Determining Ksp for Calcium Hydroxide - OSCSS
advertisement
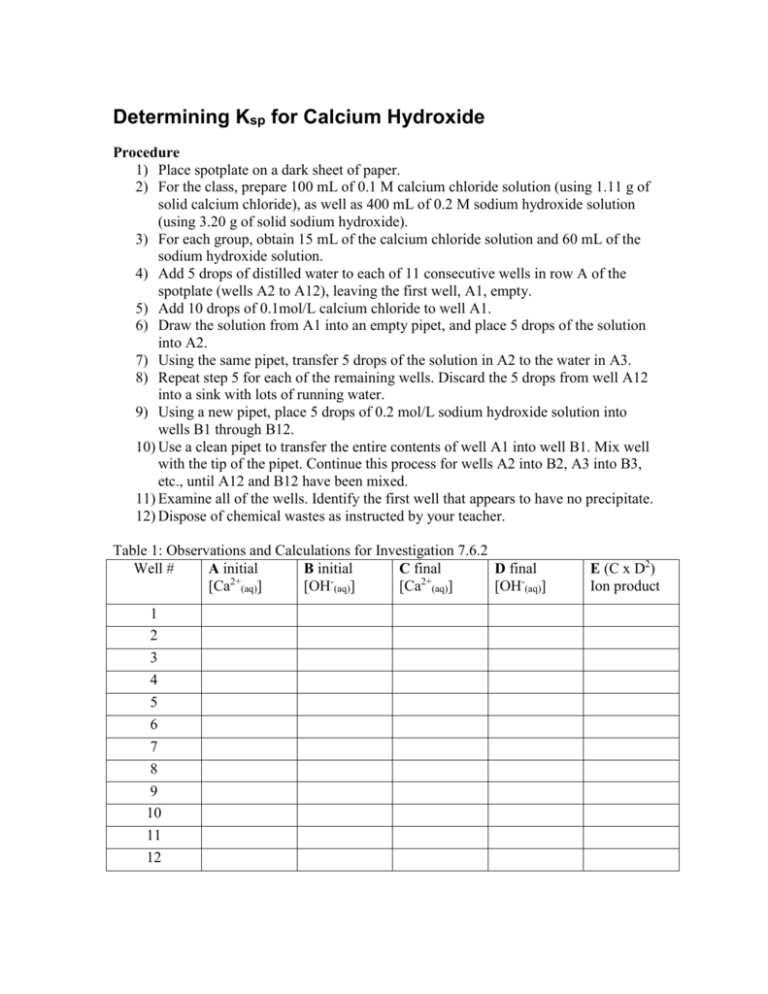
Determining Ksp for Calcium Hydroxide Procedure 1) Place spotplate on a dark sheet of paper. 2) For the class, prepare 100 mL of 0.1 M calcium chloride solution (using 1.11 g of solid calcium chloride), as well as 400 mL of 0.2 M sodium hydroxide solution (using 3.20 g of solid sodium hydroxide). 3) For each group, obtain 15 mL of the calcium chloride solution and 60 mL of the sodium hydroxide solution. 4) Add 5 drops of distilled water to each of 11 consecutive wells in row A of the spotplate (wells A2 to A12), leaving the first well, A1, empty. 5) Add 10 drops of 0.1mol/L calcium chloride to well A1. 6) Draw the solution from A1 into an empty pipet, and place 5 drops of the solution into A2. 7) Using the same pipet, transfer 5 drops of the solution in A2 to the water in A3. 8) Repeat step 5 for each of the remaining wells. Discard the 5 drops from well A12 into a sink with lots of running water. 9) Using a new pipet, place 5 drops of 0.2 mol/L sodium hydroxide solution into wells B1 through B12. 10) Use a clean pipet to transfer the entire contents of well A1 into well B1. Mix well with the tip of the pipet. Continue this process for wells A2 into B2, A3 into B3, etc., until A12 and B12 have been mixed. 11) Examine all of the wells. Identify the first well that appears to have no precipitate. 12) Dispose of chemical wastes as instructed by your teacher. Table 1: Observations and Calculations for Investigation 7.6.2 Well # A initial B initial C final D final [Ca2+(aq)] [OH-(aq)] [Ca2+(aq)] [OH-(aq)] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 E (C x D2) Ion product