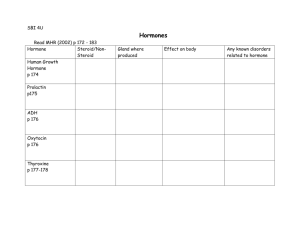
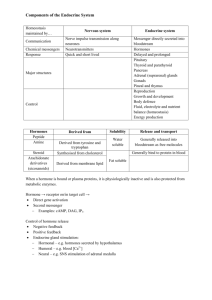
Lect E1 - Endocrine intro (K K DEV)
advertisement

Lect E1 - Endocrine intro Some learning outcomes Endocrine System Lect # 1 • • • • • • • • • • • Introduction Prof Kumlesh K. Dev D Department off Physiology Ph i l principles of feedback regulation peripheral effects of pituitary hormones how growth is regulated by hormones why puberty initiates both growth and its cessation effects of abnormal GH before and after puberty common synthesis of adrenal & gonadal steriods hypothalamo-pituitary axis function major role of pineal gland in endocrine regulation normal range of plasma free calcium conc hormonal regulation of calcium balance causes and consequences of hypocalcaemia Chapter 4 Principles of Neural and Hormonal Communication Human Physiology by Lauralee Sherwood ©2007 Brooks/Cole-Thomson Learning Types of cellular communication Classification Communication is critical for cell survival 2 major regulatory systems: – Nervous System – Endocrine System Four types of chemical messengers Classification 1) Autocrine/Paracrine • Local chemical messengers • Exert effect on neighbouring cells (paracrine) or on same cell (autocrine) 2) Neurotransmitter • Short-range chemical messengers • Diffuse across narrow space (synapse) to act on adjoining target cell (another neuron, a muscle, or a gland) Chapter 4 Principles of Neural and Hormonal Communication Human Physiology by Lauralee Sherwood ©2007 Brooks/Cole-Thomson Learning 1 Lect E1 - Endocrine intro Four types of chemical messengers 1. Autocrine/Paracrine Classification Classification 3) Neurohormones • Hormones released into blood by neurosecretory neurons • Distributed through blood to distant target cells – chemical messenger released from a cell : – can act on itself (autocrine) 4) Hormones • Long-range messengers • Secreted into blood by endocrine glands in response to appropriate signal and act on distant target cells – can act on another cell close-by (paracrine) 2. Neurotransmitters Cell #2 3. Neurohormones Classification Classification – Neurotransmitters released from synaptic vesicles – Released from synaptic vesicles by neuron – Diffuse across synapse between two cells synapse with muscles – Transmitter binds a receptor – Receptor activation stimulates the cell Secretoryy Cell synapse with another neuron synapse with glands – Released into blood – Acts in manner similar to hormones 2 Lect E1 - Endocrine intro 4. Hormones Nervous and Endocrine Systems Classification – Messengers of endocrine system – Released from endocrine gland into blood – Transported in blood – Target cell:expresses specific receptors Neuroendocrine cells Classification Property Nervous System Endocrine System Structure Wired system of neurons Wireless system of glands Chemical Messenger Neurotransmitter Hormones Target site Very close Far away Distance of Action Across synaptic cleft Carried by blood Speed of Response milliseconds mins to hours Duration of Action milliseconds mins to days Major Function fast precise responses long duration responses Types of hormone Classification Neuroendocrine cells release neurohormones and are found in, for example: • • • • • • • • adrenal medulla thyroid islet of Langerhangs pituitary cells renin-secreting cells gastro-intestinal tract pancreas lower respiratory tract Classification • Two hormone categories based on solubility – Hydrophilic (lipophobic, water soluble) • Peptide hormones • Catecholamines – Lipophilic (hydrophobic, water insoluble) • Thyroid hormone • Steroid hormones 3 Lect E1 - Endocrine intro Types of hormone: characteristics Steroid hormone Classification Property Peptide Catecholamines Thyroid Steriods Structure amino acids tyrosine derivative iodinated y tyrosine cholesterol derivative Solubility hydrophilic lipophobic hydrophilic lipophobic lipophilic hydrophobic lipophilic hydrophobic Synthesis in ER in cytosol organelles intracell Storage granules granules colloid lipd droplets Secretion exocytosis of granules exocytosis of granules endocytosis of colloid diffusion Blood Transport free hormone plasma bound plasma bound plasma bound Receptors on cell surface on cell surface inside