BIO201 Crimando Vocab 6 BIO201 Nervous System I Vocabulary
advertisement

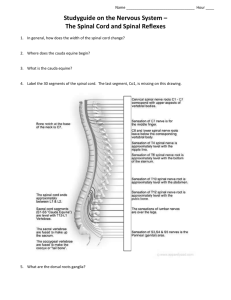
BIO201 Crimando Vocab 6 BIO201 Nervous System I Vocabulary Review Basic vocabulary is the foundational step in learning a new subject. This brief list touches many of the terms you will be learning in this section of the course. Use your notes from class, lecture powerpoints and text for references in answering these. Fill in the blanks as you take notes in class or read and study from the text. Central Nervous System (CNS) consists of the: ____________________ and ____________________ Fight-or-Flight division: ____________________ Calming and digestion-activating division: ____________________ Afferent neurons carry these types of signals: ____________________ Efferent neurons carry these types of signals: ____________________ Neurons that reside entirely within the CNS: ____________________ or ____________________ Neuron cell body: ____________________ or ____________________ Concentrated regions of rough endoplasmic reticulum: ____________________ Neuron processes that act as receivers: ____________________ Neuron process that acts as transmitter: ____________________ Junction between neuron and target cell: ____________________ Two-way movement of materials within an axon: ____________________ Supporting cells in the nervous system: ____________________ Cells in CNS that form myelin: ____________________ Small macrophages in CNS: ____________________ Epithelial cells in CNS that produce cerebrospinal fluid: ____________________ Cells that form blood-brain-barrier: ____________________ Cells in PNS that form myelin: ____________________ Protective cells in peripheral nerve ganglia: ____________________ Insulating layer of many membrane layers around neuron fiber: ____________________ Gaps or thin regions in myelin layer: ____________________ Value of the resting membrane potential on a “resting” neuron: ____________________ Cation more concentrated in extracellular fluid (ECF): ____________________ Cation more concentrated in intracellular fluid (ICF): ____________________ Ion channel that opens in response to chemical binding: ____________________ Ion channel that opens in response to local change in membrane voltage: ____________________ Short-range, non-perpetuating change in membrane potential: ____________________ Long-range, perpetuating change in membrane potential: ____________________ Change in membrane voltage shifting to more positive value: ____________________ or ____________________ Change in membrane voltage shifting to more negative value: ____________________ or ____________________ Membrane potential level at which voltage-gated Na+ channels open: ____________________ Period of time where no stimulus can elicit another action potential: ____________________ Period of time where stronger stimulus needed for another action potential: ____________________ “Jumping” conduction of action potential in myelinated fiber: ____________________ Post-synaptic potential making neuron more likely to fire: ____________________ Post-synaptic potential making neuron less likely to fire: ____________________ Ability of neurons to enhance communication pathways with increased use: ____________________ Presynaptic receptors used to clear synaptic cleft: ____________________ Enzyme that degrades acetylcholine: ____________________ Enzyme that degrades monoamine neurotransmitters: ____________________ Brain and spinal cord tissue composed of mostly neuronal cell bodies and dendrites: ____________ matter Brain and spinal cord tissue composed of mostly myelinated axons: ____________ matter Bundles of myelinated axons in the CNS: ____________________ Number of pairs of spinal nerves that exit spinal cord: ____________________ Specific area of skin supplying sensory signals to specific spinal nerves: ____________________ Tapered end of spinal cord: ____________________ Bundle of nerve roots in vertebral canal at caudal end of spinal cord: ____________________ Fibrous strand anchoring spinal cord and meninges into coccyx: ____________________ Weblike intersection and branching of several spinal nerves: ____________________ Set of membranes surrounding brain and spinal cord: ____________________ Outermost tough layer of meninges: ____________________ Space between outer layer of meninges and vertebrae: ____________________ Thin membrane and loose mesh of fibers deep to dura: ____________________ Meningeal space where cerebrospinal fluid is located: ____________________ Delicate membrane on surface of brain and spinal cord: ____________________ General structural appearance of gray matter in spinal cord: ____________________ Bundles of white matter in spinal cord: ____________________ or ____________________ Roots carrying afferent signals into spinal cord: ____________________ Roots carrying efferent signals out of spinal cord: ____________________ Bundle of sensory nerve cell bodies just outside spinal cord: ____________________ Sensory tracts in spinal cord: ____________________ Motor tracts in spinal cord: ____________________ Crossing-over of tracts from one side of spinal cord to other: ____________________ Pain perception: ____________________ Body position perception: ____________________ Ascending tract carrying pain, temp., pressure, itch, crude touch: ____________________ Ascending tract carrying body position, joint-tension signals: ____________________ “Gateway to Cortex” brain structure, sensory relation station: ____________________ Cerebral destination for somatosensory signals: ____________________ Location for upper motor neuron somas: ____________________ Location for lower motor neuron somas: ____________________ Demyelinating disease in CNS: ____________________ Degenerative disease of lower motor neurons with fibrosis in spinal cord: ____________________ Bundle of neuronal axons and connective tissue in PNS: ____________________ Cluster of neuronal cell bodies in PNS: ____________________ Stretch receptors in skeletal muscle: ____________________ Classic patellar-reflex is an example of this spinal reflex type: ____________________ Reflex that prevents excessive contraction of a muscle: ____________________ Spinal reflex activating motor-withdrawal responses: ____________________ or ____________________ Reflex activating motor extension responses on opposite side: ____________________ General term for reflex response on opposite of body from stimulus: ____________________ General term for reflex that activates antagonistic set of muscles: ____________________