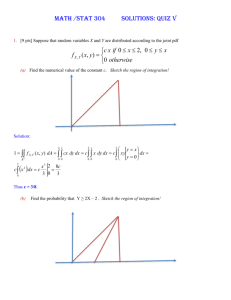
Medical Coding Exam with Answers - CPT & ICD-9
advertisement

2014 Final with Answers 10000 Series 1. The patient is seen in follow-up for excision of the basal cell carcinoma of his nose. I examined his nose noting the wound has healed well. His pathology showed the margins were clear. He has a mass on his forehead; he says it is from a piece of sheet metal from an injury to his forehead. He has an X-ray showing a foreign body, we have offered to remove it. After obtaining consent we proceeded. The area was infiltrated with local anesthetic. I had drawn for him how I would incise over the foreign body. He observed this in the mirror so he could understand the surgery and agree on the location. I incised a thin ellipse over the mass to give better access to it, the mass was removed. There was a capsule around this, containing what appeared to be a black-colored piece of stained metal; I felt it could potentially cause a permanent black mark on his forehead. I offered to excise the metal, he wanted me to, so I went ahead and removed the capsule with the stain and removed all the black stain. I consider this to be a complicated procedure. Hemostasis was achieved with light pressure. The wound was closed in layers using 4-0 Monocryl and 6-0 Prolene. What CPT® and ICD-9-CM codes are reported? a. 10121, 709.4, V90.10 c. 10121, 729.6, V90.10 b. 11010, 873.52, V90.10 d. 11010, 729.6, V90.10 ANS: C Rationale: In CPT® index, see Integumentary System/Removal/Foreign Body, you are directed to code range 10120-10121. The surgeon indicated in the note they considered this incision and removal of foreign body to be complicated leading us to code 10121. In the ICD-9-CM Index to Diseases, see Foreign body/retained/fragments/subcutaneous tissue, you are directed to 729.6. There is no mention of granuloma of the skin making 709.4 incorrect. The patient did not have an acute laceration with a foreign body in an open wound, code 872.52 is not reported. In the Tabular List, instructions for 729.6 state to use an additional code from V90.01-V90.9 to identify the foreign body. V90.10 indicates a retained metal fragment. PTS: 1 DIF: Difficult 2. The patient is here because the cyst in her chest has come to a head and is still painful even though she has been on antibiotics for a week. I offered to drain it for her. After obtaining consent, we infiltrated the area with 1 cc of 1% lidocaine with epinephrine, prepped the area with Betadine and incised opened the cyst in the relaxed skin tension lines of her chest, and removed the cystic material. There was no obvious purulence. We are going to have her clean this with a Q-tip. We will let it heal on its own and eventually excise it. I will have her come back a week from Tuesday to reschedule surgery. What CPT® and ICD9-CM codes are reported? a. 10140, 706.1 c. 10061, 706.2 b. 10060, 706.2 d. 10160, 786.6 ANS: B Rationale: The physician performed an incision and drainage (I & D) of a cyst on the chest. To find the code, see the CPT® Index for Incision and Incision and Drainage/Cyst/Skin, you are directed to code choices 10040, 10600-10061. 10040 is for acne surgery. 10060-10061 are for I & D of a cyst. Only one cyst was drained making 10060 the correct code. In the ICD-9-CM Index to Diseases, look for Cyst/skin, code 706.2 is indicated. Verification in the Tabular List confirms code selection. PTS: 1 DIF: Difficult 3. Patient has returned to the operating room to aspirate a seroma that has developed from a surgical procedure that was performed two days ago. A 16-gauge needle is used to aspirate 600 cc of non-cloudy serosanguinous fluid. What codes are reported? a. 10160-78, 998.13 c. 10140-78, 906.3 b. 10180-58, 998.12 d. 10140-58, 729.91 ANS: A Rationale: The provider performed a puncture aspiration of a seroma (clear body fluid built up where tissue has been removed by surgery). In the CPT® Index, look for Cyst/Skin/Puncture Aspiration. Code 10160 is the correct code for the puncture aspiration. Even though it does not specifically state “seroma” it is the code to report. This is not a staged return to the operative suite for the puncture aspiration of the seroma. Modifier 78 is used because the patient is returning to the operative suite with a complication in the global period. The diagnosis is reported as a post-operative complication. In the ICD-9-CM Index to Diseases, Seroma indexes to 998.13. Verification in the Tabular List confirms code selection. PTS: 1 DIF: Difficult 4. Operative Report PREOPERATIVE DIAGNOSIS: Squamous cell carcinoma, scalp. POSTOPERATIVE DIAGNOSIS: Squamous carcinoma, scalp. PROCEDURE PERFORMED: Excision of Squamous cell carcinoma, scalp with Yin-Yang flap repair ANESTHESIA: Local, using 4 cc of 1% lidocaine with epinephrine. COMPLICATIONS: None. ESTIMATED BLOOD LOSS: Less than 5 cc. SPECIMENS: Squamous cell carcinoma, scalp sutured at 12 o’clock, anterior tip INDICATIONS FOR SURGERY: The patient is a 43-year-old white man with a biopsy-proven basosquamous cell carcinoma of his scalp measuring 2.1 cm. I marked the area for excision with gross normal margins of 4 mm and I drew my planned Yin-Yang flap closure. The patient observed these markings in two mirrors, so he can understand the surgery and agreed on the location and we proceeded. DESCRIPTION OF PROCEDURE: The area was infiltrated with local anesthetic. The patient was placed prone, his scalp and face were prepped and draped in sterile fashion. I excised the lesion as drawn to include the galea. Hemostasis was achieved with the Bovie cautery. Pathologic analysis showed the margins to be clear. I incised the Yin-Yang flaps and elevated them with the underlying galea. Hemostasis was achieved in the donor site using Bovie cautery. The flap rotated into the defect with total measurements of 2.9 cm x 3.2 cm. The donor sites were closed and the flaps inset in layers using 4-0 Monocryl and the skin stapler. Loupe magnification was used. The patient tolerated the procedure well. What CPT® and ICD-9-CM codes are reported? a. 14060, 172.3 c. 14041, 172.40 b. 14040, 173.42 d. 14020, 173.42 ANS: D Rationale: In the CPT® codebook, Yin-Yang flap repair falls under Adjacent Tissue Transfer codes. Look in the CPT® Index for Skin Graft and Flap/Tissue Transfer which directs you to 14000-14350. Based on the measurement calculating to 9.28 sq cm (2.9 cm x 3.2 cm = 9.28 cm2) and the location of the scalp, the correct CPT® code is 14020. For the ICD-9-CM code look in the Neoplasm Table for Skin/scalp/squamous cell carcinoma (173.42). PTS: 1 DIF: Difficult 5. The patient is coming in for removal of fatty tissue of the posterior iliac crest, abdomen, and the medial and lateral thighs. Suction-assisted lipectomy was undertaken in the left posterior iliac crest area and was continued on the right and the lateral trochanteric and posterior aspect of the medial thighs. The medial right and left thighs were suctioned followed by the abdomen. The total amount infused was 2300 cc and the total amount removed was 2400 cc. The incisions were closed and a compression garment was applied. What CPT® code(s) are reported? a. 15830, 15832-50-51 c. 15830, 15839-50-51, 15847 b. 15877, 15879-50-51 d. 15877, 15878-50-51 ANS: B Rationale: In the CPT® Index, see Lipectomy/Suction Assisted or Liposuction. You are referred to 15876-15879. Review the codes to choose the appropriate service. There were three body areas where liposuction was performed. Code 15877 covers the liposuction of the posterior iliac crest and abdomen. Code 15879 covers liposuction of the thighs. Modifier 50 is appended to code 15879 to indicate the left and right thighs were performed on. Modifier 51 is appended to indicate more than one procedure was performed in the same surgical session. PTS: 1 DIF: Difficult 6. Operative Report PREOPERATIVE DIAGNOSIS: Diabetic foot ulceration. POSTOPERATIVE DIAGNOSIS: Diabetic foot ulceration. OPERATION PERFORMED: Debridement and split thickness autografting of left foot ANESTHESIA: General endotracheal. INDICATIONS FOR PROCEDURE: This patient with multiple complications from Type II diabetes has developed ulcerations which were debrided and homografted last week. The homograft is taking quite nicely; the wounds appear to be fairly clean; he is ready for autografting. DESCRIPTION OF PROCEDURE: After informed consent the patient is brought to the operating room and placed in the supine position on the operating table. Anesthetic monitoring was instituted, internal anesthesia was induced. The left lower extremity is prepped and draped in a sterile fashion. Staples were removed and the homograft was debrided from the surface of the wounds. One wound appeared to have healed; the remaining two appeared to be relatively clean. We debrided this sharply with good bleeding in all areas. Hemostasis was achieved with pressure, Bovie cautery, and warm saline soaked sponges. With good hemostasis a donor site was then obtained on the left anterior thigh, measuring less than 100 cm2. The wounds were then grafted with a split-thickness autograft that was harvested with a patch of Brown dermatome set at 12,000 of an inch thick. This was meshed 1.5:1. The donor site was infiltrated with bupivacaine and dressed. The skin graft was then applied over the wound, measured approximately 60 cm2 in dimension on the left foot. This was secured into place with skin staples and was then dressed with Acticoat 18's, Kerlix incorporating a catheter, and gel pad. The patient tolerated the procedure well. The right foot was redressed with skin lubricant sterile gauze and Ace wrap. Anesthesia was reversed. The patient was brought back to the ICU in satisfactory condition. What CPT® and ICD-9-CM codes are reported? a. 15220-58, 15004-58, 707.15, 250.80 b. 15120-58, 15004-58, 250.80, 707.15 c. 15950-78, 15004-78, 250.00, 707.14 d. 11044-78, 15120-78, 15004-78, 250.80, 707.15 ANS: B Rationale: The wound was prepped with sharp debridement. Look in the CPT® Index for Creation/Recipient Site (range 15002-15005). Code selection is based on location and size. Then a split thickness graft was performed. Look in the CPT® Index for Skin Graft and Flap/Split Graft referring you to range 15100-15101-15120-15121. The measurement applies to the recipient area, which is stated as 60 cm2. A split thickness autograft to the foot for the first 100 sq cm is coded with 15120. The operative note states, “The homograft is taking quite nicely, the wounds appear to be fairly clean; he is ready for autografting,” indicating this is a staged procedure and modifier 58 is appended. In the ICD-9-CM Index, see Diabetic/ulcer/foot, directing you to 250.8X [707.15]. The 5th digit 0 indicates it is Type II diabetes. Although there are complications, it does not indicate it is uncontrolled. 