UNIT - V - National College
advertisement
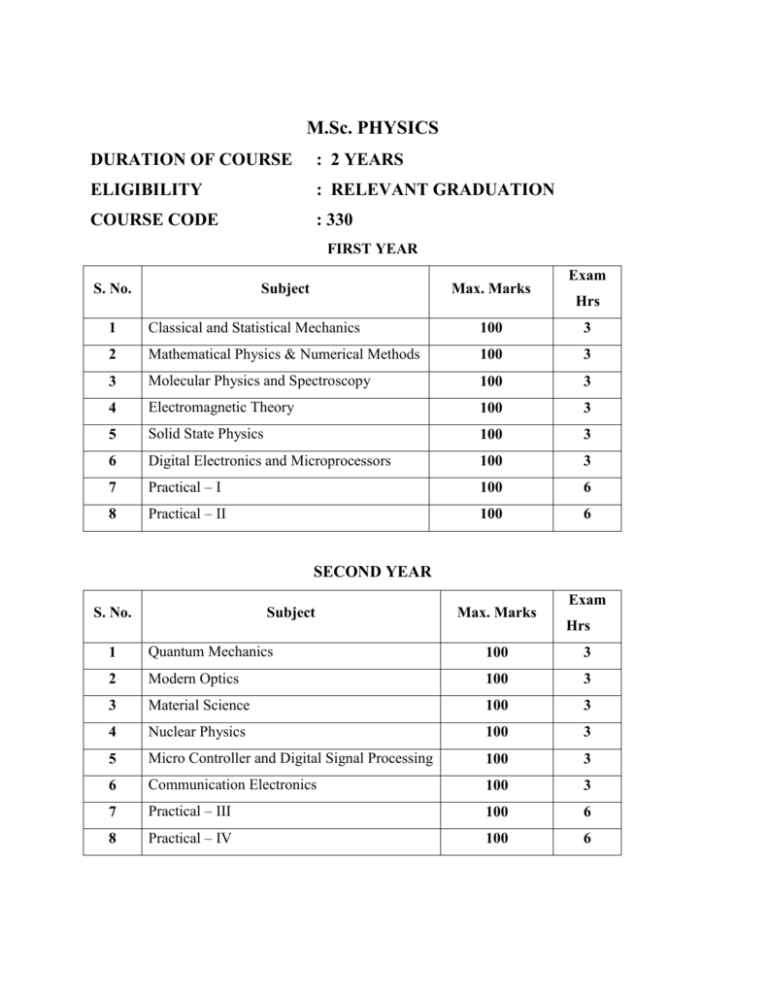
M.Sc. PHYSICS DURATION OF COURSE : 2 YEARS ELIGIBILITY : RELEVANT GRADUATION COURSE CODE : 330 FIRST YEAR S. No. Subject Max. Marks Exam Hrs 1 Classical and Statistical Mechanics 100 3 2 Mathematical Physics & Numerical Methods 100 3 3 Molecular Physics and Spectroscopy 100 3 4 Electromagnetic Theory 100 3 5 Solid State Physics 100 3 6 Digital Electronics and Microprocessors 100 3 7 Practical – I 100 6 8 Practical – II 100 6 SECOND YEAR S. No. Subject Max. Marks Exam Hrs 1 Quantum Mechanics 100 3 2 Modern Optics 100 3 3 Material Science 100 3 4 Nuclear Physics 100 3 5 Micro Controller and Digital Signal Processing 100 3 6 Communication Electronics 100 3 7 Practical – III 100 6 8 Practical – IV 100 6 SYLLABUS FIRST YEAR Paper – 1 CLASSICAL MECHANICS AND STATISTICAL MECHANICS A. Classical mechanics UNIT – I : ELEMENTARY PRINCIPLES D’ Alembert’s principles – Langrange’s equation – Hamilton’s Equation – Langragian and Hamiltonian. TWO BODY CENTRAL FORCE PROBLEM Equations of motion and first integrals – Kepler’s laws – Scattering by Central Potential – Transformation from centre of mass to laboratory frame. SPECIAL RELATIVITY IN CLASSICAL MECHANICS Relativistic Langrarian and Hamiltonian for a particle – space – time and energy – momentum four vectors – Centre of mass system for relativistic particles – invariance of maxwells equations. UNIT – II: KINEMATICS OF ROTATION Orthogonal transformation – Euler poles – rotating frames of reference and coriolis force. MECHANICS OF RIGID BODIES Angular momentum and kinetic energy – moment of inertia – Euler’s equations of motion. Torgue Free mogiton – motion of a symmetrical top under gavity. UNIT – III CANONICAL TRANSFORMATIIONS Canonical transformations and their generators – Simple examples – Poisson brackets. HAMILTON JACOB THEORY Hamilton – Jacobi equations – Action angle variables – Application to the kepler problem. SMALL OSCILLAIONS Formulation of the problem – Transformation to normal co-ordinate – Linear triatomic molecule. B. Statistical mechanics UNIT – IV THERMODYNAMICS Laws of thermodynamics – Entropy, free energy, thermodynamic potentials, phase equilibrium – Gibb’s phase rule – phase transitions and Ehrenfest’s classification – Third law of thermodynamics. CLASSICAL STATISTICAL MECHANICS Postulates – Liouville’s theorem – Micro canonical, Canonical and grand canonical examples, partition function and entropy of ideal gas – Gibbs paradox. NON IDEAL GAS Virial expansion – Derivation of Vander Waal’s equation using two particle short range interaction. DENSITY OPERATOR AND QUANTUM STATISTICAL MECHANICS Liouville’s equation – Postulates of quantum statistical mechanics – Bose – Einstein, Fermi – Dirac distributions. UNIT – V IDEAL BIST GAS Equation of state – Free electron gas in metals – heat capacity – Pauli’s paramagnetism – Thermionic emission. Reference: 1. H. Goldstein - Classical Mechanics 2. T.N.B. Kibble - Classical Mechanics 3. L.D. Landau and E.M. Lifshitz - Mechanics 4. K.R. Symon - Mechanics 5. J.L. Synage and B.A. Griffith - Principles of Classical Mechanics. 6. L.D. Landau and E.M. Lifshitz - Statistical Mechanics 7. B.K. Agarwal and M.Eisner - Statistical Mechanics Wiley Eastern, 1988. 