Solution Sheet Lab 10
advertisement
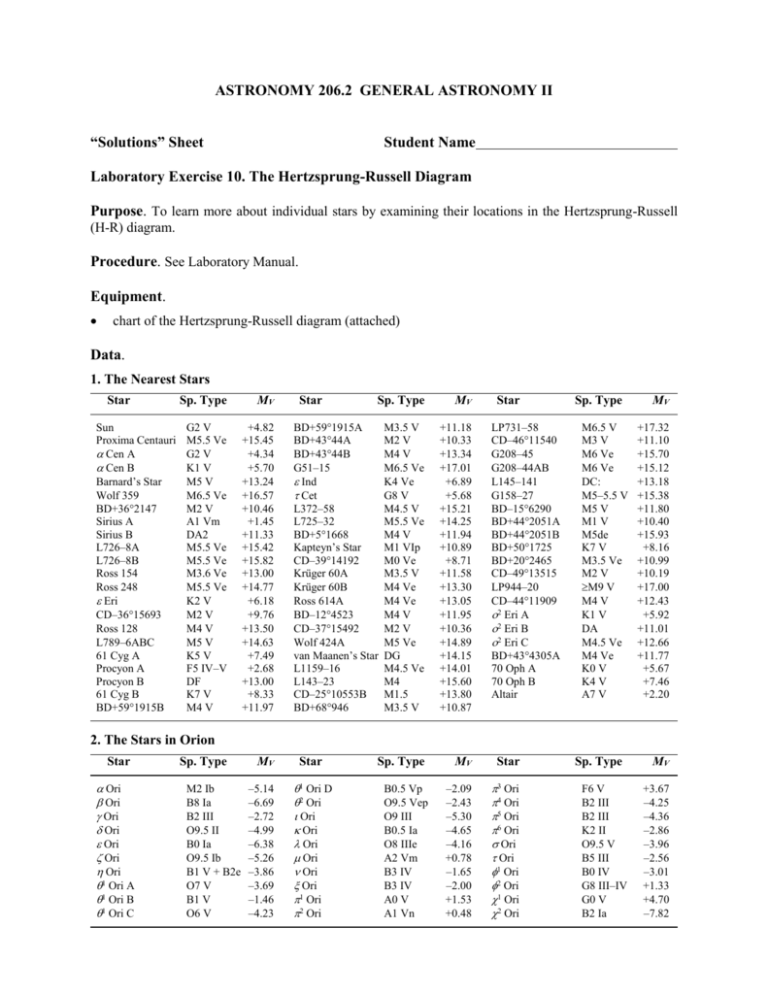
ASTRONOMY 206.2 GENERAL ASTRONOMY II “Solutions” Sheet Student Name Laboratory Exercise 10. The Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram Purpose. To learn more about individual stars by examining their locations in the Hertzsprung-Russell (H-R) diagram. Procedure. See Laboratory Manual. Equipment. chart of the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram (attached) Data. 1. The Nearest Stars Star Sun Proxima Centauri Cen A Cen B Barnard’s Star Wolf 359 BD+36°2147 Sirius A Sirius B L726–8A L726–8B Ross 154 Ross 248 Eri CD–36°15693 Ross 128 L789–6ABC 61 Cyg A Procyon A Procyon B 61 Cyg B BD+59°1915B Sp. Type MV G2 V M5.5 Ve G2 V K1 V M5 V M6.5 Ve M2 V A1 Vm DA2 M5.5 Ve M5.5 Ve M3.6 Ve M5.5 Ve K2 V M2 V M4 V M5 V K5 V F5 IV–V DF K7 V M4 V +4.82 +15.45 +4.34 +5.70 +13.24 +16.57 +10.46 +1.45 +11.33 +15.42 +15.82 +13.00 +14.77 +6.18 +9.76 +13.50 +14.63 +7.49 +2.68 +13.00 +8.33 +11.97 Star Sp. Type BD+59°1915A BD+43°44A BD+43°44B G51–15 Ind Cet L372–58 L725–32 BD+5°1668 Kapteyn’s Star CD–39°14192 Krüger 60A Krüger 60B Ross 614A BD–12°4523 CD–37°15492 Wolf 424A van Maanen’s Star L1159–16 L143–23 CD–25°10553B BD+68°946 MV Star M3.5 V M2 V M4 V M6.5 Ve K4 Ve G8 V M4.5 V M5.5 Ve M4 V M1 VIp M0 Ve M3.5 V M4 Ve M4 Ve M4 V M2 V M5 Ve DG M4.5 Ve M4 M1.5 M3.5 V +11.18 +10.33 +13.34 +17.01 +6.89 +5.68 +15.21 +14.25 +11.94 +10.89 +8.71 +11.58 +13.30 +13.05 +11.95 +10.36 +14.89 +14.15 +14.01 +15.60 +13.80 +10.87 LP731–58 CD–46°11540 G208–45 G208–44AB L145–141 G158–27 BD–15°6290 BD+44°2051A BD+44°2051B BD+50°1725 BD+20°2465 CD–49°13515 LP944–20 CD–44°11909 2 Eri A 2 Eri B 2 Eri C BD+43°4305A 70 Oph A 70 Oph B Altair Sp. Type MV Star B0.5 Vp O9.5 Vep O9 III B0.5 Ia O8 IIIe A2 Vm B3 IV B3 IV A0 V A1 Vn –2.09 –2.43 –5.30 –4.65 –4.16 +0.78 –1.65 –2.00 +1.53 +0.48 3 Ori 4 Ori 5 Ori 6 Ori Ori Ori 1 Ori 2 Ori 1 Ori 2 Ori Sp. Type M6.5 V M3 V M6 Ve M6 Ve DC: M5–5.5 V M5 V M1 V M5de K7 V M3.5 Ve M2 V M9 V M4 V K1 V DA M4.5 Ve M4 Ve K0 V K4 V A7 V MV +17.32 +11.10 +15.70 +15.12 +13.18 +15.38 +11.80 +10.40 +15.93 +8.16 +10.99 +10.19 +17.00 +12.43 +5.92 +11.01 +12.66 +11.77 +5.67 +7.46 +2.20 2. The Stars in Orion Star Ori Ori Ori Ori Ori Ori Ori 1 Ori A 1 Ori B 1 Ori C Sp. Type M2 Ib B8 Ia B2 III O9.5 II B0 Ia O9.5 Ib B1 V + B2e O7 V B1 V O6 V MV –5.14 –6.69 –2.72 –4.99 –6.38 –5.26 –3.86 –3.69 –1.46 –4.23 Star 1 Ori D 2 Ori Ori Ori Ori Ori Ori Ori 1 Ori 2 Ori Sp. Type F6 V B2 III B2 III K2 II O9.5 V B5 III B0 IV G8 III–IV G0 V B2 Ia MV +3.67 –4.25 –4.36 –2.86 –3.96 –2.56 –3.01 +1.33 +4.70 –7.82 Questions to Answer (answers given in the space to the right of the questions) General Check List. main sequence stars (dwarfs) identified on chart √ curved main sequence √ 1. Identify from the H-R diagram a star that is a white dwarf (degenerate star). What is the name of the star in the tables? 