707.15 is used for ulcer of the foot. PTS: 1 DIF: Difficult 7. Operative Report Diagnosis: Basal Cell Carcinoma Procedure: Mohs micrographic excision of skin cancer. Site: face left lateral canthus eyelid Pre-operative size: 0.8 cm Indications for surgery: Area of high recurrence, area of functional and/or cosmetic importance Discussed procedure including alternative therapy, expectations, complications, and the possibility of a larger or deeper defect than expected requiring significant reconstruction. Patient’s questions were answered. Local anesthesia 1:1 marcaine and 1% lidocaine with epinephrine. Sterile prep and drape. Stage 1: The clinically apparent lesion was marked out with a small rim of normal appearing tissue and excised down to subcutaneous fat level with a defect size of 1.2 cm. Hemostasis was obtained and a pressure bandage placed. The tissue was sent for slide preparation. Review of the slides show clear margins for the site. Repair: Complex repair. Repair of Mohs micrographic surgical defect. Wound margins were extensively undermined in order to mobilize tissue for closure. Hemostasis was achieved. Repair length 3.4 cm. Narrative: Burrows triangles removed anteriorly (medial) and posteriorly (lateral). A layered closure was performed. Multiple buried absorbable sutures were placed to re-oppose deep fat. The epidermis and dermis were re-opposed using monofilament sutures. There were no complications; the patient tolerated the procedure well. Postprocedure expectations (including discomfort management), wound care and activity restrictions were reviewed. Written Instructions with urgent contact numbers given, follow-up visit and suture removal in 3-5 days What CPT® and ICD-9-CM codes are reported? a. 13152, 11642-51, 173.31 c. 17313, 13152-51, 173.11 b. 13152, 11442-51, 173.31 d. 17311, 13152-51, 173.11 ANS: D Rationale: In the CPT® Index, see Mohs Micrographic Surgery, you are directed to code range 1731117315. Code selection is based on location and stages. This operative note indicates the location is on the face and only one stage is performed, making 17311 the correct code choice. According to subsection guidelines for Mohs Micrographic Surgery, repairs are coded separately. This is a complex repair on the eyelid measuring 3.4 cm making 13152 the correct code choice. Modifier 51 is used to indicate multiple procedures. In the ICD-9-CM Index to Diseases, look in the Neoplasm Table for skin/canthus (eye)/basal cell carcinoma/Primary (column). The code is 173.11. PTS: 1 DIF: Difficult 8. PREOPERATIVE & POSTOPERATIVE DIAGNOSES: 1. Macromastia. 2. Back pain. 3. Neck pain. 4. Shoulder pain. 5. Shoulder grooving 6. Intertrigo. NAME OF PROCEDURE: 1. Right breast reduction of 1950 g. 2. Right free-nipple graft. 3. Left breast reduction of 1915 g. 4. Left free-nipple graft. INDICATIONS FOR SURGERY: The patient is a 43-year-old female with macromastia and associated back pain, neck pain, shoulder pain, shoulder grooving and intertrigo. She desired a breast reduction. Because of the extreme ptotic nature of her breasts, we felt she would need a free-nipple graft technique. In the preoperative holding area, we marked her for this free-nipple graft technique of breast reduction. The patient observed these markings so she could understand the surgery and agree on the location, and we proceeded. The patient also was morbidly obese with a body mass index of 54. Because of this, we felt she met the criteria for DVT prophylaxis, which included Lovenox injection. The patient understood this would increase her risk of bleeding. She also made it known she is a Jehovah's Witness and refused blood products, but she did understand her risk of bleeding would significantly increase and we proceeded. DESCRIPTION OF PROCEDURE: The patient was given 40 mg of subcutaneous Lovenox in the preoperative holding area. She was then taken to the operating room. Bilateral thigh-high TED hose, in addition to bilateral pneumatic compression stockings were used throughout the procedure. IV Ancef 1 g was given. Anesthesia was induced. Both arms were secured on padded arm boards using Kerlix rolls. A similar body bear hugger was placed. The chest and abdomen were prepped and draped in sterile fashion. I began by circumscribing around each nipple-areolar complex using a 42-mm areolar marker. On each side the free-nipple grafts were harvested. They were marked to be side specific and were stored on the back table in moistened lap sponges. Meticulous hemostasis was achieved using Bovie cautery. The tail of the apex of each breast was deepithelialized using the scalpel. I amputated the inferior portion of the breast from the right side. Again, meticulous hemostasis was achieved using the Bovie cautery. There were also large feeder vessels divided and ligated using either a medium Ligaclip or 3-0 silk tie sutures. I then moved to the left and again amputated the inferior portion of the breast. Meticulous hemostasis was achieved using the Bovie cautery. Each of these wounds were temporarily closed using the skin stapler. The patient was then sat up. I felt we had achieved a very symmetrical result. The new positions for the nipple-areolar complexes were marked with a 42-mm areolar marker and methylene blue. The patient was then placed in the supine position and the new positions for the nipple-areolar complexes were deepithelialized using the scalpel. Meticulous hemostasis was then achieved again using the Bovie cautery. The free-nipple grafts were then retrieved from the back table. They were each defatted using scissors and were placed in an onlay fashion on the appropriate side, and each was inset using 5-0 plain sutures. Vents were made in the skin graft to allow for the egress of fluid on each side. A vertical mattress suture was used, tied over a piece of Xeroform in critical areas of each of the nipple-areolar complexes. A Xeroform bolster wrapped over a mineral oil-moistened sponge was affixed to each of the nipple-areolar complexes using 5-0 nylon suture. The vertical and transverse incisions were closed using 3-0 Monocryl, both interrupted and running suture, and 5-0 Prolene. The patient tolerated the procedure well. Again, meticulous hemostasis was achieved using the Bovie cautery. She was given another 1 g of Ancef at the 2-hour mark by our anesthesiologist, and was taken to the recovery room in good condition. What CPT® codes are reported? a. 19316-50, 19355-59-50 c. 19318-50, 19355-59-50 b. 19318-50, 19350-59-50 d. 19340-50, 19350-59-50 ANS: B Rationale: With breast reduction surgery “reduction mammaplasty” or “mammoplasty” (both terms are used), in the CPT® Index, see Reduction/Mammoplasty, we are lead to CPT® 19318. Because this is a unilateral code per CPT®, append modifier 50. Additionally, the operative report indicates because so much breast tissue was removed the surgeon had to create free nipple grafts to recreate the nipple. In the CPT® see Reconstruction/Breast/Nipple, you are directed to code range 19350-19355. 