8. Takwal - Classical Mechanics 9. Gupta & Kumar - Classical Mechanics 10. Satya Prakash - Classical Mechanics (TMH). Paper – 2 MATHEMATICAL PHYSICS & NUMERICAL METHOD UNIT – I Differential Equations and spatial function – Second order differential equation – series solution – generating functions – Rodrigue’s formula. Recurrence relation and orthogonally property for Bessel, Legendre. UNIT – II COMPLEX VARIABLE Functions of a complex Variable – analytic functions – Cauchy Reimann Conditions multi valued functions and branch points – Cachy’s integral theorem and formula. UNIT – III LAPLACE AND FOURIER TRANSFORMS Laplace Transforms – inverse Laplace transform application to differential and integral equation. FOURIER TRANSFORM Fourier Transform and integral theorem convolution theorem. UNIT – IV CURVE FITTING Principles of lest Squares – fitting a straight line, Para bell, exponential curve, curve of a form Y=axb and Y=abx. THEORETICAL DISTRIBUTION: Binomial distribution – formula for mean – Standard deviation – Poisson distribution – formula for mean, standard deviation moments Normal distribution - formula for mean, Standard deviation. UNIT – V SOLUTIONS OF NUMERICAL, ALGEBRIC, TRANSCENDENTAL AND DIFFERENTIAL EQUATION: Picard’s method of successive approximations - Newton – Rephson method – Euler’s method – modified Euler’s method – Runge – Kutta method (Second and third order only). Gauss elimination method. Lagrange’s interperation formula for – unequal intervals Trapezoidal rule, Simpson’s (1/3) and (1/8) rules. Reference: 1. Mathematical Physics – B.D. Gupta. 2. Mathematical Physics – Rajput. 3. Mathematical Physics – B.K. Das. 4. Special Functions – W.W. Bell. 5. Grewal B.Setal – Numerical methods in Engineering and Science – Khanna Publication. 6. Venkataraman. M.K. – Numerical methods of Science and engineering – The National Publishing Company, Chennai. Paper – 3 MOLECULAR PHYSICS & SPECTROSCOPY UNIT – I Symmetric of poly molecules – Calculation of normal modes for Raman and IR activity Czr and C3r point groups by group theoretical considerations - Calculation of F and G matrices – Normal co-ordinate analysis for H2o and NH3 and molecules. UNIT – II Electronic spectra of molecules : Born openheim approximation – vibrational structure of electronic transitions – Intensity of vibrational electronic spectra – Frank – Condor Principle – Chemical analysis by electronic spectroscopy. UNIT – III Constant deviation spectrometer – Raman effect – Characteristics of Raman lines – molecule structure – theory of lasers – types oflasers – production of COZ laser, semiconductor laser & He-Ne laser.. and application of laser. UNIT – IV NQR spectroscopy – Quadrapole Hamiltonian Theory – Energy Levels for molecules of axial symmetry – experimiental detection – super registrative oscillator – Continous wave osuvillator – Mossbauer spectroscopy – Experiment. UNIT – V Theory of NMR spectroscopy – Block equation – Relaxation process – Structural analysis – Single Coil & double coil spectrometers – NMR in liquids – ESR spectroscopy – Hyperfine structure – applications. Reference: 1. Ban well C.N – Fundamental of Molecular spectroscopy. 2. B.P. Straughen and S. Walkar – Spectroscopy. Paper – 4 ELECTROMAGNETIC THEORY UNIT – I Electrostatics : Mechanical stress on unit area of a charges conductor – application to electro field soap bubble – potential energy. Stored in unit volume of a medicine surrounding a charged body. UNIT – II Magneticstatics : Bio-Sanart Law – Ampere’s law – Magnetic vector potentials and magnetic field of a localized current distribution – Magnetic moment, force and torque on a current distribution in an external field – Magnetostatic field in macroscopic media – Boundary conditions – Uniformly magnetized sphere. UNIT – III Maxwell equations :- Fardqya law of induction – Maxwell displacement current – Maxwell equations – Wave equations and plane wave solutions – Coulmb and Lorentz gauges – Poynthing theorem – Conservation laws for a system of charges. UNIT – IV Lagrangian and Hamiltonian for a relativistic field – motion in uniform staticmagnetic field – Particle drift in non-uniform – Correction to Langrangian for interacting charged particles. UNIT – V Plane waves in non-conducting refraction medium – Propagation of waves in a rectangular wave guide. Reference: 1. J.D. Jackson, Johnwiley – Classical Electrodynamics. 