions, it is teaching me how to deal with the public for future reference as well as it has taught me the process of managing my time. Its showed me that hard work pays off. The thought of being able to purchase something without having to constantly ask your parents to provide the money or even helping around in the house; is simply amazing. It feels great to give back to my parents for all them years and even now, they have provided for all my needs. This showed me that I could take that step into making something out. See Evidence on page 1. In this class they suggested that we use a planner or even our phone to keep up with our daily assignments and activities. They said that by keeping your work written down you would remember to do it as well as keep in mind when the assignment is due. They also said that it keeps you organized because college was not a joke and it can get very hectic. They also suggested working on our time management because that skill is going to be what makes or breaks your future. See Evidence on page This course was during the summer 2012, in this class we had to do a lot of mini presentations. Every time I stepped in front of the class I began to stutter and turn red as well as fast talk. My emotion of fear took over and did not go away until I would leave that class. The professor told us that if we should take a breather and think that everyone makes mistakes before we beginning to speak. Also think that your talking to a family member because talking to a family member eases the stress. To be honest, I have not completely managed my emotions when it comes to public speaking because I still turn red and stutter while giving a presentation but they say with practice comes perfection. In another case, I’ve learned to stay quiet when the manager at work tells me that people are complaining about me. I have a bad habit to get a little haste when I am in the drive-thru window and the person takes forever to make a decision. I learned to not say anything because I know that if I continue the conversation on why I get frustrated or anything that their going to say the customer is always right. See Evidence on page One of the many event the AEC coordinates throughout the semester to help students manage their time, demonstrate different methods on how to take note, different ways in how to study, etc. In this case, this event was to learn how to relieve some stress prior to midterms. This activity was relieving some stress through dancing. They showed us some basic steps so that we can take to get our minds off studying for a bit. See Evidence on page To relieve some stress, I usually go for a walk to get some fresh air. Another thing that I like to do when I think that I am beginning to stress out is have a conversation with my mother. Not only is she my mother but also she is my rock, my best friend, and my world. She lets me know that with every rain shower there’s a rainbow after meaning that with every struggle there’s an outcome that will benefit you. I believe that if it wasn’t her to be on my side at all times telling me that things happen for a reason, my stress level will have me in the hospital. See Evidence on page A personal code of leadership is a guide to decision-making. This serves a model that demonstrates commitment regarding ethical behavior. Personal code of leadership can vary from many things such performance, authentic, etc. These characteristics describe how you and you company are and should display on an everyday basis. Sticking to your values allows others trust you; trust is something that is valuable and can be lost in a heartbeat. My personal code of ethics consists of never giving up, being humble, and trustworthy. I carry these 1. Student will demonstrate autonomy and a minimized need for approval 2. Student will demonstrate personal, organizational, and academic examples of self-discipline URI 101 Academic Enhancement Center 3. Student will demonstrate the ability to manage emotions COM 100 Work 4. Student will demonstrate knowledge of stress management methods Academic Enhancement Center Event 5. Student will demonstrate the ability to manage stress Personal Experience 6. Student will express a personal code of leadership / membership ethics 7. Student will demonstrate practice of the URI 101 Everyday Basis. Leadership Inventory Revised 8/30/2013 1 personal code of ethics 8. Student will express a personal values statement Student will demonstrate practice of the personal values statement Prior Knowledge 10. Student will demonstrate the ability to lead a project from start to finish (followthrough) Christmas Spirit 11. Student will describe goals and objective statements regarding personal issues, career issues, and community issues Student will show evidence of goals and objectives that were planned and achieved Student will show knowledge of the “Hierarchy of Needs” theory by Maslow Internet 9. 12. 13. 