Document
advertisement

Computer Organization and Architecture
SCR 1043
Semester 2, 09/10
Programming 5: Boolean and Conditional Processing
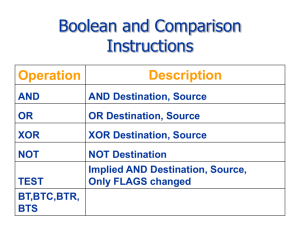
AND Instruction
• Performs a Boolean AND operation between each pair of matching bits
in two operands
• Syntax:
AND destination, source
(same operand types as MOV)
AND
cleared
00111011
00001111
00001011
unchanged
OR Instruction
• Performs a Boolean OR operation between each pair of matching bits in
two operands
• Syntax:
OR destination, source
OR
unchanged
00111011
00001111
00111111
set
1
XOR Instruction
• Performs a Boolean exclusive-OR operation between each pair of
matching bits in two operands
• Syntax:
XOR destination, source
XOR
unchanged
00111011
00001111
00110100
inverted
NOT Instruction
• Performs a Boolean NOT operation on a single destination operand
• Syntax:
NOT destination
NOT
00111011
11000100
inverted
Boolean Examples
• Task: Convert the character in AL to upper case.
• Solution: Use the AND instruction to clear bit 5.
2
•
•
•
•
Task: Convert a binary decimal byte into its equivalent ASCII decimal
digit.
Solution: Use the OR instruction to set bits 4 and 5.
Task: Jump to a label if an integer is even.
Solution: AND the lowest bit with a 1. If the result is Zero, the number
was even.
CMP Instruction
• Compares the destination operand to the source operand
• Nondestructive subtraction of source from
(destination operand is not changed)
• Syntax: CMP destination, source
destination
3
4
Conditional Jump
Conditional Jump Examples
5
Block-Structured IF Statements
Assembly language programmers can easily translate logical statements written
in C++/Java into assembly language. For example:
Implement the following pseudocode IF-ELSE statement
6
7
8
Exercises
1. In the following instruction sequence, show the changed value of AL where
indicated:
mov al,01101111b
and al,00101101b
mov al,6Dh
and al,4Ah
mov al,00001111b
or al,61h
mov al,94h
xor al,37h
AL = ____
AL = ____
AL = ____
AL = ____
2. In the following instruction sequence, show the changed value of AL where
indicated:
mov al,7Ah
not al
mov al,3Dh
and al,74h
mov al,9Bh
or al,35h
mov al,72h
xor al,DCh
AL = ____
AL = ____
AL = ____
AL = ____
3. Implement the following pseudocode in assembly language.
if (bx > cx)
x=1;
4. Implement the following pseudocode in assembly language.
if (dx <= cx)
x=1;
else
x=2;
5. Implement the following pseudocode in assembly language.
if (val1 > cx AND cx > dx)
x=x+1;
else
x=x-1;
6. Implement the following pseudocode in assembly language.
if (bx > cx OR bx > val1)
x=1;
else
x=2;
9
7. Write assembly language code to implement the following high-level
pseudo-code using these instructions MOV, ADD, CMP, JA and LOOP.
.DATA
COUNTER = 5
TOTAL
DWORD
?
ECX=COUNTER;
EAX=TOTAL;
LOOP
{
TOTAL = TOTAL +10;
IF (TOTAL > 100)
JUMP TO BREAKLOOP
}
BREAKLOOP:
8. Analyze the following code segment.
L1:
L2:
OUT:
CMP EAX, 20
JG L1
JL L2
MOV EBX, 1
JMP OUT
MOV EBX, 0
(i). If EAX=5, which conditional jump is taken. Please explain your
answer. What is the final value of EBX?
(ii). Why is the JMP OUT instruction needed for this code segment?
Please elaborate your answer.
10
Program 1
Write an assembly language program to process an array. Your program should
be able to calculate the sum, and determine the smallest and the largest value of
an array declared as
TestArray SDWORD
-10, 49,56,23,2,-121,92,15,9,-8
1. Intro
Display a message “ Array processing in progress …”
Array processing in progress …
2. Sum
Add all elements in the array.
In the main program, display the value of sum.
Sum = +107
You can use the following algorithm if you want to
1.
Set sum to zero
Set index to 0 /* first element */
DOWHILE index <= (number_of_element -1)
Sum = sum + TestArray (index)
Index = index +1
ENDDO
Return sum
3. Smallest
Find the smallest element in the array
In the main program, display the value of the smallest element.
Smallest = -121
You can use the following algorithm if you want to
Set smallest_element to array(0)
/* first element */
DO index = 1 to (number_of_elements – 1)
If TestArray(index) < smallest_element THEN
Smallest_element = TestArray(index)
ENDIF
ENDDO
Return smallest_element
4. 4. Largest
Find the largest element in the array
In the main program, display the value of largest element.
Largest = +92
11
2.
You can use the following algorithm if you want to
Set largest_element to array(0) /* first element */
DO index = 1 to (number_of_elements -1 )
If TestArray(index) > largest_element THEN
largest_element = TestArray(index)
ENDIF
ENDDO
Return largest_element
Your output for the complete program must be as shown below
12