Unit 9 Student Guided Notes Pulmonary and Systemic Circulation
advertisement

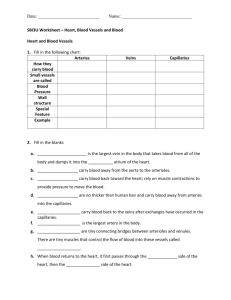
Unit 9 Student Guided Notes Pulmonary and Systemic Circulation Types of Blood Vessels Arteries: Function: ___________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________. Structure: ______________________ ______________________________. Location: Usually found deep along bones Veins: Function: _________________________ ______________________________________. Structure: ______________________ ______________________________. Location: Often on the surface surrounded by skeletal muscle. Capillaries: Function: _____________________ _______________________________________. Structure: Very thin walls (____________________). Location: ______________________; within a few cells of each other. Capillaries have __________________________ that can ______________ and ___________________ the vessel. If all capillary beds were open at one time, it would ___________________ the blood pressure. If all the capillary beds were __________________, it would increase blood pressure. Arterioles and Venules: All the features of arteries and veins apply to __________________ ____________________, but on a __________________ scale. Arterioles leading into a particular organ or region, are often equipped with sphincter muscles. When triggered, they can dilate or constrict to regulate ________________________, increasing or decreasing blood flow to that particular ____________________________. The term afferent arteriole means the ___________________ arteriole where efferent arteriole is the ______________________ arteriole Major Blood Vessels of the Body 1. Aorta: This is the major blood vessel carrying ____________________ blood _________ of the heart. It leaves the ______________________, loops over top of the heart creating the structure known as the _______________ and descends along the inside of the backbone. Function: Branches from this blood vessel _____________ __________________________. 2. Coronary Arteries and Veins: The very first branches off the Aorta are the Coronary arteries. These relatively small blood vessels can be seen on the surface of the heart. Function: Feeds the ___________________________. (The heart does not receive its nutrients from the blood that travels through it. The muscle is too dense and thick and the blood is traveling through it too hard and fast.) Coronary Vein takes the "______________________" back to the ______________. **Note that "spent blood" is the terminology used to describe blood that has delivered oxygen to the cells and picked up carbon dioxide. Therefore "spent blood" is low in oxygen and high in carbon dioxide** 3. Carotid Arteries: These branches off the aortic arch and take the blood to the ______________ including the ___________. Function: They are highly specialized in that they contain a number of different types of _____________ _________________: Chemoreceptors that ________ ______________, and Pressure Receptors that _____________________________________. These chemoreceptors help to maintain homeostasis. 4. Jugular Veins: The match for the Carotid Artery. They do not contain valves. Blood flow is through gravity. Function: They conduct blood out of the ______________________________________. 5. Subclavian Arteries and Veins: Also branch from the ______________. Travels under the ____________________. Function: Branch to feed the _____________ (brachial artery). Veins collect blood from the arms. 6. Mesenteric Arteries: These arteries branch off from the aorta as it travels _________________. They go to the intestines where they branch into capillaries that can be identified as villi. For the purpose of this course there is no corresponding _______________________. Function: Feeding the organs of the ___________________________ and picks up newly digested nutrients in the body. 7. Hepatic Portal Vein: Instead of a _______________________, it is called a ______________. Hepatic means liver; portal indicates that there is a capillary bed on both ends of it. Function: Brings ________________________________________________. 8. Hepatic Vein: Once the liver has done its thing to the blood, the blood must _____________________ ________________________. Function: Carries blood from the liver to the ________________________________. 9. Renal Arteries and Veins: The ______________________ branch off the dorsal aorta as it passes through the lumbar region of the body. Function: the _____________ take blood to the __________________________________ _____________________________________ _________________________ Vena Cava. 10. Iliac Arteries and Veins: When the __________________________ gets to the pelvic area. It branches into two Iliac Arteries, one goes down each leg. Off the ______________________ is another branch that feeds the upper leg. This is called the ___________________________. Function: To supply the legs with ______________________ and return ____________ _________________ to the ____________________________________. 