14. The Movie: A Cinderella Story Political Science 113 HDF 290 three values with great pride. I feel that one should not give up on what they desire in life. An example is me now; I feel the urge to simply drop everything that consists of school. It stresses me out more then anything. My major is not going as well as I would hope that it would be. But what is life without a couple of bumps on the road. I know that at the end of this I will have furthered my knowledge and I will be in a place I want to be. With every storm, the sun comes out right after. With being humble, simply don’t get a big head over yourself because what you perceive yourself someone else is disagreeing. Trust is by far the must important value anyone should have. It’s also the easiest thing to lose. A personal values statement is rather similar to the code of ethics but it is what you go by personally. Like humbleness, loyalty, fairness, responsible, respectful, open -minded. “Never let the fear of striking out, keep you from playing the game” Ever since I watch the movie A Cinderella Story, I fell in love with this quote because not only is this a softball terminology but its also a boost of confidence. It tells you not to give up because an obstacle has come about. Make that obstacle be the reason that you get what you desire. Since then this what I go by, this quote has made me go forward with all my decisions. See Evidence on page I was raised to have a cheerful Christmas with having lights outside of the house, decorations the inside, the Christmas tree, etc. This year my father felt the need not to set anything up because he will not be here for Christmas. My mother is not one who has any spirit or desire to decorate anything, I felt the need to take everything from the attic and start to decorate the house myself because I will enjoy my Christmas and have Christmas spirit regardless if the family is not together. So, I started to decorate the house and my dad decide to help out, it’s a family tradition and I’m not going to stop now because there’s a bump in the road. I set up the lights outside; I bought the Christmas tree as well as decorated the inside of the house. We taking action on having a Christmas inspired my dad to help out with decoration. If it was not for me the house would feel lifeless this time of year. I love Christmas so no one will ruin my spirit of joy. See Evidence on page A goal and objective statement is simply what you plan to accomplish through out the project. Goals are high-level statements that provide the whole concept of the project while the objectives are the lower level of statements that describe specific topics that the project will provide. An example of this is in my Political Science book where at the beginning of every chapter they give you the learning objectives, what you should take from reading that chapter. According to Maslow, this theory’s concept is to understand what motivates people. He states that people posse a set of motivation systems to rewards or unconscious desires, in other words people are motivated to achieve certain needs. This theory contains five motivational needs, which is also known as the hierarchical level within a pyramid. The five stages of this pyramid can b divided into basic needs, safety needs, social needs, esteem needs and self- actualization. Every person is capable and has the desire to move up the hierarchy toward a level of self-actualization but first one content lower level basic needs before moving on to the next higher level of need. According Maslow only one in a hundred people become fully self-actualized because our society rewards are based on esteem and other social needs. The original hierarchy of needs five-stage model included Biological and Physiological, which include air, food, shelter, warmth, sex, and sleep. The second need is safety, which includes protection from elements, security, order, law, limits, stability, etc. The third need is called social and consists of belongingness and love such as work group, family, affection, relationships. The fourth need is esteem and it is made up if self-esteem, achievement, mastery, independence, status. And lastly, you have self-actualization needs, which realizes personal potential, self-fulfillment, seeking personal growth and peak experiences. In the 1970’s Maslow’s five- stage model expanded to include cognitive and aesthetic needs as ell as transcendence need. Cognitive needs include knowledge and meaning. Aesthetic needs are known for appreciation and search for beauty, balance, form. The eighth need is transcendence in which helps other achieve selfactualization. Student will show application of Maslow’s Leadership Inventory Revised 8/30/2013 2 15. theory to own life Student will describe personal leadership style and/or personality style including strengths and weaknesses and examples of application (Sources = Leadership style inventories, the L.P.I., StrengthsQuest, Type Focus (MBTI), LAMP, and other career inventories, etc.) 16. Student will show knowledge of the theory of Superleadership by Manz & Sims 17. Student will show application of Manz & Sim’s theory to own life HDF 290 Retreat URI 101 HDF 290 In Type Focus, I was asked to answer a couple of questions in which would describe me. My results from this survey came out to be ESTP, which means Extraversion, Sensing, Thinking, and Perceiving. The first time that I received these