19350 is the correct code. Normally, with reduction mammaplasty the patient’s nipple is moved into place after removal of the breast tissue. The Nipple reconstruction is normally bundled into the reduction surgery making it necessary to append modifier 59. PTS: 1 DIF: Difficult 9. INDICATIONS FOR SURGERY: The patient is an 82-year-old white male with biopsy-proven basal cell carcinoma of his right lower eyelid and cheek laterally. I marked the area for rhomboidal excision and I drew my planned rhomboid flap. The patient observed these markings in a mirror, he understood the surgery and agreed on the location and we proceeded. DESCRIPTION OF PROCEDURE: The area was infiltrated with local anesthetic. The face was prepped and draped in sterile fashion. I excised the lesion as drawn into the subcutaneous fat. Hemostasis was achieved using Bovie cautery. Modified Mohs analysis showed the margin to be clear. I incised the rhomboid flap as drawn and elevated the flap with a full-thickness of subcutaneous fat. Hemostasis was achieved in the donor site, the Bovie cautery was not used, hand held cautery was used. The flap was rotated into the defect. The donor site was closed and flap inset in layers using 5-0 Monocryl and 6-0 Prolene. The patient tolerated the procedure well. The total site measured 1.3 cm x 2.7 cm What CPT® code(s) should be reported? a. 14020 c. 14040, 14060 b. 14060 d. 11643 ANS: B Rationale: A rhomboid flap is a tissue transfer flap, coded from range 14000-14350. In the CPT® Index, see Tissue/Transfer/Adjacent/Skin. Because the surgeon indicated the rhomboid flap extended into the lower eyelid area, you only code for the eyelid flap. The final measurement of the flap is 3.51 cm2 (1.3 x 2.7 = 3.51) directing us to CPT® 14060. PTS: 1 DIF: Difficult 10. Wire placement in the lower outer aspect of the right breast was done by a radiologist the day prior to this procedure. During this operative session, the surgeon created an incision through the wire track and the wire track was followed down to its entrance into breast tissue. A nodule of breast tissue was noted immediately adjacent to the wire. This entire area was excised by sharp dissection, sent to pathology and returned as a benign lesion. Bleeders were cauterized, and subcutaneous tissue was closed with 3-0 Vicryl. Skin edges were approximated with 4-0 subcuticular sutures and adhesive strips were applied. The patient left the operating room in satisfactory condition. What should be the correct code(s) for the surgeon’s services? a. 19125-RT c. 19125-RT, 19285 b. 11400-RT d. 19120-RT ANS: A Rationale: Documentation indicates a localization wire was placed prior to the surgery by a radiologist. We are asked to select the code for the surgeon’s services, code 19285 is not reported. In the CPT® Index, see Excision/Breast/Lesion indicating range 19120, 19125-19126. Code 19125 describes excision of breast lesion identified preoperatively with a radiology marker. PTS: 1 DIF: Difficult 20000 Series 11. A 22-year-old female sustained a dislocation of the right elbow with a medial epicondyle fracture while on vacation. The patient was put under general anesthesia and the elbow was reduced and was stable. The medial elbow was held in the appropriate position and was reduced in acceptable position and elevated to treat non-surgically. A long arm splint was applied. The patient is referred to an orthopedist when she returns to her home state in a few days. What CPT® code(s) are reported? a. 24575-54-RT, 24615-54-51-RT c. 24577-54-RT, 24600-54-51-RT b. 24576-54-RT, 24620-54-51-RT d. 24565-54-RT, 24605-54-51-RT ANS: D Rationale: In the CPT® Index, look for Fracture/Humerus/Epicondyle/Closed Treatment. You are referred to code 24560-24565. Review the codes to choose the appropriate service. 24565 is the correct code to report an epicondyle fracture manipulated (reduced) without a surgical incision to perform the procedure. In the CPT® Index, look for Dislocation/Elbow/Closed Treatment. You are referred to 24600, 24605. Review the codes to choose appropriate service. 24605 is the correct code because the patient was put under general anesthesia to perform the procedure. Modifier 54 is used to report the physician performed the surgical portion only. The patient is referred to an orthopedist for follow up or postoperative care. Modifier 51 is used to report multiple procedures were performed. Append modifier RT to indicate the procedure is performed on the right side. PTS: 1 DIF: Difficult 12. A 45-year-old presents to the operating room with a right index trigger finger and left shoulder bursitis. The left shoulder was injected with 1 cc of Xylocaine, 1 cc of Celestone, and 1 cc of Marcaine. An incision was made over the A1 pulley in the distal transverse palmar crease, about an inch in length. This incision was taken through skin and subcutaneous tissue. The Al pulley was identified and released in its entirety. The wound was irrigated with antibiotic saline solution. The subcutaneous tissue was injected with Marcaine without epinephrine. The skin was closed with 4-0 Ethilon suture. Clean dressing was applied. What CPT® codes are reported? a. 26055-F6, 20610-76-LT c. 26055-F6, 20610-51-LT b. 20552-F6, 20605-52-LT d. 20553-F6, 20610-51-LT ANS: C Rationale: In the CPT® Index, look for Trigger Finger Repair. You are referred to 26055. Review the code to verify accuracy. In the CPT® Index, look for Injection/Joint. You are referred to 20600-20610. Review the codes to choose appropriate service. 20610 is the correct code since the shoulder was injected. Modifier F6 is used to report the right index finger that was repaired. Modifier LT is used to indicate the left shoulder joint. Modifier 51 is used to indicate multiple procedures were performed. PTS: 1 DIF: Difficult 13. A patient presents with a healed fracture of the left ankle. The patient was placed on the OR table in the supine position. After satisfactory induction of general anesthesia, the patient’s left ankle was prepped and draped. A small incision about 1 cm long was made in the previous incision. The lower screws were removed. Another small incision was made just lateral about 1 cm long. The upper screws were removed from the plate. Both wounds were thoroughly irrigated with copious amounts of antibiotic containing saline. Skin was closed in a layered fashion and sterile dressing applied. What CPT® code(s) should be reported? a. 20680-LT c. 20670-LT b. 20680-LT, 20680-59-LT d. 20680-LT, 20670-59-LT ANS: A Rationale: When reporting the removal of hardware (pins, screws, nails, rods), the code is selected by fracture site, not the number of items removed or the number of incisions that are made. To report 20670 or 20680 more than once, there would need to be more than one fracture site involved. In this case, there is only one fracture site even though two incisions are made. We know the removal is deep because the screws were in the bone. In the CPT® Index, look for Removal/Implantation. The correct code is 20680. Modifier LT is appended to indicate the procedure is performed on the left side. PTS: 1 DIF: Difficult 14. A patient is seen in the hospital’s outpatient surgical area with a diagnosis of a displaced comminuted fracture of the lateral condyle, right elbow. An ORIF (open reduction) procedure was performed and included the following techniques: An incision was made in the area of the lateral epicondyle. This was carried through subcutaneous tissue, and the fracture site was easily exposed. Inspection revealed the fragment to be rotated in two places about 90 degrees. It was possible to manually reduce this quite easily, and the manipulation resulted in an almost anatomic reduction. This was fixed with two pins driven across the humerus. The pins were cut off below skin level. The wound was closed with plain catgut subcutaneously and 5-0 nylon for the skin. Dressings and a long arm cast were applied. What CPT® and ICD-9-CM codes are reported? a. 24579-RT, 29065-51-RT, 812.52 c. 24579-RT, 812.42 b. 24577-RT, 812.42 d. 24575-RT, 812.52 ANS: C Rationale: As noted in ICD-9-CM Tabular List at the beginning of Chapter 17, a comminuted fracture is a closed fracture; therefore, a comminuted lateral condyle fracture is listed as 812.42. In the ICD-9-CM Index to Diseases, look up Fracture/humerus/external condyle directing you to 812.42. The fracture procedure code is found in the CPT® Index for Fracture/Humerus/Condyle/Open Treatment 24579. The manipulation is included in 24579. The application of the first cast is always bundled with the 24579 and not reported separately. PTS: 1 DIF: Difficult 15. A 47-year-old patient was previously treated with external fixation for a Grade III left tibial fracture. There is now nonunion of the left proximal tibia and he is admitted for open reduction of tibia with bone grafting. Approximately 30 grams of cancellous bone was harvested from the iliac crest. The fracture site was exposed and the area of nonunion was osteotomized, cleaned, and repositioned. Intrafragmentary compression was applied with three screws. The harvested bone graft was packed into the fracture site. What CPT® and ICD-9-CM codes are reported? a. 27724-LT, 733.82, 905.4 c. 27722-LT, 733.81, 905.4 b. 27722-LT, 733.82 d. 27724-LT, 733.82 ANS: A Rationale: This is the repair of a nonunion of a tibial fracture; therefore, look in the CPT® Index for Repair/Tibia, 27720-27725. The correct code is 27724, Repair of nonunion or malunion, tibia; with iliac or other autograft (includes obtaining graft). Modifier LT is appended to indicate the procedure was performed on the left side. This was nonunion of a fracture, 733.82 which is a late effect of a fracture of the lower extremity, 905.4. In the Index to Diseases, look up Fracture/nonunion directing you to 733.82. In the Index to Diseases, look up Late/effect/fracture/extremity/lower directing you to 905.4. PTS: 1 DIF: Difficult 16. A Grade I, high velocity open right femur shaft fracture was incurred when a 15-year-old female pedestrian was hit by a car. She was taken to the operating room within four hours of her injury for thorough irrigation and debridement, including excision of devitalized bone. The patient was prepped, draped, and positioned. Intramedullary rodding was carried out with proximal and distal locking screws. What CPT® and ICD-9-CM codes should be reported? a. 27506-RT, 11044-51-RT, 821.11, E814.7 c. 27507-RT, 