2. D. Griffith – Introduction to Electrodynamics. Paper – 5 SOLID STATE PHYSICS UNIT – I Crystal Lattices : - Space lattices – lattice plans & Miller indices – formulation of Bagg and Von Law – Equivalance of Bragg & Von law formulation – geometrical structure factor and Atomic form of factor Ionic crystals – Electrostatic or Madelung energy – Madelung constant – Metal crystals – Hydrogen bond crystals. UNIT – II Lattice Dynamics : - Monoatomic lattices – Brillouim Zones – Group and phase velocity – lattice with 2 atoms per primitive cell – quantization of latticevobrations – phonon momentum – lattice heat capacity. UNIT – III Free electron theory : Drude theory metals – Hall effect – Fermi electron gs in 3D – Heat capacity – Non equilibrium distribution function – Bottzman transport equation – electrical thermal conduction – wiedmann – Franz law – de Hass Van Alphen effect – Oscillatory Phenomenon and Landaw levels. UNIT – IV Magnetic properties : - Quantum theory of Para magnetism – rare earth ions – Hunds Rule – Iron group ions – Paramagnetic Cooling – demagnetization – ferromagnetism – Quantum theory anti symmetric Wave function and exchange integral – Heisenberg interpolation of wises field – Ferromagnetic spin waves – curie’s law. UNIT – V Modern engineering and new materials : - Polymers – Ceramics – Super strong materials – Nuclear Engineering materials – Nuclear glasses – optical materials – Materials for optical sources and – dectors – Biomaterials conductors. Reference: 1. C.Kittel – Introduction to solid state physics. 2. Arumugam M. – Material Science. 3. Puri and Babber – Solid state Physics. Paper – 6 DIGITAL ELECTRONICS AND MICROPROCESSOR UNIT – I Integrated circuits – TTL and MOS logic circuits – Gating Networks Logic design: Flip – Flops – Transfer circuits – Clocks – shift registers – Counters – State diagrams and State tables – Magnitude comparator – Programmable Arrays of Logic cells. UNIT – II Elements of ALU Design and implementation of Binary Address (Half and Full) and Subtractors – BCD Adder – Multiplexer – encoder – decoder – Floating point number systems – Arithmetic operations with Floating point numbers. UNIT – III Input – output Interface modules – I / O versus Memory Bus – Isolated versus memory – mapped I / O – Asynchronous Data Transfer – Priority Interrupt – Direct Memory Access (DMA) – Input Output Processor (IOP) : CPU – IOP communication – Memory Organization : Memory Hierarchy – Main memory – Auxiliary Memory – Associative memory – Cache memory - Virtual memory. UNIT – IV Microcomputers, Microprocessor and Assembly Language – Microprocessor Architecture and Microcomputer systems: Micro processor architecture and its operations – Memory – Input and Output – The 8085 MPL – 8085 based Micro computer – Memory Interfacing. UNIT – V The 8085 programming Model – Addressing Techniques – 8085 Instruction – Code conversion – BCD arithmetic operations. PRACTICALS – 2 1. Study of Logic Gates – Discrete version & IC version: AND, OR, NOT, NAND, NOR Gates – To construct and verify the Truth Tables. 2. Karnaugh’s Reduction Technique – To find the simplified logic circuits for the given output equation. 3. Study of Half Adder and Full Adder circuits – To Construct and verify the Truth Table. 4. Study of Shift Registers using IC’s. 5. Study of Counters. 6. Study of ROM chips 7. Study of RAM chips 8. Study of Intel 8085 Microprocessors : Performing simple exercises : a) Addition b) Subtraction c) Multiplication d) Division of Decimal Numbers e) Picking up the Largest and Smallest number in the given set. f) BCD to Binary and Binary to BCD Conversions. g) HEX to Decimal and Decimal to HEX Conversions. Text Books: 1. Digital Computer Fundamentals – Thomas C. Bartee, T.M.H. 6th edition 1991. 2. Computer System Architecture – M. Morris Mano, PHI, 3rd edition. 