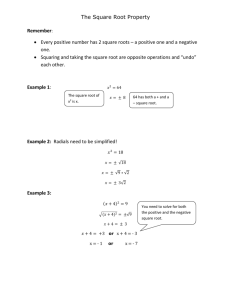
Managing Rollback/Undo Segments in AUM
advertisement

Managing Rollback/Undo Segments in AUM (Automatic Undo Management)
This document explains how to use the new Oracle9i feature Automatic Undo
Management (AUM) versus the Manual Undo Management related to conventional
rollback segments.
Managing Rollback/Undo Segments in Automatic Undo Management:
This new feature simplifies and automates the management of undo segments. DBAs
have the choice to manage rollback segments as they used to do under versions
Oracle7, Oracle8, and Oracle8i, or to let the RDBMS do it.
There are now two modes of rollback segments management and usage:
AUTOMATIC or
MANUAL
To distinguish between the two types of segments, ROLLBACK segments are called
UNDO segments when AUM is enabled.
In both cases, rollback/undo segments are still the only way for transactions to execute
and complete. This means that with either method, rollback/undo segments are present
in the database and use disk space.
**************************
INIT.ORA parameters
**************************
1. UNDO_MANAGEMENT can be set to AUTO if you want the RDBMS to manage
undo segments automatically:
RDBMS creates them when you create a new UNDO tablespace
RDBMS alters them ONLINE/OFFLINE when you choose a specific UNDO
tablespace
RDBMS drops them when you drop an UNDO tablespace
In this case, DBAs cannot manage undo segments at all, though they still do
exist as "rollback" segments.
Note: Though you can create rollback segments in UNDO tablespaces, it is
strongly recommended not to do it.
UNDO_MANAGEMENT can be set to MANUAL if you want to keep the control
on rollback segments.
2. If you decide to use AUM, you have to create at least one UNDO tablespace to
store the undo segments automatically created.
Even if AUM uses only one UNDO tablespace at the instance level, you can create
several UNDO tablespaces. In this case, specify which UNDO tablespace is to be
used:
UNDO_TABLESPACE=rbs
SQL> select name,value from v$parameter
where name in ('undo_management','undo_tablespace');
NAME
VALUE
------------------------------------ ---------------undo_management
AUTO
undo_tablespace
RBS
Having several UNDO tablespaces available in the database provides the possibility
to switch and use a different tablespace with smaller or larger global size for different
purposes of usage, such as OLTP, BATCH.
*************************
UNDO Tablespaces Creation
*************************
1. You create the UNDO tablespace at database creation.
2. Or after database creation:
SQL> create undo tablespace UNDO_RBS1 datafile 'undorbs1.dbf' size 100m;
Tablespace created.
********************************
UNDO Tablespaces Characteristics
********************************
1. They are locally-managed with system extent allocation:
SQL> select TABLESPACE_NAME, CONTENTS,
EXTENT_MANAGEMENT, ALLOCATION_TYPE,
SEGMENT_SPACE_MANAGEMENT
from dba_tablespaces where contents='UNDO';
TABLESPACE_NAME
--------------RBS
UNDO_RBS1
CONTENTS
--------UNDO
UNDO
EXTENT_MAN
---------LOCAL
LOCAL
ALLOCATIO
--------SYSTEM
SYSTEM
SEGMEN
-----MANUAL
MANUAL
2. You cannot use UNDO tablespaces for other purposes than UNDO SEGMENTS
and cannot do any operation on system generated undo segments:
SQL> create table T (c number) tablespace undo_rbs1;
create table T (c number) tablespace undo_rbs1
*
ERROR at line 1:
ORA-30022: Cannot create segments in undo tablespace
SQL> create rollback segment undo_rs1 tablespace undo_rbs1;
create rollback segment undo_rs1 tablespace undo_rbs1
*
ERROR at line 1:
ORA-30019: RBU Rollback Segment operation not supported in SMU mode
Note: You can create rollback segments on an UNDO tablespace while the database
runs in manual mode, but it is useless since these rollback segments cannot be set
online when running in AUM mode.
