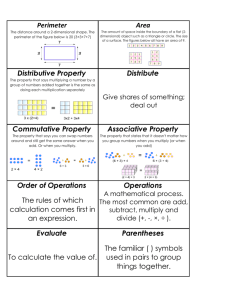
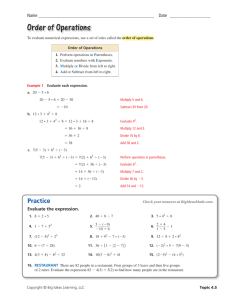
PBP Revision Notes - CA Notes and Study Material
advertisement

Prepared by : Muhammad Asif Updated &: Presented by : Faraz Ahmad Syed Atif Hassan Abidi PREFACE The Examinations of ICAP are a demanding test of student’s ability to master the wide range of knowledge and skills required of the modern professionals. Subject of “Business Management” is one of the efforts made by ICAP in this context for enhancing student’s knowledge about detailed overview of effective management of businesses. The best and recommended book for this subject is “Study Text by PBP” that covers each and every area of syllabus in extraordinary detail. The basic problems faced by the students in going through PBP are its size and the language used. Students who are new to this subject have to spend most of their precious time in understanding the theme conveyed in any chapter. Moreover students feel it very hard to revise the complete course near or on the exam day. For these reasons there arise needs to have some short and easy to revise notes for this subject that covers the extent of PBP in a concise form. For this purpose we used short notes of PBP prepared by Muhammad Asif (Ex A.M, AFF & Co Lahore) 3 years earlier. After compiling the notes Faraz Ahmad reorganized the notes and updated it using the PBP. Now those notes are finalized and presented to you in a booklet form. Hopefully it will help you all. I would suggest that first of all you should read BM from PBP and afterwards you may consult these notes for revision purposes. An Annexure has been given at the end of this booklet to help you deciding how you can use this booklet in combination with PBP. May ALLAH bless you with success in every exam of both lives. Thanks Talib e Doa Syed Atif Hassan Abidi Faraz Ahmad March 31, 2009 For notes & other study material for module E visit and download mails from E-Mail id: atifnotes@gmail.com Password: a4atif These notes are also available at www.canotes.multiply.com Chapter 1 : Objectives of Organisation Introduction to Strategy Strategy: “ Course of actions, including specification of resources required, to achieve a specific objective” Influences on /Determinants of Strategy: External o Society o Organized groups Nature of business o Market situation and conditions o Products of company o Technology used Organization’s Culture o Organizational system and structure o Leadership style o Organization’s history o Organization’s founder Stakeholders’ powers (mapping) and Internal coalition Economic objectives Social responsibility Environmental conditions affecting Strategic Planning: 1. Resources (mineral) 2. Disaster 3. Logistics 4. Government Environmental Management Accounting is a solution: examples are 1. Eco – Balance 2. Cleaner Technology 3. Lifecycle assessment 4. Performance appraisal 5. Budgetary planning and control 6. Corporate liabilities (a factor in PERT) Characteristics of Strategic Decision: Scope: Overall long-term direction. Matching: Matches activities to environment & resources capability. Affect: Affected by values, beliefs and powers of people in organization. & Affect operational decisions. Implications for change. Complex in nature. Allocation or reallocation of resources. Strategic Financial Management: It is identification of strategies able to maximize NPV and to allocate scarce resources, and implementing and monitoring of such strategy. Financial management decision: (Also see end of chapter 9) Investing decisions (merger, divestment etc.) Financing decisions (Capital structure and Working Capital Management) Dividend decisions (Cash or Bonus share) Financial objectives: Non financial objectives: Primary; to maximize wealth of shareholders Service provision. Others are Fulfillment of responsibility to suppliers & customers. o Decrease in debt. Welfare of Society o Profit retention. Welfare of Management o Sales growth. Welfare of Employees Government organizations: External Financing Limit. To create Value for Money, funds must be applied Economically, Efficiently and Effectively. www.canotes.multiply.com 1 Chapter 2 & 4 : Strategy Formulation and Choice Strategy formulation/choice 1. 2. How to gain competitive advantage?(question of survival) i. Porter’s Generic Strategies (5 forces) Which Direction to go i. Growth direction a. Organic growth Ansoff’s Product-Market Matrix b. Joint development ii. Defensive/Non growth strategies a. Capital Restructure Scheme b. Downsizing c. Divestment Porter’s Generic Competitive Strategies (to achieve competitive advantage): Competitive position is the market share, costs, prices, quality and accumulated experiences of an organization/product relative to competition. Competitive strategy is taking offensive or defensive action to create a defendable position in an industry, and to cope with competitive forces yielding superior ROI. Competitive advantage is anything which gives one organization an edge over competitors. There are following Competitive Strategies for companies to achieve Competitive Advantage. Broad Target Niche Focus Lower Cost Cost Leadership Cost Focus Differentiation Differentiation Differentiation Focus (for luxury goods) Differentiation is “creating value through uniqueness”. It could be at following levels of product i.e. 1.Actual Product a). Features. b). Quality level. c). Design. d).Brand name e). Packaging. 2. Augmented Product i. Delivery and credit ii. Warranty iii. Installation iv. After sale service Cost Leadership is “having lowest cost of producing”. It could be achieved by: Mass Production (economies of scale) Latest Technologies Favorable access to raw materials Automation Minimizing overhead by exploiting bargaining power Constantly improving efficiency and economy e.g. through value chain analysis Focus involves a restriction of activities to only part of the market (a segment) through Providing goods/services at lower cost (Cost focus) Providing a differentiated product/service (Differentiation focus) www.canotes.multiply.com 2 Advantages/Comparison of Competitive Strategies: Competitive Force Rivalry New Entrants Substitutes Customers Suppliers Cost Leadership strategy Profitable even in price competition. Low price is entry barrier. Firm is less vulnerable than competitors. Customers won’t switch. High bargaining power because of market share. Differentiation strategy Reduces direct competition. Customer loyalty is entry barrier. Brand loyalty is weapon. Low price sensitivity. Supplier may raise prices but higher margin offsets it. Ansoff’s Product-Market Matrix: Present Market New Market Present Product Market Penetration Market Development New Product Product Development Diversification Market Penetration: (low risk; no capital investment) To increase usage by existing customers or To increase market share through Competitive pricing, Advertising, Sales promotion taking share of competitors Market Development: (low risk; less investment) New geographical area New segment New packing size Product Development: (riskier; requires investment) Company can exploit followings Existing marketing arrangements (e.g. Promotion, Distribution) Knowledge of customers and habits Cost of entry will go up for competitors. Diversification (high risk; requires investments and new competence) Related diversification is when product is new but still within broad confines of industry. e.g. Vertical integration (control over supply chain) Forward integration (control/ownership over distributors or retailers) Backward integration (control/ownership over suppliers) Horizontal integration (control/ownership over competitors) Unrelated diversification is where development is beyond industry and product is entirely new having no relation with existing technology, market or products. Franchising Unrelated Diversification Forward Vertical Related Growth Backward Horizontal Organic Growth Joint Development Strategies Take Over/ Acquisition Mergers Joint Ventures Strategic Alliance Licenses Agency Agreement Franchising www.canotes.multiply.com 3 Chapter # 3 : Planning and Control Planning Planning: “ Planning involves making choices between alternatives and is primarily a decision making activity” 2 approaches to planning: Top-down approach means strategic management starts from top management and flows down the structure. Bottom-up approach means information is accumulated at lower level and presented to top management along with summary and options available. Planning cycle 1. Identify objectives 2. Identify available strategies 3. Evaluate each strategy 4. Choose strategy (course of action) 5. Implement long-term plan in the form of annual budgets Risk factors in planning: Types of risks: Physical Economical Political Financial Business Product lifecycle Accounting for Risk: Required rate of return, adjusted by Return %age Payback period Finance (strict rules of financing i.e. out of profits) Quantification risk: Rule of Thumb (best estimate of value within worst to best possible range) Probability Theory (likelihood of occurrence of a forecast result) Standard Deviation (calculate Standard Deviation of Expected Value, the higher it is the higher risk is) Budgetary Control Control: “Control is comparing actual results with planned performance and taking appropriate actions” Control Cycle 1. Actual results are recorded and analyzed for each responsibility center. 2. Feedback is reported to management. 3. Management compares actual results with plans or targets. 4. Do one of three things i. Decide to do nothing ii. Take control actions iii. Alter the plan or target Feedback: “ The process of reporting back control information to management and the control information itself” It may be Single Loop or Double Loop. It may be Positive or Negative. Feed forward Control: Control actions taken in advance. Actual results are compared with Budgeted (i.e. adjusted by past results) www.canotes.multiply.com 4 Well organized system of control should have: Hierarchy of budget center. Clearly defined responsibilities. Responsibilities for Cost, Revenue, and Capital Employed. Budget Center: “Each section of the organization for which budget is prepared” Objectives of budgeted planning and control: 1. Motivates employees 2. Establish system of control 3. Responsibility accounting 4. Achievement of goals 5. Communication 6. Coordination 7. Compel planning Responsibility Accounting: Each manager has a clearly defined area of responsibility and authority to make decisions within that area. No uncertainty as to who is responsible for what (sometimes dual responsibility exists). There are 3 different areas of responsibility. Type of responsibility center Manager has control over… Cost Center Controllable cost Profit Center Controllable cost Sales Price Sales volume Principal measures Variance analysis Profit performance Investment Center Controllable cost Sales prices Sales volume Investment in fixed and current assets Return on investment and residual income Responsibility Center is a unit of organization headed by a manager who has a direct responsibility for its performance. Controllable Cost is an item of expenditure which can be directly influences by a given manager within a given time span. Controllability of fixed cost: Committed fixed cost (e.g. PPE-------non-controllable in short term) Discretionary fixed cost ( e.g. R.&D. or Advertisement ---------- controllable in short term) Role of IT in Strategic Management IT as changing industry: With Porter’s 5 forces model. IT/IS as competitive advantage: With Porter’s generic strategies for competitive advantage. & With Peppard’s 9 ways 5 forces 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Ensure competitive pricing Establish entry barrier (cost of entry) Using information as a product Limiting access to distribution channel Affecting cost of switching Building close relationship with supplier and customer. www.canotes.multiply.com Generic strategies 7. Differentiating Product/Service 8. Increasing Cost efficiency 9. Decreasing Supply Cost. 5 Chapter 4 & 5 : Strategic Management : Traditional & other models Traditional and other models of Strategic Management Strategic Management: “Strategic Management is the analysis, choice, implementation and control of agreed strategies” Strategy is a course of action including the specification of resources required to meet a specific objective. Tactics is the deployment of resources to execute an agreed strategy. Policy is a general statement providing guidelines for management of decision-making. Levels of strategy: (by Hofer and Schendel) 1. Corporate Strategy determines the overall purpose and scope of the organization. It is concerned with what types of business the organization is in. Defining aspects of corporate strategy: Scope of activities (whole organization) Faces environment (opportunities and threats) Resources (how to obtain and allocate them) Values (of people in power in organization affect it) Time scale (long term) Complexity (uncertainty of future) 2. Business Strategy is how an organization approaches a particular product market area (applied at SBU level). 3. Functional/Operational strategies deal with specialized area of activity within an SBU e.g. Production, Marketing, HRM, Finance. Traditional approach to make strategy: (through Planning in a systematic way) o o o o Strategic analysis Analyzing Vision, Mission and Objectives (Strategic Direction) Corporate appraisal (where we are) o Analyzing external environment i. SLEPT analysis ii. Porter’s 5 forces model iii. Scenarios o Analyzing internal environment (Situation analysis/Position audit) i. Resources Audit ii. BCG and GEBS matrices iii. Value chain iv. System structure o SWOT Analysis o Gap analysis Strategy formulation/Choice (how we can go) Strategy implementation Strategy evaluation and Control Favor of rational model: (Ansoff and Drucker support it) 1. Corporate level first 2. Strategies are best generated from Top-Down 3. Provide a common thread 4. Enables decision making in conditions where i. Partial ignorance (Ansoff) ii. Risk is inevitable (Drucker) 5. Basis for strategic control 6. Improves stakeholders’ perception Problems with rational model: (Mintzberg criticizes it) 1. Organizations are incapable of having objectives because i. Objectives may conflict with each other. ii. Objectives will change from time to time www.canotes.multiply.com 6 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. iii. Objectives are unlikely to be directly related to economic benefits of shareholders. Senior management should not be only strategy- setter. In reality formulation is not a simple step by step process. Strategies that firms follow are not the same as ones they set in plans. Over reliance on formalization. Predetermination Failure in practice (suitable for only stable environment) Hinders innovation and radical change. Other models of(making strategy) Strategic Management Mintzberg’s emergent strategy model: (Considers random shocks) It is unlikely that a firm’s environment is totally predictable. Emergent strategy is a non-conscious strategy arising from patterns of behavior. Strategic Management is to control and shape/craft these emergent strategies as they arise. Intended Strategies Deliberate Strategies Realized Strategies Unrealized Strategies Patterns of behavior Unexpected Contingencies Emergent Strategies Activities affecting Crafting Strategy: Manage stability o Implement, not just plan o Obsession to change is dysfunctional; know when to change Manage patterns o Detect patterns and help them shape; grow positives and eliminate negatives. Know the business operations Detect discontinuing and significance of environmental changes. Crafting strategy---- requires natural synthesis of past, present and future. (reconcile change and continuity) Mintzberg’s 8 styles of strategic management: 1. Planned strategies (imposed by central leadership, large no. of controls, precise intentions) 2. Imposed strategies (imposed by environment e.g. influential customers) 3. Ideological strategies (collective vision of organization’s members, shared values) 4. Umbrella strategies (ends are defined, means are emergent, target based) 5. Disconnected strategies (members mind their own business, strategies are deliberate for sub-units but emergent for organization) 6. Consensus strategies ( groups shares common patterns) 7. Entrepreneurial strategies (visioned from strong leadership) 8. Process strategies Mintzberg’s 5 ways to describe strategy: 1. Plan - consciously intended course of action 2. Ploy - a competitive game (e.g discouraging competitors to enter) 3. Pattern - ideas of emergent strategies 4. Position - “environmentally fit” & relationship with other organisations 5. Perspectives - approach towards world Strategy and managerial intent: (Johnson and Scholes) not emergent The Command view: Strategy develops through the direction of an individual or group, but not necessarily through formal planning. Control of strategy direction is possessed by autocratic or charismatic leader. www.canotes.multiply.com 7 Paradigm and Politics: Paradigm (basic assumption and beliefs common in organization’s decision makers) is inhabitant and conservative than culture. Politics is process of bargaining and negotiation of strategy among powerful stakeholders. Process by which Paradigm and Politics influence process of strategy development. o Issue awareness (by internal results, customer response or environmental change) o Issue formulation (analysis of issue to get its root) o Solution development Summary: Memory search (from past experience) a) Managers do not take best Passive search (time will tell) decisions but satisfactory o Solution selection ones. Eliminate unacceptable plans (politics) b) Managers do not pursue the Endorsement to junior management whole rational model but take small-scale decisions. Incrementalism: Bounded Rationality Theory: (Herbert Simon) Mangers are limited by time, information and skills. They satisfice rather than maximize. Incrementalism: (Lindblom) It involves small-scale extension of past practices. Organizations change incrementally, during which time, strategies form gradually. Disadvantages of Incrementalism: 1. Not suitable where radical new approaches are needed. 2. Some changes are dramatic not incremental. 3. Ignores influence of corporate culture. 4. Applicable to stable environment only. Logical Incrementalism: (mid way) Managers have a vague notion as to where the organization should go, but strategies should be tested in small steps because of uncertainty about future. Knowledge as a source tacit knowledge Learning based strategy: Knowledge creation explicit knowledge Strategy development is a learning process. Learning organization will generate a flow of fresh ideas and insights, This will promote renewal and prevent stagnation. Learning organization is one which is skilled at creating, acquiring, and transferring knowledge, and at modifying its behavior to reflect new knowledge and insights. Double loop learning is where purpose is also reviewed. (derived from control theory) Future will change incrementally Future Orientation: (Hamel and Prahalad) Future will be radically different Future is not just something that happens to organization. Organizations can create the future. They offered a ‘diagnostic’ to indicate how future oriented an organization is. Diagnostic: Diagnostic statement Senior management, view about future Senior management, spending most time on Are managers…… Are employees….. The company is better at Within the industry, the company Competitive advantage is pursued by Protect the past Reactive Re-engineering current practices Engineers of present Anxious Operational efficiency Follows the rules Catching up with competitors Agenda for change is set by Competitors www.canotes.multiply.com Create the future Distinctive Regenerating core strategies Architect of future Hopeful Building new businesses Makes the rules Creating new sources competitive advantage Vision of future of 8 How to cope with future: Simply more far-sightedness Imaging products and services that do not exist. Spend less time in positioning in competitive environment Future orientation is embodied in the corporate culture. Environmental Fit: (Hofer and Schendel) Strategy is a mediating force between organization and environment. Fit or Suitability means ‘ Organizations are successful when they intentionally achieve internal harmony and external adaptation. Strategic logic requires that strategy must: o Be consistent with objectives o Match organization’s capabilities with environment. Survival and growth are process of adoptation : Why : because environment gives physical resources and financial resources Hence : choice of strategy must follow a strategic logic. Ecology Model: Organisation’s environment changes radically, it will only survivor if it adopts its environment and evolves i.e finding niche areas which provide both demands for output and resources to be used as input to the system. Pattern and Competencies: (Andrew) Corporate strategy is the pattern of management decisions in a company o That determines and reveals its objectives, purposes or goals, o That produces the principal policies and plans to achieve those goals, o Defines the range of business, and o Kind of human and economic organization it is or intends to be. Strategy is exploitation of competencies. o The distinctive competence is what it does well, uniquely or better than rivals. It comes through Experience Quality of co-ordination Talents and potentials of individuals Strategic Thinking: (Kenichi & Ohmae) Strategy is a creating process Success business strategies result not from rigorous analysis but from a particular state of mind. Aspects of strategic thinking o Flexible thinking (what if ?questions) o Keeping details in perspective (specially uncertain) o Focus on key factors and distinctive competences) How strategic thinking operates o Ask right question o Find solution of problem, not remedy or symptom. o Observe the problem o Group problems together (e.g. by brainstorming) to see key factors. Competition: (Ohmae & Porter) Competitive strategy is the taking of offensive or defensive actions to create a defendable position within an industry------ and a superior return on investment. Successful strategy is the interplay of 3 Cs (strategic triangle) 1. Competitor 2. Customer 3. Company 3 assumptions of theory: (focus: survival in competitive environment) 1. Survival of business is impossible without a competitive strategy. 2. Actual strategy will be unique. 3. Marketplace is a battlefield. www.canotes.multiply.com 9 Competitive strategy: “ A strategy by which a firm can have significant ground on its competitors at an acceptable costs” Competitive Advantage: Re-adjust current resources Relative superiority Challenge assumptions Degree of freedom i.e identify key success factors i.e exploiting competitors weakness i.e segmenting How to create sustainable strategic position: operational effectiveness doing unique things doing trade-off combining good individual activities making own choices i.e not blindly imitating competitors Realised Strategies Intended or planned strategies Emergent strategies - Senior management decisions - Imposed from top - Well planned - Well thought-out - Time consuming - Deliberately planned - not planned - not fore throught - not the result of management intentions - caused by pattern of behavior Implicit & Explicit Strategies (Depends upon extent to which strategies are deliberate or emergent) Implicit Only in head of chief executive Explicit Properly documented Flaws: - Purely deliberate strategy prevents learning from experience. A purely emergent strategy defies control Descriptive and Prescriptive Strategies Descriptive : “what is actually happening in the organisations i.e paradigm, politics, pattern of decisions, incremental approach Prescriptive : “to prescribe something” i.e rational model, strategic thinking, learning based environment, resource based model www.canotes.multiply.com 10 Chapter # 6 : SWOT Analysis ad gap analysis Corporate Appraisal Corporate appraisal (where we are) o o o o Analyzing external environment iv. SLEPT analysis v. Porter’s 5 forces model vi. Scenarios Analyzing internal environment (Situation analysis/Position audit) i. Resources audit ii. BCG and GEBS matrices iii. Value chain analysis iv. System structure SWOT Analysis Gap analysis Corporate appraisal is assessment of SWOT in relation to internal (SW) and external (OT) factors affecting organization to establish long term plans. OT Analysis---Analyzing external broad environment: Social factors Legal factors Economic factors Political factors Technical factors What Social factors affect: Changing values and lifestyle Changing pattern of work and leisure Demographic change Why social factors are considered: • Stakeholders are members of society--assessment of their values and beliefs • Good (ethical) reputation • Avoid restrictive legislation • Change = opportunities Legal factors: o Health and safety legislation o Employment laws o Environmental legislation o Information about performance. Economic key forces affecting organizations: Economic Growth Interest Rates and Tax rates Availability of Credit Inflation Rates Govt. fiscal policies (taxation, govt. spending, borrowing and repayment) and monetary policies (control of money demand and supply through rates) Foreign Exchange Rates Foreign Trade Balances Consumer income, debt and spending Govt. Subsidy Unemployment rate International economic issues: o Extent of protectionist measures o Comparative rates of growth, inflation, wages and taxation o The freedom of capital movement o Exchange rates o Economic agreements www.canotes.multiply.com 11 Exchange rate is the rate at which a national currency exchanges for other national currency. Determinants are: Demand and supply of currencies in foreign exchange market (Floating exchange rate) Govt. (Fixed exchange rate) Synthesis of above two (Managed exchange rate) Types are: Spot exchange rate (rate set for immediate delivery of a currency) Forward exchange rate (rate set for future exchange of a currency) Closing rate (Spot exchange rate at Balance Sheet date) Political factors: Type of Govt. Stability of Govt. Govt. attitude i.e. privatization or nationalization Amount of bureaucracy Pricing, dividend, tax, employment issues Political risk is the risk that political factors will affect an organization e.g. war, corruption, nationalization, political instability. Jeannet and Hennessry developed a checklist to assess political risk: 1. How stable is Political system. 