3. Microprocessor Architecture, Programming and Applications with the 8085/8080 A Ramesh S. Gaonkar, Wiley Eastern Ltd. Reference: 1. Introduction to Micrprocessor – A.P. Mathur, T.M.H. 1990. 2. Microprocessors and interfacing – Programming and Hardware – Douglas V. Hall, TMH, 1997. SECOND YEAR Paper – 7 QUANTUM MECHANICS – I UNIT – I : FORMATION OF QUANTUM MECHANICS Schrödinger equation for a free particle – statistical interpretation – conditions on the wave equation – operator, formalism – Linear operators – Self ad joint operations – expectation value – Eigen values and Eigen functions – Orthonormality – The uncertainty relation – illustration experiments (diffraction of an electron beam by a long narrow slit, position of electron under ray microscope). One dimensional problems : Particle in a central potential and particle in a periodic potential – Hydrogen atom – Reduction of two body Hamiltonian – hudrogenie eigon functions and spectra – Normal Zeeman effect of Hydrogenic atoms. UNIT – II : APPROXIMATE EVALUATION OF EIGEN VALUES AND EIGEN FUNCTIONS FOR DISCRETE LEVELS Perturbation theory in non-degenerate cases – Application to ground state of an harmonic oscillator and stark effect in Hydrogen – variation method – application to ground state of Helium atom – WKB approximation. UNIT – III : ANGULAR MOMENTUM Communication rules for Angular Momentum. Operators – Eigen value spectrum Raising and Lowering operators – Matrix representation of Angular Momentum Spin Matrices and Wave functions – Combination of two Angular Momenta – Clebsch – Gordon co-efficient. UNIT – VI : EQUATION OF MOTION Schrodinger picture – wave equation – stationary states – Heisenberg picture – correspondence with classical mechanics – The Interaction picture – Representation theory: Basis in function space – momentum and configuration representations – Direec’s Ket and Bra Vector Notation – Matric – representation – an example : Harmonic Ocillator – Quantum conditions and their variance using matrix mechanics. UNIT – V : PERTURBATION THEORY Perturbation theory, First and Second order transitions under constant perturbation – conservation of energy – application to potential scattering and inelastic collisions – Harmonic perturbations – Adiabatic and sudden approximations. Books for Study : 1. Quantum Mechanics – Theory and Applications by A.K. Ghatak & Lokanathan. 2. A text book of Quantum mechanics – Mathews & Venkatesan. 3. Quantum mechanics – Chatwal & Anand. 4. Quantum mechanics – Satya Reference: 1.Quantum Mechanics – Leonand Sehift. 2. Quantum Mechanics – P.T. Mathews. 3. Quantum Mechanics – Pauling & Wilson. 4. Fundamental principles of quantum mechanics with Elementary qpplications Edwin C. Kemble.. Paper – 8 MODERN OPTICS Unit 1 Geometrical optics: Convex lens- Principal focus and focal planes- principal points and planes- nodal points and planes- Newton’s formula for a convex lens system- Aberrations in lenses and optical instruments- Spherical aberration in lenses –methods of reducing spherical aberration-aplanatic points in lenses-condition for minimum spherical aberration in the case of two lenses separated by a distance- chromatics aberration in lenses- condition for achromatism of two lenses in contact and out of contact- Huygens and Rams dens eyepieces- construction and comparison. Unit 2 Fresnels biprism- determination of wavelength of light and thickness of thin sheet of transparent material- interference in thin films due to reflected light – colours of thin filmsAir- Wedge method of determination of diameter of wire- test for optical flatness- Newton’s rings- experimental determination of refractive index of the material of the lens- and a given liquid – Michel sons interferometer – determination of wavelength and thickness of a mica sheet. Unit 