3. Only one UNDO tablespace can be used at the instance level:
=> use UNDO_TABLESPACE=rbs in init.ora parameter file to set it before instance
startup
=> or use the SQL command to change the UNDO tablespace during instance life:
SQL> alter system set undo_tablespace=undo_rbs1;
System altered.
**************************************
Rollback Segments versus UNDO Segments
**************************************
1. When creating an UNDO tablespace, these are automatically created:
* n undo segments (based on SESSIONS parameter value)
* named as _SYSSMUn$
* owned by PUBLIC (usable for OPS configuration)
* not manually manageable
SQL> select owner,segment_name,tablespace_name
from dba_rollback_segs order by 3;
OWNER SEGMENT_NAME
TABLESPACE_NAME
------ ------------------------------ -----------------------------PUBLIC _SYSSMU1$
RBS
PUBLIC _SYSSMU2$
RBS
PUBLIC _SYSSMU3$
RBS
PUBLIC _SYSSMU5$
RBS
PUBLIC _SYSSMU7$
RBS
PUBLIC _SYSSMU9$
RBS
PUBLIC _SYSSMU10$
RBS
PUBLIC _SYSSMU8$
RBS
PUBLIC _SYSSMU6$
RBS
PUBLIC _SYSSMU4$
RBS
SYS SYSTEM
SYSTEM
PUBLIC _SYSSMU11$
UNDO_RBS1
PUBLIC _SYSSMU12$
PUBLIC _SYSSMU13$
PUBLIC _SYSSMU14$
PUBLIC _SYSSMU15$
PUBLIC _SYSSMU16$
PUBLIC _SYSSMU17$
PUBLIC _SYSSMU18$
PUBLIC _SYSSMU19$
PUBLIC _SYSSMU20$
UNDO_RBS1
UNDO_RBS1
UNDO_RBS1
UNDO_RBS1
UNDO_RBS1
UNDO_RBS1
UNDO_RBS1
UNDO_RBS1
UNDO_RBS1
2. If you choose to use AUM, you have no chance to manage any undo or rollback,
even on an non UNDO tablespace.
SQL> create public rollback segment rs1 tablespace system;
create public rollback segment rs1 tablespace system
*
ERROR at line 1:
ORA-30019: Illegal rollback Segment operation in Automatic Undo mode
3. Only undo segments of the active UNDO tablespace and the SYSTEM rollback
segment are kept ONLINE. All other rollback segments and undo segments of
other UNDO tablespaces are OFFLINE.
Nevertheless, not all undo segments of the active UNDO tablespace are ONLINE
at startup: this depends on the SESSIONS parameter. For example, if 10 undo
segments exist and you startup the instance with a lower SESSIONS parameter
value, the existing UNDO segments are kept but only a few of them are onlined. The
OFFLINE undo segments of the active UNDO tablespace are onlined when more
transactions require the use of offlined undo segments.
*******************************************************
Automatic Undo Management and Real Application CLusters
*******************************************************
The undo space management feature is also useful in Real Application Clusters
environments.
1. All instances within Real Application Cluster environments must run in the
same undo mode.
2. Set the global parameter UNDO_MANAGEMENT to AUTO in your server
parameter file.
If you use client-side parameter files, the setting for UNDO_MANAGEMENT
must be identical in all the files.
3. Set the UNDO_TABLESPACE parameter to assign the appropriate undo
tablespace to each respective instance. Each instance requires its own undo
tablespace.
If you do not set the UNDO_TABLESPACE parameter, each instance uses the
first available undo tablespace.
Remarks
1. There is another undo_ init.ora parameter: UNDO_SUPPRESS_ERRORS.
Use it very carefully: set to TRUE, it suppresses any error message issued
when attempting manual operations while in AUTO mode.
SQL> alter rollback segment "_SYSSMU1$" online;
Rollback segment altered.
SQL> alter rollback segment "_SYSSMU13$" offline;
Rollback segment altered.
SQL> alter rollback segment rs1 online;
Rollback segment altered.
All these statements seem to have executed the operation, but in reality did
not do anything.
4. Like rollback segments dropped MANUALLY, queries that need to access the
transaction undo information residing in a dropped UNDO tablespace may result in
ORA-01555 "snapshot too old (rollback segment too small)" error, if the snapshot is
older than the DROP-SCN of the UNDO tablespace.