2. Identify from the H-R diagram a star that is a red supergiant. What is the name of the star in the tables? 3. Identify from the H-R diagram a star that is a blue supergiant. What is the name of the star in the tables? 4. Identify from the H-R diagram a star that is a red giant. What is the name of the star in the tables? 5. Identify from the H-R diagram the star that is most similar to the Sun in terms of its luminosity and spectral type (it need not be identical). What is the name of the star in the tables? The Nearest Stars 6. Are there any giant or supergiant stars located near the Sun? 7. Identify from the H-R diagram the hottest star in the Sun’s vicinity. What is the name of the star in the tables? 8. Identify from the H-R diagram the most luminous star in the Sun’s vicinity. What is the name of the star in the tables? 9. Identify from the H-R diagram the coolest star in the Sun’s vicinity. What is the name of the star in the tables? 10. Roughly what proportion of stars in the Sun’s vicinity are similar to the Sun in temperature and luminosity? 11. Are white dwarfs (degenerate stars) a common constituent of the solar neighbourhood: a. relative to supergiant stars? b. relative to M dwarfs? c. relative to stars like the Sun? 12. What is the approximate mass of the most typical type of star found in the Sun’s neighbourhood, in solar units? The Stars in Orion 13. Identify from the H-R diagram the hottest star in Orion. What is the name of the star in the tables? 14. Identify from the H-R diagram the star in Orion that has the lowest surface temperature. What is the name of the star in the tables? 15. For stars in Orion that fall on the main sequence, which one is the most massive? Identify it by name. 16. Roughly what is the mass of the star identified in question 15? 17. For stars in Orion that fall on the main sequence, which one is the least massive? Identify it by name. 18. What is the mass of the star identified in question 17? 19. What is the name and spectral type of the intrinsically least luminous star in Orion? 20. What is the name and spectral type of the intrinsically most luminous star in Orion? 21. What is the name of the largest star in Orion? 22. What proportion (percentage) of the bright stars in Orion are over 100 times (5 magnitudes) brighter than the Sun? 23. In terms of the Sun’s radius, how large is the star in question 21? (calculations given below) Discussion. Conclusions.