Foundations Review Sheet
advertisement

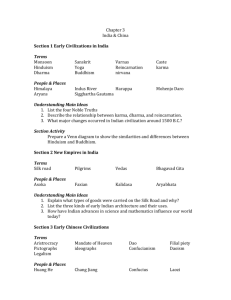
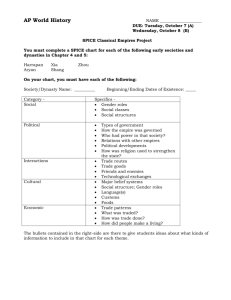
Foundations Review Sheet I) G) H) Neolithic Age Hunter-gatherers, nomads vs. agriculturalists Neolithic Revolution and consequences Agriculturalists vs. Pastoralists Patriarchal vs. Egalitarian Urbanization and effects on society 1) -specialization 2) -classes 3) -religion 4) -disease 5) -environmental impact Demography 1) What factors influence population growth and decline? 2) Immunity? Disease pools? Impact of climate Labor vs. Leisure A) B) C) D) River Valley Civilizations: Be able to compare and contrast Mesopotamia Egypt Indus Valley Yellow River Valley A) B) C) D) E) F) II) III) Ages A) Be able to sequence the “Big Picture” ideas and events of the Bronze, Iron and Classical Age peoples B) Bronze Age C) Iron Age D) Dark Age of Mediterranean E) Classical Age 1) Poleis 2) Impact of Alexander F) Persia, Rome, Han, Maurya, Gupta, Greek 1) Classes 2) Government 3) Belief systems G) Be able to compare and contrast the Classical empires listed above IV) Axial Age A) Belief Systems 1) Locations 2) Impact 3) Comparisons Examples of Foundations Exam Questions 1. Which ONE of the following indicators would lead to population growth, rather than decline? a. Densely populated cities encouraged the spread of diseases. b. Interaction with virgin soil locations. c. Democratization of metallurgy with new iron farming tools. d. High infant mortality among newcomers. 2. Which of the following contributed significantly to the fall of both the western Roman and the Han empires? a. The destruction of overland trade routes, b. irregularities in the flow of the silver trade, c. new military technologies, d. invasions by borderland peoples. 3. Most early civilizations before 600 BCE shared which of the following characteristics? a. animal herds and portable houses, b. large standing armies, and elected governments, c. urban centers, growing populations, and writing systems, d. caravan trade, underground cities, and large ships. 4. Initiated under the Qin, this system maintained that human nature is essentially wicked and that people behave in an orderly fashion only if compelled by strict laws and harsh punishments. a. Confucianism, b. Legalism, c. Daoism, d. Centralism, e. Mandate of Heaven 5. Which, from earliest to most recent, is the correct sequence? a. Zhou, Shang, Han, Qin, b. Shang, Zhou, Qin, Han, c. Han, Qin, Shang, Zhou, d. Qin, Shang, Zhou, Han 6. Which of the following would best fit in with the beliefs of a practicing Buddhist? a. Justice should be based on the principle of an eye for an eye, a tooth for a tooth, b. each individual should place his or her trust in a personal savior in order to ensure a place in heaven, c. at the end of the world, God will judge all sinners and condemn them to eternal torment, d. Yogic discipline and mastery of the body helps to improve the quality of one’s spirit, e. people are born and reborn into lives of suffering but can escape this cycle by attaining enlightenment. Examples of types of questions you should attempt to figure out: 1. Compare Greek systems with the South Asian and East Asian systems. 2. How did sedentary life lead to the Agricultural Revolution? 3. How did the Agricultural Revolution lead to urbanization and complex governmental systems? 4. How do empires develop? What do empires have in common? Definitions? Historical Examples? Ancestor worship Holocene Buffer states Humanism Bureaucrats Linguistics Centralization Monotheism City-state Nomadic Codified law Oligarchy Colonization Pastoralists Cultural diffusion Patriarchy Cuneiform Polis Desertification Propaganda diaspora Salinization Domestication Sedentary Dualism Social structure Empire Tyrant Epidemiology Vedas Fertile crescent Virgin soil Filial piety Ziggurat