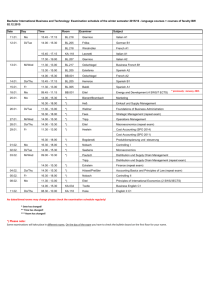
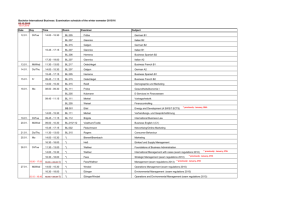
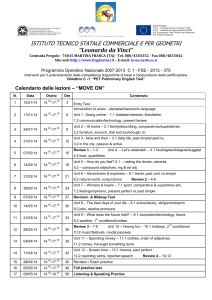
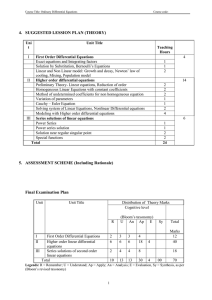
Physics 151 – Exam Equation Sheet Exam 1 Equations
advertisement
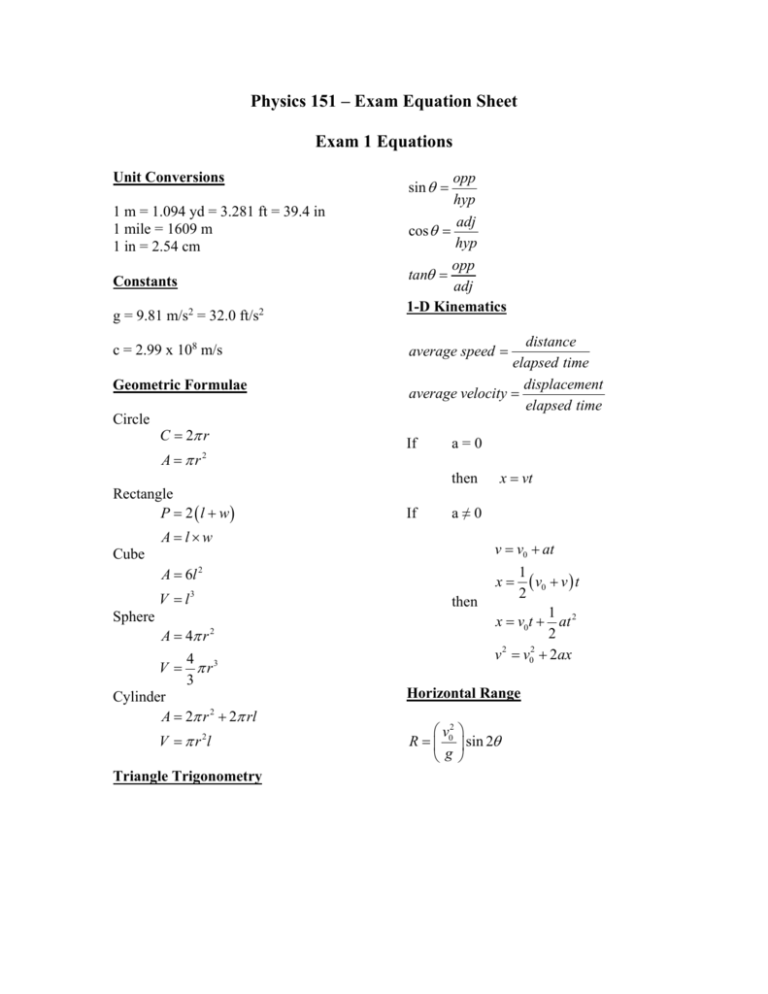
Physics 151 – Exam Equation Sheet Exam 1 Equations Unit Conversions 1 m = 1.094 yd = 3.281 ft = 39.4 in 1 mile = 1609 m 1 in = 2.54 cm Constants g = 9.81 m/s2 = 32.0 ft/s2 c = 2.99 x 108 m/s Geometric Formulae Circle C 2 r A r2 Rectangle P 2 l w opp hyp adj cos hyp opp tan adj 1-D Kinematics sin distance elapsed time displacement average velocity elapsed time average speed If a=0 then If a≠0 A lw v v0 at Cube A 6l 2 V l3 Sphere A 4 r 2 4 V r3 3 Cylinder A 2 r 2 2 rl V r 2l Triangle Trigonometry x vt 1 v0 v t 2 1 x v0t at 2 2 2 2 v v0 2ax x then Horizontal Range v2 R 0 sin 2 g Exam 2 Equations Friction Static Friction f s s N Kinetic Friction f k k N Springs Hook’s Law Fx kx Centripetal Acceleration v2 ac r Newton’s 2nd Law F ma Torque rF sin Torque Equilibrium 0 Exam 3 Equations Work W Fd cos Work-Energy Theorem Wtotal KE 1 2 1 2 mv f mvi 2 2 Energy 1 2 mv 2 Gravitational Potential Energy PE mgh 1 Elastic Potential Energy PE kx 2 2 Kinetic Energy KE Conservation of Energy KEi PEi KE f PE f Work Done by NonConservative Forces WNC KE PE Momentum p mv Impulse I Fave t p Exam 4 Equations Simple Harmonic Motion Position vs. Time 2 x A cos t T 1 f T Mass on a Spring F kx 1 2 kx 2 m T 2 k PEElastic T 2 Pendulum Waves Fluids Density M V F A 5 Pa = 1.01 x 10 Pa Pressure P L g vf Waves on a String T where μ is the linear density v (mass/length) Wave Formula 2 2 y x, t A cos x t T Sound vSound = 343 m/s (at room temperature) I Standing Waves String v n T fn n n 1, 2,3... 2L 2L Open-Closed Pipe v fn n n 1,3,5... 4L v Open-Open Pipe f n n n 1, 2,3... 