11. Anterior (Superior) and Posterior (Inferior) Vena Cava: ______________________________________. Function: Large vein that collects all the "_________" __________ from smaller veins and carries it to the heart (right atrium). The _______________________ ___________ collects blood from the ____________ ______________, while the Posterior Vena Cava collects blood from the lower body. The Pulmonary and Systemic Circuits 12. Pulmonary Veins and Arteries: The Pulmonary Circuit is comprised of the ___________________________ and arteries that deal strictly with _______________________________. It is the only artery in the body that ____________________________________ and the only vein in the body that carries ____________________ blood. (remember the function of arteries is to carry blood away from the heart and the function of veins is to carry blood to the heart) Function: The arteries bring _______________________ blood from the right side of the heart to the lungs to get oxygen for the body, while the veins return _________________ blood from the lungs to the left atrium of the heart. Plumonary Circuit: Path that goes _____________________________. From right ventricle through the pulmonary trunk-->pulmonary arteries-->lung capillaries-->pulmonary veins-->left artium. Carries ___________________________ filled blood to lungs for cleaning. Returns ________________________________________________. Systemic Circuit: Path from ________________________________________________________ of heart. Carries _______________________ blood to the body tissues. Returns ___________________________________________________________. Summary of Systemic and Pulmonary Circulation Click on the Flash Video to enlarge Animation http://www.pbs.org/wnet/redgold/journey/circulation.swf Cross Sectional Area Cross sectional area of the blood vessels (sum of the cross sectional area of all blood vessels of one type) has a major effect on blood flow. ____________________________________________________ _____________________________________________. Velocity of the blood decreases from aorta to arteries to capillaries and increases in venules and veins. __________________________ _____________________________________________. Once the blood pressure is lost in the capillaries it can not be regained even though CSA of venules and veins increases. Can you answer these 3 questions? 1.____________________________________________ ______________________________________________ 2.____________________________________________ _____________________________________________ 3.____________________________________________ ______________________________________________ Now You Try Trace the path of blood around the body for the following: 1. From the head to the toe 2. From the arm to the liver 3. From the heart muscle to the kidney Fetal Circulation: Fetal systems have FOUR features not present in adult systems: 1. OVAL OPENING an opening between the _______________. it is covered by a _________________________ that acts like a valve. blood flows directly from the right atrium to the ______________________. ________________________________________ _________________, which do not work yet. 2. ARTERIAL DUCT a ______________________ between the Pulmonary Artery and the Aorta. Blood flows from the ____________________________ ___________________, again allowing blood to bypassing the lungs. 3. UMBILICAL ARTERY AND VEIN Umbilical ____________________________ (Carbon Dioxide and Urea) to the Placenta from the fetus. Umbilical Vein takes nutrients (Oxygen and Glucose and Amino Acids) to the ______________ from the ____________. 4. VENOUS DUCT a connection between the Umbilical Vein and the Vena Cava. blood coming from the ___________________________ _________________________________ through the venosus duct allowing ___________________________ ______________________________. http://www.indiana.edu/~anat550/cvanim/fetcirc/fetcirc.html Components of Blood A. Plasma: _______________________________ B. Formed Elements: 45% o o o FEATURE Erythrocytes (Red Blood Cells) ___________________________ (White Blood Cells) ___________________________ (Platelets) RED BLOOD CELLS WHITE BLOOD CELLS SHAPE PLATLETS Variable, Amoeboid FUNCTION Blood Clotting ORIGIN Bone Marrow and Lymphoid Tissue ALSO CALLED Thrombocytes NAME A. Water (90%) B. Plasma Proteins Albumen, Fibrinogen, Globulins FUNCTION Blood Volume Transport