Chp. 4b - Cisco Networking Academy
advertisement

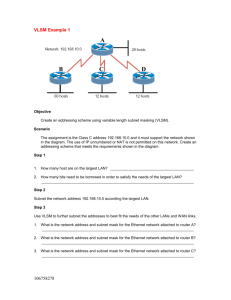
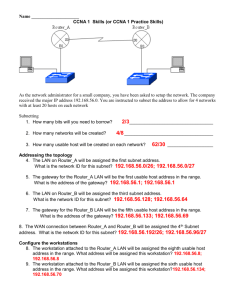
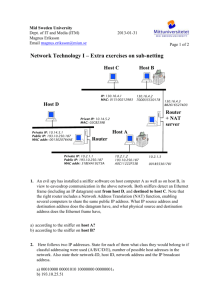
CCNA Discovery 2 Chp. 4 Review 1. What 3 needs arose from the explosive growth of networks in the 1980’s and 90’s? 2. Which RFC defines subnets? 3. When a router reads a subnet mask, bits set to to are read as part of the host ID. are read as part of the network ID, bits set 4. When subnetting, what 3 hierarchical levels exist in an IP Address? 5. What are the 4 characteristics of classful subnettting? 6. Why do all the subnets have to be the same size when using classful subnetting? 7. VLSM (variable length Subnet Masking) addressing allows an address space to be divided into . VLSM is accomplished by subnetting the . 8. In order for VLSM to be successful, routers must share as network addresses. information, as well 9. CIDR is a type of network addressing that identifies networks based on 10. CIDR is defined in RFC 11. CIDR enables ISPs to request addresses it requires. addresses based on the number of host 12. What is a supernet? 13. How are supernets useful? 14. When 2 routers are connected in a WAN link, there must be a separate the connection between them. Each router interface in this WAN link must have a in that subnet. assigned to 15. When a Router’s LAN interface is connected to a network or Subnet the router interface must have a in the same subnet as the devices connected to it. 16. Usually, the router interface is assigned either the available in the subnet. This assures consistency. or host address 4.3: NAT & PAT 1. What is NAT used for? 2. What are 4 advantages of NAT? 3. What are 3 disadvantages of using NAT? 4. Define these networking terms: a. Inside Local Network: b. Outside global network: c. Inside local address: d. Inside Global address: e. Outside Local address: f. Outside Global address: 5. List each of the addresses in this diagram as Inside Global, Outside Global, Inside Local, or Inside Global Destination Source : 6. How does Dynamic NAT translate inside local addresses to an inside Global address? 7. How does Static NAT translate inside local addresses to an inside Global address? 8. What is PAT? 9. What port numbers does PAT use to keep track of the different inside local addresses? 10. Why is PAT a more secure method of Address Translation? 11. What are 3 issues with using NAT? 12. What 3 solutions were created to help alleviate the problem of IPv4 address depletion? 13. IPv6 uses a bit address represented by hex digits separated by 14. IPv6 Addresses have a 3-part hierarchy –describe what each one signifies a. First 12 hex digits: b. 4 Hex digits: c. 16 Hex digits: 15. What are 5 improvements that IPv6 offers over IPv4?