2. How long will govt. remain in power. 3. How strong is govt.’s commitment to specific rules of game. 4. If present govt. is succeeded, how specific rules of games would change. 5. What would be the effect of change in specific rules of game. 6. In light of these effects, what decisions and actions should be taken now? Technological factors: o Change in production techniques o Invention and innovation OT Analysis ---Analyzing external specific and direct environment: (Porter’s 5 forces model) i) When costumers have powers: •Small number of customers •They make high volume purchases •Products they are buying are undifferentiated •Alternative sources of supply are available (substitute or switching) ii) When Suppliers Have Power: •Small number of suppliers •Few substitutes exist •Suppliers are not dependent on the buyer for a lot of their sales •Suppliers have differentiated their products •It is costly to switch suppliers iii) When Rivalry Among Existing Competitors Is Intense: www.canotes.multiply.com 12 •Slow industry growth •High fixed costs (plants, machinery, outlets) •Undifferentiated products •A large number of competitors •High exit barriers (what you lose if you leave the business) •Small changes in market share have a big pay-off iv) Barriers That Block New Entrants •Economies of scale •Large capital requirements •Product differentiation •High switching cost •Limited access to distribution channels •Some government policies and regulations •Other advantages that are hard to duplicate such as patents, great locations, subsidies, partnerships, etc. •History of aggressive retaliation toward new entrants v) Indirect Competitors/Substitutes •Close substitutes place a ceiling on the price that can be charged for a product or service •Close substitutes also set indirect performance comparisons •Main product is sensitive to price of substitute. Responding to the Organization/Marketing environment: Companies can passively take environment as uncontrollable and they must adapt to. Companies can take environmental management perspective i.e. actively working to change the environment. Wherever possible, companies should try to be proactive rather than reactive. Strategic Intelligence: Strategic Intelligence is the knowledge of business environment, which enables an organization to anticipate changes and design appropriate strategies that will create business value for customers and profit for co. Process of creating strategic intelligence: Sensing (Identify appropriate external indications of change) Collecting (Gather information in ways that ensure it is relevant and meaningful) Organizing (Structure the information in the right format) Processing (Analyze information for implication) Communicating (Package and simplify information for users) Using (Apply strategic intelligence) Sources for strategic intelligence = Sources of information SW Analysis ---Analyzing internal environment: Internal analysis consists of: Resources Audit BCG Matrix GEBS matrix Value Chain analysis Core Competence (critically underpins organization’s competitive advantage) Critical Success Factors (CSF are factors on which strategy is fundamentally dependent for its success. www.canotes.multiply.com 13 Marketing Is market and share increasing? Finance/Accounting Sufficient working capital? Operation Production capacity R&D Adequate R&D facilities? Segmented effectively? Can we raise capital or borrowings? Economies of scale Outsourcing is cost effective? Channel of distribution reliable and cost-effective? Return on investment & Cost of capital Are R&D resources allocated effectively? Communication Conduct market research? Effective budgeting process? Inventory control policies and procedures, effective? Is machinery technically updated? Labor relations User friendly IS? Product priced appropriately? Accounting ratios, strong or weak? Is equipment in good condition? Communication between R&S and other units? Are present products technologically competitive? Turnover and absenteeism Training provided? Under or over staffing? Continuous improvement? Effective promotion? Quality control policies and procedures, effective? Brand strength Products Product quality and brand reputation Age and life of products Price elasticity of demand Margin and contribution HRM Efficient Or experience manpower Recruitment and Training MIS Is IS updated regularly? Contribution by all functional managers? Effective passwords for entry? How much expensive? Stocks Sources of supply Turnover periods Storage capacity Obsolescence and deterioration Market share and growth Miscellaneous concepts: A Cruciform chart summarizes significant SWOT. Critical Success Factors are those components of strategy in which organization must excel to outperform competition. Gap analysis (objects – existing strategies = Gap) is a comparison between objectives and expected performance of projects both planned and underway. E.g. Profit Gap (Target profit – Forecast Profit) Forecasting is the identification of factors and quantification of their effect on an entity as a basis for planning. It includes judgment. Projection an expected future trend pattern obtained by extrapolation. It includes quantitative factors. Extrapolation is a technique of determining projection by statistical means. Scenario Planning: “ A scenario is an internally consistent view of what the future might turn out to be” An industry scenario is concerned with the future of industry. Macro scenario uses macro economic or political factors, creating alternative ways of the future environment. 6 steps in planning scenarios: 1. Decide on the driver for change i. Environmental analysis ii. Important issues and degree of certainty (time horizon is 10 years) 2. Bring drivers together into a viable framework 3. Provide 7 to 9 mini scenarios. 4. Group mini scenarios into two or three larger scenarios containing all topics. 5. Write the scenario. 6. Identify issues arising. www.canotes.multiply.com 14 Chapter 7 : Performance Appraisal & Analysis Performance Appraisal Measurement of Performance: Costs: Measurement of Growth and effects of inflation: 1. Revenue 2. Profits 3. Assets 4. Cash Flow 5. ROCE/ROI 6. Market share 7. Number of employees 8. Number of products Fixed costs Variable costs -------------------------------------Directly attributable costs Shared general overheads -------------------------------------Controllable costs Uncontrollable costs 4 profit concepts to measure performance of divisions: Contribution (sales – variable cost) Controllable profit ( sales - variable costs - Fixed cost controllable) Controllable margin ( Controllable profit – other costs directly traceable) Net Profit/Margin ( Controllable margin – allocated service center costs and general management overhead) Value added is cost of material and bought in service. Measuring performance of Profit Center: 1. ROI/ROCE 2. Residual Income (measure of center’s profit after deducting notional or imputed interest cost) Benchmarking: (adoption of best practices) Benchmarking is establishment of targets and comparators (through data gathering) through which relative levels of performance can be identified. Types of Benchmarking: Internal Benchmarking comparing one operating unit with another within same industry. Functional Benchmarking internal functions compared with best external regardless of industry. Competitive Benchmarking information about direct competitors is gathered through techniques e.g. reverse engineering. Strategic Benchmarking aimed at strategic action and organizational change. Levels of Benchmarking: 1. Resources through resources audit 2. Competences in separate activities through analyzing activities 3. Competences in linked activities through analyzing overall performances. Inflation: - Effect of inflation on accounting system Effect of inflation on strategy in reference to operating in competitive market and exporting goods overseas Performance measurement and inflation: i) Fixed asset values & depreciation ii) Cost of sales and inflation iii) iv) v) vi) Need for working capital Borrowing benefits in period of inflation Comparability of financial figures Ratios for control www.canotes.multiply.com historical costing problem increased profits but low stock turnover (overstated profits) real value of loan decreases over times figures are ditorted ratios will be unaffected, as both side of balance sheet will be inflated 15 Chapter 8 : Mission Goals and Objectives Analyzing Vision, Mission and Objectives Hierarchy Vision--------Mission----------Goals (objectives and aims) at 3 levels----------strategy at 3 levels Vision: “ Where the organization wants to be” Advantages of vision: gives general directions to organisation gives hope and motivation establishes scope and boundaries enables flexibility in choice Problems with vision It ignores real, practical problems It can degenerate into wishful thinking Strategic intent: “Vision with an emotional core to energize and stretch” similar to vision stretch current competencies gives sense of direction gives coherence to plans Mission Statement: This is a statement purpose of existence-What it wants to accomplish in the larger environment. Mission statement includes Purpose, Competence, Strategic Scope, Product, Targeted customers, and Values of various stakeholders. It should be market oriented, specific, realistic, motivating and consistent with market environment. e.g. “To provide best satisfaction to customers and fair return on investment, keeping environment healthy and clean and promising secure future to employees”. Place of mission statement: Annual reports Publicity materials In chairman’s office Communal work area Elements of mission statement: Purpose ( e.g creating wealth, satisfy shareholders) Strategy ( e.g logic, product, service) Scope Politics & behaviors Values & culture (e.g commitment) Characteristics of mission statement: Bravity Flexibility Distinctiveness Problems with mission statement: Ignorance in practice Only for public showment and not for internal decision making Only rationalising existence of organisation Wish list, full of generalisations www.canotes.multiply.com 16 Functions/Importance of mission 1. Employee motivation 2. Contributes to profitability 3. Focus for strategic decision making 4. Replaces national or divisional subculture with a corporate culture 5. Communicates nature of organization to insiders and outsiders Problems with mission = Problems with Rational model of Strategic Management Goals: Goals could be Objectives (quantifiable) Aims A goal must be SMART. S M A R T Goals Specific Measurable Attainable result-oriented time-bounded Operational goals Non-operational goals Measurable not measurable 3 levels of goals/objectives and strategy: Corporate level SBU level Operational level Corporate level objectives: (trade off between objectives) 1. Profit (Accounting Profit = Economic Profit = Sale price – Explicit Cost – Implicit Cost i.e. Opportunity Cost) 2. Market share and growth Objectives 3. Cash flow 4. Customer satisfaction Primary Secondary 5. Quality of product 6. Industrial relations Long-term Short-term 7. ROCE 8. EPS Unit Objectives: Commercial sector Increase number of customer by 15% (sales department) Decrease number of rejects by 50% (production department) Public sector To provide cheaper, subsidized bus traveling (local transport department) Responding more quickly to calls (police, fire station, hospital) Types of Goals: 1. System Goals 2. Ideological Goals 3. Formal Goals 4. Shared Personal Goals [Derived from organization’s existence] [Focus on organization’s mission] [Imposed goals; e.g. from Shareholder’s] [Consensus b/w individual and collective goals] System goals (subverting Mission) Survival Efficiency Control Growth Dealing with goal conflict (inter departmental): Rational evaluation (financial criteria) Satisficing (not aiming to maximize profit) Bargaining (b/w different goals of managers) Sequential attention (one by one) Priority setting www.canotes.multiply.com 17 Goal Congruence Trade off between objectives: Primary and secondary objectives: State of individuals to take actions which are in their own interest and also in best interest of organization. [One at expense of other.] [Based on importance.] Stakeholders Stakeholders are Groups or Individuals whose interests are directly affected by activities of a firm or organization. Stakeholder Shareholders Lenders Trade creditors Employees Retailers customers Management Society Govt. and Objectives To maximize wealth Increased by (dividend, capital gain of shares, EPS, ROCE) Measured by (increase in Retained earnings, Market Value listed or non-listed) Timely repayment of interest and principal Timely payment High prices Continuing profitable relations High wages Job security Job satisfaction Continued supply Quality products Maximize own reward Training and career development SHE Issues Level of employment Taxes Legislation compliance 2 approaches to stakeholders: 1. Strong view (To balance all stakeholders is important) 2. Weak view (Primary objective is profit, stakeholders are satisfied indirectly) Stakeholders’ mapping: (Mendelow) High Interest Key Players High Strategy must be acceptable for them Power E.g. major customer Influence powerful stakeholders Low Should be kept informed Power E.g. Community representatives/Charities Low Interest Pessimist Should be kept satisfied. E.g. large institutional stakeholders Negligible Organization’s Culture Culture/Organization’s Culture: “ Culture is sum total of belief, knowledge, attitudes, norms, customs, values and peculiarities that prevail in a society/ an organization”. Influences on organization’s culture: Organization’s founder Organization’s history Leadership and management style Structures and Systems Levels of Culture: There are 3 levels of culture in an organization: 1. Basic, underlying assumptions (guide the behavior of individuals and groups in organization) 2. Overt beliefs (expressed by organization and its members) 3. Visible artifacts (e.g. style of offices, display of trophies etc.) www.canotes.multiply.com 18 Some Important concepts: Belief is what we feel to be the case on the basis of objective and subjective information. Values are beliefs which are relatively general and widely accepted as culturally appropriate behavior. Customs is culturally accepted behavior in response to given situation. Artifacts are physical tools designed by human beings for their physical and psychological well being including works of arts and technology. Rituals are activities which take on symbolic meanings. Ethics is a set of moral principles to guide behavior. McKinsey’s 7-S model Explains relationship of different aspects of business: [Link b/w organizational & individual behavior] 3 Hard elements: [Formal Aspects] 1. Structure (division of tasks and hierarchy of authority) 2. System (technical system e.g. Accounting, HRM, MIS) 3. Strategy (org plans, tackling competitors, achieving objectives) 4 Soft elements: [Informal Aspects] 4. Shared values 5. Staff (own concerns and priorities) 6. Style (ways of working, attitude of management) 7. Skills French and Bell’s iceberg: Overt formal aspects (= 3 hard S) i. Goals ii. Structure iii. Policies and procedures iv. Products v. Financial resources Covert informal aspects ( = 4 soft S) i. Attitude, belief, feelings, perception ii. Value iii. Informal interactions iv. Group norms Theories on Culture Harrison and Handy’s Work: (gods of management) There are 4 types of culture in organizations: i) Power Culture (Zeus) All decisions are centered on one person i.e. founder of business For small entrepreneurial companies ii) Task Culture (Athena) No dominant leader Principal concern is to get the job done iii) Role Culture (Apollo) Organization has formal structure and well established rules and procedures People do their jobs as specified in their contracts For large organizations where work is predictable iv) Person/Existential Culture: (Dionysus) Organization’s purpose is to serve interest of individuals within it. Miles and Snow’s Work: (models of strategic culture) There are 4 approaches to strategy in organizational culture. www.canotes.multiply.com 19 1. Defenders (doing things right) Low risk, low profits Secured niche market Tried and trusted solution e.g. accountants, engineers etc 2. Prospectors (doing the right thing) High risk, high profits Move into new ways Take initiatives 3. Analysers Balance risk and profit Using core stable products & markets Follow the change, do not initiate change e.g. designers e.g. managers 4. Reactors Do not have viable strategy Denision’s model: Stable environment Changing environment Strategic orientation of firm towards environment Focus on internal Focus on external Consistency Culture Mission Culture Formal ways of behavior, predictability and Customer oriented. (hospital, church) reliability(bureaucratic) Involvement Culture (satisfied employees give Adaptability Culture ( fashion co.) performance e.g. Orchestra) Focus on external environment which is changing. Deal and Kennedy’s work: (Association of culture & risk) Culture is function of “willingness of employees to take risk” and “Their feedback” High risk Low risk Slow feedback Bet your company Culture “Slow and steady wins the race” Long decision cycles Stamina required Oil company, Aircraft company, Architects Process Culture “It is not what you do, it is the way you do” Attention to excellence of technical detail. Risk management Procedures and Status symbol Banks, Financial services, Government Fast feedback Hard ‘Macho’ Culture “Find a mountain and climb it” Entertainment, Advertisement, Consultancy Work hard/Play hard culture “Find a need and fill it” All action and fun Team spirit Computer companies Peter and Waterman’s Excellence Culture: “Dominance and coherence of culture was an essential feature of excellent companies”. Employees are loyal and make efforts if: Cause is great. They are treated as winners. They can satisfy dual needs of team and own interest. Key attributes of excellence 1. Autonomy and Entrepreneurship 2. Bias for action 3. Customer orientation 4. Stick to core activities 5. Simple organizational structure 6. Simultaneous loose-tight properties (competition between individuals and group within organization) www.canotes.multiply.com 20 Pumpin’s dynamic company (Cultural characteristics of dynamic companies) “Dynamic company is one that considerably increases the benefits for its stakeholders within a relatively short time” 4 aspects of such a culture Speed Productivity Expansion Risk taking Weak areas in a dynamic company Customer service Innovation Technology Attitude to workforce Company spirit and loyalty Strategic Excellence Position: (similar to excellence) SEP will fall into 3 fields: 1. Product related 2. Market related 3. Functional SEP can be developed only if culture supports it. www.canotes.multiply.com 21 Chapter 9 : Mergers and Acquisitions Take Overs: “Purchase by a company of a controlling interest in the voting share capital of another company” Mergers: “Merger is a business combination that results in the creation of a new reporting entity formed from the combining parties” (Mutual sharing of risks and benefits) Reasons for Mergers/Take Overs: 1. Synergy (1+1=11) 2. Eliminating competition 3. Entry in new market 4. Spread risk (diversification) 5. Acquisition is cheaper than internal expansion 6. Assets backing 7. Management acquisition 8. Operating economies (by eliminating duplicate and competing facilities) 9. Improvement of liquidity and finance-raising ability Deciding factors in a takeover decision: 1. Cost 2. Value a. Earning basis b. Assets basis c. Prospects for sale and growth basis d. Saving brought and additional expenditure basis 3. Will it be desirable for shareholders and stock market 4. What will be form of purchase consideration a. Cash (borrowed) b. Equity shares c. Debentures d. Convertible Loan Stock 5. How takeover would be reflected in published accounts Risks for shareholders of acquiring company in takeover: 1. Decrease in EPS of own company 2. Decrease in Share Price of own company 3. Decrease in Assets backing per share (decrease in net assets) 4. Entry in risky industry When takeover resisted by Target Company: Unwilling to sell Under bidding Unattractive after tax value Terms are poor Opposed by employees Founder appeals loyalty of shareholders Counter steps by Target Company: 1. Issuing a forecast of attractive future profits and dividends. 2. Launching advertising campaign against the takeover bid. 3. Finding a “White Knight”, i.e. a company which will make a welcome takeover bid. 4. Making a counter bid for the predator company. 5. Arranging a management buyout 6. Introducing a “Poison-Pill” , i.e. anti takeover advice Tactics by Acquiring company: Persuading dissatisfied shareholders High prices www.canotes.multiply.com 22 Payment Methods Cash Purchase Share exchange Use of convertible loan stock Earn out arrangements Methods are affected by Availability of cash Desired level of gearing Changes in control Changes in structure Choice of Cash or Paper offer or Both for payment depends on view of parties: Acquiring company and its shareholders: If purchase consideration is in equity shares, EPS might fall. If purchase consideration is in debentures (or cash borrowed elsewhere), it will be cheaper because Interest will be allowable for tax purposes and earnings will not be diluted. Issue of additional loan stock will be unacceptable for parties if company is highly geared. Issuance of large new shares will significantly change controlling structure. Payment in shares preserves cash available. Company might have to increase authorized share capital or borrowing limits. Target Company: If Cash is received, tax on capital gain will become payable immediately. If other consideration is received, it is to be ensured that o Existing income is at least maintained, and o Shares retain their value. If shareholders want to have stake in business, they will prefer shares. Mezzanine Finance: (by biding company; to pay for shares) Lies between equity and debt finance. It is short to medium term, unsecured, high rate of return loan It has option to exchange loan for share after takeover. It is also used in MBO. Earn-out arrangement: When consideration is payable upon the target company reaching certain performance targets. EPS before and after a takeover: Share purchased at higher P/E ratio will give fall in EPS, and vice versa. Company may accept dilution of earnings on acquisition if: There is increase in net assets backing.(from a company having more assets and less earnings) Quality of earnings is superior. Post acquisition integration: (Drucker’s 5 golden rules) 1. There must be common core of unity. 2. Acquirer must ask, “What is in for us” and “ What we can offer” 3. Acquirer must treat product, market and customers of acquired company with respect. 4. Acquirer must provide top management with relevant skills within one year. 5. Cross company promotions should occur within one year. 5 steps of Integration sequence: (C S Jones) 1. Decide and communicate initial reporting relationships 2. Achieve rapid control of key factors which will require access to right, accurate information 3. Human and physical Resource audit to get a clear picture 4. Redefine corporate objectives and to develop strategic plans 5. Revise the organizational structure Failure of mergers and takeovers: 1. Strategic plan fails to produce expected benefits 2. Over optimism about future market conditions 3. Poor integration management 4. Cultural differences www.canotes.multiply.com 23 5. 6. 