results were in my URI 101 class and then again in my HDF 290 course. An extravert is a person directs their energy to the outer world, they have high energy, talk more then listen, think out loud, act before thinking, can get easily distracted, prefer to do many things at once and are outgoing and enthusiastic. Sensing, notice thing with your five senses. This type of people focus on details and specifics, work at a steady pace, live in the here-and-now, notice details and remember facts, like step-by-step instructions as well as like to use established skills. A Thinker, a person base their ideas by evidences, these people usually make decisions objectively, are honest and direct, are convince by rational arguments, take very few thins personal and value honesty and fairness. And lastly, perceivers are people who are prefer flexibility and spontaneous results. These people like to keep their opinions open, are playful and casual, play first, work later, usually have a hard time making decisions and want the freedom to be spontaneous. See Evidence on page According to Manz a Superleadership consists of “being a leader that can lead others to lead themselves”. The purpose of this theory is to enable worker to gain control over his or her own behaviors (DeBrin 97). Practicing to be a Superleader involves three main attitudes first is identifying and replacing destructive assumptions and beliefs. After identifying negative thoughts they are should be replaced with more useful thought. Second, to change to positive and constructive self- talk. “Any negative thoughts are changed to positive ones” (DeBrin, 97). And lastly, methods of effective performance. Visualize and practice the way you want to perform. Mans states in his book that “to be a leader of others, you must learn to lead yourself first”. See Evidence on page Outcome Category: Leadership Theories Outcome Target class 18. Student will show knowledge of the “Authority and Bureaucracy” theory of leadership Weber HDF 290 A German sociologist who developed another theory for the classical management theory. He was curious I finding out the reason employees and people accept the authority of their superiors and follow the rules. He defines the difference between power and authority, which power “educes obedience through force” and authority means “entails that individuals agree that authority is exercised upon them by their superiors”. He then describes three types of authority: Traditional authority, Charismatic authority, and Rational-legal authority. Traditional authority, which is found in tribe and monarchies, consist of accepting and unquestioned folks derived from customs and traditions. Charismatic authority which means a person who has gained respect and trust from his/her followers. Usually a leader of a small or large group with similar attributes. The third authority is Rational-legal authority where a setup of an organization and position held by the person in authority. Weber also finds another authority called bureaucracy, bureaucracy refers to management by rules; a set of rules that control the function of the organization, division of labor; authority and responsibility are clearly defined and officially authorized, formal hierarchal structure; follows a clear chain of command, personnel hired on grounds of technical competence; work is assigned based on experience and capability, managers are salaried officials; trained and experienced specialists and written documents; All decisions, rules and actions taken by the organization are formulated and recorded in writing. 19. Student will describe personal application of the above theory (Weber) Student will show knowledge of the “Scientific Management” theory of HDF 290 Also known as Taylorism, this theory revolves on a management theory that measures workers productivity to improve economic efficiency. Scientific Management consists of analysis, synthesis, 20. Additional Experiences Descriptive notes regarding learning and practice Leadership Inventory Revised 8/30/2013 3 leadership by Taylor 21. logic, rationality, empiricism, work ethic, efficiency, and elimination of waste and standardized best practices. In this process, Taylor introduced studies of measuring workers productivity, such as time studied; breaks down each job into component parts timing each part to determine the most efficient method of working and motion studies; timing each part to determine the most efficient method of working. Continues to be big contribution to management theory today. Student will describe personal application of the above theory (Taylor) Student will show knowledge of the “Management by Objectives” theory of leadership by Drucker HDF 290 A management theory that targets to improve performance of an organization by defining objectives that both managers and employees agree with. The theory states that if you have an input in setting goals or making actions for example then the participation will be better. There is a five-step process to MBO in which consist of setting organizational objectives, next, you cascade employees with objectives, monitor, and evaluate performance and finally, reward performance. MBO