of Cells and Materials Helps maintain Osmotic pressure in blood. Transports, Blood Clotting, Infection Fighting C. Gases Oxygen, Carbon Dioxide For respiration, Waste D. Nutrients A.A. Clucose, Fatty Acids, Glycerol E. Salts F. Wastes Energy Souce - raw materials for the body Osmotic Pressure Waste production of Cellular Reaction Helps in Metabolism Blood Cells Shape, Function and Origin of Blood Cells 1. Red Blood Cells - Erythrocytes Live about _____________ days. Produced in _______________ Bone Marrow (In skull, ribs, vertebrae, and long bones.) Myeloid stem cells form RBC. These stem cells are called Erythroblasts. _____________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________. Produces about _______________________________________________________. RBC contains a protein called _______________________________________. Hemoglobin contains iron (gives blood its ______________________________). Picks up _______________________ in the lungs (cooler blood) It combines with oxygen in the lungs and releases it in the _______________________ tissues. Approximately ________________________________________ hemoglobin molecules in one RBC. If hemoglobin was not packaged up in RBC, ___________________would leak out of circulatory system. RBC allow the blood to remain liquid so the heart does not have to work as hard. Destroyed in the ________________________________________________________. http://www.wisc-online.com/objects/ViewObject.aspx?ID=AP14604 LUNGS BODY Cooler less acidic Warmer more acidic Causes Hemoglobin Causes Hemoglobin (HG) to pick up oxygen (HG) to drop off oxygen 2. White Blood Cells - Leukocytes Larger than ___________ They have ______________________ (RBC do not) less numerous than RBC (700:1) Do not have a definite shape. Function: Fights against ______________________________ __________________________ __________________________________________________ http://www.wisc-online.com/objects/ViewObject.aspx?ID=AP14704 3. Platelets - (Thrombocytes) Produce _______________________________________. Broken fragments of larger cells. Very important role in ________________________. o Blood Clotting - Need three things in blood 1. __________________________ 2. __________________________ 3. __________________________ Platelets clump at the site of the "____________" and __________________________. The platelets and the injured tissue together release an ___________________ called _____________________. Thrombolplastin converts a blood protein (prothrombin) (produced by the liver) to a new substance called _________________. Calcium is needed for this to occur. Prothrombin (activator protein) is made up of Potassium. If potassium is missing from the diet, it can cause _________________________ to occur. Thrombin acts as an ___________ and breaks the ends off another blood protein called _____________. (also produced by the liver) Fibrinogen is then converted into __________________. Fibrin has sticky ends and forms a _________ or network over the leak. Blood cells get _____________________________________. Fibrin clot is only _____________________. As soon as the blood vessel repair is initiated, and enzyme called _____________________________________________. Blood Types Blood Group Proteins on Red Blood Cells (Antigen) A A B B AB A AND B O NONE Clumping Chemicals in Plasma (Antibody) Can Accept Transfusions From Group(s) Identify Blood Types Find a "bed-side blood type test" (SeraFoil(tm) or similar). If you or someone you know happens to work in a medical setting, see if you can get your hands on one of these tests. 1. Dispense one drop of your blood to each field on the test card. Use a sterilized needle. The fields contain antibodies, which will provoke a reaction with antigens on your red blood cells. 2. Use a new toothpick for each field to mix the blood with the impregnation, creating about a dime-sized smear. o o o o If you have blood type A, clumping will appear in following fields: anti-A If you have blood type B, clumping will appear in following fields: anti-B If you have blood type AB, clumping will appear in fields anti-A, anti-B If you have blood type O, no clumping will appear. Rhesus Factor Red Blood cells may have another antigen called antigen D. This antigen is know as the ___________________. This distinguishes blood as being RH+ or RH-. Therefore there are 8 possible blood types. If mother is RH- and father is RH+ then baby has a chance of being RH+. This could be a concern. RH factor plays a role in childbirth. If _________ mother is carrying a RH+ baby then the situation has to be monitored. If the baby's blood comes in contact with mom's the antigen D in the baby's blood would be perceived as foreign and mother's immune system