7. Little or no post acquisition planning Lack of knowledge of target company or industry Little or no experience of acquisition. Impact of mergers and takeovers on stakeholders: On acquiring company’s shareholders EPS may fall especially in equity-financed bids and first time players Cost of mergers exceeds gains. On target company’s share holders Greatest benefit through significant premium over market price. Acquiring company management Increased status and influence Increased salary and benefits Target company management Key personnel will be kept others will be fired Other employees Economies of scale will be achieved by loss of job and eliminating duplication of services. Financial institution Outright winners The more complex, longer and problematic the deal is, the greater their fee income regardless of result. Joint Ventures Joint ventures: (1st step of acquisition) “ It is an arrangement where two or more firms join forces for manufacturing, financial and marketing purposes and each has a share in both equity and management of business” Advantages: Joint contribution of o Production technology o Corporate expertise o Market knowledge Access to foreign markets Eliminating competition Cheaper than internal expansion Spread risk Suitable for smaller companies Problems: Conflict of interests Where profits will go (in resident company or shareholders of foreign company) Local partners may wish to export to other countries where foreigner is already supplying. Transfer pricing issues (on transfer of expertise, technology and components) Cultural differences e.g. Equal employment opportunity Commercial practices Short term and long term planning Lack of smooth coordination, control and decision making Who will lead Who is responsible Confidentiality issues Strategic Alliances Strategic Alliance: “ When two or more firms agree to work together to exploit common advantages” e.g. alliance between national airlines to cross-book passengers. Licenses Licenses are very similar to Franchising in their financial aspects, however degree of central control and support is usually less. www.canotes.multiply.com 24 Franchising This gives limited right to franchisee (e.g. in a geographical area) to exploit patent product or production process, brands, manufacturing know how and/or technical advice and assistance. e.g. KFC, McDonald Mechanism: Franchiser grants permission. Franchisee pays for permission and assistance. Franchisee is responsible for day to day running of franchise. Franchiser may impose Quality Control Measures to ensure that goodwill is not damaged. Franchisee supplies capital, personal involvement and local market knowledge. Benefits to Franchiser: Rapid expansion (franchisee provides capital). Local knowledge. Economies of scale. Problems to Franchiser: Limited control over quality. Conflicts of interest. Franchisee may become competitor. Key Financial management decisions: Strategic Tactical Operational www.canotes.multiply.com Investment Selection of products and markets Required level of profitability Fundamental fixed assets Efficient and effective use of resources Pricing Working capital management Financing Target debt/equity mix Dividend Capital growth or high dividend payout Lease Vs. Buy Scrip or dividend Working management capital cash ------ 25 Chapter 10 : Corporate Reorganisation Defensive Strategies Capital Restructuring Scheme “ A capital reconstruction scheme is a scheme whereby a company reorganizes its capital structure”. Procedure of designing a capital restructuring scheme: 1. Calculate what each party’s position would be in a liquidation 2. Assess possible sources of finance 3. Design the reconstruction 4. Assess each party’s position as a result of the reconstruction 5. Check that the company is financially viable. Exit strategies for a venture capitalist: 1. Sale of shares to public or institutional investors following a flotation 2. Sale of shares to another company 3. Sale to company itself or its owners 4. Sale to institution management Downsizing Divestment- (selling of business) “Divestment is a proportional or complete reduction in ownership stake of an organization” e.g. Demerger Sell off Liquidation Spin off Management Buy Out (MBO) Privatization Reasons for Divestment: To concentrate on a particular part of business Selling a loss making unit Liquidity problems Selling a subsidiary with high risk Selling a subsidiary at profits Provide an exit route for investors Remove value gaps to avoid takeover Demerger is splitting up of a corporate body into two or more separate and independent bodies. Sell off is a form of divestment involving the sale of a part of a company to third party usually another company. Liquidation is extreme form of liquidation where the entire business is sold and funds are distributed to shareholders in their proportion. Management Buy Out. (MBO) management buyout is the purchase of all or part of a business from its owners by its managers. Management Buy Out.(MBI) where purchase of a business is made by group of managers from outside the business. Spin Off : a new company is created whose shares are owned by the shareholders of the original company which is making the distribution of assets. www.canotes.multiply.com 26 Management Buy Out: Possible reasons for MBO: All reasons of Divestment Best offer from management Sale can be arranged quickly Group can still maintain relations Success factors of MBOs: (Advantages) Favorable buyout price Personal motivation and determination Quicker decision making and more flexibility Saving in overheads Healthy relationship with subsidiary Questions in evaluating MBOs for investment: Does management has full range of skills? Why is the company for sale? Projected benefits and cash flows? What is being bought? Price? Fund availability? Exit routes? Problems faced by MBOs: (Disadvantages) Little experience of financial management Tax and other legal complications Changing the attitude of employees Deciding the bid price Cash for maintenance of fixed assets Change in HR (loss of key employees) Maintenance of relations with suppliers/customers Going Private “A public company goes Private when a small group of individuals buys all of the company’s shares (possibly including existing shareholders)” Advantages: Cost saving (cost of meeting statutory requirements are saved) Limited number of members Similar objectives of shareholders Shareholders are close to management Protection against volatility in share price Disadvantages: No trading of shares on stock exchange Loss of repute Loss of some value of share Disadvantages of De-Merger Loosing economies of scale Lower turnover Higher overhead cost Less ability to raise finance www.canotes.multiply.com 27 Chapter # 11 : Ethics and Social Responsibility Ethics Ethics: Ethics is a set of moral principles to guide behavior. It concerns with what is right and what is wrong. Individual Levels of Practicing ethics Personal ethics professional ethics Organisation Org. culture Org. System Ethical problems faced by organization: While achieving a higher ROI, an organization faces following problems: SHE Issues (Safety, Health, Environment) Extra payments to govt. officials Extortion (when officials threaten company with complete closure) Bribery (where organization is not entitled to services) Grease money ( where organization is entitled but unable to receive services) Gifts Honesty in advertisement (e.g Marketing ethics) Competitive behavior (e.g putting others to competitive disadvantage) Ethical systems in an organization: Personal ethics (e.g religious, political, personality ethics) Professional ethics (e.g CA code of ethics, medical ethics, fit and proper criteria) Organization culture (e.g. customers first) Organization system (ethics must be contained in formal code e.g part of ethical sys. and mission statement) 2 approaches to manage ethics: Compliance based approach aims to remain within letter of law by establishing system of audit and review so that violations are prevented, detected and punished. It works from outside the system. Integrity based approach combines a concern for the law with an emphasis on managerial responsibility. This approach incorporates ethics in organization’s culture in which managers will do the right thing e.g shared accountability, sound behavior, defining values. It works from within the system Whistle blowing: It is the disclosure by an employee of illegal, immoral or illegitimate practices on part of the organization. Four types of ethical leaderships in organisations: i) Creative :reflecting founder, such leaders create ethical style. ii) Protective :they sustain value of customer services iii) Integrative :aim through consensus through people iv) Adaptive :changing culture as per new environment Social Responsibility Objectives of a company: Economic objectives Social/Ethical objectives Boundaries (Imposed rules; they restrict management’s freedom of action) Responsibilities (Voluntarily undertaken obligations e.g. charities) Social/Ethical objectives of a company: SHE Issues (e.g minimum wages, job security) Good employer (e.g good working environment, job satisfaction) Good Public image (e.g good quality products) Society well being (e.g regular order and timely payments to suppliers) Pollution Financial assistance (e.g. Charity, Sports) (For other objectives see Stakeholders’ objectives) www.canotes.multiply.com 28 Arguments against and favoring Social Responsibility recognition: Social responsibility is expected from all types of organizations. AGAINST: Organizations should concern wealth only because Shareholders own assets. Shareholders are part of society. Taxes on revenues are given to build society. Businesses exist for profit. FAVOUR: (by Mintzberg) Most shareholders are passive. Ultimately consumer pays taxes via higher prices. Govt. support Firms produces 2 outputs: Goods and services Social consequences of activities e.g. Pollution Responsibility recognition (e.g. charity) improves: Public relations. Business success and development as part of society. Decisions by organization affects society Externality is a social/environmental cost of organization’s activities not borne by organization. Boundary Management: - Good public image - Protect environment from pollution - Good employer - Welfare of local community - securing political environment - improving quality of life - protecting minorities Compliance Based Approach e.g - Audit - Review - Questioning - System for employees - Disciplinary procedures (lawyers) www.canotes.multiply.com Integrity Based Approach e.g - Internal commitment - Guiding values - Pattern of thoughts - Share accountability (managers) 29 Chapter 12 : Corporate Governance Corporate Governance is the system by which companies are directed and controlled. Patterns of share ownership: (Who are shareholders of company) Types of institutional investors: Pension funds Insurance companies Investment trusts Unit trust Venture capital organizations Range of shareholders: Advantages: Greater activity in firm’s shares No individual controlling whole firm Less effect on share price if anyone sells No threat of takeover Disadvantages: Administrative cost is high. Various objectives in holding shares. Why knowing shareholders: To get support by exchanging views. Knowledge of shareholders’ preference about Dividend Policy. To explain recent share price movement. Shareholders’ attitude to risk and gearing. Key shareholders to consult in the event of takeover bid. Agency Theory: “Although individual members of the business team act in their own self-interest, the well being of each individual depends on the well being of other team members and on performance of the team in competition with other teams” Assumptions of theory: Behavioral Individual welfare maximization. Individual rationality. Individuals are risk-averse. Investments are not infinitely divisible. Individuals vary in their access to funds and their entrepreneurial ability. Structural Agency Problem: Arises from separation of ownership from management. Goal Congruence: (solution for agency problem) It is accordance between objectives of agents (acting within organization) and objectives of organization as a whole. Via (e.g.) Profits related pay e.g. bonuses, commission, incentive etc. Rewarding managers with shares Executives Share Option Plans Non-executive directors are directors not running the day to day operations of the company. www.canotes.multiply.com 30 Chapter 13 : Human Resource Management Human Resource Management-Introduction Human Resources Management is concerned with people at work and their relationship as they arise in working environment. Roles/Scope of HR Manager: Staffing: Job Analysis HR Planning Recruitment Selection Retirement, Resignation, Redundancy HR Development: Performance Appraisal Career Planning Training Development Motivation/ (Individuals): Job Analysis and Design Pay and Promotion Leadership and Groups: Creating effective teams Managing conflicts between teams Other Aspects: Health and Safety Workforce diversity (Equal Employment Opportunity) Maternity Compliance with legal and other standards Personnel record and Information System Necessity of separate HR Department depends on Size and Activities of organization. Objectives of HRM: Cooperative Relationships Development of motivated employees Effective response to change Fulfilling social and legal requirements Advantages of HRM: Decrease in Staff Turnover Increase in Productivity Increase in Group learning Increase in initiative Decrease Absenteeism Lesser conflicts Increase quality Increased co-operation Increased commitment HRM Theories Scientific management Human Relation Rational Contingency theory [Clearly defined principals] [Fulfillment of needs] [Division of authority] [Change according to situation] 4 Roles/Areas of HR Planning: (by Tyson as per new strategic viewpoint) To represent organization’s central value system To maintain boundaries of organization www.canotes.multiply.com 31 To provide stability and continuity To adapt the organization to change Views of HRM: Traditional Odd Job view “It is a collection of incidental techniques without much internal cohesion” (Drucker) Manager was partly a Clerk, housekeeper, social worker and fire fighter. It dealt mainly with Hiring and Firing. Reactive and defensive role Employee’s Consent was obtained. New Strategic Viewpoint It is concerned about Organization, Employee’s relations and service. Proactive and constructive role Employee’s Commitment is obtained. Motivation, HR Planning Human Resource Planning: “HR Planning is forecasting demand of human resources, forecasting its supply and closing gap between demand and supply” It considers When employees needed. How many employees needed. So basically HR Plan deals with recruitment, retention, downsizing & training of workforce. Process of Human Resource Planning 1. Strategic Analysis (of) a. Environment b. Organization’s objectives c. Manpower’s SWOT 2. Job Analysis a. Job description b. Job specification c. Employee specification 3. 4. Forecasting of a. Internal Demand and Supply b. External Supply Implementation a. HR Plan Job Analysis The process of collecting, analyzing & setting out information about the contents of job in order to provide basis for job description and data for recruitment, training, job evaluation & performance management. Systematic way to gather and analyze information about the Content Context Human requirements of the job. Type of information needed Purpose of the job Content of the job Relations to other job Performance criteria Responsibility Accountabilities Organizational factors Development factors Environmental factors Job analysis results in: Job description Job specification Employee specification www.canotes.multiply.com 32 Job Description A written statement of duties, responsibilities and tasks of job. It should be written in outputs and performance levels. Purpose of Job description: Organizational--------- Defines job’s place in organizational structure (job evaluation). Recruitment------------ Provides person specification Legal-------------------- Provides basis for contract of employment Performance----------- Performance objectives can be set. Contents of Job description: A job description should be a formal, written document, usually from one to three pages long. It should include the following: Date written. Job Status (full-time or part-time; salary or wage). Position title. Job summary (a synopsis of the job responsibilities). Detailed list of duties and responsibilities. Supervision received (to whom the jobholder reports). Supervision exercised, if any (who reports to this employee). Principal contacts (in and outside the organization). Related meetings to be attended and reports to be filed. Competency or position requirements. Required education and experience. Career mobility (position[s] for which job holder may qualify next). Alternative to Job Description is Role Definition. (wider) Job Specification Minimum acceptable qualification (i.e. knowledge, skills, abilities, experience and other characteristics needed to do a particular job.) Person Specification Identifies the type of person needed to do a particular job. Following characteristics are assessed: (Fraser’s 5 point to assess pattern of personality) 1. Impact on other 2. Motivation 3. Acquired knowledge or qualification 4. Innate ability (initiative, innovative) 5. Adjustment and emotional balance Competencies Capacity of a person that leads to behavior that meets the job demands. Intellectual Competence (Strategic, judgment, planning) Interpersonal Competence (managing staff) Adaptability (flexibility with change) Results Methods of Job Analysis: Logos/Diaries Interviews Observations Questionnaires HR managers write job description & specification for review by managers Managers identify performance standards based on job analysis information. Forecasting Demand and Supply of manpower: Demand is estimated from: New markets New product/service New technology Divestment Organizational restructuring www.canotes.multiply.com 33 Supply is estimated from: Current workers’ Stocks and Flow analysis External labor market A Position Survey compares demand and supply. (Grade, skills, location etc) Closing the gap between Demand and Supply- HR Plan: (along with subsidiary plans of HR Plan) HR Plan is prepared on the basis of personnel requirements, productivity and cost. Meeting Shortage of HR (Less supply More Demand) Internal Promotions, Transfers (Redevelopment Plan) and Training (Training Plan) etc. Reducing Labor turnover (Retention Plan) Overtime (Productivity Plan) External recruitment (Recruitment Plan) Meeting Surplus of HR (Less Demand More supply) Restricting recruitment Part-time working Redundancies (Redundancy Plan) Recruitment(a part of HR plan) Definition: “ Recruitment is the process of generating a pool of qualified applicants for organization’s job” Strategic Recruitment Decisions: 1. Organization based Vs. Outsourcing 2. Regular Vs. Contractual Vs. Leased 3. Internal Vs. External recruitment 4. EEO and Diversity issues Systematic approach to recruitment and selection: HR Planning Job analysis Identification whether employee is to be recruited from outside or promoted inside (from HR Plan) Evaluation and use of Sources of Recruitment Selection Notification of result Induction training Sources of Recruitment: Internal Search: 1. Organizational database (HRIS) to sort employee data according to job requirement. 2. Employee referrals 3. Promotion and Transfers Advantages: Good employee relations Encourages ambitious individuals Less costly No adjustment or orientation time required, because already familiar i. Individual with organization and policies ii. Organization with individual Disadvantages: No new blood, no innovation and new perspectives Political fight for promotion Morale problems of those not promoted Diversity lacking Requires training www.canotes.multiply.com 34 External Search: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Advertisement (method depends on organization and nature of job) Newspaper T.V. Net Agencies and Professional organization Blind Box ads Schools, Colleges and Universities Unsolicited applications Creative recruitment methods Banners Announcing prizes for Referee Applicants What must be included in job advertisement: Information about organization Primary business EEO Employer Information about job and application process Title and responsibility Job location Starting pay range Contact address Closing date for application Desired qualification of candidate Experience 3----5 Characteristics needed Internet Search: 1. 2. Employer website Professional career websites Advantages: Cost saving Time saving Global in nature Disadvantages: Non-serious application Difficult to process large number of application Not accessible to all Selection: (part of Recruitment) “The process of choosing individuals who have needed qualification to fill job in an organization” Purpose of selection: “Filling a right person to the job” ensuring Person fits job (matching people with job characteristics) Person fits organization (Objectives, culture, values etc. of organization) Steps in selection process: Initial screening Complete application (on specific form) Employment tests Comprehensive interview (keeping in mind job description & job specification) Background information (depends on nature and sensitivity of job) Medical examination Conditional job offer Permanent job offer www.canotes.multiply.com 35 Why and What tests are conducted Cognitive ability tests o Thinking, memory, reasoning o Mathematical abilities o Communication abilities Physical ability tests Writing analysis Performance simulation test (requiring to perform actually a small segment of the job) Advantages of interview Most valid to determine applicant’s Organization fit Level of motivation Interpersonal skills Limitations of Interviews Unreliable assessment (wrong decision) Fail to provide accurate prediction (error of judgment) Halo and Horns Effect (based upon single attribute) Stereotyping candidates on the basis of dress, hairstyle, accent etc. Discrimination in selection is justified only if required by law. Induction Training: Identify area for later learning or training (e.g. detailed technical knowledge) Explain nature of job and goal of each task Explain working hours Explain structure of organization hierarchy and his position Introduce with people in office. Plan and implement training program. Appraise after 3,6 or 12 months. www.canotes.multiply.com 36 Chapter 14 : Motivation and Performance Individuals Variables affecting Job performance: Organizational and Social variables Social environment Type of Incentives Type of Training and Supervision Situational variables Characteristics of Organization Physical environment Physical and Job variables Methods of work Work space and arrangements Designing and condition of work equipment Individual (non work) variables Age Sex Physique Education Experience Intelligence Aptitude Motivation Personality Personality and individual Development: (Individuals are different because their personality is difference and personality differences affect work behavior). Personality is the total patterns of thinking; feeling and behaving that constitute the individual’s distinctive method of relating to the environment. According to Chris Argyris, as people mature they display certain characteristics: 1. Increasing self awareness 2. Acceptance of equal or superior relationship to others 3. A tendency to move from dependence towards independence 4. Diversification of behavior patterns 5. An increasing tendency to activity, rather than passivity 6. Deepening and more stable interests Factors affecting personality differences: Authoritarinism Self-esteem Feedback on performance Moderately difficult tasks Psychological success Commitment Motivation - Need of achievement - Attitude - controls and standard - levels of risk taking - challenging goals and achievement - willingness (Content theories VS Process Theories) Motivational Theories McGregor’s theory X and theory Y: Theory X---People dislike work and responsibility, they have to be controlled, threatened, punished to get work done. Theory Y---Work is as natural as play and rest, they accept responsibility, they give way to consultation and self growth. www.canotes.multiply.com 37 Maslow’s hierarchy of needs: ( A ranked structure of behavior stimulating within individual which explains motivation) Self actualization (fulfillment of personal potential, freedom, fairness, justice) Esteem needs (Independence, status, respect, gaining knowledge) Social needs (relationship, affection, belonging) Safety needs (security, threat) Physiological needs (food, cloth, shelter) Alderfer’s ERG theory: E-----Existence R---Relatedness G---Growth McClelland’s needs: Need for achievement, Need for power, Need for affiliation These needs could be taught from top to lower managers. Top management Entrepreneur Achievement Employees Power Affiliation Herzberg’s two factor theory: There are 2 groups of work related factors. Hygiene factors (remove dissatisfaction e.g. Salary, Job security, Working conditions, Interpersonal relations) Motivators (creates satisfaction e.g. Status, growth in job, power authority and responsibility) Vroom’s expectancy theory: Motivation shall depend upon expected results of his efforts i.e value attached to an outcome. F (Force i.e. motivation) = V (valence i.e. strength for preference of outcome) * E (Expectancy i.e. expectation that performance will lead to outcomes) Porter and lawler’s model: (extension of expectancy theory) Force Valence Ability Satisfaction Expectancy Understanding Actual Performance Importance of reward Intrinsic rewards (interest, enjoyment) Success/Failure Extrinsic rewards (pay, bonus) Equity theory: Reward of 1/Output of 2 = Reward of 2/ Output of 2 Satisfaction = (atleast fair reward, not maximum reward) people compare results and rewards people get upset if inequity in rewards Goal theory: Goals can motivate. Psychological contracts “Members will expend efforts and organization will reward them in exchange” Coercive contract (returns are inadequate compensation; involuntary contribution) www.canotes.multiply.com 38 Calculative contract Cooperative contract (returns are defined; voluntary contribution) (employees