goals are suppose to S.M.A.R.T, Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Realistic and Time Bound. Student will describe personal application of the above theory (Drucker) Student will show knowledge of “Theory X and Theory Y” theory of leadership by MacGregor HDF 290 A theory created by Douglas McGregor in 1960. This theory is useful in Human Resources, Organization Behavior Analysis and Organizational Department and consists of human motivation and describes two different attitudes toward work motivation. The first theory, Theory X, assumes that employees are lazy and will avoid working as well, as they are only interested in the money and need close supervision. It continues by saying that employees have little to no ambition, avoid responsibility and need to be driven. It is based on an authoritarian style where threats of punishment occur. On the other hand the second theory, Theory Y consist of employees being ambitious, self-motivated and accept grater responsibility as well as exercise empowerment, creativity, self-govern and self-control. These theories help future generations understand human behavior, which is constantly changing. Student will describe personal application of the above theory (MacGregor) Student will show knowledge of the “Servant Leadership” theory of leadership by Greenleaf HDF 290 This theory is considered to be the most effective theory. A servant leader is effective when he/she gives attention to his or her follows and their needs. According to Greenleaf, a servant leader emphasizes on collaboration, trust, empathy and ethics. A servant leader should be a servant first before leading, he or she should want to serve better rather then gain more power. The assumption to this theory is if the leader pays attention to the follower’s desires then the followers will be more willingly to have a better performance. This theory is outlined to have ten principles, which are listening, empathy, healing, awareness, persuasion, conceptualization, foresight, stewardship, commitment to the growth of others, and building community. 28. Student will describe personal application of the above theory (Greenleaf) Student will show knowledge of the “Principle Centered Leadership” theory by Covey HDF 290 Steven Covey created this leadership theory and it is based on the servant leadership theory. Mr. Convey describes this theory as “if you focus on principles, you can empower everyone who understands those principles to act without constant monitoring, evaluating, correcting, or controlling”. There are eight characteristics that define the Principle Centered Leadership. The first one is they continue to learn, learning from their experience. Second one is service oriented where it states that life is a mission. Positive Energy, the third characteristic, which should consist of being cheerful and optimistic. Believing in others, the next trait, in which the leader should see the potential in others and help to achieve. The next one consists of leading a balanced life meaning you stay current with social events. See life as an adventure, synergistic and finally exercise self-renewal. Tis theory also consist of seven directives which are be proactive, begin with the end in mind, put first things first, think win-win, seek first to understand and then to be understood, synergies and sharpen the saw. This theory also promotes shared vision, creativity, interdependency, continued learning, emotional stability, servant leadership and super-supervision. 29. Student will describe personal application 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. Leadership Inventory Revised 8/30/2013 4 30. 31. 32. 33. 34. of the above theory (Covey) Student will show knowledge of the “14 Points / TQM” theory of leadership by Deming Student will describe personal application of the above theory (Deming) Student will show knowledge of the “Visionary Leadership” (now often cited as “Transformational Leadership”) theory by Sashkin Student will describe personal application of the above theory (Sashkin) Student will show knowledge of the “Individuals in Organizations” leadership theory by Argyris HDF 290 An American statistician by the name of W Edwards Deming invented the Total Quality Management (TQM). He set out 14 points for management in which he believed can save the US from industrial doom at the hands of the Japanese. These 14 points where the first sight of radical ideas but the key to understanding a number of them lies in Deming’s thoughts. The first one is “create constancy of purpose towards improvement meaning replace short-term effects into long-term effects. Next, “adopt the new philosophy” which intends to talk about the management should actually adopt his new philosophy; rather then only expect the workforce to do so. “Cease dependence in inspection, which means if variation is reduced then there is no need to inspect manufactured items for defects because there will not be any. As well as “move towards a single supplier for any one item, meaning that many suppliers mean variations between feedstock. “Improve constantly and forever come after that and suggest to constantly striving