2L P P A 4 r 2 I I0 10 log10 I 2 1 10 log10 2 I1 where I0 = 10-12 W/m2 Pressure at Depth P Pa gh Pascal’s Principle – An external pressure applied to an enclosed fluid is transmitted unchanged to every point within the fluid P1 P2 F1 F2 A1 A2 Archimedes’ Principle – An object completely immersed in a fluid experiences an upward buoyant force equal in magnitude to the weight of fluid displaced by the object. FB flV fl g Equation of Continuity v1 A1 A2 v2 Bernoulli’s Equation 1 1 P1 v12 gy1 P2 v22 gy2 2 2 Exam 5 Equations Temperature Scales Q mcT 9 TF TC 32 5 TK TC 273.2 Substance Thermal Expansion L L0 T V BV0 T For many substances β=3α Substance Lead Aluminum Brass Copper Steel Concrete Coefficient of Linear Expansion, α (Cº-1) 29 x 10-6 24 x 10-6 19 x 10-6 17 x 10-6 12.2 x 10-6 12 x 10-6 Thermal Conductivity Q AT A t L L Substance Silver Copper Gold Aluminum Steel Lead Ice Concrete Glass Wood Air Calorimetry Thermal Conductivity κ (W/(m·Cº) 417 395 291 217 66.9 34.3 1.6 1.3 0.84 0.10 0.0234 Water Ice Steam Air Aluminum Glass Steel Copper Silver Gold Lead Specific Heat c (J/(kg·Cº) 4186 2090 2010 1004 900 837 448 387 234 129 128 One can convert c values to cal/g-Cº by dividing by 4186 Latent Heats Q mL f Q mLv For water these values are: Lf = 33.5 x 104 J/kg = 79.7 cal/g Lv = 32.6 x 105 J/kg = 540 cal/g One can convert L values to cal/g by dividing by 4186 Ideal Gas Law PV = nRT, PV = NkT where n = amount of substance and N the number of particles, R=8.314 J/mol·K NA=6.02 1023 particles k =1.38 10-23 J/K n = N / NA and n = m/M where m is the total mass and M the molar mass Young’s Modulus Stress Y F A Strain L L0 Stress FL0 Strain AL Thermal Stress Y FL0 AL L T L0 F Y T A Substance Tungsten Steel Copper Brass Aluminum Pyrex Lead Substance H2 O2 CO2 N2 Methane, CH4 CO Air Water vapor Young’s Modulus Y (N/m2) 36 x 1010 20.1 x 1010 11 x 1010 9.0 x 1010 6.9 x 1010 6.2x 1010 1.6 x 1010 Molar mass (g/mol) 2.016 32 44.01 28.01 16.04 28.01 28.966 18.02 Exam 6 Equations Electric Charge Photons cf Coulomb’s Law E hf hc F k h = 6.626 10-34 J·s c=2.99 10 m/s 8 q1q2 R2 where k = 8.99 109 N·m2 /C2 Doppler Shift Fundamental charge u f ' f 1 c e = 1.602 x 10-19 C Reflection Electric Circuits i r V IR Spherical Mirrors 1 f convex R 2 1 f concave R 2 1 1 1 d o di f m hi d i ho do Refraction n1 sin 1 n2 sin 2 sin c n2 n1 Thin Lenses 1 1 1 d o di f m hi d i ho do P IV I 2 R V2 R Resistivity R L A Resistors Series Reff R1 R2 ... Parallel 1 1 1 ... Reff R1 R2