11012-51-RT, 821.01, E814.7 b. 27506-RT, 11012-51-RT, 821.11, E814.7 d. 27507-RT, 11044-51-RT, 821.10, E814.7 ANS: B Rationale: This was an open femoral shaft fracture, 821.11, thus eliminating C and D. In the ICD-9-CM Index to Diseases, look up Fracture/femur/shaft/open directing you to 821.11. The E code is indexed in the Index to External Causes under Collision/motor vehicle/and/pedestrian (conveyance) referring you to subcategory code E814, fourth digit “7” to indicate the pedestrian. For the first procedure code, look in the CPT® Index under Fracture/Open Treatment directing you to several codes. In reviewing the codes, 27506 is the correct choice. The debridement prior to the intramedullary rodding is reported with 11012 which is found in the CPT® Index under Debridement/Bone/with Open Fracture and/or Dislocation which eliminates choice A. Modifier RT is appended to indicate the procedure is performed on the right side. PTS: 1 DIF: Difficult 17. A 49-year-old female had two previous rotator cuff procedures and now has difficulty with shoulder function, deltoid muscle function, and axillary nerve function. An arthrogram is scheduled. After preparation, the shoulder is anesthetized with 1% lidocaine, 8 cc without epinephrine. The needle was placed into the shoulder area posteriorly under image intensification. It appeared as if the dye was in the shoulder joint. She was moved and a good return of flow was obtained. The shoulder was then mobilized and there was no evidence of any cuff tear from the posterior arthrogram. What CPT® codes are reported? a. 20551, 73040-26 c. 23350, 73040-26 b. 20610, 73040-26 d. 20552, 73040-26 ANS: C Rationale: Contrast material is being injected into the shoulder joint for a radiographic look of the joint and internal structures (arthrogram). Look in the CPT® Index for Arthrography/Shoulder/Injection for 23350. In the Musculoskeletal Section, there is a parenthetical note under code 23350 that states to use code 73040 for radiographic arthrography. Modifier 26 is required to indicate the radiologic professional service. PTS: 1 DIF: Difficult 18. A 31-year-old secretary returns to the office with continued complaints of numbness involving three radial digits of the upper right extremity. Upon examination, she has a positive Tinel’s test of the median nerve in the left wrist. Anti-inflammatory medication has not relieved her pain. Previous electrodiagnostic studies show sensory mononeuropathy. She has clinical findings consistent with carpal tunnel syndrome. She has failed physical therapy and presents for injection of the left carpal canal. The left carpal area is prepped sterilely. A 1.5 inch 25 or 22 gauge needle is inserted radial to the palmaris longus or ulnar to the carpi radialis tendon at an oblique angle of approximately 30 degrees. The needle is advanced a short distance about 1 or 2 cm observing for any complaints of paresthesias or pain in a median nerve distribution. The mixture of 1 cc of 1% lidocaine and 40 mg of Kenalog-10 is injected slowly along the median nerve. The injection area is cleansed and a bandage is applied to the site. What codes are reported? a. 20526, J3301 x 4 c. 20526, J3301 b. 20551, J3301 x 4 d. 20550, J3301 ANS: A Rationale: Look in your HCPCS codebook in the Table of Drugs and Biologicals for Kenolog-10, you are referred to code J3301and then check the tabular listing to verify. Code J3301 is reported for 10 mg, you need to report 4 units to cover the 40 mg given. For the CPT® code, look in the CPT® Index for Injection/Carpal Tunnel/Therapeutic, 20526. PTS: 1 DIF: Difficult 19. An elderly female presented with increasing pain in her left dorsal foot. The patient was brought to the operating room, and placed under general anesthesia. A curvilinear incision was centered over the lesion itself. Soft tissue dissection was carried through to the ganglion. The ganglion was clearly identified as a gelatinous material. It was excised directly off the bone and sent to pathology. There was noted to be a large bony spur at the level of the head of the 1st metatarsal. Using double action rongeurs, the spur itself was removed and sequestrectomy was performed. A rasp was utilized to smooth the bone surface. The eburnated bony surface was then covered, utilizing bone wax. The wound was irrigated and closed in layers. What CPT® codes are reported? a. 28122-LT2, 28090-51-LT c. 28045-LT, 28090-51-LT b. 28111-LT, 28092-51-LT d. 28100-LT, 28092-51-LT ANS: A Rationale: Look in the CPT® Index for Excision/Metatarsal/Head for 28110-28114, 28122, 28140. Code 28122 reports a partial excision or sequestrectomy of metatarsal bone. The CPT® Index for Lesion/Foot leads to 28080, 28090. Code 28090 reports the excision of the ganglion of the foot. Modifier 51 is appended to indicate multiple procedures performed during the same session. Modifier LT is appended to indicate the procedure is performed on the left side. PTS: 1 DIF: Difficult 20. Under general anesthesia, a 45-year-old patient was sterilely prepped. The wrist joint was injected with Marcaine and epinephrine. Three arthroscopic portals were created. The articulating surface between the scaphoid and the lunate clearly showed disruption of the ligamentous structures. We could see soft tissue pouching out into the joint; this was debrided. There was abnormal motion noted within the scapholunate articulation. At this point the C-arm was brought in; arthroscopic instruments were placed in the joint and confirmed the location of the shaver as a probe in the scapholunate ligament. There was a significant gap between the capitate and lunate. K-wire was utilized from the dorsal surface into the lunate, restoring the space. Further examination revealed gross instability between the capitate and lunate. With the wrist in neutral position, a K-wire was passed through the scaphoid, through the capitate and into the hamate. This provided stabilization of the wrist joint. Stitches were placed, and a thumb spica cast was applied. What CPT® code(s) should be reported? a. 29847 c. 29840 b. 29846 d. 29847, 29840-51 ANS: A Rationale: The wrist arthroscopy and stabilization was surgically performed to provide stabilization. Look in the CPT® Index for Arthroscopy/Surgical/Wrist directing you to 29843-29847. Check the tabular listing and 29847 reports arthroscopy of the wrist with internal fixation for fracture or instability. Although several K-wires were passed, 29847 is reported only once. The diagnostic arthroscopy is included in the procedure code, 29847 and is not coded separately. PTS: 1 DIF: Difficult 30000 Series 21. A patient underwent bilateral nasal/sinus diagnostic endoscopy. Finding the airway obstructed the physician fractures the middle turbinates to perform the surgical endoscopy with total ethmoidectomy and bilateral nasal septoplasty. What CPT® codes are reported? a. 30930, 31255-51, 30520-51 b. 31255-50, 30520-50-51 c. 31231, 30130-51, 31255-50 d. 31255, 30520-51 ANS: B Rationale: According to the CPT® guidelines for coding of endoscopies, a surgical sinus endoscopy includes a sinusotomy and diagnostic endoscopy. In the CPT® Index, look for Ethmoidectomy/Endoscopic directing you to 31254-31255. Code 31255 represents a total ethmoidectomy. In the Index, look up Septoplasty; this directs you to code 30520. The fracturing of the turbinates is inclusive to the procedures and not reported separately, since the physician is fracturing the turbinates to perform the ethmoidectomy. Modifier 50 indicates these procedures were both performed bilaterally and modifier 51 is reported with code 30520 to indicate multiple procedures performed at same session, for maximum reimbursement. PTS: 1 DIF: Difficult 22. 55-year-old female smoker presents with cough, hemoptysis, slurred speech, and weight loss. Chest X-ray done today demonstrates a large, unresectable right upper lobe mass, and brain scan is suspicious for metastasis. Under fluoroscopic guidance in an outpatient facility, a percutaneous needle biopsy of the lung lesion is performed for histopathology and tumor markers. A diagnosis of small cell carcinoma is made and chemoradiotherapy is planned. What CPT® and ICD-9-CM codes are reported? a. 32098, 77002-26, 162.3, 786.50, 786.39, 784.5, 783.21 b. 32400, 77002-26, 162.9 c. 32607, 77002-26, 786.6 d. 32405, 77002-26, 162.3 ANS: D Rationale: In the CPT® Index, look up Biopsy/Lung/Needle. This directs you to code 32405. Code 77002 is the appropriate code for the fluoroscopic guidance as indicated by the parenthetical statement under code 32405 and by reviewing the code descriptor for 77002. Modifier 26 is appended to report the professional component. We have a diagnosis of small cell carcinoma of the lung which is code 162.3. In the Index to Diseases, go to the Neoplasm Table and look under lung/upper lobe and the “Primary” column code 162.3 is listed. The signs and symptoms are no longer codes to report because we do have a definitive diagnosis (ICD-9CM Guidelines Section I.B.6) Brain metastasis is suspected but not confirmed so it would not be reported. The chemotherapy is planned but not performed so it would not be reported either. PTS: 1 DIF: Difficult 23. A surgeon performs a high thoracotomy with resection of a single lung segment on a 57-year-old heavy smoker who had presented with a six-month history of right shoulder pain. An apical lung biopsy had confirmed lung cancer. What CPT® and