3 Diffraction – Fresnels explanation for rectilinear propagation of light- zone plateFresnels diffraction at a straight edge- Fraunhoffer diffraction at a single slit, double slit and N Slits- plane diffraction grating – wavelength determination- resolving power- Rayleighs criterion- resolving power of telescope, microscope, prism, grating-comparison of prism and grating spectra. Polarization-Huygens explanation of double refraction in uni-axial crystalspolarizing prisms- quarter and half wave plates- production and detection of a plane, circularly and elliptically polarized light- optical activity- specific rotatory power-Fresnels explanation- SP. Rotatory power by Laurent half- shade Polarimeter. Unit 5 Non-linear optics: history of fiber optics- fiber characteristics and classification mode theory of fibers- transverse mode and hybrid mode-linearly polarized mode-single mode fiber- multimode fiber- fiber Losses-absorption, scattering, bending losses-claw and cladding losses- Dispersion in fiber. Optical fiber communication system- analog optical fiber communication system-digital optical fiber communication system- advantages of optical fiber communication system-requirements of communication light sources-(laser)different types of modulation and demodulation (elementary ideas only). Books: Brijlal and subrahmanian- A text book of light Vasudev, D.N- A text book of light Ajoy Ghatak- Optics (2nd edition) DR.S.Arumugam- Semi conductor physics and Opt electronics Kennedy Davis- Electronics communication system Paper – 9 MATERIAL SCIENCE UNIT 1 Crystal structure and bounding: Space lattice- crystal lattice and unit cell- seven crystal system- Brava is lattice- Symmetry elements of a crystalline solid- structure of SCC, BCC, FCC and HCPCharacteristics of cubic system- condition number- atomic radius -number of atoms per unit cell-density of packing –relation between Lattice constant and density of the crystal- Miller indices-miller indices of cubic crystal planes- relation between interplanar spacing and cube edge. UNIT 2 Elementary crystallograohy and crystal imperfections: Origin of X-rays-X-Ray spectrum- Mosley’s law- Diffraction of X-rays by crystal method and powder photograph method- Compton scattering of X-rays. Points defects- lines, surface and volume- Freckle defect- Dislocation- edge dislocation, screw, dislocation and Burgers vector. UNIT 3 Magnetic properties and super conductivity: Magnetic types of magnetic matericals- classical theory of diamagnetism (Langevin theory)- Langevin theory of paramagnetism-Weis theory of parramagnetism- quantum theory of magnetism. UNIT 4 Dielectric properties: Fundamental definition in dielectrics- Different types of electric polarization – Frequency and temperature effects on polarization – dielectric loss. Clausius- Mosottis relation- determination of dielectric constant –dielectric breakdown-properties of different types of insulating materials- schotcky effect. UNIT 5 Modern engineering material and new materials: Polymers- ceramics- super strong materials-high temperature materials-thermo electric materials-elecrets- nuclear engineering material –plastics- metallic glasses- optical materials- materials for optical source and detector- Fibre optics material and their application = Acoustic material and their application- Biomaterials- conductor. Books: Arumugam M- Material science Puri and babbar- solid state physics Paper – 10 NUCLEAR PHYSICS UNIT 1: NUCLEAR STRUCTURE Nuclear radius, charge distribution,spin and magnetic moment- Determination of nuclear mass-Binding energy –semiempirical mass formula- Nuclear stability- mass parabolas-Nuclear shell model-Liquid drop model- Optical model-Collective model NUCLEAR PROCESS :Exchange forces-Yukawas meson theory-Yukuwa potential- Ground state of deuteron-Magnetic moment –Tensor