to reduce the variation. Next, “Institute leadership”, in this point Deming differentiates the difference between leadership and supervision. Then, “drive out fear”, where Deming sees management by fear as counter-productive in the long-term because it does not enable workers from acting in be half of the organization’s best interest. After that, “break down barriers between departments”, mean that each department serves not the management, but the other departments that use its outputs. The tenth point suggests that you “eliminate slogans”, it’s considered to be counterproductive to harass the workforce without improving the processes they use. Point eleven asks the “eliminate management by objectives”, which production targets encouraging the delivery of poorquality goods. Next, “remove barriers to pride of workmanship”, the less problems calls for a higher satisfaction rate. Then, “institute education and self-improvement”. And lastly, “the transformation is everyone’s job”. HDF 290 This theory came from the book called “Leadership That Matter” and was written by Michelle Sashkin. It consists of three unique ways in which it focuses on leadership behavior, leadership characteristic and the social context of leadership as well as the purpose of leadership which says that leaders not only provide “vision” but they also create conditions that allow followers to make meaning in their lives. This theory provide personal characteristics of a leader and specific leader behavior incorporated while being an effective leader as well. The Transformational leaders are visionary leader possess three characteristics which are self -confidence, the pro-social need for power and the complex thinking skills. This measures a leader ability to deal with complexity and future time spans. It acknowledges the important role played by the personal behaviors of the leader in shaping the culture of the organization. The purpose of this theory is to work to define shared values and belief. It enables followers to commit themselves to organizational goals and they help them to develop strategies for accomplishing those goals. This theory empowers to go beyond self-interest and often influences them to perform beyond expectations, both their own and their organization. Also it enables a culture of high-performance while at the same time making an organization a great place to work. Sashkin believes that every leader has the ability to be a better leader that what they are today. Acquiring this type of leadership has its perks like making your organization a better and rewarding place for everyone to work at. HDF 290 The father of organizational learning is considered to be Chris Argyris. This theory introduces the concept of the significance of individuals’ behavior and it impact on learning within an organization. Argyris debates that “ the manner in which people related to one another with an organization prevented them from questioning the reasons underlying problems which were often rooted in their own behavior. Changes made were superficial and the organization as a whole never learned from their mistakes” (PIckerd). He also believed that the definition of learning was flawed and breakdown the learning within organizations. He also states that the individuals are the key when they are acting in order to learn or when they are acting to produce a result. This theory is divided into two methods in which individuals use to dictate behavior. These theories are considered to be theories of action. The Leadership Inventory Revised 8/30/2013 5 first part is called espoused theory where individuals use words to express what it is we do or would others to think we do in a particular situation. The second part consists of theories-in-use, which are theories that govern the actual behavior of what we do in a particular situation. Argyris states that these theories are in tended to be tactic structures, they contain assumptions about self, others and environment. 35. 36. 37. 38. 39. 40. Student will describe personal application of the above theory (Argyris) Students will demonstrate knowledge of the “4 V’s” theory of leadership by Grace (Center for Ethical Leadership) HDF 290 The first thing that we have to do for this theory is define the definition of ethical leadership, ethical leadership is defined as “knowing your core values and having the courage to live them in all parts of your life n service of the common goods”. The four V’s model for the ethical leadership is a framework that supports internal beliefs and values with external behaviors and actions. The goal of this theory is to benefit the common good. The four V’s that make up this theory is values, virtue, voice, and vision. For values we need to understand our own individual. Assimilate our values with our decision- making. Next, we have vision, where this is the ability to frame our actions. We must picture what we should do. Voice, we should convey our visions to the others in a convincing way, the goal is that our will motivate others. And lastly, virtue, this is the idea that we become what we practice. W should strive to do what is right. The four V’s model also consists