ICD-9-CM codes are reported? a. 32100, 729.5 c. 32503, 162.3 b. 32484, 162.3 d. 19271, 32551-51, 786.50 ANS: B Rationale: A segment of the lung is removed. In the CPT® Index, look up Removal/Lung/ Single Segment. This directs you to code 32484. We have a confirmed diagnosis of apical lung cancer, a cancer in an upper lobe, which is code 162.3. The term apical means the tip of a pyramidal or rounded structure, so apical lung cancer means the tumor/cancer is located at the top or upper lobe of the lung. We find this by looking in the Neoplasm Table under lung/upper lobe. In the primary malignant column we are directed to code 162.3. PTS: 1 DIF: Difficult 24. A 3-year-old girl is playing with a marble and sticks it in her nose. Her mother is unable to dislodge the marble so she takes her to the physician’s office. The physician removes the marble with hemostats. What CPT® and ICD-9-CM codes are reported? a. 30300, 932, E912 c. 30150, 932, E915 b. 30310, 932, E912 d. 30320, 932, E915 ANS: A Rationale: Since the marble is a foreign body, look in the CPT® Index for Nose/Removal/Foreign Body. Here you are directed to use code 30300. For the ICD-9-CM code first look up in the Index to Diseases (Volume 2) Foreign Body/entering through orifice/nose or nostril. This directs us to code 932.The E code is indexed in the Index to External Causes under Foreign Body, object or material/air passage/nose (with asphyxia, obstruction, suffocation) directing you to code E912.Verify codes in the Tabular List.. PTS: 1 DIF: Difficult 25. An ICU diabetic patient who has been in a coma for weeks as the result of a head injury becomes conscious and begins to improve. The physician performs a tracheostomy closure and since the scar tissue is minimal, the plastic surgeon is not needed. What CPT® and ICD-9-CM codes are reported for this procedure? a. 31820, 250.30, V44.0 c. 31825, V55.0, 250.30, 959.01 b. 31820, V55.0, 959.01, 250.00 d. 31825, V55.0, 250.00, 959.01 ANS: B Rationale: In the CPT® Index, look for Tracheostomy/Surgical Closure/without Plastic Repair. This directs you to code 31820. In the Index to Diseases, look up Attention to/tracheostomy, and report V55.0. It is reported as a primary code since the closure of the tracheostomy is the reason for the procedure performed. Diabetic coma (250.30) is not reported because the coma resulted from a head injury not diabetes. Coma (780.01) would not be reported because it is resolved and the patient no longer has it. In the Index to Diseases, look up Injury/head directing you to 959.01. Diabetes is reported with 250.00. PTS: 1 DIF: Difficult 26. A patient has a complete TTE performed to assess her mitral valve prolapse (congenital). The physician performs the study in his cardiac clinic. a. 93303 c. 93308 b. 93306 d. 93312 ANS: A Rationale: Patient has a congenital cardiac anomaly.Procedure was performed in the physician’s clinic; therefore, the global service is reported – meaning no modifier is necessary. This code is found in the CPT® Index under Echocardiography/Transthoracic/Congenital Cardiac Anomalies, and you are referred to 93303-93304. Code 93303 Transthoracic echocardiography for congenital cardiac anomalies; complete is correct. PTS: 1 DIF: Difficult 27. A patient has a Transtelephonic rhythm strip pacemaker evaluation for his dual chamber pacemaker. It has been more than two months from his last evaluation due to him moving. The physician evaluates remotely retrieved information, checking the device’s current programming, battery, lead, capture and sensing function, and heart rhythm. The monitoring period has been 35 days. What can the physician report for the service? a. 93293-52 c. 93296 b. 93295 d. 93293 ANS: D Rationale: According to CPT® guidelines, codes 93293-93296 may be reported once every 90 days; his last evaluation was more than two months ago. Also, the monitoring period has been more than 30 days. Modifier 52 is not an acceptable modifier for 93293. Look in the CPT® index under Pacemaker, Heart/Evaluation and Programming/Remote, you are referred to 93293-93294, 93296. Code 93293 is reported because of the transtelophonic rhythm monitoring for a dual chamber pacemaker. PTS: 1 DIF: Difficult 28. A patient is brought to the operating suite when she experiences a large output of blood in her chest tubes post CABG. The physician performing the original CABG yesterday is concerned about the postoperative bleeding. He explores the chest and finds a leaking anastomosis site and he resutured. a. 35761 c. 35820-78 b. 35761-78 d. 35241 ANS: C Rationale: This is a postoperative exploration and modifier 78 is necessary because this is an unplanned return to the OR by the same physician during the global period of another procedure. Modifier 78 is used for a return to the OR for complications. This was an exploration for postoperative hemorrhage of the chest, 35820, which can be found in the CPT® Index under Exploration/Blood Vessel/Chest, 35820. PTS: 1 DIF: Difficult 29. MAZE procedure is performed on a patient with atrial fibrillation. The physician isolates and ablates the electric paths of the pulmonary veins in the left atrium, the right atrium, and the atrioventricular annulus while on cardiopulmonary bypass. a. 33254 c. 33256 b. 33255 d. 33259 ANS: C Rationale: The procedure described above is extensive according to CPT® definition. Look in the CPT® Index for Maze Procedure/Open, and you are referred to 33254-33256. The patient was on bypass; therefore, the correct code is 33256. PTS: 1 DIF: Difficult 30. Patient undergoes a mitral valve repair with a ring insertion and an aortic valve replacement, on cardiopulmonary bypass. a. 33464, 33406-51 c. 33430, 33405-51 b. 33426, 33405-51 d. 33468, 33426-51 ANS: B Rationale: 33426 reports mitral valve valvuloplasty with a prosthetic ring, and 33405 reports an aortic valve replacement with cardiopulmonary bypass. Modifier 51 is required on the second procedure to indicate multiple procedures performed during the same setting. Look in the CPT® Index for Valvuloplasty/Mitral Valve, you are referred to 33425-33427. You can find the aortic valve replacement in the Index under Replacement/Aortic Valve. You must examine the range of codes given for this procedure. PTS: 1 DIF: Difficult 40000 Series 31. 66-year-old female is admitted to the hospital with a diagnosis of stomach cancer. The surgeon performs a total gastrectomy with formation of an intestinal pouch. Due to the spread of the disease, the physician also performs a total en bloc splenectomy. What CPT® codes are reported? a. 43622, 38100-51 c. 43634, 38115-51 b. 43622, 38102 d. 43634, 38102-51 ANS: B Rationale: CPT® code 43622 represents the complete gastrectomy with intestinal pouch formation. In the CPT® Index, look for Gastrectomy/Total directing you to 43620-43622. Code 38102 represents the en bloc total splenectomy and is an add-on code so it is modifier 51 exempt. In the CPT® Index, look for Splenectomy/Total/En bloc directing you to 38102. PTS: 1 DIF: Difficult 32. A patient suffering from cirrhosis of the liver presents with a history of coffee ground emesis. The surgeon diagnoses the patient with esophageal gastric varices. Two days later, in the hospital GI lab, the surgeon ligates the varices with bands via an UGI endoscopy. What CPT® and ICD-9-CM codes are reported? a. 43205, 571.6, 456.20 c. 43400, 571.6, 456.21 b. 43244, 571.5, 456.21 d. 43235, 571.5, 454.2 ANS: B Rationale: Ligation of esophageal gastric varices endoscopically is coded with CPT® code 43244.This is indexed in CPT® under Ligation/Esophageal Varices. The patient has cirrhosis reported with code 571.5, in the ICD-9-CM Index to Diseases, look up Cirrhosis/liver directing you to 571.5 and reporting 456.21 for the esophageal varices. PTS: 1 DIF: Difficult 33. A patient was taken to the emergency room for severe abdominal pain, nausea and vomiting. A WBC (white blood cell count) was taken and the results showed an elevated WBC count. The general surgeon suspected appendicitis and performed an emergent appendectomy. The patient had extensive adhesions secondary to two previous Cesarean-deliveries. Dissection of this altered anatomical field and required the surgeon to spend 40 additional intraoperative minutes. The surgeon discovered that the appendix was not ruptured nor was it hot. Extra time was documented in order to thoroughly irrigate the peritoneum. What CPT® and ICD-9-CM codes are reported? a. 44960-22,789.00, 787.01, 288.60 540.1 c. 44960-22, 540.0 b. 44950-22, 789.00, 787.01, 288.60 d. 44005, 44955, 789.00, 787.01, 540.0 ANS: B Rationale: Code 44950 represents the appendectomy performed. In the CPT® Index, look for Appendectomy/Appendix Excision. Modifier 22 is appropriate here due to the extensive adhesions that required 40 additional minutes be spent in order to perform the procedure safely and correctly. The signs and symptoms are reported since the surgeon suspected appendicitis. In the ICD-9-CM Index to Diseases, look for Pain(s)/abdominal, directing you to 789.0 and note a 5th digit is required. Next, in the Index to Diseases, look up Nausea/with vomiting directing you to 787.01. Next, in the Index to Diseases, look for Leukocytosis (elevated WBC count) directing you to 288.60. PTS: 1 DIF: Difficult 34. The patient was taken to the operating room and placed in the dorsal lithotomy position, prepped and draped in the usual sterile fashion. A vertical