participate also in decision making) Pay and Job satisfaction Under Herzberg’s theory, Pay is the most important of all hygiene factors. Under Expectancy theory, Pay motivates if pay is linked with performance and is valued by individual. Difficulties in incentive schemes: No motivation if employee already enjoys good package. External factors may affect output and reward. Not suitable in groups Assessment of satisfaction and moral: Through Productivity, Absenteeism and Turnover. Types of incentive schemes: performance related pay (PRP) i.e commission bonus schemes profit sharing e.g opportunity of being member of the company. Job Design (with parameters of Mintzberg) “Job design is the process of determining the specific tasks to be performed (Job specialization), methods used in performing these tasks (training and indoctrination in organizational values), and how job relates to other works in organization (regulation of behavior). Change in job design may be : Job enrichment Vertical expansion of responsibilities Change in the content and responsibility of job to provide greater challenge Job enlargement Horizontal expansion of duties Provides greater variety of tasks Job Components: Occupation------Jobs-----------Position----------Duties------------Tasks (Responsibilities) Job restructuring and redesign: Job redesign Job rotation Job enlargement Job enrichment suiting of jobs according to motivational factors. allowing variety and understanding, development of extra skills adding extra and related tasks to current job increases depth of responsibility by adding planning and control of current job. Working arrangements: attitude and values high performance work systems empowerment compressed week part-time work i) ii) iii) www.canotes.multiply.com flexible working arrangement multi-skilling flexitime job sharing home-working (distant working) Numerical flexibility Financial flexibility Task flexibility 39 Employee Appraisal “Appraisal is a systematic review and assessment of an employee’s performance” Why: Employee Development: Specific Job performance feed back Career opportunity information Assessing employee potential Decision Making for Action by Administration: (Results of appraisal) Promotion Demotion Transfer Termination Organizational Research: (Importance of appraisal) HR Planning (Promotability and Potential) Evaluation of Selection and Training methods To motivate employees giving feedback Inventory assessment for planning To assess training needs Purpose of appraisal: Reward review for deserving employees Performance review to confirm whether any training is required or not Potential review to confirm whether any management career planning is required or not. Objectives: Achieving objectives Performance levels Training needs Identifying lacking areas Communication 360-degree feedback -Sources: Self Senior Peers Juniors Assessment centers Customers [Upward appraisal is better.] Types: (What could be assessed) Traits Behavior Performance Methods: 1. Check list appraisal (yes/no) 2. Forced choice appraisal (MCQs) 3. Essay appraisal/ Overall assessment (paragraph) 4. Grading, result oriented schemes, and self appraisals An appraisal system: i) ii) iii) iv) v) vi) www.canotes.multiply.com Identify criteria for assessment Preparation of appraisal report Appraisal interview Review assessment Action/plan preparation Monitoring progress (follow-up) 40 Methods of appraisal: i) Upward appraisal ii) Customer appraisal iii) 360 degree appraisal sub-ordinates upraise their seniors internal & external Mair’s 3 approaches to appraisal interview: The tell and sell method The tell and listen method The problem solving approach Effective Appraisal: Job related criteria Standardization Trained appraisers Employee access Purpose must be understood by both It must be participative, problem solving activity Regularly conducted. Effort, integrity and ability of line managers. Lockett’s appraisal barriers: Lack of agreement on performance level Rater is biased. Recency effect (weighting recent events) Disagreement on long term prospects One sided process Central tendency Many targets at annual meeting become out of date. Central tendency (giving average rating to anyone) Sampling Error (available information is insufficient or inaccurate) Interview and counseling: 1) Tell and sell method 2) Tell and listen method 3) Problem solving approach (manager tells, and then try to gain acceptance) (manager tells, the subordinates responds, and consensus is achieved) (manage becomes counseller, and ask work problems) Managing Careers: Career management is a technique whereby the progress of individuals within an organization from job to job is planned keeping organization needs and individual capacity in mind. Difference between Functional Manager and General Manager: Goals Orientation Role Information www.canotes.multiply.com Functional Manager Short term Task oriented Organizer Defined sources Formal channels General Manager Long term Goal oriented Facilitator Coordinating interdepartmental activities Obtaining and allocating resources Poorly defined sources Informal channels 41 Chapter 15 : Training Appraisal and Career Management Training and Development HR Development: “The process of extending personal abilities and qualities through development activities e.g. training, appraisal, career planning, job rotation etc.” Training: “The process of providing employees with specific skills to carry out work effectively or to correct deficiencies in their performance” Development: “ An effort to enhance a person’s abilities that organization will need in future”. Development purpose: Ensures firm meet current and future performance objectives by Maximizing people’s potential Continuous improvement Development activities: Training (on job and off the job) Career planning Job rotation Appraisal Other learning opportunities Benefits of training and development: For Organization Training supports business strategy Higher productivity Management of SHE issues Less need for detailed supervision Multi skilled people Succession planning Increased commitment For employees: Enhanced skills Psychological benefits (valuable) Social benefits (e.g. contact) Job management When training does not work: Bad management Poor Job design Poor equipment Motivation Poor recruitment Other characteristics of employee (e.g. intelligence) Types of training courses: Day release Distant learning Evening classes Revision courses Sandwich course Full time course Learning organization: An organization that facilitates the learning of all its members and continuously transforms itself. A learning organization creates, exploits and shares knowledge. Characteristics of learning organization: www.canotes.multiply.com 42 Learning approach to strategy Participation in decision making Information is used as a resource Formative accounting Reward flexibility Enabling structural responsiveness to external changes All employees are environmental scanners Intercompany learning Learning climate Training Process: Step 1. Training needs are identified: Training need analysis Current state Desired state Existing knowledge and skills Required knowledge and skills Individual performance Required standard Organization’s current results Desired results Difference between two columns is Training Gap. Training surveys Corporate strategy Appraisal and performance review Attitude surveys Evaluation of existing training programs Job analysis Step 2. Specify knowledge, skills and competence required: Step 3. Define training objectives: These objectives should be clear, specific, measurable, and observable. Step 4. Plan training program Step 5. Implement the training Methods of training Formal training On Job Training Course training (lectures, discussions, exercises, role-plays, case studies) Computer based training Instructions/Demonstrations Coaching Job rotation Temporary promotion ‘Assistant to’ Positions Action learning Committees Project work Step 6. Evaluate the training Ways to evaluate. Organizational changes as a result of training Trainees’ learning test Trainees’ reaction to experience Changes in job behavior following training Impact of training on organization’s goals Validation of training means observing results of training and measuring whether training objectives have been achieved. Evaluation of training means comparing costs incurred with benefits obtained to redesign/withdraw scheme. Personnel Development Plan: “Development plan for individual” www.canotes.multiply.com 43 Skill analysis: Aim is to put interest into actual role. Liking of skills High Low Performance High Likes and does well (Motivated) Dislikes but does well Low Likes but does not do well (Requires training) Dislikes and does not do well Learning cycle by Kolb: Concrete experience Applying/testing the implications of concepts in new situations Observation and reflection Formation of abstract concepts and generalizations Learning styles of individuals by Honey and Mumford: Theorists Understand underlying concepts Preference for concepts or analysis Take intellectual ‘hand-off’ approach based on logical argument Observe phenomena, think about them and then choose how to act Find learning difficult if forced into hurried program. Tend to be fairly slow, non participative and cautious. Require training on hand-on Excited by participation and pressure e.g. new projects Flexible, optimistic, rush without preparation, take risks and get bored. Good at learning new techniques in OJT Aim is to implement action plans and/or do the task better May discard as impractical good ideas which require development. Reflectors Activists Pragmatists Competence “ Capacity that leads to behavior that meets job demands within organizational environment and brings desired results” Types of competence: 1. Personal/Behavioral (Personal characteristics and behavior required for successful performance). 2. Work based/Occupational competence: (expectation of work performance and outputs and standards that are expected by people in specific roles) 3. Generic competence can apply to all people in an occupation. Competence of managers: Intellectual i. Strategic Perspective ii. Analytical Judgment iii. Planning and Organizing Interpersonal i. Managing staff ii. Persuasiveness iii. Assertiveness and Decisiveness iv. Interpersonal sensitivity v. Oral communication Adaptability results i. Initiative ii. Motivated iii. Business sense www.canotes.multiply.com 44 Chapter 16 : Management and Human Resource Leadership Trait Theories: Leaders have certain qualities (Inborn or Acquired) e.g. Helicopter factor i.e certain traits makes a person good leader. Style theories: A manager’s style is the way in which the manager handles his relationship with the task and with subordinates. Leadership is an interpersonal process and is affected by behavior. To create an effective group, characteristics of followers should match with characteristics of leader. Huneryager and Heckman: Dictatorial Manager makes decisions and enforces them Manager makes decisions and announces them Manager sells his decisions Manager suggests own ideas and asks comments Manager suggests his idea and amends as per comments Manager presents problem, asks for ideas and makes a decision Manager presents a problem and asks to solve it. Manager allows his subordinates to act freely within prescribed limits. Autocratic Democratic Laissez-faire Leadership: Definition Management vs Leadership Manager VS Leader Key leadership skills Developing managers as leaders Theories of leadership i) Trait theory ii) Style theory iii) Contingency theory Leadership skills: Entrepreneurship Interpersonal skills Decision making Time management Self development skills Competitive Goal oriented Team empowering motivated Wholly task oriented Leaders Wholly people oriented Lickert’s 4 elements presented in effective managers: 1. Expect high level of performance 2. Employee centered 3. No close supervision 4. Participative style www.canotes.multiply.com 45 4 styles of leadership: Style Tell (autocratic) Characteristics Manager makes decisions and enforces them Sell (persuasive) Manager makes decisions but convince staff to motivate them. Manager presents problem, asks for ideas and makes a decision Consults Joins (democratic) Strengths Quick decision making Suitable for routine work. Leader and followers make decisions on consensus. Reasons are told to staff. They have better idea of what to do Employees contribute knowledge and experience. Initiative and commitment High motivation and commitment Shares knowledge and experience Weaknesses No initiative and commitment One way communication No initiative and commitment One way communication Slow decision making Staff may not be mature. Slow decision making Staff may not be mature. Conflict may arise. Blake and Mouton’s managerial grid: High Country club Concern for people Low Team Middle road Impoverished Task Low High Concern for production Contingency approach to leadership: (by Charles Handy) Factors which contribute to the success of leader: Leader’s personality Subordinates Task Environment Power, authority and responsibility: Power is ability to do. Following are different forms of powers in an organization: Position power/legitimate power Enjoyed by senior management. It is associated with particular job, almost authority. Resource power (reward power) Enjoyed by senior management Control over resources and power to grant them e.g. promotion Physical power (coercive power) Enjoyed by senior/middle management Power of superior force but mostly absent. Expert power Enjoyed by middle/low management Power based on expertise Negative power Enjoyed by middle/low management Use of disruptive attitude to stop things, it may be destructive. Personal power Power in personality of individuals Authority is right to do. (decision-making power) Responsibility is obligation to do. www.canotes.multiply.com 46 Influence is ability to change behavior of others. Accountability managers are accountable for their action. Delegation of authority sharing of decision making power. Discipline Discipline promotes good order and behavior in an organization by enforcing acceptable standards of conduct. Disciplinary problems: Absenteeism Poor punctuality Poor job performance Poor attitudes Breaches of safety regulations Refusal to carry out legitimate instructions Disciplinary actions: Informal talk Oral warning Written or official warning Disciplinary lay-offs or suspension Demotion Discharge Warning Action Retirement, Resignation, Redundancy Why retirement is encouraged: Promotion opportunities for younger. Early retirement is an alternative to Redundancy. Age structure may become unbalanced. Cost of pension rise with age. Resignation: Exit interview Period of notice. Fair grounds for dismissal: Redundancy o Employer has ceased to carry on business all or in part o Requirements of employees have ceased or diminished. o No compensation if Suitable alternative offer made. Employee is of pension-able age or has less than 20 years of continues service. Legal impediment Non-capability Misconduct Other substantial reasons Unfair Dismissal (See PBP) Discrimination and Equal opportunities Discrimination could be Direct Indirect Positive (law protected) Measures to address underlying problems of equal opportunity: Support from the top Appoint equal opportunity managers Encourage disadvantaged groups to apply Monitoring of minority Maternity leaves, Maternity Pay, Work place nurseries Flexible hours www.canotes.multiply.com 47 Career break Accommodate wheelchair users Health and Safety Importance of Health and Safety at work: 1. Legal obligation 2. Accidents cost money i. Compensation + Repair cost + Increased insurance premium ii. Time lost iii. Subsequent performance is reduced. iv. Recruitment and training of replacement has cost. 3. Corporate image is improved. Employer’s Duties: Work environment must be safe and healthy. Plant and equipment must be maintained to standard. Work practices must be safe. Health and Safety Policy should be communicated to all employees. Statement of principles Detail of safety procedures Detailed instruction of how to use equipment Training requirement Compliance with law Risk assessment should be made. Hazard and risk information should be shared. Identify employees who are especially at risk. Controls must be introduced to reduce risks. There must be safety and health advisors. Employee’s duties: Take reasonable care of themselves and others. Allow the employer to carry out his duties. Inform the employer of any situation which may cause danger. Use all equipment properly. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. National legislation on important labor matters Industrial and Commercial Employment (Standing Orders) Ordinance 1968 i. Appointment, transfer, promotion ii. Leaves iii. Insurance iv. Bonus v. Termination vi. Gratuity Industrial Relations Ordinance 1969. Employee Social Security Ordinance 1965 i. Medial expenses ii. Compensation in lieu of wages during illness Employee Old age Benefits Act 1976 i. Rules for pension Company Profit (Workers Participation) Act 1968. i. 5% of net profit + adjustments ii. Fund could be maintained. Workers Welfare Fund Ordinance 1971. www.canotes.multiply.com 48 Chapter 17 : Groups in Organisation Groups: “A group is any collection of people who perceives themselves to be a group”. Sense of identity Loyalty to group Purpose & Leadership Team: “A team is a small number of people with complementary skills who are committed to a common purpose, performance goals for which they hold themselves accountable” A team could be: Multi-disciplinary teams Contains specialists in different areas Freer and faster communication between disciplines in organization Multi skilled teams Contains people who possess many skills Tasks can be shared in flexible way. Development of team: (by Tuckman) Forming (collection of individuals) Storming (targets are set and trust increases) Norming (work sharing, individual requirements and expectations) Performing (execution of task) Members/Roles of team: (by Belbin) Coordinator (presides and coordinates) Shaper (dominant, extrovert, task oriented) Plant (introverted, source of ideas) Monitor evaluator (analytical rather than creative) Resource investigator Implementer (administrator not leader, scheduling, planning) Team worker (supportive, noticed in absence) Finisher Problems with team: Group norms restrict individual personality. Conflict in roles and relationship Personality problems Rigid leadership Not suitable for all jobs Too much harmony (group think) or differences of opinion Creating an effective team work: (A contingency approach by Handy) The Given Group’s members Group’s task Group’s environment Intervening factors Motivation Leadership Process Procedure The Outcomes Productivity Effectivity Objective is met within time Group satisfaction Management can operate on both ‘givens’ and ‘intervening factors’ to affect the ‘outcomes’. www.canotes.multiply.com 49 Indications of Effective Team: Quantitative factors Productivity Absenteeism Turnover rate Accident rate Targets Interruption to work rate Qualitative factors Commitment Understanding Communication Feed back Job satisfaction Motivation Conflict in organizations: (Individual / Group level) Different views conflict in organizations: The happy family view: Organizations are essentially harmonious. There are cooperative structures to achieve common goals with no systematic conflict of interest. The conflict view: Organizations have conflict on individual and group level. Members battle for limited resources, status and reward. Conflict could be destructive if not handled carefully. The evolutionary view: Conflict is seen as a useful basis for evolutionary change and not for revolutionary change. Could be constructive if handled by arguments or competition(Handy). Causes and tactics of conflicts between departments: Operative goal incompatibility Personality differences Task interdependence (if managed badly) Scarcity of resources Power distribution (Boundaries of authority) Uncertainty (in change) Reward systems (not being fair) Conflict – constructive and destructive How constructive Different solutions Creativity and testing of ideas Attention on individual contribution Brings emotions into open Motivational factors brings out Effects of Conflicts within groups: How destructive Distract attention from task. Objectives may be subverted for secondary goals. Disintegration of the group Emotional/ Win-lose conflicts may arise. (Close competition) (Sherif and Sherif) PTCL vs. Union Within a group: Group becomes more structured and organized. Members eliminate their differences, get close and demand loyalty. Climate becomes task oriented. Members’ individual needs are subordinated to achievement. Leadership moves from democratic to autocratic with group’s acceptance. Winning group: Cohesion Relaxation www.canotes.multiply.com 50 Return to group maintenance and concern for members’ needs. Assertion for group self-concept with little reevaluation. Losing group: It may deny defeat or blames on others. Loses cohesion. Turn to regrouping. Reevaluates perception of itself and other group. Might become cohesive and effective unit if defeat is accepted. Managerial response to conflicts: (by Hunt) Denial/Withdrawal Suppression Dominance Compromise Integration/Collaboration (if conflict is trivial) (preserve working relations despite minor conflicts) (application of power to settle the conflict) (bargaining, negotiating, conciliating) (emphasis must be put on task and individuals must modify behavior) To reduce conflict behavior: Limited communication Structural separation Bureaucratic authority (use of) To encourage cooperative behavior: Job rotation Inter-group training Integration devices (e.g. problem solving teams, force to work together) Group think: (IL Janis) “Psychological drive for consensus at any cost, that suppresses dissent and appraisal of alternatives in cohesive decision making groups” Symptoms of group think: Moral blindness (might is right) Perception of unanimity Strong group pressure to quit dissent Rationalization for inconsistent facts. Mutual support to guard the decision. Group subculture: Subcultures are cultures which exist within cultures. Characteristics: Group share distinctive way of life, beliefs. Learned from others in the group. Way of life has somehow become traditional. Political behavior: Organizations are political systems because people within them have their own objectives and priorities. Political behavior is concerned with competition, conflict, rivalry and power relationships in organization. Political Game: Mintzberg identifies various Political Games played in organization which can be useful or harmful. Game resist authority Game to counter this resistance Game to build power basis (control over resources and superiors, colleagues, subordinates etc.) Game to defeat rivals (interdepartmental) Game to change the organization At senior level political activities occur in following cases Allocation of resources. Management Succession Interdepartmental coordination Structural change www.canotes.multiply.com 51 Chapter 18 : Strategies for Critical Periods Large Vs. Small organizations Issues/problems in large organizations: Organization’s structure: Sharing roles and responsibilities (who does what?) How much specialization How many levels of management Delegation of authority (centralized or decentralized) Planning and control: Vague accountability MIS should be in place Coordination Reward Slow adoption to change Motivation is down No self-esteem Slow decision-making Solutions: Decentralized and delegation of authority Fair pay policies with bonus, awards and rewards MIS Delayering in hierarchy Job design Issues/problems in small organizations: Over reliance on a few key persons No economies of scale Small market area/ restricted range of products Low bargaining power Cannot raise money Can not afford help (from experts) Solutions: Growth Specialist servicing Key person’s insurance Corporate decline 3 types of decline: 1. Declining industries (i.e. Environment entropy; environment is no longer supportive) Temporary decline (product revitalization) Permanent decline (end game) 2. Vulnerability SLEPT Porter’s 5 forces 3. Declining company (i.e. organization atrophy) Symptoms (by Stuart Slatter) Decrease in sales revenue Decrease in profitability Decrease in liquidity Decrease in market share Lack of planning www.canotes.multiply.com 52 Increase in gearing Top management fear Change in senior executive Financial engineering (change in accounting policies, auditors etc.) Restriction on dividend policy 4 stages in the crisis (by Stuart Slatter) Blind stage/Crisis denial Inaction/Hidden crisis Faulty action/Disintegration Crisis/Collapse/Dissolution Causes of decline and strategies to overcome: Causes Poor management Poor financial controls High cost structure Poor marketing Competitive weakness Big projects/acquisition Escalation of commitment of bad decisions Strategies New management + restructuring Tighter controls + delegation of responsibilities Cost focus strategy + Ansoff’s matrix Redevelop marketing mix + motivate sales force Porter’s generic strategies Feasibility reports Reasons for escalation: They think decision was right; implementation was wrong. Humiliation of climb down. Consistency is valued. Mistakes are viewed as failure not learning Outcomes are uncertain. Failure to understand principle of relevant cost. Turnaround of decline: Visionary leader required. Contraction and cost cutting. Reinvestment in organization’s capability. Rebuilding with innovation. www.canotes.multiply.com 53 Chapter 19 & 20 : Change Management and Changing Environment Change Types of change: Changes in environment (Cause) Changes in organization (Effect) Changes in products/services Changes in technology and working conditions Changes in management and working relations Changes in organizational structure and size Change is small and gradual whereas Transformation is crucial and significant. Factors forcing change: Changes may occur due to Threat of new entrants Bargaining power of suppliers Bargaining power of customers Threat of substitutes Rivalry between competitors Environmental factors: SLEPT Porter’s 5 competitive forces Changes in Technology: Computerization New products Better MIS Change in Working conditions: New offices Varied work times Emphasis on health Govt. regulations Change in Management: New style of leadership Participation in decision making Collaboration between management staff & unions Change in Personal policies: Change in rules and procedures (e.g. smoking) Promotion, transfer, training , development Change in structure and size: Due to Takeovers Delegation of authority Centralization Downsizing Nature of strategic change: Incremental Change may be Transformational Reactive Management may Be Types of Changes Pro-active Step change Planned change Emergent change Model for change: Determine need/desire for change in a particular area. Prepare tentative plan (via Brainstorming) Analyze probable reactions to change. Make a final decision (Coercive or Adaptive) Establish time table for change. Speed of implementation will depend on: Type of change (Coercive, Adaptive or Managed resistance change) Reaction of people (Acceptance, Indifference, Passive resistance, Active resistance) Driving and Restraining forces (Force Field Analysis) Communicate the plan for change Implement, review and modify change. Review the change Approaches to change: i) Unfreeze – Move /Shake– Refreeze ii) Adaptive change approach iii) Coercive change approach iv) Using Change agent v) Integrative VS segmentalist vi) Theory E & Theory O www.canotes.multiply.com Resistance to change Active resistance passive resistance 54 Force Field Analysis: (Lewin) It is an interplay of restraining and driving forces that keeps things in equilibrium. Introducing change: 3 factors to consider to minimize resistance. Pace of change: Adapt strategy according to time available. Manner of change: Resistance should be welcomed. Reasons and results of change should be circulated. Change must be sold to people concerned. Individuals must be helped to learn. Scope of change: Small or Transformation. Change process: (by Lewin/Schein) Unfreeze existing behavior: Most difficult and neglected stage. Selling the change. Give motive for change. Behavior change: Identify new behavior. Encourage individuals to own change. Refreeze new behavior: Through positive or negative reinforcement Effect of change on People: Physiological effect (e.g. pattern of shift working affect eating, walking and sleeping habits) Circumstantial effect (e.g. working environment and working relations) Psychological effect (e.g. feeling of disorientation, Insecurity, risk of rejection, feeling of misfit) Effect on Self concept (New psychological contract, Uncertainty affects sense of competence) Changing culture: Hamper Turner suggests 6 modes of intervention: 1. Find the dangers (locate black sheeps) 2. Brings conflicts in open. 3. Discuss culture with members (play out corporate drama) 4. Reinterpret the corporate myths. 