of three other subjects, which are polis, renewal and service. Service involves being connected with ones vision to their values. You exhibit your visions while doing your service. Next you have Polis, which comes about from the word politics. We need to voice our visions. Let the public know. Lastly we have the renewal part, which means that we must make sure that our voice, and values and actions are always balanced out. Student will describe personal application of the above theory (Grace) Student will show knowledge of the “Situational Leadership” theory by Hersey & Blanchard HDF 290 According to Dr. Paul Hersey, professor and author of “the Situational Leader” thinks that instead of using one style, a successful leader should change their style based on the maturity of the people they are leading. He also states that leaders should be able to place emphasis on the task and emphasis on the relationships with the people they are leading. This theory is made up of four main leadership styles: Telling, Selling, Participating and Delegating. The first style is telling which allows leaders to tell their people what to do and how to do it. As for selling, a leader should provide information and direction, but there’s more communicating with the followers. When it comes to participating, a leader should focus more on the relationship and less on direction. This leader works with the team and shares decision-making tasks. For the last style, delegating, the leader is opposite from a participating style, here you pass almost all of the responsibilities to the follows, while still monitoring but being less interactive with the team. The first two styles concept is getting the task done while the last two are about the ability of working independently. Hersey also states that knowing when to use each style depends primarily on the maturity level of a person or group. In this theory the maturity level is divided into four different levels. The first maturity level pertains to the bottom level of the scale. They lack the knowledge, skills or confidence to work alone and they need a constant nudge to complete a task. The second level involves a worker to have a slight willingness to take a task on but still don’t have the skills to complete it successfully. The next maturity level revolves on the followers being ready to complete the task but lack the confidence of being to complete it successfully. The fourth maturity level is having the ability to work on your own with very high confidents, skills and is fully committed to the work. Student will describe personal application of the above theory (Hersey & Blanchard) Student will show knowledge of the “Relational Leadership” model by Komives, McMahon & Lucas HDF 290 Relational Leadership is defined as a relational process people attempt to accomplish change or make a difference to benefit the common good. To be a successful relational leader you must also be inclusive and ethical. A rational leader should be an open-minded type of person. Having a relationship under this theory is the key to effectiveness. This theory comprises of five elements, which govern relationships between people who have united in order to bring a positive change, the five e components compose of purpose, inclusion, empowerment, process-oriented and ethical. The first Leadership Inventory Revised 8/30/2013 6 concept is purpose, which means having a commitment to a goal or activity. The individual’s ability to collaborate with one another and finding a common ground with others to establish a common vision. Next, you have inclusiveness where knowledge and understanding of one self and others and belief in fairness and equality. The third concept of this theory is empowerment, which means that the leadership is shared. All members of a group should assume responsibility of the group’s outcome. The group as a whole should be willing to participate and feel good contributing. The next concept, processoriented, includes on how the group conducts themselves as a group and how they accomplish the groups purpose. This concept is the planning and developing of the project. Finally, you have ethical; being ethical involves behavior driven by values or high standards. Make actions that benefit the group as a whole of just a single individual. 41. 42. 43. 44. 45. 46. 47. 48. 49. 50. 51. 52. 53. 54. 55. Student will describe personal application of the above theory (Komives et al) Student will show knowledge of the concept of constructivism HDF 290 A type of learning theory that explains human learning as an active attempt to construct meaning in the world around us. This theory believes that learning is more active and self-directed. Constructivism is divided into two types; accommodation and assimilation. The main concept of this theory is the individual’s desire and ability to learn. Students will describe personal examples of implementing constructivism Student will demonstrate knowledge of experiential learning in leadership development (Kolb) Student will describe personal application of experiential learning in leadership development (Kolb) Student will show knowledge of the “Social Change Model of