paramedian incision was made along the left side of the umbilicus from the symphysis and taken up to above the umbilicus. This incision was carried down to the rectus muscles, which were separated in the midline. The peritoneal cavity was entered with findings as described. The ascitic fluid was removed and hand-held retractors were used to assist in surgical exposure. The tumor was resected from the hepatic flexure into the mid transverse colon. The resection was extended into the left upper quadrant and the attachments were also clamped, cut and suture ligated with 2-0 silk sutures in a stepwise fashion until mobilization of the tumor mass could be brought medial and hemostasis was obtained. Attempts to find a dissection plane between the tumor mass and the transverse colon were unsuccessful as it appeared that the tumor mass was invading into the wall of the bowel with extrinsic compression and distortion of the bowel lumen. Given the mass could not be resected without removal of bowel, attention was directed to mobilization of the splenic flexure. Retroperitoneal dissection was started in the pelvis and continued along the left paracolic gutter. The ligamentous and peritoneal attachments were taken down with Bovie cautery in a stepwise fashion around the splenic flexure of the colon until the entire left colon was mobilized medially. Similar steps were then carried on the right side as the right colon and hepatic flexure were mobilized. The peritoneal and ligamentous attachments were taken down with Bovie cautery. Vascular attachments were clamped, cut, and suture ligated with 2-0 silk until the right colon was mobilized satisfactorily. The GIA stapler was introduced and fired at both ends to dissect the tumorous bowel free. The bowel was delivered off the operative field. Attention was then directed towards re-anastomosis of the colon. Linen-shod clamps were used to gently clamp the proximal and distal segments of the large bowel. The staple line was removed with Metzenbaum scissors, and the colon lumen was irrigated. The silk sutures were used to divide the circumference of the bowel into equal thirds, and the proximal and distal edges of the bowel were reapproximated with silk sutures. The posterior segment of the bowel was then retracted and secured with a TA stapler, ensuring a full thickness bowel wall insertion into the staple line. The additional two thirds were also isolated and, with the TA stapler, clamped, ensuring that all layers of the bowel wall were incorporated into the anastomosis. A third staple line was fired and the integrity of the anastomosis was checked. First complete hemostasis was noted. There was well beyond a finger width lumen within the large bowel. The linen-shod clamps were released and gas and bowel fluid were moved through the anastomosis aggressively with intact staple line, no leakage of gas or fluid. The abdomen was then irrigated and water was left over the anastomosis. The anastomosis was manipulated with no extravasation of air. The abdomen and pelvis were then irrigated aggressively. The Mesenteric trap was then reapproximated with interrupted 3-0 silk suture ligatures. All sites were inspected and noted to be hemostatic. Attention was directed towards closing. What is the correct CPT® and ICD-9-CM coding for this report? a. 44140, 153.0, 153.1, 153.8 b. 44140, 44139, 153.0, 153.8 c. 44160, 153.8 d. 44147, 44139, 153.1, 153.8 ANS: B Rationale: CPT® codes 44140 and 44139 accurately represent the tumor resected from the hepatic flexure and transverse colon (partial colectomy 44140) and the mobilization of the splenic flexure (44139) due to inability to resect the mass without removal of the bowel. In the CPT® Index, look for Colectomy/Partial directing you to 44140. For the second code, in the CPT® Index, look for Colectomy/Partial/with Splenic Flexure Mobilization directing you to 44139. ICD-9-CM codes are 153.0, in the Neoplasm Table, look for hepatic/flexure (colon), in the Malignant Primary column directing you to 153.0. 153.8 in the Neoplasm Table, see intestine, intestinal/large/contiguous/sites, in the Malignant Primary column directing you to 153.8. PTS: 1 DIF: Difficult 35. Margaret has a cholecystoenterostomy with a Roux-en-Y; five hours later she has an enormous amount of pain, abdominal swelling and a spike in her temperature. She is returned to the OR for an exploratory laparotomy and subsequent removal of a sponge that remained behind from surgery earlier that day. The area had become inflamed and peritonitis was setting in. What is the correct coding for the subsequent services on this date of service? The same surgeon took her back to the OR as the one who performed the original operation. What CPT® code is reported? a. 49000-58 c. 49402-77 b. 49000-77 d. 49402-78 ANS: D Rationale: CPT® code 49402 represents the removal of a foreign body (sponge from previous surgery) from the peritoneal cavity. In the CPT® Index, look for Removal/Foreign Body/Peritoneum. Modifier 78 indicates this was an unplanned return to the OR, by the same physician for a related procedure following an initial procedure during the initial procedures postoperative period. PTS: 1 DIF: Difficult 36. Operative Report Indications: This is a third follow-up EGD dilation on this patient for a pyloric channel ulcer which has been slow to heal with resulting pyloric stricture. This is a repeat evaluation and dilation. Medications: Intravenous Versed 2 mg. Posterior pharyngeal Cetacaine spray. Procedure: With the patient in the left lateral decubitus position, the Olympus GIFXQ10 was inserted into the proximal esophagus and advanced to the Z-line. The esophageal mucosa was unremarkable. Stomach was entered revealing normal gastric mucosa. Mild erythema was seen in the antrum. The pyloric channel was again widened. However, the ulcer as previously seen was well healed with a scar. The pyloric stricture was still present. With some probing, the 11 mm endoscope could be introduced into the second portion of the duodenum revealing normal mucosa. Marked deformity and scarring was seen in the proximal bulb. Following the diagnostic exam, a 15 mm balloon was placed across the stricture, dilated to maximum pressure, and withdrawn. There was minimal bleeding post-op. Much easier access into the duodenum was accomplished after the dilation. Follow-up biopsies were also taken to evaluate Helicobacter noted on a previous exam. The patient tolerated the procedure well. Impressions: Pyloric stricture secondary to healed pyloric channel ulcer, dilated. Plan: Check on biopsy, continue Prilosec for at least another 30 days. At that time, a repeat endoscopy and final dilation will be accomplished. He will almost certainly need chronic H2 blocker therapy to avoid recurrence of this divesting complicated ulcer. What CPT® and ICD-9-CM codes are reported? a. 43245, 43239-51, 537.0, V12.71 c. 43235, 43239-51, 537.1, V12.79 b. 43236, 43239-59, 537.0, V12.71 d. 43248, 43239-59, 537.2, V12.79 ANS: A Rationale: The procedures performed are correctly represented by codes 43245 (balloon dilation) and 43239 (biopsies). In the CPT® Index, look for Esophagogastroduodenoscopy/Transoral/Dilation of Gastric/Duodenal Stricture directing you to 43245 and Esophagogastroduodenoscopy/Transoral/Biopsy directing you to 43239. Modifier 51 is reported to indicate multiple procedures performed on the same day, same session. In the operative note the diagnosis codes are reported from the Impressions. ICD-9CM codes are 537.0 for the pyloric stricture, in the Index to Diseases, look up Stricture/pylorus, which was acquired due to peptic ulcer disease which is healed, reported with history code V12.71. In the Index to Diseases, look up History of/digestive system disease/peptic ulcer directing you to V12.71. PTS: 1 DIF: Difficult 37. A patient with hypertension presents to the same day surgery department for removal of her gallbladder due to chronic gallstones. She is examined preoperatively by her cardiologist to be cleared for surgery. What ICD-9-CM codes are reported? a. 574.21, V72.83, 401.9 c. V72.81, 574.20, 401.9 b. 574.20, 401.9, V72.81 d. 401.9, V72.84, 574.20 ANS: C Rationale: In the Index to Diseases, look for Examination/preoperative/cardiovascular V72.84. Next, in the Index to Diseases, look up Cholelithiasis directing you to 574.20. Code 401.9 is for Hypertension and is indexed in the Hypertension Table. Correct codes and sequencing are V72.81, 574.20 and 401.9. Sequencing of preoperative clearance first, next the reason for the surgery, last any other findings or diagnoses. Sequencing rule from Official Coding Guidelines of ICD-9-CM Section IV.N. PTS: 1 DIF: Difficult 38. A patient presents for esophageal dilation. The physician begins dilation by using a bougie. This attempt was unsuccessful. The physician then dilates the esophagus transendoscopically using a balloon (25mm). What CPT® code(s) is/are reported? a. 43450, 43220 c. 43220, 43450-52 b. 43450-53, 43220 d. 43220 ANS: D Rationale: Because the esophageal dilation by using a bougie (43450) was unsuccessful it is not reported. The esophagus was successfully dilated by performing transendoscopic balloon dilation (43220). This is the only code reported. In the CPT® Index, look for Esophagus/Dilation/Endoscopic directing you to several codes. PTS: 1 DIF: Difficult 39. Surgical laparoscopy with a cholecystectomy and exploration of the common bile duct, for cholelithiasis. What CPT® and ICD-9-CM codes are reported? a. 47610, 574.20 c. 47562, 47552, 574.30 b. 47564, 574.20 d. 47610, 47560, 574.30 ANS: B Rationale: Code 47564 is accurate for laparoscopic cholecystectomy when the exploration of the common bile duct is also performed. In the CPT® Index, look for Cholecystectomy/Laparoscopic directing you to 47562. We have a diagnosis of cholelithiasis but no mention of obstruction and not with cholecystitis, thus the correct ICD-9-CM code is 574.20. In the Index to Diseases, look for Cholelithiasis directing you to 574.20 PTS: 1 DIF: Difficult 40. 