5. Look at symbols, images, rituals. 6. Create a new learning system. Pattern of unhealthy culture: (by Edwin Baker) Flourished initially by founder. Founder retired, employees become rigid and insular. Speed, innovation, flexibility, concern for survival and customer disappeared. Formalization Departmentalism/ Sub optimization Coercive actions needed to compete. Organizational life cycle: Handy’s sigmoid curve: Application of concept of lifecycle to organization with 4 broad stages: 1. The organization is established. 2. Organization grows in size and scope. 3. Period of maturity 4. Organization begins to decline. Such a lifecycle is not inevitable, if organization is able to adapt. www.canotes.multiply.com 55 Greiner’s growth model: (Growth & Organisational Development) As an organization ages, it grows in size. This growth takes place in 5 discrete phases. Each phase has 2 characteristics i.e. Evolution (distinctive factor that directs growth) and Revolution. (crisis to pass to enter next phase) Phase 1: Phase 2: Phase 3: Phase 4: Phase 5: Growth (“Move” Stage) Crisis (“Unfreeze” Stage) (Focus) Evolution (Small organization focusing on operations, personnel issues and innovation) Revolution (Need for leadership skills) (Management/group) Evolution (Management is professionalized, there are more employees but less enthusiasm) Revolution (delegation is problem; lack of detailed control; no initiation) (System) Evolution (decentralized decision making) Revolution (no coordination between departments, sub optimization occurs) (Internal Controls) Evolution (Internal control systems and procedures are developed for coordination and optimal use of resources) Revolution (new procedure inhibits useful actions) (Communication / collaboration) Evolution (Increased informal collaboration; control is cultural rather than formal) Revolution (Crisis of psychological saturation in which individuals become exhausted by teamwork) Criticism on lifecycle models: Formation could also be by Merger or Joint venture. i.e not always founded by visionary ppl. Too many issues for growth and control. (i.e org. structure, org. culture) Growth is not the same as effectiveness. (i.e not a normal state of affair) No idea of time scale involved in any stage. (i.e Linear development) Growth seen as linear development over time; there might be different rates of growth at different times and even loss. Model does not clearly indicate relationship with environment. (i.e it ignores environment) Effect of competition in market is also ignored. Measurement of Growth: (how Adamjee is the largest insurance co.) Sales revenue Profit (in absolute term or ROCE) No. of goods/services sold. No. of outlets No. of employees No. of countries reached. No. of markets served. www.canotes.multiply.com 56 Chapter 22 : The evolution of marketing concept “the right product or service to the right customer, at the right price, at the right time and right place” Marketing Department: Functions (Research, Demand, Design, Selling) Marketing Environment: PESTEL (Political, Economical, Social, Technological, Ecological, Legal) Chapter 1- Introduction Marketing, : Managerial definition: Managing profitable customer relationships, by delivering superior value to customers. Social definition: “a social and managerial process by which individuals and groups obtain what they need and want through creating and exchanging products and value with others.” Core Marketing concepts: Market: A market is the set of actual and potential buyers of a product. Needs, wants and demands: Needs are fulfilled : a state of felt deprivation. Wants are satisfied : the form taken by a human need as shaped by culture and individual personality. Demands are extinguished : Human wants that are backed by buying power. Marketing Offer: Combination of good-service offered to market to satisfy need or want. Value and Satisfaction Customer’s perceived value is the difference between the values that the customer gains from owning and using a product and the costs of obtaining the product. Satisfaction is whether performance meets or exceeds expectations. Exchange, Transaction and relationship: Exchange is an act of obtaining a desired object from someone by offering something in return. Transaction is a trade of value between two parties. Elements of Marketing: Company Supplier Market Intermediaries Competitors ENVIORNMENT End user Customer’s life time value: Value of entire stream of purchases by customer over his lifetime. Customer Equity: Total lifetime value of all of company’s customers. Marketing Management: Marketing management has four functions: Analysis, Planning, Implementation and control. Demarketing’s aim is to reduce demand temporarily or permanently. It is done when product is not feasible from supplier or customers’ point of view. i.e intentional and non-intentional reduction in demand. Marketing Management Orientations The production concept holds that consumers will favor products that are available and highly affordable and that management should, therefore, focus on improving production and distribution efficiency. The product concept states that consumers will favor products that offer the most quality, performance, and features, and that the organization should, therefore, devote its energy to making continuous product improvements. The selling concept is the idea that consumers will not buy enough of the organization’s products unless the organization undertakes a large-scale selling and promotion effort. The marketing concept holds that achieving organizational goals depends on determining the needs and wants of target markets and delivering the desired satisfactions more effectively and efficiently than competitors do. The societal marketing concept holds that the organization should determine the needs, wants, and interests of target markets. It should then deliver the desired satisfactions more effectively and efficiently than competitors in a way that maintains or improves the consumer’s and the society’s well-being. www.canotes.multiply.com 57 CONCEPT Production concept CUSTOMER WANTS Availability and affordability Product concept Selling concept Marketing concept Quality, performance, features No feelings to purchase Needs & wants of target market COMPANY SHOULD Improve production, distribution efforts Continues product improvement Large scale selling, promotion Effective & efficient than competitor Two Steps of marketing: Determine Need, Wants And Interest Of Target Market Then Satisfy Them Effectively And Efficiently Marketing Vs. Selling: Selling concept Starting point Factory Focus Existing products Marketing concept Market Customer needs Means How to increase demand How to satisfy demand Ends Profits through sales volume Profits through satisfaction customer Despite adoption of market oriented approach; there is need for sales force: To create awareness To convince to buy from company, not from competitors To reassess benefits to customers To convince that average customers’ requirements are met Problems in introducing the marketing approach: Understand what marketing orientation actually means Organizational, structural and cultural changes are required. Assessment of Product, logistic, level of services and marketing techniques Organization wide dedication Types of Marketing Working together as whole Scope of Marketing = Marketing Planning Strategic Marketing Tactical Marketing Tied with corporate strategy e.g which product of market to choose Short term, and focuses on place, promotion, price Marketing Vs. R&D department: Marketing has commercial and competitive atmosphere whereas R&D has University atmosphere with open-end work and consumption of substantial resources. Customers’ needs and change in product specification tighten them. Consumerism is a term describing importance and power of consumers. Customer Database Customer Relationship Management: Customer Portfolio Defined narrowly as a customer database management activity. “CRM is managing detailed information about individual customers and carefully managing customer touch points to maximize customer loyalty”. Companies look for touch points. These includes customer purchases, sales force contact, service, and support calls, Web site visits, satisfaction surveys, credit and payment interactions, market research studies, etc. To be effective in CRM, the marketer must forego short-term profit maximization on individual transactions. Elements of Marketing Mix: Controllable: Product Price Place Promotion Uncontrollable: (Marketing environment) SLEPT Analysis www.canotes.multiply.com How to Get Customer Touch Points: Purchasing trend Payment trend Service obtaining trend Family trend History Support calls Website visits Emotional attachments 58 Porter’s 5 forces model i) ii) iii) iv) v) Threat of new entrants Threat of substitutes Bargaining power of customers Bargaining power of suppliers Rivalry among competitors Service industry: People Processes Physical evidence Important Points for discussion questions: 1. Expectation = Perceived value 2. Customers often do not judge product’s value and cost accurately and objectively. 3. A Customer buys the highest perceived value. 4. Satisfied customers give benefits of i. Loyal ii. Being less price sensitive iii. Talk favorably 5. Two fold object of marketing i. Retain existing customer by providing satisfaction ii. Attract and grow new customers by promising superior value Marketing Approaches Push Approach Focused on pushing goods to Reseller and customer. The focus Is on sale volumes. Pull Approach Focused on pulling resellers and customers by satisfying them, Fulfilling their demands to attract Them to the company Three Important Concepts: Value-Chain : How activities of organisation contributes towards creating value in goods or services. Internal Customer Concept: Department in an organisation treat each other as ‘customers’, it encourages serviceoriented attitude. Hence when every department is satisfied ultimately the quality will be enhanced. Relationship Marketing: To build long term relationship with existing customers, rather than focusing on products, focus is on relationship i.e selling more products to same customer, rather than to new customers. Model of Consumer behavior: A model of consumer behavior helps managers answer questions about what, where, how and how much, when and why they buy. The stimulus-response model of buyer behavior shows that marketing (made up of the four P’s—product, price, place, and promotion) and other environmental stimuli (Micro and Macro) center on the consumer’s “black box” and produce certain responses. Marketers must figure out what is “in” the consumer’s “black box.” Marketing and other environmental stimuli: (i.e Stimulus – response model) Already discussed Consumer’s Black box: The “black box” has two parts. 1). The buyer’s characteristics influence how he or she perceive and react to stimuli. (Uncontrollable) 2). The buyer’s decision process itself affects the buyer’s behavior. (Semi-controllable) Characteristics affecting consumer behavior: Marketer can not control them but should learn them. Cultural o Culture o Subculture o Social class www.canotes.multiply.com 59 Social o Reference group o Family o Roles and status Personal o Age and lifecycle stage o Occupation o Economic situation o Lifestyle o Personality and self concept Psychological o Motivation o Perception o Learning o Beliefs and attitudes Culture is the set of basic values, perceptions, wants, and behaviors learned by a member of society from family and other important institutions. Subculture is a group of people with shared value systems based on common life experiences and situations. Subcultures might be nationality groups, religious groups, racial groups, or geographic area groups. Social classes are society’s relatively permanent and ordered divisions whose members share similar values, interests and behaviors. Reference group has a direct (face to face) or indirect points of comparison or reference in forming a person’s attitudes or behavior. Aspirational group is one to which an individual wishes to belong. Opinion leader is a person within a reference group who, because of special skills, knowledge, personality or other characteristics, exerts influence on others. Personality is a person’s unique psychological characteristics that lead to relatively consistent and lasting responses to his or her own environment. A motive (drive) is a need that is sufficiently pressing to direct the person to seek satisfaction. Perception is the process by which people select, organize, and interpret information to form a meaningful picture of the world. Learning is changes in an individual’s behavior arising from experience. Belief is a descriptive thought that a person holds about something. Attitude is a person’s consistently favorable or unfavorable evaluations, feelings, and tendencies toward an object or idea. Purchase Decision Process i) Problem Recognition: Perceiving a need. It can be stimulated by: Consumer’s depleted assortment (e.g. empty paste) or Marketing efforts ii) Information Search: To clarify options available to consumers. o Internal search: Scanning of memory (experience) or knowledge about solution of problem/need sufficient For frequent/regular purchases. o External search: Personal sources (family, friends, neighbors, acquaintances) Commercial sources (advertisement, dealers, websites, salesmen) Public sources ( Mass media, consumer rating organizations) For new products. “Word of Mouth” or “Personal sources” has 2 major advantages (through satisfied customers): 1. Convincing, i.e. of consumers by consumers for consumers 2. Costs are low. At the end of this stage, customer arrives at a set of final brand choices. iii) Evaluation of alternatives: Assessing value. Customer may be interested in many attributes. E.g. for Camera Picture tube Ease of use www.canotes.multiply.com 60 Size Price However sometimes consumer has to base his decision only on one attribute. iv) Purchase Decision: [The best rated camera will be bought.] v) Post-Purchase behavior: Dissatisfied Satisfied Delighted A policy by firms is to understate performance because customers are delighted with better-than-expected performance. Why satisfaction of Customer/study of this stage is important: 1. To attract new customers cost more than to retain current customers. 2. Satisfied customers are less price sensitive. 3. Satisfied customers tell others (words of mouth). Bad words travel farther and faster. Decision process for new product i.e. stages in adoption process (from hearing to adoption): 1. Awareness: 2. Interests: seek information i.e. through external sources 3. Evaluation: whether to try or not 4. Trial: on small scale to improve estimate of value 5. Adoption: decides to make full and regular use Chapter 2 Company and marketing strategy Strategic Planning Process: “Strategic Planning is the process of developing and maintaining a strategic fit between organization’s goals and capabilities and its changing marketing environment. Following are steps of strategic planning: 1. Defining mission 2. Analysis of Business Portfolio 3. Setting strategic objectives and goals 4. Developing Competitive strategies i. Porter’s 5 forces ii. Cost-Differentiation-Focus Triangle iii. Growth Strategies (product/market expansion grid) 5. Developing detailed marketing and departmental plans and strategies Mission Statement: This is a statement of organization’s purposes- What it wants to accomplish in the larger environment. It should be market oriented, specific, realistic, motivating and consistent with market environment. e.g. “To provide best satisfaction to customers and fair return on investment, keeping environment healthy and clean and promising secure future to employees” Designing the business portfolio: Business portfolio is the collection of businesses and products that make up the company. Business portfolio planning involves 2 steps: 1. Analysis of current business portfolio. 2. Developing strategies 1. Portfolio Analysis: A tool by which management identifies and evaluates SBUs to determine which business should receive more, less or no investment. BCG growth-share matrix is used to evaluate a company’s SBUs in terms of market growth rate and relative market share. SBU is a unit of company that has a separate mission and objectives and that can be planned independently from other company businesses. 2.Developing strategies for growth and downsizing: The product/market expansion grid is a portfolio-planning tool for identifying company growth opportunities through: www.canotes.multiply.com 61 Existing Market Existing Product Market Penetration New Product Product Development New Market Market Development Diversification Downsizing: When a firm reduces business portfolio by eliminating products or business that is not profitable or no longer fit its overall strategy.. Setting strategic objectives and goals: Firm’s mission is translated into set of objectives for the current period for each SBU. Developing plans and strategies Marketing Process: The marketing process is the process of 1. segmenting the market, 2. selecting target markets, 3. marketing positioning 4. developing the marketing mix, and 5. managing the marketing effort. Marketing mix: The marketing mix is the set of controllable factors that the firm blends to produce the response it wants in the target market. i.e. Product, Price, Place, Promotion Managing the Marketing Effort: Marketing Management has four functions of analysis, planning, implementation, and control.. 1. Marketing Analysis o Analysis of company’s Strength and Weakness [Internal] o Analysis of environment’s Opportunities and Threats. [External] 2. Marketing Planning involves deciding on marketing strategies to attain its overall strategic objectives of company. 3. Marketing Implementation is the process that turns marketing strategies and plan into marketing actions in order to accomplish strategic marketing objectives. Implementation addresses the who, where, when, and how. 4. Marketing control is the process of evaluating the results of marketing planning and its implementation, and taking corrective action to ensure that marketing objectives are attained. Two broad forms of control are important: 1). Operating control involves checking ongoing performance against the annual plan and taking corrective action when necessary. 2). Strategic control involves looking at whether the company’s basic strategies are well matched to its opportunities. The major tool for accomplishing this form of control is the marketing audit. The marketing audit is a systematic analysis and evaluation of organization’s marketing position and performance. It may cover all marketing activities or some of them. Audit will focus on 3 things: 1. Marketing capabilities 2. Performance evaluation (are sales meeting forecasts?) 3. Competitive effectiveness (competitive advantage, product differentiation) Partnership relationship management: “Working closely and jointly with Other departments of company Other companies to bring greater value”. Value Chain and Value delivery network: Value Chain is series of departments within the company carrying out value-adding activities e.g. Designing Producing Marketing Delivery Supporting Value delivery network is network of suppliers, company, intermediaries, and consumers who partner with each other to improve performance of entire system. www.canotes.multiply.com 62 Chapter 23 : Strategic Marketing & Planning 1. Market Segmentation Market segmentation is dividing a market into smaller group of distinct buyers who have different needs, characteristics or behavior and might require different marketing mixes. Market segment is a group of buyers who respond in a similar way to a given set of marketing mix. Basis of segmenting markets: Segmenting consumer market Geographic segmentation calls for dividing the market into different geographical units such as states, regions, counties, cities, or neighborhoods. Demographic segmentation calls for dividing the market into groups based on variables like age, gender, family size, family life cycle, income, occupation, education, religion, race, generation, and nationality. Psychographic segmentation calls for dividing a market into different groups based on social class, lifestyle, or personality characteristics. There are four possible lifestyle categories: 1. Upward mobile, ambitious i. Seek better or more affluent lifestyle ii. Higher standard of living iii. Will try new products 2. Traditional and sociable i. Compliant and conform to group norms ii. Purchasing pattern will be ‘conformist’ 3. Security and Status seeking i. Stresses security and ego-defensive needs ii. Purchase of known and established products and brands e.g. Insurance 4. Hedonistic preference i. Emphasis on “enjoying life now” ii. Immediate satisfaction of needs and wants Behavioral segmentation involves dividing a market into groups based on consumer knowledge, attitudes, uses, or responses to a product. E.g. Occasion segmentation: dividing market according into groups according to occasions when buyers get the idea to buy, actually make their purchase, or use purchased item. Benefit sought: Dividing market into groups according to different benefits that consumers seek from the product. Consumers seek unique combination of benefits e.g. for a laundry detergent, from cleaning and bleaching to economy, fresh smell, strength or mildness etc. User status and user rate Loyalty status Segmenting Business Markets Demographic segmentation Industry (which industry) Company size (what size) Location Operating variables Technology (what technology to focus) User- nonuser status (heavy, medium or light user) Customer capabilities (many services or few services) Purchasing approaches Purchasing function organization (centralized or decentralized) Power structure Nature of existing relationship General purchasing policies (leasing, service contracts, or sealed bidding) www.canotes.multiply.com 63 Purchasing criteria (quality, service or price) Urgency (quick delivery/service?) Specific application Size of order Situational factors Personal characteristics Buyer-seller similarity of values Attitude towards risk (risk taking or averse) Loyalty (to companies who show high loyalty to suppliers) Segmenting International Markets Companies can segment international markets using one or more of a combination of variables. The chief factors that can be used are: 1). Geographic location: location or region 2). Economic factors: Population income or level of economic development 3). Political and legal factors: Type / stability of government, monetary regulations, amount of bureaucracy, etc. 4). Cultural factors: Language, religion, values, attitudes, customs, behavioral patterns. Requirements for Effective Segmentation Substantial—segment must be substantially large or profitable. Accessible—segment must be reached and served easily. Differentiable—It must be conceptually distinguished and should have the ability to respond differently to different marketing mix elements and programs. Actionable—It should be possible to design effective programs for attracting and serving market segment. Measurable—Size, purchasing power, and profiles of a market segment should be measurable. 