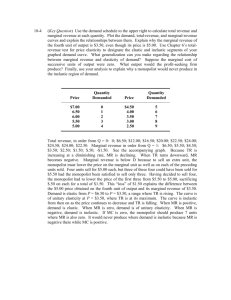
Price
advertisement

Pure Monopoly True or false : 1) The monopolist's demand curve is more elastic than the industry demand curve. 2) A purely competitive firm is a price maker, but a monopolist is a price taker. 3) If a monopolist discovers that it is operating at a level of output where P < AVC, it will continue to operate in the short run. 4) A monopolist will not charge the highest price it can get. 5) In a monopoly, price is greater than marginal cost. 6) The supply curve for the pure monopolist is upsloping. 7) Equilibrium for the monopolist occurs where P > MR > MC > average total cost. 8) In a monopoly, price is less than minimum average total cost. Essay questions : What are the major characteristics of pure monopoly? What are the major barriers to entry that explain the existence of monopoly? In what ways, if any, do the demand schedules for a purely competitive firm and a pure monopolist differ? What significance does this have for the price-output behavior of each? Do you agree or disagree with the statement that: “A monopolist always charges the highest possible price.” Explain. How does monopoly compare with pure competition in terms of price, output, and efficiency? Multiple choice: (1) Which is most characteristic of a pure monopoly ? A) There is a dominant firm in a multifirm industry . B) The firm produces a good or a service for which there are no close substitutes . C) The firm has considerable control over the quantity of the output produced, but not over price . D) Exit from the industry is blocked but entry into the industry is relatively easy. (2) Which phrase would be most characteristic of pure monopoly ? A) close substitutes B) efficient advertiser C) price taker D) single seller (3) Which is a barrier to entry ? A) patents B) revenue maximization C) profit maximization D) elastic product demand (4) One feature of pure monopoly is that the demand curve : A) is vertical . B) is horizontal . C) slopes upward . D) slopes downward. (5) Under pure monopoly, a profit-maximizing firm will produce : A) in the inelastic range of its demand curve . B) in the elastic range of its demand curve . C) only where total costs are zero . D) only where marginal revenue is zero. (6) Given a downsloping linear demand curve, when total revenue is decreasing, marginal revenue is : A) positive and demand is elastic . B) negative and demand is elastic . C) positive and demand is inelastic . D) negative and demand is inelastic. (7) At which combination of price and marginal revenue (P, MR) is the price elasticity of demand greater than 1 ? A) P = 15 , MR = 8 B) P = 12 , MR = 0 C) P = 8 , MR = -2 D) P = 4 , MR = -4 (8) Marginal revenue is positive whenever : A) demand is price-elastic . B) demand is price-inelastic . C) demand is unitary-elastic . D) a firm operates at a point on the lower half of a linear demand curve. (9) Suppose a monopolist produces output where total revenue is maximized. At that output, the price elasticity of demand for the monopolist's output is : A) greater or equal to one . B) less than one . C) equal to one . D) impossible to determine. (10) Which is true with respect to the demand data confronting a monopolist? A) Demand is perfectly price inelastic. B) Price increases as the output of the firm increases. C) Marginal revenue increases as price decreases. D) Marginal revenue is less than price. (11) The profit-maximizing monopolist will usually set a price : A) equal to marginal revenue . B) where demand is unitary-elastic . C) in the elastic portion of the demand curve . D) in the inelastic portion of the demand curve. (12) A monopolist can sell 20 toys per day for k.d 8.00 each. To sell 21 toys per day, the price must be cut to k.d 7.00. The marginal revenue of the 21st toy is: A) - 10 k.d B) - 13 k.d C) - 18 k.d D) - 21 k.d (13) Many people believe that monopolies charge any price they want to without affecting sales. Instead, the output level for a profit-maximizing monopoly is determined by : A) B) C) D) marginal cost = demand . marginal revenue = demand . average total cost = demand . marginal cost = marginal revenue. (14) In the figure below, the profit-maximizing monopolist will set its price and output at : A) B) C) D) 0J and 0V , respectively . 0G and 0Y , respectively . 0K and 0T , respectively . 0H and 0X , respectively. ** Answer the question(s) below on the basis of the following demand and cost data for a pure monopolist. Demand data Cost data Price Quantity Qutput Total k.d demanded Cost k.d 2.75 3 3 4.00 2.50 4 4 4.50 2.25 5 5 4.75 2.00 6 6 5.75 1.75 7 7 7.75 (15) Refer to the above table. Equilibrium price of the monopolist will be: A) k.d 2.50 B) k.d 2.25 C) k.d 2.00 D) k.d 1.75 (16) Refer to the above table. The monopolist will realize a: A) Profit of k.d 10 B) Profit of k.d 6.50 C) Profit of k.d 4.50 D) Loss of k.d 7.23 (17) Refer to the figure. In the short run, this monopolist will : A) B) C) D) shut down . produce 0A . produce 0B . produce 0C. (18) Pure monopolists: A) B) C) D) maximize MR . are price takers . sell where P > MC . confront demand curves that are perfectly inelastic. (19) A profit-maximizing monopolist facing the situation shown in the graph should : A) B) C) D) shut down immediately . continue producing to minimize losses . continue producing to make economic profits . continue producing as long as price is greater than marginal cost. (20) When compared with the purely competitive industry with identical costs of production, a monopolist will produce: A) more output and charge the same price. B) more output and charge a higher price. C) less output and charge a higher price. D) less output and charge the same price. (21) Based on the graph, what is the difference between the purely competitive equilibrium level of output and the pure monopolist equilibrium level of output ? A) B) C) D) 0 20 70 90 Problem sets : ( 1 ) The demand schedule for the product produced by a monopolist is given in the table below. Complete the table by computing total revenue and marginal revenue. Quantity Total Marginal demanded Price revenue revenue 1 kd 325 kd ______ 2 300 ______ kd ______ 3 275 ______ ______ 4 250 ______ ______ 5 225 ______ ______ 6 200 ______ ______ 7 175 ______ ______ 8 150 ______ ______ 9 125 ______ ______ 10 100 ______ ______ 11 75 ______ ______ 12 50 ______ ______ 13 25 ______ ______ 14 0 ______ ______ (a) What do the data in the table indicate about the relationship between total revenue and marginal revenue? Explain. (b) What do the data in the table indicate about the elasticity of demand? ( 2 ) The following data represent costs and revenues for a monopolist : Quantity Price TC demanded 1 100 40 2 90 80 3 80 120 4 70 160 5 60 200 6 50 240 7 40 280 a) Determine the equilibrium output and price . b) What is the level of profits ( losses ) received by the monopolist . ( 3 ) In the following table are demand and cost data for a pure monopolist. Complete the table by filling in the columns for total revenue, marginal revenue, and marginal cost. Answer these three questions: (a) What output will the monopolist produce? (b) What price will the monopolist charge? (c) What total profit will the monopolist receive at the profit-maximizing level of output? Totat Marginal Quantity Price revenue revenue 0 kd 34 kd ______ 1 32 ______ kd ______ 2 30 ______ ______ 3 28 ______ ______ 4 26 ______ ______ 5 24 ______ ______ 6 22 ______ ______ 7 20 ______ ______ 8 18 ______ ______ 9 16 ______ ______ 10 14 ______ ______ Total Marginal cost cost kd 20 36 kd ______ 46 ______ 50 ______ 54 ______ 56 ______ 64 ______ 80 ______ 100 ______ 128 ______ 160 ______