Hominoid Skull Lab new
advertisement

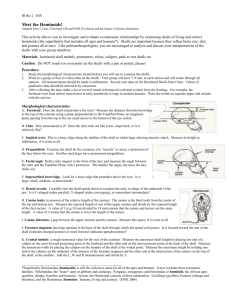
Upward Bound Math/Science 2010 Mr. McDowell Name: HOMINOID SKULL COMPARISON Introduction: In this activity you will make detailed observations and measurements of skull casts of seven modern and extinct hominoids. You will then use your data to determine if the extinct hominoids are more ape-like or more human-like in appearance. Your data will also provide a basis for drawing some conclusions about patterns of hominoid evolution. Materials per class: 1 skull cast of each of the following: Homo sapiens (modern human), Pan troglodytes (modern chimpanzee), (Gorilla gorilla (modern gorilla), Homo neanderthalensis Neanderthal), Homo erectus, Australopithecus boisei, and Australopithecus afarensis Materials per team: 1 metric ruler 1 protractor 1 caliper Procedure: 1. Your team will move from station-to-station as you examine the skull casts. At each station you will find a skull, metric ruler, protractor, and caliper. A few “rules” should be followed: Do not make pencil or pen marks on the skulls. Be careful with the skulls. They are expensive reproductions that are breakable. Be sure to take turns in making the measurements. Measure in millimeters (mm). Round off to whole numbers. 2. Complete the “Hominoid Skull Comparison Data Table”, as you move from station-to-station. Refer to the “Hominoid Comparison Checklist” for a description of each hominoid characteristic you observe. 3. Using observations and data from your completed “Hominoid Skull Comparison Data Table”, answer the analysis question on the “Analysis of Hominoid Skulls” chart. HOMINOID SKULL COMPARISON CHECKLIST 1. FOREHEAD: Does the forehead (frontal bone) look more vertical or does it slope backward? 2. CHIN: Does the chin stick out or does it recede back? 3. SAGITTAL CREST: A sagittal crest is a bony ridge that runs from front to rear on top of the cranium. Is it small, medium, large, or absent? 4. FACIAL PROGNATHISM: How much does the snout protrude when looking at the skull from the side? Is the protrusion large, medium, small or absent? 5. BROWRIDGE: The brow ridge is a heavy mass of bone directly over the eye orbits. Rate it large, small, medium. 6. DENTAL ARCADE: This refers to the shape of the arrangement of the teeth in the jaw when looking directly at the chewing surface of the teeth. Does the arrangement form a parabolic (rounded) shape with a relatively continuous outward curvature or is the arrangement rectangular with the premolars and molars in parallel rows? a = incisors b = canines c = premolars d = molars Parallel Arcade Parabolic Arcade 7. CANINE TOOTH: What is the length in millimeters of the exposed part of the upper canine tooth? 8. DENTAL FORMULA: Record the number of incisors, canines, premolars and molars present in the upper jaw. (ICPM) 9. CANINE DIASTEMA: Is there a gap present on the upper jaw between the canines and incisors? 10. ANGLE OF INCISOR: Do the incisors rise vertically from the lower jaw or do they slant out? 11. FORAMEN MAGNUM: The foramen magnum is a large opening in the back or bottom of the skull through which the spinal cord enters the cranium. Determine if it is more to the rear or towards the bottom of the skull. 12. WIDTH OF CRANIUM: Use the caliper and ruler to determine the maximum width of the brain case. Measure from temple-to-temple and record your answer in millimeters. 13. LENGTH OF CRANIUM: Use the caliper and ruler to determine the maximum length of the brain case. Measure from the forehead to the back of the skull. 14. FACIAL SLOPE: Use the protractor to measure the angle make by the face and the upper jaw when viewed from the side. Angle of facial slope Length of cranium Width of cranium HOMINOID SKULL COMPARISON DATA TABLE FEATURES A Gorilla gorilla Gorilla Modern B Pan troglodytes Chimpanzee Modern C Homo sapiens Human D Homo Neanderthalensis Neanderthal E Homo erectus F Australopithecus boisei G Australopithecus afarensis Modern 30,000 YA .4 -.5 MYA 1.8 MYA 2.9-3.6 MYA France 1908 China 1920’s Tanzania 1959 Africa 1975 Age of Specimen Location and Date of Fossil Discovery 1.Forehead: more vertical or slopes back 2.Chin: sticks out or recedes back 3.Sagittal Crest: large, small medium or absent 4.Facial Prognathism: (snout protrusion) large, small, medium, absent 5.Browridge: large, small medium 6.Dental Arcade: rows of molars parallel or parabolic 7.Canine Tooth: length of exposed upper canine tooth in mm 8.Dental Formula: # of incisors-canine-premolarsmolars in upper jaw (ICPM) 9.Canine Diastema: gap between upper incisors and canines present or absent 10.Angle of Incisor: vertical or slanted out 11.Foramen Magnum: towards rear or underneath 12.Width of Cranium: maximum width of brain case in mm 13.Length of Cranium: maximum length of brain case in mm 14. Facial Slope: the angle made by the face and the upper jaw viewed from side ANALYSIS OF HOMINOID SKULLS What evidence indicates that modern humans and the extinct hominids you examined evolved from a common ancestor? List and Discuss several SPECIFIC pieces of anatomical evidence that support your answer. Explain the significance of each piece of evidence. In other words, what function does the anatomical feature have, and how has that function changed as humans evolved? How does the shape and location of the anatomical feature support your answer?