2. Target Marketing Target market is a set of buyers sharing common needs or characteristics that the company decides to serve. Target marketing strategies: (Product affecting Promotion) The firm can adopt one of four target marketing strategies: A. Undifferentiated marketing (or mass marketing) a market-coverage strategy in which a firm decides to ignore market segment differences and go after the whole market with one offer B. Differentiated marketing (or segmented marketing) a market-coverage strategy in which a firm decides to target several market segments and designs a separate offer for each. C. Concentrated marketing (or niche marketing) a market-coverage strategy in which a firm goes after a large share of one or a few segments or niches. D. Micromarketing is the practice of tailoring products and marketing programs to suit the tastes of specific individuals (individual marketing) and local customer groups (Local marketing). Market offers can be differentiated along the lines of: Product Service Channels People Image Considerations while choosing strategy: Company, resources and objectives Competitor, strategies Product o stage in the life cycle o variability Market, variability Evaluating Market Segments Segment size and growth Segment structural attractiveness Level of competition www.canotes.multiply.com 64 Substitute products Power of buyers Power of suppliers Company objectives and resources 3. Product Positioning Product positioning is imaging the product in the minds of consumers relative to competing products. Positioning task (or choosing a positioning strategy) consists of following four steps: 1. Identifying possible competitive advantages 2. Choosing right competitive advantages 3. Selecting an overall positioning strategy 4. Developing a positioning statement 1) Identifying possible competitive advantages: Competitive advantage (making a difference) is an advantage over competitors gained by offering consumers greater value, either through lower prices or by providing more benefits that justify higher prices. 2) Choosing the right competitive advantages: How many to promote: Only one difference. Aggressive approach More than one differences. Where more than one firms are claiming to be the best at same attribute. However it risks disbelief and a loss of clear positioning. Which ones to promote: Important for buyers Distinctive than competitors offer Superior Communicable and visible difference Competitors can not copy easily Affordable for buyers Profitable for company 3) Selecting an overall competitive positioning strategy: What offer to make in relation to competitor’s offer (Use 2x2 or 3x3 Grid) Price More Same Premium brand More Quality Average Same Less Cow bow brand Less Super bargain brand Bargain brand Economy brand Other strategies are: More for same (Penetration) Same for less Less for much less 4) Developing positioning statement: Positioning statement is a statement that summarizes company or brand positioning, it takes following form: “To (target segment and need) our (brand) is (concept) that (point of difference)” e.g. “To young, active, soft-drink consumers who have little time for sleep, Mountain Dew is the soft drink that gives you more energy than any other brand because it has the highest level of caffeine”. www.canotes.multiply.com 65 Chapter 24 : Marketing Research Marketing Research Marketing Research: “It is the objective gathering, recording, and analyzing of all facts about problems relating to the transfer and sales of goods and services from producer to consumer or user” Marketing research helps in a. Regulating systems b. Reducing risks c. Decision making Types of Marketing Research: Market research: Study and analysis of Characteristics of market Market share Market trends Sales forecasting for all products Market potential for existing products Likely demand for new products Product research: Comparative study between competitive products Studies into packaging and design Forecasting new uses for existing products Customer acceptance of proposed new products Development of new product lines Test marketing Price research: Analysis of elasticity of demand Analysis of cost and profit margins Effect of change in credit policy on demand Customers’ perception of price and quality Place (Distribution) research: The location and design of distribution centers Analyzing the packaging for transportation and shelving Cost of different methods of transportation and warehousing Dealer supply requirements Dealer advertisement requirements Promotion research: Analyzing the effectiveness of sales force Analyzing the effectiveness of advertising on sales demand Establishing sales territories Research procedure: The marketing research process consists of following steps: 1. Defining the problem 2. Designing the research (basis of research objectives) 3. Collection of data 4. Analysis of data (Pre and Post testing etc) 5. Presentation of report 6. Management decision www.canotes.multiply.com 66 Defining the problem and designing the research After the problem has been defined carefully, the manager and researcher must set the research objectives. Collection of data (Research work) Marketing Research data comprises of Primary Data (Field search) Secondary Data (Desk Search) Researchers usually start from secondary data. 1. Collecting secondary data: (Desk research) Secondary data collection is information that is neither direct nor specific. Sources of secondary data: Internal databases: (i.e. MkIS) Advantages Quick access Cheaper Regular & Reliable Confidentiality Disadvantages Incomplete Wrong form Ages quickly Not expert External sources: Information about Competitors (annual reports, press releases, web pages, business publications, advertisements etc.) Analyzing competing products Rival companies’ personnel (executives, engineers, sales force, purchasing agents) Trade suppliers Outside suppliers Online databases New patents or applications for patents 2. Collecting primary data:( Field research) Primary data is information collected for the specific purpose at hand. A plan for primary data collection calls for a number of decisions on Research approaches, Observational research Survey research Experimental research Research methods EPOS (Electronic Point of Sale system) DSS (Decision Support system) Data Warehousing Internet Contact methods, Mail questionnaires Telephone interviewing Personal interviewing Individual interviews Group interviews (including focus-group interviews) Online (Internet) marketing research Mechanical instruments i. People meters ii. Supermarket scanners iii. A galvanometer measures strength of interest or emotions aroused by a subject’s exposure to different stimuli, such as an ad or picture. iv. Eye cameras are used to study respondents’ eye movements to determine at what points their eyes focus first and how long they linger on a given item. www.canotes.multiply.com 67 Sampling plans As surveying the whole population would be too expensive & time consuming, so a sample is selected. Sample is a segment of population selected for marketing research to represent population as a whole. Sample should be a true representative of population and should not be biased Types of samples: Random sampling: Every member has a known and equal chance of selection) Non-random sampling: 1. Systematic (Every nth item is selected) 2. Stratified (Population is divided into mutually exclusive groups e.g. age groups and selecting random samples from each group. 3. Multistage (Process of subdividing population and selecting sample again and again till a suitable selection is made) 4. Quota (Different categories of populations are made and a specific quota from each category is selected) 5. Cluster (Investigators are told to examine every item in a small population that fits the required definition) Potential faults in sampling: Insufficient data Unrepresentative data Bias (where chance of occurrence is not equal) Omission of an important item in questionnaire Carelessness Misinterpretation of data 3—Implementing the Research Plan This involves processing, and analyzing the information. 4—Interpreting and Reporting the Findings Distributing the information: MkIS: “Marketing Information System represent a systematic attempt to supply continuous, useful, usable marketing information within an organization to decision makers often in the form of a database”. Audits: Trade audits: count of stock at wholesalers and retailers Retail audits: count of stock at retailers only Marketing in the Digital age E.Business is the all electronic based information exchange within company or between companies and consumers using following platforms: Intranet Extranet Internet Intranet is a network that connects people within a company to each other and to the company network. Extranet connects a company with its suppliers, distributors, and other outside partners. Internet is a vast public web of computer networks, which connects users of all types all around the world to each other. E.Commerce is more specific than E.Business. It is the ability to buy and sell goods and services electronically primarily by internet. E. Marketing is the marketing side of E.Commerce. Company efforts to communicate about, promote and sell products and services over internet. It includes only Business and Consumers. Advantages: Geographical reach Speed Information sharing of any kind e.g. text, audio, video, animation, graphics Shopping at home (Consumer) No physical barriers (Consumer) www.canotes.multiply.com 68 Doing business 24 hours (Business) Paperless business (Business) Disadvantages: Security concerns (consumer) Whom to complaint (consumer) What you see is sometimes not what you get (consumer) Sometimes physical presence is necessary e.g. smelling a perfume or fitting clothes (consumers) Logistic, shipping, distribution and delivery challenges (business) Availability of secure and affordable communication network E.Business Models: Government Business Consumer Employee Government G2G G2B G2C G2E Business B2G B2B B2C B2E Consumer C2G C2B C2C X B2C E.Commerce occurs when an average citizen interacts with a company (like Bata Pakistan or amazon.com) through a website to buy shoes or books online or making inquiries. B2B E.Commerce is companies doing business electronically with other businesses e.g. a business selling up, down or across the supply chain involving business partners. Such as All Pakistan Textile Association Mills B2E E.Commerce is use of intranet technology to handle activities that take place within a business. Using B2E E.Commerce employees collaborate with each other, exchange data and information and access in-house database, sales information, market news and competitive analysis. Its need arises when branching out and spreading business across geographical areas. E.g. H/O receiving and processing Timesheets, Expense Claims, and Absent forms. C2C E.Commerce is consumers selling goods directly to consumers in an auction process. E.g. EBay Chat rooms for information and advertisement Over personal websites Advertisement on E.news papers G2C E.Commerce is the use of E.Commerce technology by the government to handle activities electronically in which govt. is involved with. E.g. To publish and disseminate information by Govt. Change in address, marital or family status Submission of tax returns To cast vote Customization and Customerization: Customization is individualizing the marketing offer. E.g. taking measurement of jeans for a customer. Customerization is leaving it to individual customers to design the marketing offer, allowing customers to be prosumers rather than consumers. E.g. adding specific features to jeans like colorful patches. New technology in Distribution: DRTV Internet (B2C) o Websites o Email www.canotes.multiply.com 69 Chapter 25 : Product Product A product is anything that can be offered to a market for use, or consumption and that might satisfy a want or need such as soap. Product includes: Goods Services Other entities e.g. People, idea, places, organizations Services are a form of product that consist of activities, benefits offered for sale that are essentially intangible and do not result in the ownership of anything. such as a doctor’s exam. Levels of Products and services: The core product, What is the buyer really buying? The actual product may have as many as five characteristics that combine to deliver core product benefits. They are: Quality level.. Features Style and design. A brand name. Packaging. The augmented product includes any additional consumer services and benefits built around the core and actual products. b. Delivery and credit c. Warranty d. Installation e. After sale service Classification of products: 1. Consumer Products i. ii. iii. iv. Convenience Shopping Specialty Unsought Types of consumer products Marketing Consideration Consumer buying behavior Convenience Shopping Specialty Unsought Frequent purchase Little planning Little effort and involvement Little comparison Special effort Little comparison Strong brand loyalty Low price sensitivity Either no awareness or no interest Price Low Less frequent purchase Much planning Much effort & involvement Much comparison Higher Very high Varies Place Intensive distribution at convenient locations Selective distribution in fewer outlets Varies Promotion Mass promotion Advertising and personal selling Exclusive distribution in only one or few outlets per market area Targeted promotion by producer and reseller Examples Tooth pastes Magazines Televisions Furniture Clothing Luxury goods e.g. Rolex watches Aggressive advertising and personal selling Life insurance Red cross blood donation 2. Industrial (Business) Products,: i. Material and parts ii. Capital items iii. Supplies and Services www.canotes.multiply.com 70 Key Decisions about product: Individual product o Standardized or adapted Market offers can be differentiated along the lines of: Product Service Channels People Image o Product attributes Tangible Quality Features Style and design Brand name Packaging Intangible Image Perceived value o Packaging & Labeling o Product support service Product Line Decisions o Product line length Product Mix/Assortment/Portfolio Decisions o Width (No. of product lines of a company) o Depth (No. of items per product line) o Consistency (how closely related the various product lines are in end use, production requirements, distribution channels, or in some other way. A brand is a name, sign, symbol, or design, or a combination of those that identifies the maker or seller of a product or service. Packaging is the activity of designing and producing the container or wrapper for a product. Labeling is also part of packaging and consists of printed information appearing on or with the package Product support services are the services that augment actual products. A product line is a group of products that are closely related because they function in a similar manner, are sold to the same customer group, are marketed through the same types of outlets, or fall within given price ranges. Product line length is the number of items in the product line. Long/short depends on increase of profit by adding/deleting items. An organization with several product lines has a product mix. Product-Market Matrices: It is a simple technique used to classify a Product/Business according to the features of the product and market to determine the Relative positions of Businesses/Products and Strategies for resources allocation between them. There are 2 commonly used techniques: 1. Boston Consulting Group’s Growth-Share Matrix 2. General Electric Business Screen (GEBS) 1) BCG growth-share matrix is used to evaluate a company’s SBUs/Product in terms of market growth rate and relative market share. Growth rate (%age) Star Needs heavy investment to finance rapid growth potential Question Mark Requires a lot of cash (Problem Child) Cash Cow Established, successful Needs less investment Dog Enough to maintain themselves No future Relative market share www.canotes.multiply.com 71 After determination of position of a SBU in BCG matrix, following strategies are available: Build Hold Harvest Divest The BCG and other formal methods revolutionized strategic planning. Such approaches, however, have limitations: 1). They can be difficult. 2). They can be time consuming. 3). They can be costly to implement. 4). Management may find it difficult to define SBUs and measure market share and growth. 5). The approaches focus on classifying current businesses but provide little advice for future planning. SBU is a unit of company that has a separate mission and objectives and that can be planned independently from other company businesses. 2) General Electric Business Screen (GEBS): This approach is like BCG matrix but includes a broader range of company and market factors. Matrix classifies products according to: Industry attractiveness (market size, market growth, competitive climate, stability of demand, ease of market entry, industry capacity, level of investment, nature of regulation, profitability) Company strength (market share, company image, production capacity, production costs, financial strengths, product quality, distribution systems, control over prices/margins, benefits of patent protection) Classification is highly subjective assessment. Strategy for an individual SBU/Product is then suggested on the basis of the position of the matrix. Business Strength Strong Average Weak Market attractiveness Attractive Average Invest for growth Invest selectively for growth Invest selectively and build Develop selectively; build on strength Develop selectively for income Harvest Unattractive Develop for income Harvest or Divest Divest Nature and Characteristics of a Service 1). Service intangibility (cannot be touched) 2). Service inseparability (from provider) 3). Service variability (standard will vary each time) 4). Service perishability (cannot be stored) 5). Service ownership (not transferred to service taker) Marketing mix of services: Along with 4 normal Ps, 4 extra Ps are also required i.e. 1. Personal selling (greater reassurance, information and reliance required) 2. Process 3. People (sometimes people and services are inseparable; first line importance) 4. Physical evidence ( remedy for intangibility) Service Profit Chain: “Profit of service firm is linked with satisfaction of employees and customers” i. Internal service quality ii. Satisfied and productive service employees iii. Greater service value iv. Satisfied and loyal customers v. Healthy service profits and growth It requires more than just traditional external marketing: External marketing (B2C) Internal marketing (B2E) Interactive marketing (E2C) www.canotes.multiply.com 72 Product Development: (New Product) What is a new product: That opens up an entirely new market That replaces an existing product That broadens the market of an existing product. When an old product can be new: Introduced into a new market Packaged in different way Different marketing approach is used Mix variable is changed. Degree of newness: Unquestionably new product Partially new product Major product change Minor product change Sources for new products: Licensing Internal product development Customers External innovators Competition Acquisition Academic institutions Patent agents Why so many new products fail: 1). Overestimated market size. 2). Poorly designed product. 3). Poorly priced, placed, promoted or positioned. 4). Result based on poor market research findings. 5). The costs of producing the product may have been higher than expected. 6). Sometimes competitors fight back harder than expected. 5 product characteristics affecting rate of adoption for new product: Relative advantage i.e. new technology making it superior Compatible with values and experience of potential consumers Ease of understand and use Trial option Communicability of results of using product. Product Development Process 1. Idea generation which is the systematic search for new product ideas rather than haphazard? a. Internal sources (R&D) b. External sources (customers, competitors, distributors, suppliers) 2. Idea screening Evaluation against criteria to spot good ideas and drop poor 3. Concept development and testing Product concept is a detailed version of the new-product idea stated in meaningful consumer terms. Concept testing involves testing the concepts with a group of target consumers to find out if the concepts have strong consumer appeal. 4. Marketing strategy development A marketing strategy statement should be produced. This is a statement of the planned strategy for a new product that outlines the target market, positioning, market mix and market share, long term sales, profit goals and marketing budget for the first few years. 5. Business analysis Review of the sales, costs, and profit projections for a new product to find out whether these factors satisfy the company’s objectives www.canotes.multiply.com 73 6. Product development Developing the product concept into a physical product in order to ensure that the product idea can be turned into a workable product 7. Test marketing The basic purpose is to test the product itself in real markets. 8. Commercialization Introducing a new product into the market. Stages of Product Life Cycle (PLC) 1. Introduction 2. Growth 3. Maturity 4. Decline Exceptions are Fad, Style, and Fashions. Strategies change with change in stage of PLC. Product life cycle- Characteristics, objectives and strategies: [very nice table] Introduction Growth Characteristics Sales Cost Low High per customer Profit Customers Competitors Negative Innovators Few Rapidly rising Average cost customer Rising Early adopters Growing Marketing objectives Create product awareness and trial Maximize share Strategies Product Offer Basic product Price Use cost-plus Place Selective distribution Offer product extensions, service, quality Price to penetrate/skim market Intensive distribution Promotion Use heavy promotion Targeting Early adopters (build awareness) sales per market Reduce to take advantage of heavy demand Mass market (build awareness) Maturity Decline Peak sales Low cost per customer High profit Middle majority Stable number beginning to decline Maximize profit defending market share Declining sales Low cost per customer Declining profit Laggards Declining number Diversify brand and model Phase out weak items or Repositioning Cut price Price to match or beat competitors More intensive distribution Increase to encourage brand switching Stress brand differences and benefits Reduce expenditure and milk the brand Go selective; phase out unprofitable Reduce to minimal level Reduce to needed to core-loyals level retain Assessment of PLC: Regular review of existing products Analysis of past trends History of other products Market research Analysis of competitors Estimate of future life and profitability should be discussed with experts R&D Deptt. ----------------------Product life Marketing staff-------------------Price and demand Management accountant------- Cost Decide to continue, stop or change strategy. Criticism on PLC approach: Relevant only for products where consumer demand is high Underlying stage of PLC is determined by marketing actions. Stages can not be easily defined. “S” shape does not always occur in PLC Strategic decisions can change PLC www.canotes.multiply.com 74 Packaging: Functions of packaging: Protection Quality standard (e.g. expiry) Distribution Selling (Advertising, attractive, motivating,) User convenience (value depicting) Conforms to govt. regulations (e.g. ingredients, price, expiry etc.) Usually goods are packaged in more than one layer. Qualities required of a packing: Size and variety should be minimized. Attractive and distinctive to target consumer. All functions of packing are also required. Cost effective Fitting for storage purposes Product Portfolio Planning All product lines and items that company offer for sale [Overall product range of organization] Width (No of product lines carried by Company) Depth (No of items carried divided by No of product lines) Consistency (closeness of items in range in terms of marketing/production characteristics) www.canotes.multiply.com 75 Chapter 26 : Price PRICING CONSIDERATIONS AND APPROACHES “Price is the sum of the values that consumer exchange for the benefits of having or using the product. Only element to produce revenues Most flexible element Could be Fixed or Dynamic Price Setting Cost Competition Demand (Elastic / Inelastic) Common Pricing Mistakes 1). Pricing is too cost-oriented. 