forces-Scattering length,Phase shift,scattering amplitude-low energy n-p scattering- Effective range-spin dependence and charge independence of nuclear forces. UNIT 2: RADIOACTIVE DECAYS: Alpha decay-Garmows theory-Geiger nuttal law-Neutrino hypothesis-Fermis theory of beta decay-selection rules-non conservation of parity in beta decay-Gammay decayselection rules-internal conversion- nuclear isomerism. DETECTION OF NUCLEAR RADIATION: Intercation of charged particle and X-rays with matter- Basic principle of particle detector- Proportional counters and Geiger- Muller counters-BF3 counters-solid state and semiconductor detector- scintillation counters. UNIT 3: NUCLEAR FISSION: Characteristics of fission-mass and energy distribution of nuclear fragments-nuclear chain reactions-four factor formula –Bohr wheelers theory of nuclear fission –fission reactors-power and breeder type reactor.Nuclear fussion basic processes-solar fusion-cold fusion-controlled thermonuclear reaction-pinch effects-laser fusion techniques. UNIT 4 : NUCLEAR REACTIONS: Energetics of reactions-Q-equation- level width in nuclear reaction –nuclear reaction –nuclear reaction cross sections-partial wave analysis-compound nucleus model-Resonance scattering-Breit Wigner one level formula –Direct reactions-stripping and pick up teactions. SCATTERING: The scattering cross section –scattering amplitude- expression in terms of Greens function-born approximation and its validity-screened coulombs potential-alpha particle scattering-Rutherfords formula. UNIT 5 :ELEMENTRY PARTICLE: Four types of interaction and classification of element ry particle –Isospin-Isospin quantum numbers-Strageneous and hyper charge- Hadrons- Baryons-Leptons –Invariance principle and symmetrics-Invariance under charge-parity (CP0 ,time (T) and CPT-CP violation in neutral K-meson decay- Quark model-SU(3) symmetry- Gell-Mann.NISHIJMA FORMULA-Gauge theory of weak and strong interaction Charm , bottom and top quarks. BOOKS: 1. R.R ROY and B.P. Nigam,nuclear physics,Wiley eeastern ltd.,new delhi (1986). 2. B.L.Cohen, concepts of nuclear physics, Tata mcgraw hill,new delhi(1983). 3. H.A.Enge, Introduction to nuclear physics,addision Wesley , New york(1971). 4. H.Semat ,Introduction to atomics and nuclear physics ,Chapaman and Hall,new delhi. 5. D.Griffiths, Introduction to elementary particle wiley Intrnational edition,newyork(1987). 6. W.S.C.Williams, nuclear and particle physics, clarendon press,London(1981). 7. K.S.Krane ,Introduction nuclear physics, jhon wilesy, new york (1987). 8. K.S.Krane, Modern physics,john wiley and sons Inc, New york(1988). Paper – 11 MICRO CONTROLLER AND DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSING UNIT I SIGNALS AND SYSTEMS Classification of signals – Singularity function – Amplitude and phase spectra – Classification of systems – Fourier transform – Properties of Fourier transform – Fourier transform of some important signals – Fourier transform for power and energy signals. LINEAR TIME INVARIENT SYSTEMS Introduction – Properties of a DSP systems – Difference equation and its relationship with system function, impulse response and frequency response. UNIT II DISCRETE AND FAST FOURIER TRANSFORMS (DFT AND FFT) Discrete convolution – DTFT – FFT computing an inverse DFT by doing a direct DFT – composite radix FFT – Fast convolution – Correlation – Z transform – Definition of the z transform – Properties of z transform – Evaluation of the inverse z transform. UNIT III FIR AND IIR Magnitude and phase response of digital filter – Frequency response of linear phase FIR filter – Design techniques for FIR Filters – Design of optimal phase FIR filter. IIR filter design by approximation of derivatives – IIR filter design by impulse invariant method and the bilinear transformation – Butterworth and cheby swev