Leadership Development” by Astin et al Student will describe personal application of the above theory (Astin et al) Students will demonstrate knowledge of the “Leadership Identity Development Model” by Komives et al Students will describe personal application of the above theory. (Komives et al) Students will demonstrate knowledge of the Strengths-Development Model by Hulme et al Student will describe personal application of the above theory (Hulme et al) Student will demonstrate knowledge of behavior theories of leadership from Michigan and Ohio State Student will describe personal application of the above theories (Michigan & Ohio State) Student will demonstrate knowledge of Charismatic leadership Student will describe personal application of the above theory Leadership Inventory Revised 8/30/2013 7 56. 57. 58. 59. 60. 61. 62. 63. 64. 65. 66. 67. Student will demonstrate knowledge of contingency approach to leadership by Fiedler Student will describe personal application of the above theory (Fiedler) Student will demonstrate knowledge of Path-Goal theory by House Student will describe personal application of the above theory (House) Student will demonstrate knowledge of Leader Member Exchange (LMX) theory Student will describe personal application of the above theory Student will demonstrate knowledge of Leadership Substitutes Theory Student will describe personal application of the above theory Student will demonstrate knowledge of Models of leader emergence Student will describe the impact of traits on leadership emergence and performance Student will demonstrate knowledge of Chaos approach to leadership by Wheatley Student will describe personal application of the above theory (Wheatley) Leadership Inventory Revised 8/30/2013 8 Outcome Category: Inclusive Leadership / Diversity and its Application to Leadership 68. 69. 70. 71. 72. 73. 74. 75. 76. 77. 78. 79. 80. 81. 82. 83. Outcome Target class Student will demonstrate how cultural anthropology / paradigms relate to leadership Student will describe personal example of using cultural anthropology / paradigms as a leader Student will demonstrate knowledge of the “Cycles of Socialization” (Harro) theory and its uses in leadership Students will demonstrate personal application of the “Cycles of Socialization” (Harro) Student will demonstrate knowledge of the “Cycles of Liberation” (Harro) theory and its uses in leadership Student will demonstrate personal application of the “Cycles of Liberation” (Harro) Student will demonstrate knowledge of the “Configuration of Power” (Franklin) and its relationship to leadership Student will demonstrate personal application of the “Configuration of Power” (Franklin) Student will demonstrate knowledge of racial identity development via the Cross, Helms or other models (Ferdman & Gallegos; Kim; Horse; Wijeyesinghe etc.) Student will demonstrate personal application of model(s) of racial identity development above Students will demonstrate knowledge of McIntosh’s theory of privilege and its relationship to leadership Student will demonstrate personal application of McIntosh’s theory Student will describe the differences and similarities of individual and institutional oppression and relationships to leadership Student will show knowledge of effective leadership as it relates to change agency Student will describe personal examples of being a change agent Student will create a personal code of URI 101 Additional Experiences Descriptive notes regarding learning and practice Vision, learning, service and sharing Leadership Inventory Revised 8/30/2013 9 84. 85. 86. 87. inclusive leadership Student will demonstrate knowledge of the “Model of Intercultural Sensitivity” by Bennett and its uses in leadership Students will demonstrate personal application of the “Model of Intercultural Sensitivity” by Bennett Student will demonstrate knowledge of the ally Action Continuum by Griffin & Harro Student will demonstrate personal application of the Action Continuum by Griffin & Harro Outcome Category: Critical Thinking Outcome 88. 89. 90. 91. 92. 93. 94. 95. 96. 97. Target class Additional Experiences Descriptive notes regarding learning and practice Student will show knowledge of principles of critical thinking (logic is used in this minor) Student will demonstrate proficiency of critical thinking Student will show knowledge of metaphorical analysis to critically analyze self and leadership situations Student will demonstrate proficiency of metaphorical analysis to critically analyze self and leadership situations Student will show knowledge of at least five decision making methods Student will describe personal examples of having used five decision making methods Student will show knowledge of at least five problem solving / conflict management methods, as well as understanding the roots of conflicts Student will describe personal examples of having used five problem solving / conflict management methods (if student has been trained in mediation, that information goes here) Student will describe what it means to analyze, criticize, synthesize and utilize information as a leader Student will demonstrate knowledge of leadership that is used in crisis Leadership Inventory Revised 8/30/2013 10 98. Student will describe examples of leadership in crisis situations Outcome Category: Interpersonal and Organizational Concepts & Skills Outcome 99. 