2). Prices are not revised often enough to reflect market changes. 3). Prices do not take into account the other elements of the marketing mix. 4). Prices are not varied for different products, market segments, and purchase occasions. Internal Factors Affecting Pricing Decisions 1. Marketing objectives 2. Marketing mix strategies 3. Costs 4. Organizational considerations 1. Marketing objectives: • Survival • Current profit maximization • Market share leadership • Product quality leadership • Other objectives To prevent competitors To keep loyalty and support of reseller To avoid govt. intervention To create excitement or draw attention of new customers To help the sale of other product in product line 2. Marketing mix strategy: Price decisions must be coordinated with product design, place, and promotion decisions to form a consistent and effective marketing program. Companies often make their pricing decisions first and then base other marketing-mix decisions on the prices that they want to charge. Target costing is positioning of product on price and then tailoring other marketing decisions to the price they want to charge. But remember that consumers rarely buy on price alone. 3. Costs Set the floor for the price that the company can charge. (price below this is not acceptable) Companies want to charge a price that covers all its costs for producing, distributing, and selling the product, and provides a fair rate of return for its effort and risk. To price wisely, management needs to know how its costs vary with levels of production. The experience curve (or the learning curve) indicates that average cost drops with accumulated production experience 4. Organizational considerations. Management must decide within the organization who should set prices. Small companies: CEO or top management Large companies: Divisional or product line managers Some companies have pricing departments www.canotes.multiply.com 76 External Factors Affecting Pricing Decisions 1) Nature of market and demand 2) Competitors’ costs, prices, and offers 3) Other environmental elements 1) Nature of market and demand Pure competition No single buyer or seller has much effect on the going market price. Monopolistic competition Market consists of many buyers and sellers who trade over a range of prices because they can differentiate their products. Oligopolistic competition Market consists of a few sellers who are highly sensitive to each other’s pricing and marketing strategies. Pure monopoly Monopolists do not always charge a full price because: 1]. They do not want to attract competition. 2]. They want to penetrate the market faster. 3]. They fear government regulation. Price-demand relationship Demand curve Price elasticity of demand Factors affecting Demand / Price elasticity of demand/ Consumer choice Price Price of substitute and complementary goods Consumer income Taste and fashion Advertisement and Training After sale services and grant of credit 2) Competitors’ costs, prices, and offers 3) Other environmental elements a). Economic conditions (such as boom or recession, inflation, or interest rates). b). Reseller’s policies (reactions) must be considered especially if they do not match the supplier’s. c). The government (because of its regulatory power) must be considered. d). Social concerns may affect the firm’s short-term sales, market share, and profit goals. General Pricing Approaches/Methods Price will be set between 2 extremes. Roof / Ceiling i.e. Customer’s value Floor i.e. Cost Price will be set between these 2 levels after consideration of Competitors’ prices and Other internal and external factors Approaches Cost based pricing Cost plus pricing Break even or target profit pricing Customer value based pricing (i.e. demand based ) Competitive based pricing Going rate pricing Sealed bid pricing Why Cost based pricing is popular 1. Sellers are more certain about cost than demand 2. Price is simplified being tied to cost. 3. Fairer to both buyer and seller 4. Price competition is minimized New-Product Pricing Strategies • Market-Skimming Pricing “Setting a high price for a new product to skim maximum revenues layer by layer from segments willing to pay the high price”. Product image must support price Competitors must not be able to enter the market Prices are lowered when demand falls www.canotes.multiply.com 77 • Market-Penetration Pricing “Setting a low price for a new product to attract a large number of buyers and a large market share”. High volume reduces cost Spare resources are utilized Eliminates competition May promote related products. Product Mix Pricing Strategies • • • • • Product Line Pricing Setting price steps between product line items. Kodak prices different types of films at different level. Optional-Product Pricing Pricing optional or accessory products sold with the main product Car buyer may choose to order power windows, cruise control, and a CD changer. Captive- product pricing. Setting a price for products that must be used along with a main product. Examples of captive products are blade with razors, game cassettes with system. By-Product Pricing Pricing low-value by-products to get rid of them Product Bundle Pricing Pricing bundles of products sold together Theater and support teams sell season tickets. Price adjustment strategies: “To account for various customer differences and situation differences” Discount and allowance pricing Reduction in price to reward customer response for paying or promoting product. Segmented pricing Adjusting prices to allow for differences in customers, products, or locations. Psychological pricing Seller considers the psychology of prices and not simply the economics e.g. consumers usually perceive higher priced products as having higher quality in the absence of past experience or information. Promotional pricing Temporarily reducing pricing to promote short term sales. Geographical pricing Adjusting prices to account for the geographic location of customers. International pricing Adjusting prices for international markets. Assessing and responding to competitor’s price changes Has competitor cut prices? Hold current price and continue to monitor competitor’s prices N Y Will lower price negatively affect our market share and profit? N Y Can/Should affective action be taken? Y N Reduce price Raise perceived quality Improve quality and reduce price Launch low-price “fighting brand” Some other concepts that could not be covered here in Details Price Leadership Price elasticity of demand Absorption & Marginal Costing and breakeven analysis www.canotes.multiply.com 78 Chapter 27 : Place Place / Distribution Channels / Delivery System Place is selection of distribution channels to deliver goods to consumers. Key issues in Distribution Channel:: Coverage and density (Exclusive, Selective, Intensive) Channel length (no. of intermediaries between consumer and producer) Power and alignment of different elements Logistic and physical distribution Support and after sale service Channel design decision (Customer, Product characteristics, Distributor characteristics, Channel choosed by competitors, Supplier’s own characteristics) Nature and Importance and Functions of Marketing Channels: Marketing Channel (distribution channel) is a set of interdependent organizations (intermediaries) involved in the process of making a product or service available for use or consumption by consumer or business user. Each organization performs a specialized and specified role. Importance includes: 1. Channel decisions affect other marketing decisions 2. Competitive advantage could be gained. 3. Involves long term commitments to other firms 4. Channel members add value through a. Their contacts, experience, specialization and scale (economies) of operation. b. Matching supply and demand c. Bridging Time, Place and Possession gap Functions performed by members of marketing channel: Functions that help to complete transactions: 1. Information (Marketing research and intelligence information) 2. Promotion (Developing and spreading persuasive communication) 3. Reselling (Finding and communicating with prospective buyers) 4. Matching (shaping and fitting to the buyers’ needs e.g. assembling, packing) 5. Negotiation Functions that help to fulfill the completed transactions: 6. Physical distribution (Transportation, storing and Inventory management) 7. Financing (Acquiring and using funds) 8. Risk taking (Assuming the risk of carrying out the channel work) “You can eliminate middle man, but not middle man’s functions” Types of Distribution channels: Direct distribution channel has no intermediary. Intermediaries don’t get their share. Intermediaries don’t get dominant Own sales force is best for geographically centered buyers. Indirect distribution channel has one or more intermediaries. Where resources are insufficient to finance large sales force. Where no local knowledge of market Suitable for geographically spread buyers. Types of Distributors: a) Franchisees: “Trade in name of parent in exchange of initial fee + share of sales volume” www.canotes.multiply.com 79 b) Distributors/Dealers: “Buy and resell at profit” Dealing in narrow range of products; Sometimes exclusive distribution or dealing only one manufacturer; Also provide after sale services. c) Agents: (vs. Dealers) “Consigned for commission on sale) d) Wholesaling: “Selling goods to business buyers” e) Retailing: “Selling goods to consumer buyers” f) Multiple Stores: “Sell under the ‘own label’ brand name” How do channel firms interact and organize to do the work of the channel: Channel Conflict is disagreement among marketing channel members on goals, roles and rewards (who should do what for what reward). It may be Horizontal, conflict among firms at same level of channel e.g. dealers may complain that others are pricing too low or selling beyond their territory. Vertical, conflict among firms at different level of channel e.g. conflict with dealers when opening online stores even though for hard to reach customers. Disintermediation is eliminating or replacing intermediaries. e.g. opening online stores Marketing logistic and Supply Chain Management (SCM): Marketing logistic (or physical distribution) involves planning, implementing and controlling the physical flows of goods, services form points of origin to points of consumption. Marketing logistic addresses whole Supply Chain Management i.e. Outbound distribution (moving product form factory to reseller and ultimately to consumers) Downstream Inbound distribution (moving products from supplier to factory) Upstream Revere distribution (moving broken, unwanted or excess products returned by consumers or resellers) Major logistic functions/ Functions in distribution process: Warehousing o Production and consumption cycles rarely match. o A company must decide, how many, what types and where o Company might use either storage ware house or distribution centers. Inventory management o Managers must maintain balance between too little and too much inventory. o Just in time requires accurate forecasting along with fast, frequent and flexible delivery o Just in time substantial cost saving in carrying and handling cost and low obsolescence. Logistic information management, In VMI (Vendor Managed Inventory) customer share real-time data on sales and current inventory levels with supplier and supplier then takes full responsibility for managing inventories and deliveries. Transportation Promotion Display New technology in Distribution: DRTV Internet (B2C) o Websites o Email www.canotes.multiply.com 80 Chapter 28 : Promotion Two basic strategies of Promotion: Push strategy using sales force to push the product through the channels, the producer promotes the product to wholesalers, the wholesalers promote to the retailers, and the retailers promote to the final consumers. Pull strategy spending a lot on advertising and consumer promotion to build up consumer demand; if successful, consumers will ask their retailers for the product, the retailers will ask the wholesalers, and the wholesalers will ask the producers. Communication media 1. Personal communication channels, through which people communicate directly with each other. i. Face to face ii. Person to audience iii. Over telephone iv. Through mail v. Through internet chat 2. Nonpersonal communication channels, media that carry messages without personal contact or feedback. i. Print media (newspapers, magazines) ii. Broadcast media (radio, television) iii. Display media (signs, posters) iv. Online media (online services, Websites) Marketing communication mix or Promotional mix It is a blend of A. Advertising B. Personal selling C. Sales promotion D. Direct Marketing and E. Public relations tools That a company uses to communicate with its customers. A range is better than only one. A) Advertising: “Any paid form of nonpersonal presentation and promotion of ideas, goods, or services by an identified sponsor” Advertising objectives (AIDA) are as follows: 1. Informative advertising a. To communicate information b. To create awareness c. In Early stage of PLC or on modification 2. Persuasive advertising a. To create a desire for a product and to stimulate actual purchase b. In growth stage of PLC 3. Reminder advertising a. Reinforcing knowledge and b. Reminding of benefits c. In Maturity stage of PLC Advertising media Above the line (Press, Radio, TV, Cinema) Below the line (Direct mail, Exhibition, Package design, Merchandizing) Advantages (Vs. Personal selling): Mass communication Expressive advertisement Standardization and legitimacy Seller is able to repeat a message many times Disadvantages (Vs. Personal selling) Costly One way communication Impersonal Not so persuasive www.canotes.multiply.com 81 B) Personal Selling (face to face via sales force): “ Personal presentation by the firm’s sales force for the purpose of making sales and building customer relationships i.e. paid form of personal communication” Sales force structures: 1. Salary only 2. Salary with bonus 3. Commission only C) Sales Promotion: “Marketing activities other than personal, selling & advertising that stimulates customer purchasing” “ Short-term incentives to encourage the purchase or sale of a product or service”. Major tools are: 1. Samples 2. Coupons 3. Rebates 4. Premiums (buy 2 get 1 free) 5. Contests, sweepstakes, and games 6. Free gifts Objectives of sales promotion: To increase in sales revenue To launch a new product To attract new customers To attract resellers to stock To clear out old stock Counteraction for competitors D) Direct Marketing: (one to one marketing) “Direct connections with carefully targeted individual consumers to obtain and immediate response and cultivate lasting customer relationships” It is the use of mail, telephone, fax, email, internet and other tools to communicate directly with specific consumers. Characteristics of Direct marketing: Non public Immediate and customized Interactive Forms of direct marketing: 1. Face to face selling 2. Telephone marketing i. Outbound calls ii. Inbound calls (toll free numbers) 3. Catalog marketing 4. Direct mail marketing e) Public relations: “Building good relations with the company’s various publics by obtaining favorable publicity, and building up a good corporate image” Publicity is non-paid, non-personal communication dealing mass audience. Planning a Promotion campaign: Identify the target audience Specify the promotional message Select media Schedule media Set the promotional budget Evaluate promotional effectiveness Branding: Expenditures on promotion gives rise to brands. A Brand is a name, term, sign, symbol or design intended to identify the product of a seller to differentiate it from those of competitors. www.canotes.multiply.com 82 Reasons for branding: Product differentiation Conveying lot of information quickly and concisely Advertisement needs a brand name. The more similar a product is to competing goods; the more branding is necessary. It facilitates self selection. It reduces price sensitivity. Brand loyalty gives control over marketing strategy. Other products (i.e. new flavors/sizes) can be introduced into brand name/range. (Brand extension) Eases personal selling Eases market segmentation Brand strategies: Brand extension Multi branding (different names for similar nature goods serving similar consumer habits) Product----------------Names----------------Brands in each name Family branding Relationship Marketing: (Keeping customers; not getting customers) Sale is not end of process; but start of relationship. It is easy, cheaper and profitable to retain old customers than to make new customers because: Old are valuable Old have trust in company Old are satisfied. Key account management: (Key Customer Database) Like relationship marketing but more specific It refers to how an organization manages its relationship with those customers identified as key to the organization in achieving its objectives. Factors used to identify a key account: Historic value of purchases Expected future purchases Other competitive factors o Status within the marketplace o Personal relationship of people o To prevent a competitor getting a hold in market Extra services given to key account Time Finance Procedure Hospitality Auditing Customer satisfaction: (why customers are not satisfied ? ) Customer satisfaction surveys Work won and lost Changes in market shares Revenue from newly released products Rude and unhelpful staff A policy is to encourage customers to complain( 96% do not) Technology Development – Interactive marketing: Interactive marketing in instant communication and responses between promoter and customers. It may be called sometimes as Computerized Personal Selling e.g. DRTV (Direct Response Television) Interactive Internet websites Interactive Kiosk www.canotes.multiply.com 83 Part F : International Business Theories on International Trade Scarce resource is a resource for which the quantity demanded at a nil price would exceed the available supply. 4 scarce resources are Land, Labor, Capital and Enterprise. Scarcity is the excess of human wants over what can be produced. Production Possibility Curve illustrates limits of possible production of two products within given resources. Opportunity Cost is the cost of sacrificed alternative. Mercantilism: Export > Import Zero-sum game (benefit at the expense of other) Absolute advantage: Absolute advantage is producing goods more efficiently than any other country. Country should produce goods for which they have an absolute advantage and then trade these goods for other goods produced by other countries. Comparative advantage: One step further than absolute theory introducing concept of opportunity cost. Country should specialize in the production of those goods in which it has lowest opportunity cost. Why countries avoid specialization Comparative advantage is never stable. Diversification protects fall in world demand. Agriculture industry is subject to uncertainties of climate. Import restrictions are possible by other governments to develop self sufficiency. Multi nationals may assemble or manufacture in different countries for political or logistic reasons. Competitive advantage (national): Porter states that Comparative Advantage is too general concept to explain success of individual companies and industries. He believes 4 conditions (diamonds) within a country help firms to compete.i.e. 1. Factor conditions 2. Demand conditions 3. Firm strategy, structure and rivalry 4. Related and supported industries Orientations of International Business Management (by Perlmutter) Ethnocentrism: Company focuses on domestic market and export is secondary. No local research, marketing mix is standardized. Same products with same market programs. Polycentrism: Each country is unique and requires customization. Product and market programs must match with local environment. Company establishes independent local subsidiaries and decentralizes marketing management. Geocentrism: Synthesis of two approaches. Think globally, act locally. Integrated approach to create a global strategy that is fully responsive to local market. Regiocentrism: It is Geocentricism but that it recognizes regional differences. www.canotes.multiply.com 84 Evolution and Reasons of Global Business (by Ohmae) Evolution: Ethnocentrism 1. Export (extension of home sales) 2. Overseas branches (when turnover is large, greater investment) 3. Overseas production (exploits cheap labor and reduces exporting cost) Polycentrism 4. Insiderisation (full functional organization having production and distribution system is set-up overseas, company is multinational) Geocentrism 5. The Global Company Reasons: 5 Cs 1. Customer (market convergence) 2. Company (economies of scale) 3. Competition (Keeping up) 4. Currency (exchange rate risk) 5. Country (Absolute and comparative advantage, local orientation) Other reasons: For Govt. Surplus deficit balance Political advantages To support govt. policies (e.g. Balance of Payment) For Company Large market encouraging economies of scale. Increased competition at home market Mature or declining home market To dispose excessive/discontinued products. Exchange rate: Purchasing Power Parity theory calculates exchange rate based on relative cost of purchasing same basket of goods in two countries. A currency’s exchange rate is also determined by Demand and Supply. They in turn are determined by Inflation, Speculation, Interest rates, Govt. policies and Balance of Payment. Exchange rate risk is the risk that foreign currency will exchange in smaller amount of domestic currency in future. Types: This can arise under any of three Exchange Rate Systems i.e. 1. Fixed (Central bank interferes to fix the rate) 2. Managed (Like fixed but allowed to vary between preset limits) 3. Floating (depends on supply and demand) Managing exchange risk: Hedging devices Flow of money in both direction Design for global business (by Bartlett and Ghoshal ) High pressure Globalize to Low Pressure Globalize to www.canotes.multiply.com Low requirement for local adaptation and responsiveness Global environment Geocentric orientation Global product divisions Chemicals, Construction International Environment Ethnocentric orientation International division Paper, textile High requirement for local adaptation and responsiveness Transitional environment Polycentric orientation Integrated system and structure Pharmaceutical, motor vehicles (focus of organization is heteroarchy) Multinational environment Polycentric orientation National or regional divisions Fast food, tobacco 85 Planning to enter Foreign Market Phase 1: Preliminary analysis and screening: Evaluation of available markets (to exclude obvious unfit) Applying screening criteria to evaluate remaining markets (criteria might include Profit, Market Share, Quality) Analysis of environment conditions in each country Porter’s 5 forces analysis Choosing country (i.e. Target Market) Screening Process consists of : (by Jeannet and Hennessy) Marco level research Environmental analysis Climate and demographic General Market factors Size of market Regulations Culture Micro level research Competition Transportation Healthcare Education Labor Target Market Phase 2: Adapting the marketing mix to target markets: Deciding Adaptation or Standardization Phase 3: Developing the marketing plan: Situation analysis Objectives Strategic options Budgets Action programs Phase 4: Implementation and Control Objectives and Standards Assign responsibilities Measure performance Corrective actions Problems in International Planning: Foreigners don’t know local culture, feelings, attitudes Local level problems Different attitude to product and marketing task Lack of strategic outlook and marketing expertise Resentment at being bossed around Unclear goals Inadequate control HR considerations to be managed at local level Poor IS and Communication Diversification of countries over population, income, development, education etc. Time horizon International Marketing Research Objectives: Availability and quality of information is enhanced for planning. Change in customers needs and preferences is timely observed. Competitors’ plan and strategy www.canotes.multiply.com 86 Finding of new markets Opportunities and Threats Trends of market SLEPT analysis Technology – Quality of information Information sources for International Markets: Human sources Managers of subsidiaries, associates, branches (relevant + unpublished + biased) Consumers, Customers, Distributors, Suppliers and even Competitors Documentary sources (Publications etc., not to the point) Direct sources Direct observation and specialist knowledge Direct observation and background information Personal experience supporting indirect information Export publications Export Market Information Centers IMR Process: Monitoring Passive information gathering (Market not yet targeted) Identification of market for which information needs to be gathered. Investigation (accurate assessment of market opportunities) Existing demand; where customer’s needs are already being served. Latent demand; where potential customers are currently recognized but are not being served. Incipient demand; where there is