would try and destroy the baby's Red blood cell by producing antibody D. This is know as __________________________________________________. Mother and child would be fine, but there may be a problem with the next birth. If second baby is RH+ then _____________________________ (clumping of the blood) would occur and the baby will be in trouble. This is why doctors would strongly suggest mothers not to have more children after the first RH+ baby. It still has to be monitored today, but ____________________ (an enzyme) can be injected into Mom, which eliminates antibody D. Lymphatic System Functions of the Lymphatic Sysytem: 1. Takes excess tissue fluid and sends it to the _________________________________. The Lymphatic System joins the _____________________ at the subclavian veins. 2. Products of fat digestion are ____________________ _______________, which lead to the Lymph Vessels and ________________. 3. Lymph Nodes produce ______________________. (A type of White Blood Cell) 4. Lymph Nodes act as __________________________ __________________. (helps to purify the body fluids) Examples: Spleen: Largest lump of Lymphatic Tissue. Produces _________________________________________________. If your blood pressure is high, it stores blood so that ___________________________ ___________________________. If your blood pressure is low, it ____________________________________________ _____________________________________________, so that blood pressure rises. Thymus Gland: Bi-lobed structure which is important in the maturing of some Lymphocytes. Becomes smaller with age. Tonsils and Appendix: Also contain Lymphoid Tissue. Thought to help remove ________________________________________________. Lymphatic Tissue: Produce __________________________________________________________. Structures in the Lymphatic System Lymph Vessels: Similar to veins, but fluids only travel in one direction. Contain lymph veins and capillaries, but NO lymph Arteries. Lymph Nodes: Small oval or round tissues which ____________________________ and __________ __________________________. Lacteals: Blind sacs in villi of Digestive System which __________________________________. http://www.umm.edu/patiented/articles/lymph_nodes_animation_000486.htm Infection Fighting - Inflammatory Response 1. Attacks foreign substance (_______________________________). Monocytes and Neutrophils engulf the bacteria or viruses in ______________________ fashion (Phagocytosis). These WBC are able to __________________ to the site of the infection through the capillary network. Dead tissue, cells, bacteria, dead and living neutrophils all together make up _________________. 2. Lymphocytes produce _________________________. Each antibody fights a specific antigen (foreign protein). Antigen + Antibody --> Inactive complex. Antigens are proteins found in the ___________________________________ and it is the type of protein found that determines the type of blood. Antibodies are proteins that ___________________ unwanted proteins which results in agglutination. Capillary Tissue Fluid Exchange ________________ is oxygenated as it passes through ______________________. Oxygen (higher in concentration in the inhaled air) ____________________ through the thin walled tissues of the lung to capillaries and into the blood where it ___________________________ (the iron containing protein that is part of the RBC). A single hemoglobin molecule has _________________________________ for oxygen and is called ______________________ when transporting oxygen. The blood reaches ______________ _____________________________ ___________ where blood pressure _________________. Nutrients (products of digestion) and oxygen _____________________________ __________________. The larger particles in blood stay where they are because they are too big to get out. Because of these large molecules, the blood is said to be ___________ to the tissues. As a result, the water from the tissues is drawn back into the _______________ of the capillary bed. When the fluid returns it carries __________________________________ ________________ with it. Blood pressure on arteriole side of the capillary bed is _____________________________ _______________________ and will try and push substances such as _____________________________ _____________________________ out of blood into the tissues of the body. Blood pressure on the venuole side of capillary is _________________ ___________________________ and therefore wastes such as ________________________ ______________________________ are forced from the tissues of the body into the blood. Click on the Flash Video to enlarge Animation http://msjensen.cehd.umn.edu/1135/Links/Animations/Flash/0029-swf_fluid_exchange.swf