Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston
advertisement
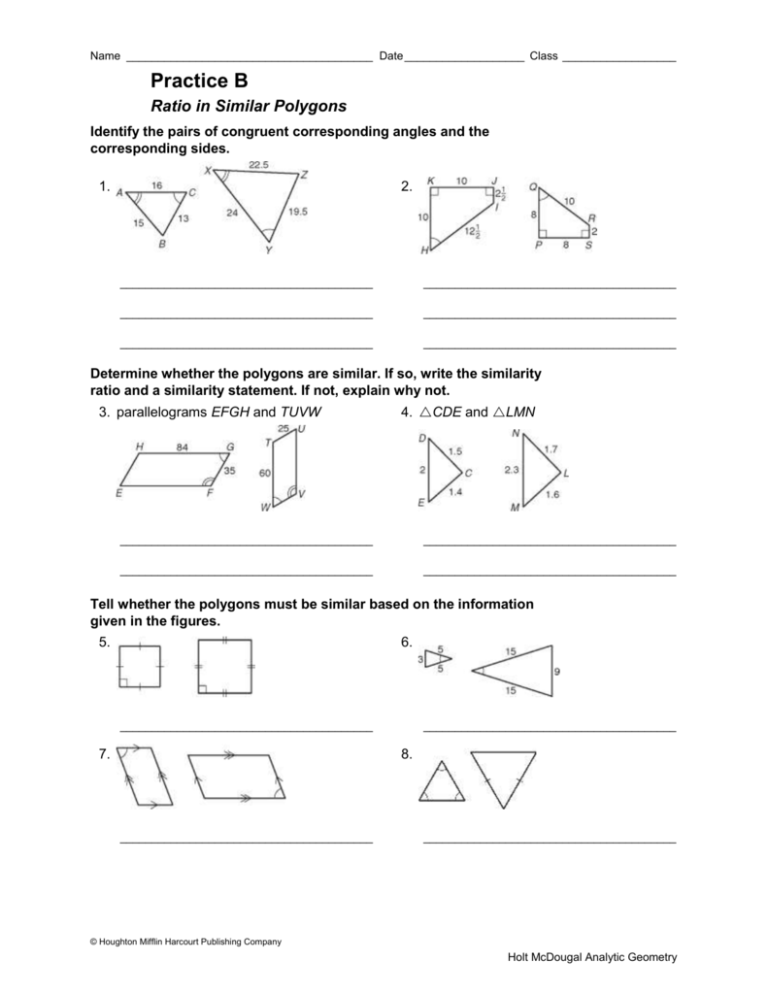
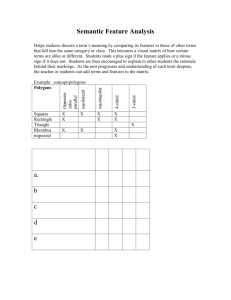
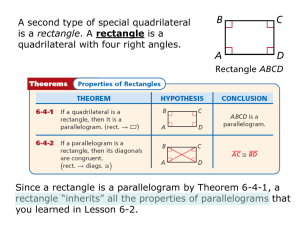
Name _______________________________________ Date ___________________ Class __________________ Practice B Ratio in Similar Polygons Identify the pairs of congruent corresponding angles and the corresponding sides. 1. 2. ________________________________________ ________________________________________ ________________________________________ ________________________________________ ________________________________________ ________________________________________ Determine whether the polygons are similar. If so, write the similarity ratio and a similarity statement. If not, explain why not. 3. parallelograms EFGH and TUVW 4. CDE and LMN ________________________________________ ________________________________________ ________________________________________ ________________________________________ Tell whether the polygons must be similar based on the information given in the figures. 5. 6. ________________________________________ 7. ________________________________________ 8. ________________________________________ ________________________________________ © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company Holt McDougal Analytic Geometry Name _______________________________________ Date ___________________ Class __________________ Reading Strategies 14. midsegment triangle 1. rectangle 2. rhombus 3. square 4. rectangle 5. square 6. rhombus 7. rhombus RATIOS IN SIMILAR POLYGONS Practice A 1. corresponding Reteach 2. congruent; proportional 1. valid E 3. valid 5. 4. Not valid; need to know that EFGH is a . 5. rhombus 6. rectangle, rhombus, square 7. rectangle 8. rectangle, rhombus, square Challenge 7. a. The measure of each angle should be 108. All the sides should be congruent. b. Results will vary. 8. Proceed as in Exercises 1–5. Draw bisectors of all sides of pentagon; mark intersection of bisectors and the circle as the other 5 points of the decagon; draw line segments. 9. Choices will vary. Problem Solving 1. Diagonals bisect each other, so the quad. is a . The diagonals are , so EFGH is a rect. because with diags. rect. 2. No; from the given information, you can conclude only that ABCD is a rhombus. 3. Both pairs of opposite sides are , so STUV is a . STUV is a rectangle because with diags. rect. 4. A 6. D 4. F 3. size 2. Not valid; need to know that MPQR is a . 7. D AB CB AC FE DE FD KJL 6. RSQ RS SQ QR KJ JL LK 8. Possible answer: Every angle in a rectangle is a right angle, and all right angles are congruent. 9. 4 5 10. 8 4 ; 10 5 Practice B 1. A X; B Z; C Y; AC AB BC 2 XY XZ ZY 3 2. H Q; I R; J S; K P; KJ KH HI JI 5 PS PQ QR SR 4 7 ; Possible answer: 5 WTUV 3. yes; EFGH 4. No; sides cannot be matched to have corresponding sides proportional. 5. yes 6. yes 7. no 8. yes 5. F 7. G © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company Holt McDougal Analytic Geometry