cell inside cell Hormone hypothalamic, pituitary, pineal, pancreas, parathyroid, GIT, kidney, liver, heart adrenal medulla thyroid follicular adrenal cortex gonads, Vit D Steroid hormone Synthesis female sex hormone male sex hormone adrenal cortex hormone - adrenal cortex hormone female sex hormone steroid hormones derived from cholesterol are small lipid-soluble molecules diffuse throw cell membrane receptor is intracellular Surface Receptors Synthesis Receptors • all cells maybe exposed to hormones via circulation peptides & catecholamines ion channel • only cells with receptors for hormone can respond • extracellular chemical (hormone) binds to surface receptor • receptor activation alters – channel function – second-messenger systems enzyme change in ion flow (e.g. Na, Ca, K, Cl) Increased product signal (eg cAMP) All steroid hormones are produced via cholesterol modification 4 Lect E1 - Endocrine intro Nuclear Receptors Surface Receptor Structure Receptors • steroid receptors bind steroid hormone Receptors thyroid & steroid hormones • Receptor Domains • plasma protein carrier • hormone-receptor complex becomes a transcription factor (alters gene transcription) • each steroid receptor binds a unique DNA sequence (response element within an enhancer region) oestrogen receptor oestrogen protein synthesis ligand binding domain (LBD) • 7 transmembrane domains (TMDs) • G-protein coupled LBD • Mechanism mRNA transcription trans locati on • peptide hormone binds to receptors on the surface of the cell • activates G-protein • induces intracellular signals TMDs • Nuclear Receptor Structure Neuropeptide Examples: Prolactin, Adrenocorticotrophic hormone (ACTH), Antidiuretic hormone (vasopressin), Oxytocin, Insulin, Somatostatin • Receptor Domains • DNA bi binding di d domain i bi binds d steroid t id response element (SRE). • Nuclear Localization Signal (NLS) covered by heat shock proteins (HSP) LBD NLS • Mechanism • receptor+hormone enters nucleus • acts as a transcription factor HSP SRE-BD binding of hormone induces detachment of HSP; uncovers NLS • e.g. glucocorticoid receptor p transcription SRE • Examples: Estrogen, Glucocorticoid (Cortisol), Mineralocorticoid (Aldosterone), Progesterone, Androgen (Testosterone) cAMP IP3 DAG PKA Ca2+ PKC Steroid hormone receptors Receptors Hormone/Ligand binding domain (LBD) PLC AC • this alters the rate of transcription • G-prot Receptors • Type I receptors – Sex hormone receptors • Androgen receptor • Estrogen receptor • Progesterone receptor – Glucocorticoid receptor – Mineralocorticoid receptor • Type II receptors (No HSP association) – Vitamin A receptor (vitamin A) – Vitamin D receptor (vitamin D) – Retinoid receptor – Thyroid hormone receptor nucleus 5 Lect E1 - Endocrine intro Receptor Regulation Summary so far Receptors • target cell may be unresponsive due to lack of receptors (physiological, genetic, disease) • one hormone h can iinfluence fl activity ti it off another th h hormone by regulation of its receptor: Permissiveness Summary 9 Four types of chemical signals 9 1) Autocrine/Paracrine 9 2) Neurotransmitter 9 3) N Neurohormones h 9 4) Hormones 9 Four types of hormones – one hormone is required for another hormone to work Synergism – actions of several hormones are complimentary p y – combined effect is greater than sum of separate effects Antagonism – one hormone inhibits another hormone’s receptors – reduces effectiveness of second hormone Primary & Secondary Endocrine Glands 9 1) Peptide hormones 9 2) Catecholamines 9 3) Thyroid hormone 9 4) Steroid hormones 9 Types of receptors 9 1) Extracellular 9 2) Intracellular ? Types of glands Endocrine System Endocrine System – endocrine glands are derived from epithelial tissue – these glands are composed of clumps of secretory cells – surrounded by capillaries (fenestrated) – unlike exocrine glands, endocrine glands have no duct system – endocrine glands may exist in Primary Endocrine Organs (discrete organs - pituitary, thyroid, parathyroid, adrenal and pineal glands) Endocrine System Overall functions – regulate organic metabolism – controls water and electrolyte balance – induces adaptive changes to help cope with stress – promotes growth and development – controls reproduction – regulates red blood cell production – controls circulation, digestion, absorption of food Secondary Endocrine Organs (dispersed in organs with other major functions – heart, kidney, liver, etc..) 6 Lect E1 - Endocrine intro Neuroendocrine System Hormone Signalling Endocrine System ¾ many a yp physiological ys o og ca functions u ct o s a are e co co-regulated egu ated by the nervous system and the endocrine system ¾ study of this relationship is the focus of neuroendocrinology ¾ neuroendocrinology primarily concerns the way the brain regulates pituitary hormone secretion Hormone Concentrations Endocrine System hormones secreted by endocrine gland cells • enter blood and distributed throughout g body y • can act at distant target sites hormone secretion by endocrine glands triggered by many signals: • insulin secretion regulated by blood glucose conc • secretion of sex hormones from ovaries and testes controlled by anterior pituitary hormones • oxytocin secretion from posterior pituitary regulated by neurotransmitter release Endocrine Dysfunction: Hyposecretion Endocrine System • plasma conc. of hormones is controlled by rate of secretion • secretory output of endocrine cells controlled by – neural input – another hormone • plasma p conc. also influenced by y – rate of removal from blood by metabolism and excretion – rate of activation or its extent of binding to plasma proteins Endocrine System Primary hyposecretion • due to abnormality within gland • causes – – – – – – – genetic dietary (eg lack of iodine) chemical or toxic immunologic (autoimmune diseases) cancer Iatrogenic (eg surgical removal) idiopathic (unknown) Secondary hyposecretion • deficiency of tropic hormone 7 Lect E1 - Endocrine intro Endocrine Dysfunction: Hypersecretion Feedback Endocrine System Endocrine System • Causes – Tumours continuously secrete hormone – Immune factors ─ hormone production is regulated by status of tissue which is under hormonal control • Primary hypersecretion – too much hormone secreted due to abnormality within gland ─ in pituitary and hypothalamus, target tissues communicate hormonally, neurally, or via metabolic factors ─ two types yp of feedback loops p are long-loop and short-loop feedback • Secondary hypersecretion – excessive stimulation of gland causes oversecretion ─ adrenal cortex provides examples of both Control by Feedback Mechanisms Tropic Hormones Endocrine System Gland 1 - Positive Feedback e.g. Hormone 3 activates Gland 2 Hormone 1 Gland 2 Negative g Feedback Hormone 2 e.g. Hormone 3 inhibits Gland 1 Gland 3 Hormone 3 + Endocrine System • hormones regulating secretion other hormones are called releasing factors or inhibitory factors and classified as trophic hormones • these can stimulate/maintain endocrine target tissues • example – thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) – secreted from anterior pituitary – stimulates thyroid hormone secretion from thyroid gland – maintains structural integrity of thyroid gland Anterior pituitary Thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) Thyroid gland Thyroid Hormone (T3.T4) 8 Lect E1 - Endocrine intro Exocrine Glands: Classify by Morphology Exocrine System Exocrine Glands: Classify by Secretion Exocrine System Simple Types Merocrine (eccrine) Secretion • exocytosis y • most common type of secretion Endocrine glands ─ secret hormones into bloodstream Exocrine glands ─ discharge products via duct tubular large intestine acinar urethra branched tubular stomach branched coiled tubular acinar sweat glands Apocrine Secretion • membrane-bound vesicles • example: breasts, sweat glands Compound Types Exocrine Types ─ simple / compound Holocrine Secretion • rupture of secretory cells • example: sebaceous glands tubular acinar Summary Summary Four types of chemical signals 1) Autocrine/Paracrine 2) Neurotransmitter 3) Neurohormones 4) Hormones Four types of hormones 1) Peptide hormones 2) Catecholamines 3) Thyroid hormone 4) Steroid hormones Types of receptors 1) Extracellular 2) Intracellular Feedback and Tropic hormones 1) Long and short loops 2) Positive and negative Types of glands 1) Primary 2) Secondary Causes and types of 1) hyposecretion 2) hypersecretion 9