Reflection and Refraction Vocabulary Reflection – When light, heat
advertisement
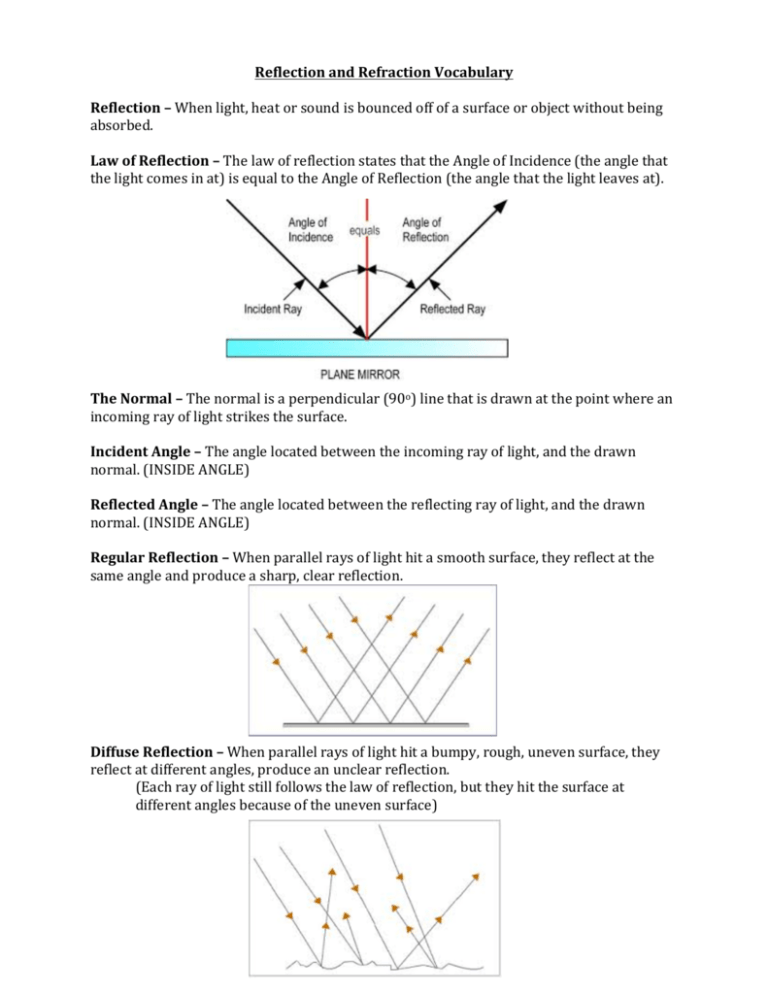
Reflection and Refraction Vocabulary Reflection – When light, heat or sound is bounced off of a surface or object without being absorbed. Law of Reflection – The law of reflection states that the Angle of Incidence (the angle that the light comes in at) is equal to the Angle of Reflection (the angle that the light leaves at). The Normal – The normal is a perpendicular (90o) line that is drawn at the point where an incoming ray of light strikes the surface. Incident Angle – The angle located between the incoming ray of light, and the drawn normal. (INSIDE ANGLE) Reflected Angle – The angle located between the reflecting ray of light, and the drawn normal. (INSIDE ANGLE) Regular Reflection – When parallel rays of light hit a smooth surface, they reflect at the same angle and produce a sharp, clear reflection. Diffuse Reflection – When parallel rays of light hit a bumpy, rough, uneven surface, they reflect at different angles, produce an unclear reflection. (Each ray of light still follows the law of reflection, but they hit the surface at different angles because of the uneven surface) Virtual Images – An upright image that forms where light seems to come from. “Virtual” describes something that does not really exist. * Virtual images appear to come from behind a mirror, but you can’t reach behind the mirror and touch it. Real Images – An image that forms when rays actually meet. Real images are upside down and may be smaller or larger than the actual object. Optical Axis – An imaginary line that divides a mirror in half (much like the equator). Focal Point – The point at which rays of light parallel to the optical axis meet. *The location of the focal point depends on the curvature of the mirror. The more curved the mirror is, the closer the focal point is to the surface of the mirror. Plane Mirrors – Plane mirrors are a FLAT sheet of glass which has a smooth, silver-­‐colored coating on one side which reflects the light. *Plane mirrors produce virtual images that are upright, and the same size as the object being reflected. *However, the image being reflected has the left and the right side of the image reversed. (For example – when you look in a mirror and raise your right hand, it appears to be the left hand of the image). Concave Mirrors – A mirror with a surface that curves inward, like the inside of a bowl. When light rays strike a concave mirror they are reflected inward, converging (meeting) at the focal point and then continue outwards from each other once passing. *Concave mirrors can form either real (upside down) or virtual (right side up) images. *If you are looking into a concave mirror at a point BEFORE the focal point the image will be virtual, upright and larger than the object = Magnified image (Make-­‐up mirrors) *If you are looking into a concave mirror at a point AFTER the focal point the image will be real. The image will be upside down and could be smaller OR larger than the actual object. Convex Mirrors – A mirror with a surface that curves outward. When light rays strike a convex mirror they spread out (but appear as if they would come to a focal point located behind the mirror surface). The focal point for a convex mirror is the place where the rays APPEAR to meet (doesn’t actually exist). *The rays of light on a convex mirror NEVER ACTUALLY MEET, so they produce ONLY virtual images (right side up), which are SMALLER than the actual object. *Convex mirrors are used on car mirrors (Objects in mirror are closer than they appear). Convex mirrors allow you to see a larger area then you could with a plane mirror however things get reduced in size so things look farther than they actually are. Refraction – When light rays enter a substance at an angle, the change in speed causes the light rays to bend, or to change direction. Index of Refraction – a material’s measure of how much a ray of light bends when it enters that material. The higher the index of refraction, the more the light bends. Index of Refraction of Air = 1.00 Index of Refraction of Water = 1.33 Index of Refraction of Corn Oil = 1.47 Index of Refraction of Glass = 1.52 Mirage – The image of a distant object caused by refraction of light. Light travels faster in hot air, and slower in cooler air. Rays near the ground/road in a hot environment are bent upwards, making it appear as if there is a haze or puddle on the ground ahead. Lens – A curved piece of glass (or other transparent material) that is used to refract (bend) light. Convex Lens – A lens that is thicker in the center than at the edges, the lens curves outwards. *As light rays enter a convex lens they are bent towards the center of the lens, the rays continue converging, until they meet at the focal point and cross over. They then travel away from each other once more. *The more curved the lens, the more the light is refracted. *If you are looking at a convex lens BEFORE the focal point (where the rays cross), you will see a virtual image (right side up) will form on the same side as the lens. *If you are looking at a convex lens AFTER the focal point you will see a real image (upside down) on the other side of the lens. Concave Lens – A lens that is thinner in the center than at the edges, the lens curves inwards. *As light rays enter a concave lens they bend away from the optical axis, and NEVER MEET – THERE IS NO FOCAL POINT. *A concave lenses’ rays NEVER meet. Therefore, they can ONLY produce VIRTUAL images. The image is ALWAYS upright and smaller than the actual object.