Cell Transport Study Guide: Diffusion, Osmosis, Tonicity
advertisement

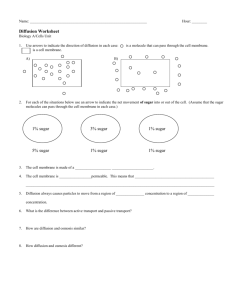
Cell Transport Study Guide Solutions – mixtures of solute & solvent Concentration = grams/liters (solute ÷ solvent) 12 grams salt = 4 g/L 3 liters water Left = Concentration of A & B Right = Concentration of C Two Types of Transport: 1. Passive – no energy Particles move HIGH to LOW Examples: 2. Active – energy Particles move LOW to HIGH Examples: A. Ion Pumps B. Endocytosis C. Exocytosis A. Diffusion B. Osmosis C. Facilitated Diffusion: 1. Diffusion Moving Particles Goal? Equilibrium 2. Osmosis Moving Water (equal concentrations) 3. Facilitated Diffusion Moving Particles with Proteins Tonicity – difference in concentration across a membrane Hypertonic Hypotonic Isotonic Higher Solutes/Less Water Water moves TOWARDS Cells will SHRINK Lower Solutes/More Water Water moves AWAY Cells will SWELL Equal Solutes & Water Water moves BOTH WAYS Cells will STAY THE SAME Active: Ion Pumps Endocytosis Exocytosis Cell Transport Study Guide 1. Solutions are mixtures of ________________________ and ____________________________________. 2. A __________________ is a fluid in which a substance is dissolved. 3. A __________________ is a substance dissolved in a solution. 4. What is the concentration of the following: a. 36 mg of salt in 2 Liters of water: __________________________ b. 20 mg of sugar in 4 Liters of water: ________________________ c. 15 g of salt in 5 Liters of water: ___________________________ 5. What are the two main types of transport? ______________________________ & ______________________________ 6. The main difference between the types of transports in #3 is that: a. ____________________________ = energy needed b. ____________________________ = no energy 7. Diffusion is the movement of ________________________ from areas of _____________ concentration to _________ concentration. 8. Osmosis is the movement of ________________________ from a ___________tonic solution to a _________tonic. 9. Facilitated diffusion moves particles from high to low concentrations using _________________________. 10. 11. The goal of passive transport is to achieve ________________________________________. Use arrows to indicate the direction of diffusion in each case: is a molecule that can pass through the cell membrane. A) is a cell membrane. B) 12. For each of the situations below use an arrow to indicate the net movement of sugar into or out of the cell. (Assume that the sugar molecules can pass through the cell membrane in each case.) 1% sugar 3% sugar 1% sugar 5% sugar 1% sugar 1% sugar 13. For each of the situations below use an arrow to indicate the net movement of water into or out of the cell. 1% sugar 3% sugar 1% sugar 5% sugar 1% sugar 1% sugar Use your knowledge of OSMOSIS to use the diagram below to answer questions in #14. 14. Use the diagram above to answer the following: a. The animal cell is ________________________ to solution A. b. The animal cell will ____________________________________ in solution A. c. The animal cell is ________________________ to solution B. d. The animal cell will ____________________________________ in solution B. e. The animal cell is ________________________ to solution C. f. The animal cell will ____________________________________ in solution C. 15. Decide whether the following movements across the membrane requires energy: (answer by each) a. Endocytosis ____________ b. Diffusion ______________ c. Facilitated diffusion ______ d. Exocytosis _____________ e. Osmosis _______________ f. Active transport _________ 16. Ion pumps are a type of active transport. The process requires the use of ____________________ to transport particles across a membrane from an area of ___________________ to ________________ concentrations. 17. Endocytosis brings large particles _______ the cell (using energy or not using energy). 18. Exocytosis brings large particles _______ the cell (using energy or not using energy).