filter – Elliptic filter – Frequency transformation. UNIT – IV Introduction of Microcontrollers-8051 Microcontroller- architecture-special function registers-adderssing modes –instruction set. Origin of PIC Micro:- Introduction to PIC micro -Architecture and hardware:- Block diagram – working registers – program memory – data memory – file registers – program concepts – status register – stack file selection register – option register – indirect data addressing register – digital I/O port – clock oscillators – timer modules – prescalar – watch dog timer – reset circuitry – instruction cycle – long word instruction – power down mode / sleep – configuration fuses UNIT - V Instruction set and program development:- Instruction set types – MPASM – source code formats – labels – mnemonics – operands – comments – files with default extension – lists file format – error file format (EPR) – operators – procedure – redix – text strings – numeric constants and radix key to PIC 16/17 form instruction sets. 1.TEXT BOOK : . S.Salivahanan, A. Vallavaraj and C. Gnanapriya, “DIGITAL SIGNALPROCESSING”, Tata McGraw Hill Publishing Company Limited, ISBN-0-07-463996-X. 1. .Embedded control hand book, volume 1995/96 2. PIC 16/17 microcontroller data book, volume 1996/1997 3. MPASM online help files. Paper – 12 COMMUNICATION ELECTRONICS UNIT – I : COMMUNICATION SYSTEM Theory of amplitude modulation – theory of frequency modulation – theory of phase modulation Noise : Intern noise – external noise – noise calculation – noise figure noise temperature – super heterodyne receiver – Antenna antenna equivalent circuits – coordinated system – radiatiadar. Fields – Polarization – power gain of a antenna – effection area of antenna – effective length of an antenna – Hertzi dipole – Half wave dipole – vertical antennas – loop fiernrod antenna – non resonant antenna – driver array – plus arrays – UHF – UHF antenna – microwave antenna. UNIT – II : DIGITAL COMMUNICATION Pulse amplitude modulation – Pulse code modulation – pulse frequency modulation – pulse time modulation – pulse position modulation – Pulse width modulation – base digital communication systems – synchronization a synchronous transmission – probability of bit error in bas band transmission – notched filter – bit, timing recovery eye diagram – digital carrier systems – carrier recover circuits – differential phase shift keying error control coding – multiplex transmission – frequency and time division multiplexing. UNIT – III : MICROWAVE ELECTRONICS AND RADAR Generation of microwaves – klystron: Reflex Klystorn Multicavity Magnetron – detection of microwaves IMPATT, TRAPATT and Gunn diodes – radar – radar quation – pulse and CW radar – MTI and automatic tracking radar. UNIT – IV : OPTIC FIBER COMMUNICATION Fiber optics – Different types of Fibers: Step indexed Graded index fibers – Ray theory of step index Fiber – ignal degradation in fibers: Absorption , attenuation, catering losses and dispeision – optical sources and electros : Laster fundamentals – laser action – different inds of laser – LED – photo detectors – power launching coupling: Source to fiber power launching – fiber joints splicing techniques. UNIT – V : ATELLITE COMMUNICATION Satellite links – eclipses – orbits and inclination – satellite construction – satellite communication Frequencies – Different domestic satellites – INTELSAT system MATISAT satellites – telemetry. Reference: 1. Dennis Rooddy. John Coolen electronic Communication – fourth edition, PHI Private Ltd.1999. 2. Sanjeevan Gupta – Electronic Communication systems – Khanna Publications, 1995. 3. N.D. Deshpandae, D.A. Deshpandate, P.K. Rangola Communication Electronics – Tate McGraw Hill Pvt, Ltd.1998. 4. M. Arumugam, Optical Fiber Communication and Sensors, first Edition 2002 Anuradha Agencies, Kumbakonam.