45-year-old patient with liver cancer is scheduled for a liver transplant. The patient’s brother is a perfect match and will be donating a portion of his liver for a graft. Segments II and III will be taken from the brother and then the backbench reconstruction of the graft will be performed, both a venous and arterial anastomosis. The orthotopic allotransplantation will then be performed on the patient. What CPT® codes are reported? a. 47140, 47146, 47147, 47135 c. 47140, 47147, 47146, 47136 b. 47141, 47146, 47135 d. 47141, 47146, 47136 ANS: A Rationale: In the CPT® Index, look for Hepatectomy/Partial/Donor. Code 47140 represents the portion of the liver taken from the donor to be allotransplanted. Codes 47146 and 47147 represent the backbench work with venous and arterial anastomosis. In the CPT® Index, look for Transplantation/Liver/Allograft Preparation to find these codes. We have a vein and an artery anastomosed so we only report each of these codes one time. The final code of 47135 represents the orthotopic allotransplantation into the patient; this is found in the CPT® Index with Transplantation/Liver. PTS: 1 DIF: Difficult 50000 Series 41. 67-year-old gentleman with localized prostate cancer will be receiving brachytherapy treatment. Following calculation of the planned transrectal ultrasound, guidance was provided for percutaneous placement of 1-125 seeds into the prostate tissue. What CPT® code is reported for needle placement to insert the radioactive seeds into the prostate? a. 55860 c. 55875 b. 55920 d. 55876 ANS: C Rationale: Brachytherapy is a form of radiation in which radioactive seeds or pellets are implanted directly into the tissue being treated to deliver their dose of radiation in a direct fashion and longer period of time. The placement of the seeds is performed percutaneously (going through the skin by needle). The code is indexed in CPT® under Prostate/Insertion/Needle guiding you to code 55875. PTS: 1 DIF: Difficult 42. Benign prostatic hypertrophy with outlet obstruction and hematuria. Operation: TURP Anesthesia: Spinal Description of procedure: The patient was placed on the operating room table in sitting position and spinal anesthesia induced. He was placed in the lithotomy position, prepped and draped appropriately. Resection was begun at the posterior bladder neck and extended to the verumontanum (a crest near the wall of the urethra). Posterior tissue was resected first from the left lateral lobe, then right lateral lobe, then anterior. Depth of resection was carried to the level of the circular fibers. Bleeding vessels were electrocauterized as encountered. Care was taken to not resect distal to the verumontanum, thus protecting the external sphincter. At the end of the procedure, prostatic chips were evacuated from the bladder. Final inspection showed good hemostasis and intact verumontanum. The instruments were removed, Foley catheter inserted, the patient returned to the recovery area in satisfactory condition. What CPT® code is reported for this service? a. 52601-50 c. 52640 b. 52630 d. 52601 ANS: D Rationale: TURP is a TransUrethral Resection of the Prostate and reported with 52601. In the CPT® Index, TURP directs you to See Prostatectomy, Transurethral. A TURP isn’t a bilateral procedure and is not reported with modifier 50. Code 52630 is reported when it is done for residual or regrowth of the obstructive prostate tissue. Code 52640 describes postoperative procedures on the bladder neck PTS: 1 DIF: Difficult 43. The patient presents to the office for CMG (cystometrogram). Complex CMG cystometrogram with voiding pressure studies is done, intraabdominal voiding pressure studies, and complex uroflow are also performed. What CPT® code(s) is/are reported for this service? a. 51726 c. 51728, 51797, 51741-51 b. 51726, 51728-51, 51797 d. 51728-26, 51797-26, 51741-51-26 ANS: C Rationale: In the CPT® Index, look for Cystometrogram directing you to 51725-51729. Code 51728 describes a Complex cystometrogram with voiding pressure studies. In the CPT® Index, look for Voiding Pressure Studies/Abdominal directing you to 51797. Add-on code 51797 is used for intraabdominal voiding pressure studies. The parenthetical directs us to use 51797 in conjunction with 51728 or 51729. Code 51741 is used to report the complex uroflometry. The procedures were performed in the office setting, under the direct supervision of the physician and you would not use modifier 26 for the professional component. When multiple procedures are performed in the same investigative session modifier 51 should be appended. PTS: 1 DIF: Difficult 44. A 56-year-old woman with biopsy-proven carcinoma of the vulva with metastasis to the lymph nodes has complete removal of the skin and deep subcutaneous tissues of the vulva in addition to removal of her inguinofemoral, iliac and pelvic lymph nodes bilaterally. The diagnosis of carcinoma of the vulva with 7 of the nodes also positive for carcinoma is confirmed on pathologic review. What are the CPT® and ICD-9-CM codes reported for this procedure? a. 56637, 184.4, 196.9 c. 56632-50, 233.32 b. 56640-50, 184.4, 196.5 d. 56633, 38765-50, 184.4, 196.5 ANS: B Rationale: The patient has her vulva removed to treat malignancy (vulvectomy, radical complete). She also has removal of skin and deep subcutaneous tissue from of the vulva, inguinofemoral, iliac and pelvic lymph nodes. In the CPT® Index, look for Vulvectomy/Radical/Complete/ with Inguinofemoral, Iliac, and Pelvic Lymphadenectomy giving you code 56640. All these parts being removed are found in the code description for code 56440. There is a parenthetical note under this code stating: For bilateral procedure, report 56640 with modifier 50. This scenario needs two ICD-9-CM codes. The first one is to show the carcinoma of the vulva. This is indexed in the ICD-9-CM Index to Diseases under, Neoplasm (table)/Vulva/Malignant/Primary (column) guiding you to code 184.4. The second diagnosis code is for the metastasis of the cancer to the lymph nodes. This is indexed in the Neoplasm Table under subinguinal/Malignant/Secondary (column), guiding you to code 196.5. PTS: 1 DIF: Difficult 45. A woman with a long history of rectocele and perineal scarring from multiple episiotomies develops a rectovaginal fistula with perineal body relaxation. She has transperineal repair with perineal body reconstruction and plication of the levator muscles. What are the CPT® and ICD-9-CM codes reported for this procedure? a. 57250, 618.04 c. 57300, 56810-51, 619.1, 624.4 b. 57308, 619.1, 624.4 d. 57330, 619.0 ANS: B Rationale: The physician is closing a rectovaginal fistula (abnormal passage between the rectum and vagina). The repair is performed by a transperineal approach by reconstructing the perineal body (pertaining to the vulva and anus area between the thighs) by using a levator muscle plication. In the CPT® Index, look for Fistula/Closure/Rectovaginal giving you codes 57300, 57305, 57307- 57308. Code 57308 is closure of rectovaginal fistula transperineal approach, with perineal body reconstruction, with or without levator plication. Two diagnoses are reported for this scenario. The first diagnosis is rectovaginal fistula. This is indexed in the ICD-9-CM Index to Diseases under, Fistula/rectovaginal guiding you to code 619.1. Your second diagnosis is perineal scarring. This is indexed under, Scarring/labia guiding you to code 624.4. PTS: 1 DIF: Difficult 46. An 88-year-old widow with uterine prolapse and multiple comorbid conditions has been unsuccessful in the use of a pessary for treatment elects to receive colpocleisis (LeFort type) to prevent further prolapse and avoid more significant surgery like hysterectomy. The treatment is successful. What are the CPT® and ICD-9-CM codes reported for this procedure? a. 59320, 618.3 c. 57120, 618.1 b. 57130, 654.50 d. 57020, 618.2 ANS: C Rationale: This surgical procedure of a colpocleisis is performed to prevent uterine prolapse. In this procedure, the walls of the vagina are sewn together. This obliterates the vagina and prevents uterine prolapse. It is only done in patients not sexually active. In the CPT® Index, look for Colpocleisis, guiding you to code 57120. The reason for the operation is uterine prolapse. In the ICD-9-CM Index to Diseases, look for Prolapse/uterus, guiding you to code 618.1. PTS: 1 DIF: Difficult 47. A 37 year old woman presents with abdominal pain, bleeding unrelated to menses and an abnormal pap showing LGSIL (low grade squamous intraepithelial lesion). Treatment is hysteroscopy with thermoablation of the endometrium and cryocautery of the cervix. This is performed without difficulty. What are the CPT® and ICD-9-CM codes reported for this procedure? a. 58555, 58353-51, 182.0 c. 58350, 57510-51, 182.0 b. 58565, 57511-51, 795.03 d. 58563, 57511-51, 795.03 ANS: D Rationale: The endometrium is destroyed with thermoablation under the guidance of the hysteroscope. In the CPT® Index, look for Hysteroscopy/Ablation/Endometrial, guiding you to code 58563. The abnormal pap smear (LGSIL) is treated with cryocautery. In the CPT® Index, look for Cervix/Cauterization/Cryocautery leading you to code 57511. This diagnosis is indexed in the ICD-9-CM Index to Diseases under Findings/Papanicolaou (smear)/cervix/with low grade squamous intraepithelial lesion (LGSIL) guiding you to code 795.03. PTS: 1 DIF: Difficult 48. A patient is diagnosed with an injury to the facial nerve. The surgeon performs a neurorrhaphy with nerve graft to restore innervation to the face using microscopic repair. The surgeon created a 2 cm incision over the damaged nerve, dissected the tissues and located the nerve. The damaged nerve was resected and removed. The 3.0 cm graft taken from the sural nerve was sutured to the proximal and distal ends of the damaged nerve. What CPT® and ICD-9-CM codes are reported? a. 64885, 959.09 c. 64886, 69990, 959.09 b. 64886, 951.4 d. 64885, 69990, 951.4 ANS: D Rationale: In the CPT® Index, look for Nerves/Graft and you are directed to code range 64885-64907. Code selection is based on the number of strands, location, and length of the grafts. This is a 3cm graft in the head which is coded with 64885. 