Heat Energy: Study Guide for Elementary/Middle School
advertisement

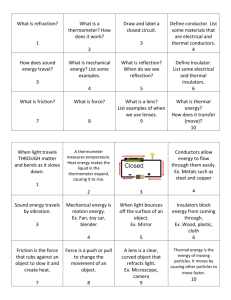
Heat Energy Physical Science S3P1. Students will investigate how heat is produced and the effects of heating and cooling, and will understand a change in temperature indicates a change in heat. a. Categorize ways to produce heat energy such as burning, rubbing (friction), and mixing one thing with another. b. Investigate how insulation affects heating and cooling. c. Investigate the transfer of heat energy from the sun to various materials. d. Use thermometers to measure the changes in temperatures of water samples (hot, warm, cold) over time. Main Concepts About Heat -Heat moves from hotter to cooler objects. -As objects heat up, the molecules (particles) get larger and move quickly. -As the object transfers its heat to cooler objects, the molecules become smaller and move less. -Heat continues to transfer from one object to another until the two objects are the same temperature (equilibrium). -Darker colors attract heat while lighter colors reflect heat. thermal energy: the form of energy that causes molecules to vibrate and move. The more thermal energy something has, the faster its particles move. Thermal energy is produced by the sun, fire (burning fuel such as gas, wood, paper, cloth, etc.), mixing chemicals, shaking objects, electricity, and friction. temperature: the measurement of the heat energy (degrees) thermometer: a tool used to measure how hot or cold something is. It measures temperature. Celsius: the metric temperature scale. This heat measurement is typically used by scientist. Boiling point=100° C / Freezing point= 0° C Fahrenheit: U.S. measuring standard for temperature- Boiling point= 212° F / Freezing point= 32° F heat: the transfer of thermal energy from hotter, faster- moving particles to cooler, slower-moving particles. equilibrium: when two objects or areas have reached the same temperature friction: heat produced from one object rubbing against another (a force that acts against motion causing objects to slow down) conduction: the movement of heat between objects that are touching each other. radiation: when thermal/heat energy moves without touching anything (empty space) convection: heat transfer by a vertical (up/down) direction. This type of heat transfer takes place in liquids and gases. insulator: objects that slow down heat transfer conductor: objects that speed up heat transfer Sources of Heat Energy Thermal energy is produced by the sun, fire (burning fuel such as gas, wood, paper, cloth, etc.), mixing chemicals, shaking liquids together, electricity, and friction. Types of Conductors and Insulators Conductors: Metals are the best conductors used to speed up the transfer of heat. (Silver, Copper, Aluminum, iron, etc.) Insulators: Non-metal objects are used to slow down the transfer of heat. Different materials are better insulators than others. Good insulators include: wood, cloth, Styrofoam, cork, and plastic. (Glass and air also act as insulators.) Thermometers Each line is 2 degrees. These thermometers are filled with red alcohol. The alcohol’s molecules expand when heated and Each line is causes the liquid to go up. 1 degree. The scale (temperature markings) can be different on thermometers. Pay attention to the difference between each marked line. Each line is 10 degrees.