100. 101. 102. 103. 104. 105. 106. 107. 108. 109. 110. 111. Student will demonstrate knowledge of active listening techniques Student will describe examples of using active listening skills Student will demonstrate functions of group communication by Hirokawa Student will describe personal application of functions of group communication (Hirokawa) Student will show knowledge of techniques regarding giving and accepting of feedback Student will describe examples of giving and accepting feedback. Target class Writing 104 Additional Experiences Descriptive notes regarding learning and practice In this class, we had a couple of writing assignment where we had to poof read someone in the classrooms work. The way the professor did it was she separated the people that know each other and placed them with a person that was unfamiliar to them. We were not allowed to simply read the students work we had to actually revise the paper as well as give them feedback on how the paper was structured, if we needed to add something else and comments about the paper. This was a little hard for me because I consider myself to not be a good writer, so making corrections on another persons paper when I know that my paper is far from being perfect felt kind of wrong to me. I was one of them kids that would read the student’s paper and tell them that I found nothing wrong with it. Student will demonstrate knowledge of facilitation and de-briefing techniques Student will demonstrate proficiency of facilitation and de-briefing techniques Student will demonstrate knowledge of framing and breaking the frame Student will demonstrate proficiency of framing and breaking the frame Student will show knowledge of organizing meetings / setting agendas / and leading meetings Student will describe personal examples of organizing meetings / setting agendas / leading meetings Student will show knowledge of Parliamentary Procedure Leadership Inventory Revised 8/30/2013 11 112. 113. 114. 115. 116. 117. 118. 119. 120. 121. 122. 123. 124. 125. 126. 127. 128. 129. 130. 131. 132. Student will show knowledge of techniques for working with difficult people Student will describe personal examples of using techniques to work effectively with difficult people Student will show knowledge of the stages of group development (Tuckman, Bennis or others) Student will describe personal examples of group development in use (Tuckman, Bennis or others). Student will show knowledge of group dynamics and group roles Student will describe personal examples of group dynamics and group roles Student will show knowledge of effective memberships skills in groups Student will describe personal examples of membership skills in use Student will show knowledge of the Challenge and Support theory by Sanford, and its relationship to organizations Student will describe personal examples of using the theory of Challenge and Support (Sanford) Student will show knowledge of the construction / elements of informative and persuasive speeches Student will demonstrate proficiency in informative and persuasive public speaking Student will show knowledge of planning and conducting interviews (as the interviewer) Student will describe personal examples of planning and conducting interviews (as the interviewer) Student will show knowledge of preparing for and effective answers in interviews (as the interviewee) Student will describe personal examples of preparing for and being interviewed Student will show knowledge of effective collaboration / coalition building Student will describe personal examples of working in collaboratives/coalitions Student will show knowledge of Intercultural communication considerations Student will demonstrate proficiency in intercultural communication Student will describe ways to maintain Leadership Inventory Revised 8/30/2013 12 133. 134. 135. 136. 137. 138. 139. 140. 141. 142. 143. accountability in leadership / member relationships Student will describe personal examples related to maintaining accountability as a leader Student will describe ways to build relationships between leaders and members Student will describe personal examples of building relationships with members as a leader Student will describe how credibility applies to leadership, as well as the characteristics and skills of a credible leader Student will describe personal examples of building, maintaining, and repairing his/her own credibility as a leader Student will describe ethical standards in influence Student will describe influence applies to leadership Student will describe principles of effective mentoring, as well as problems particular to the mentoring relationship Student will describe personal examples of mentoring and being mentored Student will describe principles of effective peer leadership, as well as problems particular to peer leadership Student will describe personal examples related to being a peer leader and being led by peers HDF 413 Leadership Inventory Revised 8/30/2013 13