foreseeable, but not a present, market for products. Research Define scope of project Define projects, information needs Evaluate available sources for required information Undertake desk research Undertake field research Using IMR data: To estimate patterns of demand/consumption in individual markets by Demand pattern analysis Income elasticity of demand To compare patterns of demand/consumption in different markets by Comparative analysis Intermarket timing differences To identify clusters of markets with similar characteristics To identify strategically equivalent segments Problems in IMR: Secondary data problems Lack of data Not timely, out of date information gathered on unpredictable schedules Not comparable, different data definitions in different countries Lack of reliability Response problems (People’s unwillingness to provide info) Tax evasion and avoidance of responsibilities Wish to preserve secrecy Cultural taboos and norms General problems (developed vs. undeveloped) No suitable list (sampling frame) Inadequate communication infrastructure Low level of literacy Problems of language and comprehension www.canotes.multiply.com 87 Entry in International Market Entry in International Market could be through: Foreign Direct Investment/Overseas production 100% owned subsidiary Joint venture o Industrial cooperation/Contractual (fixed period) o Joint-equity venture (continued) Export Direct (greater control but lesser market knowledge) o To Branch office o To Agents between importer and exporter o To Wholesaler, Retailer or Consumers Indirect (greater market knowledge but lesser control) o Through Export houses o Through Specialist export management firms o Through UK buying offices of foreign stores and government o Through Complimentary Export (i.e. Piggy back export) Licensing Giving right to use production process for Royalty. Critical analysis of entries Foreign Direct Investment is direct investment in business operations in a foreign country. It may be: 1. Horizontal FDI (investment in same industry abroad) 2. Vertical FDI (investment in an industry abroad which provides input to firm’s domestic operations. i. Backward Integration (to acquire raw material) ii. Forward Integration (to establish final product) Selection criteria for entry mode: (Factors to be considered) Mode varies among firms, according to markets and over time. Firm’s marketing objectives (in relation to volume, time scale and coverage) Low ----------export High----------produce locally Firm’s size Small--------export Mode availability Govt. may restrict modes Mode quality Qualified, trained staff is necessary for export of high technology goods. Human Resource Requirement If staff is suitable---------Direct export If staff is not suitable----Indirect export (agent based) Market information feedback Is received in case of Direct export. Learning curve requirement Heavy investment calls for learning curve i.e. close observation through direct export before investment. Political risks Control needs Advantages FDI vs. Export vs. License: FDI(Foreign Direct Investment) Lower production cost Better understanding of Market and Customers. Lower transportation cost. Overcomes tariff and nontariff barriers. www.canotes.multiply.com Export Concentration on production Economies of scale Consistency of product quality International experiment on small scale Easiest, cheapest, most common Political risks are avoided. License Avoids costs and hassle of setting up overseas. Rapid penetration No investment No Political risk, No Protectionism 88 Key Issues Political risks. Partnership Managing overseas facilities Usually more involvement but subsidiary may act independent. Protectionism Exchange rates Usually less involvement Small cash inflows Quality standards issues Indirect competition where both export Licensee may become competitor (by transfer of knowledge and technology) If FDI, 100% owned subsidiary or Joint venture: Wholly owned subsidiary (as compared to Joint venture) Advantages: Key Issues: No sharing in profit Heavy investment needed No sharing in decision making Suitable managers not available No communication problem Govt. discourages 100% ownership Operation of integrated international No local knowledge systems Varied experience Protectionism (discouraging imports) by Govt. Government and Local producers get benefit not consumers. 1. Tariff (tax on imports) 2. Non-tariff barriers a. Official i. Subsidy ii. Import Quotas/ Export Restraint iii. Local Content Requirement (specific fraction must be produced locally) iv. Anti-dumping policies (e.g. special duty) v. Administrative policies (informal instruments or bureaucratic rules) vi. Embargo (total ban) b. Un-Official i. Quality and inspection procedures ii. Packing safety and documentation standards iii. Restriction of distribution 3. Exchange control (making difficult to obtain required currency) 4. Exchange rate policies (e.g. competitive devaluation of currency) Dumping is selling goods in foreign market below cost or market value to: Unload excessive production Capture market. Political risk in FDI for multinationals Political risk is the risk that political actions will affect the position and value of a company. How Political actions can affect: 1. Tariff and non-tariff barriers e.g. Quotas 2. Govt. interference in contracts 3. Imposition of i. Increased tax rates ii. Price controls iii. Exchange controls through a. Rationing supply of foreign exchange b. Blocking funds of foreign parent (counter ways) Dividend Selling goods/services (volume and transfer pricing) Royalty Loan and high interest rates Management charges 4. Nationalization How to cope with political risk: 1. Negotiation (agreement) with Government i. Transfer of capital www.canotes.multiply.com 89 ii. iii. iv. v. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Access to local finance Govt. interference Taxation Transfer policy Insurance Contacts with markets Management structure (joint venture or giving control to local) Financial management (obtain finance locally) Production strategies (giving control to local to produce Or to supply chain management) Regional trading groups/blocks--- A way to overcome Protectionism and Political risks Regional trading group promotes trading between members of group. Following are common types: Free trade area: Internal barriers to trade are removed. Each company determines its own external trade policy. Customs Union: Internal barriers to trade are removed. Common external trade policy is adopted. Common Market: Similar to customs union except it allows factors of production to move freely between countries. Economic Union: It is Common market but more closer integration including establishment of common currency and tax rates. Taxation issues in FDI By structuring the group, tax advantages could be availed. Foreign tax credit avoids double taxation in both countries. Tax havens is a country with exceptionally low or even no income tax but there should be: Stable currency and Govt. Adequate financial services support facilities. Capital Structure Decisions Equity or borrowing If equity, Parent’s or Subsidiary’s If externally, from host or other country What Currency (same to avoid fluctuation and symmetry) How much and what period Factors influencing choice of financing: 1. Local finance cost 2. Taxation system 3. Restriction on dividend remittance 4. Flexibility in repayment Global Capital Market International banks (provide financial and other services) Factors affecting development of international banks: 1. Globalization (Trade of securities world wide e.g. Euro equity) 2. Securitization (Debt via issuance of securities e.g. Euro bonds, Euro commercial papers) 3. Deregulation (national barriers) 4. Disintermediation (directly from investor) 5. Increased foreign exchange and interest rate volatility Benefits of international banks: 1. Financing of foreign trade 2. Financing of capital projects 3. Provision for advice and information 4. Providing full local banking services in different countries 5. International Cash Management services 6. Trading in foreign exchange and currency options 7. Participation in syndicated loan facility 8. Lending and borrowing in foreign and euro currency markets 9. Underwriting of euro bonds www.canotes.multiply.com 90 Borrowing in Euro market Vs. Domestic market Domestic banking is subject to tighter regulation Domestic banking is subject to security requirements Euro finance may have i. Flexibility in draw-down dates ii. Early redemption penalties iii. Commitment fee Euro is suitable for very large finance requirements Euro Currency: Following types of currency is available in Euro Markets: 1. Euro equity 2. Euro bond 3. Euro currency 4. Euro Currency loan 5. Euro credits 6. Commercial papers 7. Syndicated credits 8. MOFs Euro equity issue: Issue of equity in a market outside the company’s own domestic market. Not developed like Euro bonds, hence ‘sweeteners’ are added e.g. Rolling Put Option Euro bond: Currency differs country of issue (underwritten by international syndicate of banks and sold internationally) Euro bonds are suitable when: Large organization with excellent credit rating Requires long term loan for capital expansion Requires borrowing not subject to national exchange control Interest rates are fixed or floating with minimum. Investors of Eurobonds will be concerned about: Marketability Anonymity Return on Investment Security Euro currency: Eurocurrency is any currency banked outside of its country of origin e.g. Eurodollars are dollars banked outside United States. Euro Currency loan: UK company borrows in US $ from a UK bank, it is a Euro Dollar loan. Euro credits: like Euro currency loan Commercial papers: An example of Securitization. Short term financial instruments Issued in the form of unsecured promissory notes with a fixed maturity date. Issued in bearer form Issued on discount basis Companies with net capital of 25 million can issue it. Syndicated credit market: Provides credit at high rates over LIBOR. Suitable for Takeover bids Govt. borrowings Project financing Credit is a facility whereas Loan is a transaction. www.canotes.multiply.com 91 MOFs: Multiple Options Facilities (MOF) comprise variety of instruments through which company can raise funds and include: Note Issuance Facilities (NIF) Revolving Underwriting Facilities (RUF) Counter Trade Counter trade is a trade of goods and services for other goods and services. Types/arrangements of Counter Trade: Barter (direct exchange of goods/services between two parties without a cash transaction) Counter purchase (A reciprocal buying agreement between two parties whereby seller also undertakes to purchase a certain amount of merchandize from other country) Offset (like counter purchase but party can purchase from any firm in the country) Switch Trading (A third party trading house buys the firm’s counter purchase credits and sells them to another firm that can better use them) Buyback (One country supplies capital goods and receives its output as partial/full payment) Advantages of Counter Trade: 1. A mode to finance exports when other modes are not available. 2. Competitive advantage over parties preferring cash transactions. Disadvantages of Counter Trade: 1. Goods received may be unusable, poor quality, or unprofitable. 2. Expensive and time consuming to develop a separate in-house trading department to dispose those goods 3. Unrealistically high value may be impose on goods. 4. Cost may exceed expectation. (Cost includes Consultancy fee, Discount, Bank fee, Insurance, Any fee paid to third party) Why Countries do Counter trade: Countries lack commercial credit or convertible FCY. Countries use it as an instrument of political, economical policies (e.g. Balance of Trade, relationships) To boost developing manufacturing industries To obtain more trade or new technology Which Countries do Counter trade: Oil exporting companies. Less developed and developing countries. Unusual in industrial countries with exception of defense, aviation and big advanced technology. Financial problems in Foreign Trade Foreign Trade raises special financial problems i.e. Bad debts’ risk is greater Large investment appears in receivable and stocks Reducing bad debts’ risk: 1. Export factoring 2. Forfeiting 3. Documentary Credit (L/C) 4. International Credit Unions 5. Export Credit Guarantee Schemes Export factoring: Factoring company provides administration of: Client invoicing Sales accounting Debt collection Credit protection Forfeiting: (providing medium term export finance) Exporter sends Capital goods to overseas buyer who wants medium term loan. Buyer makes down payment and issues notes/ accepts draft. Notes/drafts are guaranteed by Availising bank. Exporter discounts them from Forfeiting bank. www.canotes.multiply.com 92 Documentary Credit (L/C): 1. Importer orders. 2. Exporter accepts. 3. Importer’s bank issues L/C to exporter’s bank. 4. Exporter’s bank authorizes exporter to ship merchandize. 5. Exporter ships and gives documents and draft to own bank. 6. Exporter’s bank sends documents to importer’s bank and gets the draft accepted. 7. Importer’s bank informs importer about arrival of documents and merchandize. 8. Importer pays (or not pays) his bank. 9. On maturity, importer’s bank pays to exporter’s bank who pays to exporter. International Credit Unions: These are organizations/associations of finance houses/banks in different countries having reciprocal arrangements for providing installment credit finance. Export Credit Guarantee Scheme: (where L/C is not acceptable by strong importer) Preshipment Facility: Guarantee is issued to banks to indemnify them against losses on finance given to exporters to manufacture and process goods for export. Risks covered are: o Insolvency of exporter o Inability to repay or deliver on due date Postshipment Facility: Exporter submits application with required particulars to ECGS. ECGS will issue a guarantee specifying maximum amount covered and rate of premium. Risks covered are: o Insolvency of buyer o Political and Economic risks o Risks of refusal to take delivery o Risk of any loss (beyond control of buyer or exporter) Reducing large investment in Receivables and Stocks: Advance against collection Documentary credit Negotiation of bills or cheques International Marketing Mix Policies International place policies: Exclusive Selective Intensive International product policies: Standardized/Undifferentiated marketing (same product, price, marketing program for all markets) Adapted/Differentiated marketing Concentrated marketing Standardization Vs. Adaptation: whether to adopt or not is linked with promotional issues. Communication Standardization Communication Adaptation Product Standardization Occasional exporters Also major companies seeking economies of scale Same product for different uses in different countries Product Adapted Single product meets the same need in all markets but need to be adapted. Costly Required to exploit market fully Barriers to International Standardization: Law Price control Product regulation Distribution restrictions www.canotes.multiply.com 93 Competition Culture Economy Advertising and media restrictions Nature of existing products Competitors’ prices Consumers’ tastes and habits Language and attitude differences Income level Media availability Domestic business as compared to International business: Social factors: No language problem. Homogenous market. Rules of game are understood. Similar purchasing habits. Economic factors: Single currency Uniform financial climate Stable business environment Competitive factors: Data collection is easy and accurate. Political factors: Relatively unimportant Technological factors: Standard production and measurement systems Motivating international agents: Communication Assuring long term business relationships Regular and frequent personal contacts Exclusivity Hofstede’s model of national culture: Hofstede pointed out that countries differ on following dimensions: 1. Power distance how for superiors are expected to exercise power 2. Uncertainty avoidance some cultures prefer clarity and order while others prefer novelty 3. Individualism in some cultures, it is individual achievement what matters. 4. Masculinity in such culture, roles of sexes are clearly differentiated. Hofstede grouped countries into eight clusters: 1. More developed Latin 2. Less developed Latin 3. More developed Asian 4. Less developed Asian 5. Near Eastern 6. Germanic 7. Anglo 8. Nordic Type of industry and size of company is also important. Finance in International Business Treasureship: Treasureship is the function used with provision and use of finance. It covers Provision of short term borrowings/ capital Foreign Currency management Banking Collection Money market investment Treasury department should be cost center or profit center? www.canotes.multiply.com 94 Cash Management: Centralized Cash Management: 1. Avoids mix of cash Surplus and overdraft. 2. Large volumes of cash are available to invest 3. Any borrowing could be arranged in bulk at lower rates. 4. Foreign currency risk management in improved. 5. Specialist Treasury Department will employ experts. Decentralized Cash Management: 1. Great autonomy 2. Quick and more response to needs of individual operating units 3. More opportunities to invest on short-term basis. Float is amount of money tied up between initialization and finalization of payment. Measures to reduce Float include: Lodgment delay should be minimum BACS CHAPS Standing orders/ direct debit for regular payments Lock boxes for international payments Cash Pooling is netting of Debit and Credit balances with same bank to reduce interest cost. How Cash surplus arises By profitability By low capital expenditures By receipt from selling part of business How Cash surplus is utilized Takeover bids Buy back of shares Short term investments o Banks o Investment in listed shares o Investment in debt instruments Certificate of Deposits (certificates by bank acknowledging deposit for specified time) Treasury bills (IOUs by govt. issued weekly for 91 days to finance govt. projects) Eligible bank bills (IOUs by those top rated banks whose bill Bank of England agrees to buy) Bills of exchange Local authority bonds Commercial papers Certificate of Deposits, Treasury bills and Eligible bank bills are Negotiable and Resalable. International payment modes: Cheque Lock boxes (speeds up payment by cheque) Bills of exchange Bank draft (cheque by a bank drawn on one of its own account) Mail Transfer It is a written payment order authenticated by official in sending bank which Instructs by Airmail to pay a certain sum of money to a beneficiary. Telegraphic Transfer Like mail transfer but instructions are sent by cable or telex instead of by airmail. Speeder, Costly and Confidentiality than Mail Transfer. SWIFT (Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunication) Provides rapid electronic fund transfer In addition to banks, users include Security houses, Exchanges, Money brokers, Fund managers etc. International Money Orders www.canotes.multiply.com 95 Transfer pricing: Basis include Standard Cost Marginal Cost/ Full Cost/ Opportunity Cost Market Price Market Price – discount Negotiated Price (any other basis) Advantages of having Market Price as Transfer Price 1. For buying department i. Better quality of services ii. Greater flexibility iii. Dependability of supply 2. For both departments i. Lower cost of administration, selling and transportation Disadvantages of having Market Price as Transfer Price 1. Market prices may be temporary. 2. Disincentive to use spare resources as compared to incremental cost approach. 3. Buying department may enforce discount. 4. Many products don’t have equivalent market prices. HRM in International Business HRM issues in International Business: 1. Expatriate or local management Expatriate (as compared to local) Advantages: Poor educational/technical opportunities in local market Greater control Better central communication Corporate picture is clear 2. 3. 4. 5. Key Issues: Costs more Lesser local knowledge Culture shock Language/Communication training required Recruitment and Training Career management within firm Appraisal schemes Communication with staff (e-mails, conferences and news letters etc.) Changes in World marketplace: (by Jerry Wind) Globalization of businesses Science and Technology development Strategic alliances Changing customer value and behavior Increased scrutiny of business decisions by govt. and public. Increased deregulation Changing business practices (e.g. outsourcing,, downsizing, reengineering) Changing social and business relationship between companies, employees, customers and other stakeholders. Porter’s national competitive advantage: There are 4 determinants of national competitive advantage. Factor conditions These are a country’s endowment of inputs to production e.g. Human Resources, Physical resources, Capital, Knowledge and infrastructure. These factors could be Basic (inherited and creation involves less investment e.g. natural resources) or Advanced (include modern digital communications, highly educated people and research laboratories etc.) Demand conditions The home market determines how firms perceive, interpret and respond to buyer needs. Related and supported industries Competitive success in one industry in liked to success in related industries. Firm strategy, structure and rivalry www.canotes.multiply.com 96 Annexure “A” Topic Chapter 4 & 5 : Strategic Management : Traditional and other models Levels of strategy Traditional approach to make strategy Activities affecting Crafting strategy Learning based strategy Competitive strategy Chapter 6 : SWOT Analysis and Gap Analysis Porter’s 5 Forces model Chapter 7 : Performance Appraisal & Analysis Measuring performance of profit center. Inflation Chapter 9 : Mergers and Acquisition Strategic alliances – benefits to franchiser Chapter 10 : Corporate Re-organization Management buy-out Chapter 11 : Ethics and Social Responsibility Social responsibility – Favors - Externality Chapter 13 :Human Resource Management Different concepts Termination Chapter 14 : Measurement and Performance Factors affecting personality differences Job restructuring & redesign Employee appraisal – working arrangements and types of organizations Types of incentive schemes Employee appraisal – Methods of appraisal Chapter : 15 Training, Appraisal and Career Management Competence Chapter 16 : Management and Human Resource` Trait theory Leadership Discipline – Disciplinary problems in organizations Retirement, Resignation, Redundancy – Unfair Dismissal Chapter 17 : Groups in Organization Effects of conflicts within groups – Groups & Departments Chapter 18 : Strategies for Critical periods Corporate Decline – 3 types of decline Chapter 19 & 20 : Change Management and Changing Environment Nature of strategic change Model for change Approaches to implement change Force Field Analysis Change process Pressure groups Chap 20 : Strategic intelligence Chap 20 : Environmental data *Details *Explanation *Example *Figure → → → → PBP Reference Figure Explanation Explanation Explanation Overview Figure & Explanation Topic Chapter 22 : The Evolution of Marketing Concept Marketing management Elements of marketing mix – Promotion Value-chain Marketing process Chapter 23 : Strategic Marketing & Planning Development in segmentation Benefits of market segmentation PBP Reference Explanation Details Explanation & examples Details Details Details Target Market Explanation Evaluating market segments – porter’s 5 forces Explanation Competitive strategy options Identifying gap in market through positioning Chapter 24 : Marketing Research Details Explanation Research procedures - Analysis of data Collecting secondary data – internal and external databases Questionnaires Marketing Information System (MkIS) Marketing Decision Support System Market Sensing Service Quality (SERVQUAL) Sales Forecasting [Forecasting demands] Marketing Communication Chapter 25 : Product Nature and characteristics of a service Explanation Details Stages of product life cycle Product Portfolio Planning Chapter 26 : Price Details Explanation Details Price leadership Price Elasticity of Demand Explanation & Example Explanation & Example Explanation Absorption and Marginal costing, and breakeven analysis Chapter 27 : Place Explanation Explanation Details Channel conflict – Horizontal and Vertical Conflict Consideration in distribution Details Channel design decision Benefits of direct and indirect sales Explanation Details Distribution strategy Marketing and Information System Customer Dynamics and internet as distribution channel Chapter 28 : Promotion Push and Pull Strategy Merchandising Planning a promotion campaign Relationship Marketing Chapter : International Business Explanation Details Details Competitive advantage Protectionism Details Explanation Explanation & examples Detail Details & examples Details Explanation Pg : 298 Details Concepts Details Explanation & examples Details Details Explanation & examples Details Explanation Explanation Explanation Explanation Explanation Details Explanation & examples Details Details Topic included in these notes and needs further detail from PBP Topic not included in these notes at all so needs to be read from PBP For examples relating to the topic, see PBP For graphical representation relating to the topic, see PBP Details Explanation Explanation Explanation Explanation Explanation Explanation Explanation Details Details Explanation Details Details