69990 is reported to indicate the use of an operating microscope. In the ICD-9-CM Index to Diseases, look for Injury/nerve/facial and you are directed to 951.4. Verification in the Tabular List confirms code selection. PTS: 1 DIF: Difficult 49. 47-year-old male presents with chronic back pain, and lower left leg radiculitis. A laminectomy is performed on the inferior end of L5. The microscope is used to perform microdissection. There was a large extradural cystic structure on the right side underneath the nerve root as well as the left. The entire intraspinal lesion was evacuated. What CPT® code(s) is/are reported for this procedure? a. 63267, 69990 c. 63272 b. 63252, 69990 d. 63277 ANS: A Rationale: In the CPT® Index, look for Laminectomy/for Excision/Intraspinal Lesion/Other than Neoplasm and you are directed to code range 63265-63268 and 63270-63273. The code range is divided based on whether the lesion is extradural or intradural. In this case, it is extradural narrowing the range to 63265-63268. The range is further divided based on the section of the spine the lesion is located. Laminectomy with evacuation of an intraspinal lesion in the lumbar spine is described by code 63267. The use of a microscope is documented by 69990. In the CPT® Index, look for Operating Microscope. PTS: 1 DIF: Difficult 50. A patient with primary hyperparathyroidism undergoes parathyroid sestamibi (nuclear medicine scan) and ultrasound and is found to have only one diseased parathyroid. A minimally invasive parathyroidectomy is performed. What CPT® and ICD-9-CM codes are reported for the surgery? a. 60500, 252.00 c. 60505, 252.01 b. 60502, 252.00 d. 60500, 252.01 ANS: D Rationale: In the CPT ® Index, look for Parathyroidectomy or Parathyroid Gland/Excision and you are directed to code range 60500-60505. The diseased gland is determined prior to the surgery, so only the parathyroidectomy is coded with 60500. In the ICD-9-CM Index to Diseases, look for Hyperparathyroidism/primary and you are directed to 252.01. Verification in the Tabular list confirms code selection. PTS: 1 DIF: Difficult 60000 Series 51. A physician uses cryotherapy for removal trichiasis. What CPT® and ICD-9-CM codes are reported? a. 67820, 127.3 c. 67830, 086.5 b. 67825, 374.05 d. 67840, 124 ANS: B Rationale: In the CPT® Index, look for Trichiasis/Repair/Epilation, by Other than Forceps. Verify this code in the numerical Index. Code 67825 describes the correction of trichiasis by other than forceps, eg cryotherapy. In the ICD-9-CM Index to Diseases, look for Trichiasis/eyelid that directs to code 374.05 and is verified in the Tabular List as Trichiasis without entropian. PTS: 1 DIF: Difficult 52. A patient receives chemodenervation with Botulinum toxin injections to stop blepharospasms of the right eye. What are the procedure and diagnosis codes? a. 64650, 780.8 c. 64612-RT, 333.81 b. 67345-RT, 378.10 d. 64616-RT, 781.93 ANS: C Rationale: In the CPT® Index, look for Chemodenervation/Facial Muscle 64612, 64615. Code 64612 is used for chemodenervation of muscles that are innervated by the facial nerve for conditions such as blepharospasm. Botulinum toxin is the substance most commonly used for chemodenervation of muscle tissue innervated by the facial nerve. Blepharospasm in the ICD-9-CM Index to Diseases directs you to 333.81 and is verified from the Tabular List. PTS: 1 DIF: Difficult 53. The surgeon performed an insertion of an intraocular lens prosthesis discussed with the patient before the six-week earlier cataract removal (by the same surgeon). What CPT® code is reported? a. 66985-58 c. 66984 b. 66983-58 d. 66985 ANS: A Rationale: In the CPT® Index look for Insertion/Intraocular Lens/Manual or Mechanical Technique/Not Associated with Concurrent Cataract Removal and directs you to code 66985. The procedure was planned, because it was decided to perform this procedure with the patient before the cataract removal was performed six weeks earlier. This “planned” procedure indicates the need for modifier 58 Staged or related procedure or service by the same physician during the postoperative period. PTS: 1 DIF: Difficult 54. The physician performs an iridotomy using laser on both eyes for chronic angle closure glaucoma; procedure includes local anesthesia. What CPT® and ICD-9-CM codes are reported? a. 66710-50, 365.11, 365.9 c. 66762-50, 66990, 365.01, 365.9 b. 66625, 365.23, 365.70 d. 66761-50, 365.23, 365.70 ANS: D Rationale: In the CPT® Index, look for Iridotomy/by Laser Surgery directing you to 66761. Code 66761 describes the use of laser surgery to perform an iridotomy for glaucoma. Modifier 50 would be used to identify the procedure is performed on both eyes. In ICD-9-CM Index to Diseases, look for Glaucoma/angle closure/chronic directs you to code 365.23 and is verified in the Tabular List as Chronic angle-closure glaucoma. There is an additional instructional note under code 365.23 to use an additional code to identify the glaucoma stage (365.70-365.74). The stage is not documented in the question, code 365.70 is reported. PTS: 1 DIF: Difficult 55. A physician extracts a tumor, using a frontal approach, from the lacrimal gland of a 14-year-old patient. What CPT® and ICD-9-CM codes are reported? a. 68500, 190.7 c. 68520, 224.7 b. 68505, 190.2 d. 68540, 239.89 ANS: D Rationale: In the CPT® Index, look for Lacrimal Gland/Tumor/Excision/Frontal Approach directs you to 68540. This code is used to describe the excision for a lacrimal gland tumor using the frontal approach. In ICD-9-CM Index to Diseases, look for Tumor directing you to see also Neoplasm, by site, unspecified nature. In the Neoplasm table locate lacrimal gland and select the code from the Unspecified column. Verify code 239.89 in the Tabular List. PTS: 1 DIF: Difficult 56. 72-year-old patient is undergoing a corneal transplant. An anesthesiologist is personally performing monitored anesthesia care. What CPT® code and modifier(s) are reported for anesthesia? a. 00144 c. 00144-AA-QS b. 00144-AA d. 00144-QK-QS ANS: C Rationale: An anesthesiologist who is personally performing services reports the service with a modifier AA. The service performed was MAC (Monitored Anesthesia coverage); therefore, modifier QS is also reported. Modifier QS always follows the anesthesia provider modifier. PTS: 1 DIF: Difficult 57. A CRNA is personally performing a case, with medical direction from an anesthesiologist. What modifier is appropriately reported for the CRNA services? a. QX c. QK b. QZ d. QS ANS: A Rationale: A CRNA with medical direction is appropriately reported with modifier -QX. PTS: 1 DIF: Difficult 58. An anesthesiologist is medically supervising six cases concurrently. What modifier is reported for the anesthesiologist’s service? a. AA c. QK b. AD d. QX ANS: B Rationale: An anesthesiologist who is medically supervising reports anesthesia service separately from the CRNA. The anesthesia modifier for the anesthesiologist depends on the number of concurrent cases. There are six concurrent cases; therefore, the appropriate modifier to report is AD for the anesthesiologist. PTS: 1 DIF: Difficult 59. When an anesthesiologist is medically supervising six cases, what modifier is reported for the CRNA’s medically directed service? a. AD c. QX b. QK d. QZ ANS: C Rationale: Modifier QX must be reported for the CRNA. Reporting modifier QZ indicates the anesthesia was performed by non-medically directed CRNA and results in overpayment for the anesthesia service provided. The other two modifier selections are only reported for physician services. Modifier QX is assigned, as there is no way the CRNA knows medical direction changed to medical supervision. PTS: 1 DIF: Difficult 60. 30-year-old patient had anesthesia for an extensive spinal procedure with instrumentation under general anesthesia. The anesthesiologist performed all required steps for medical direction and was not medically directing any other services at the time. What modifier(s) and CPT® code(s) are reported for the anesthesiologist and CRNA services? a. 00670-AA c. 00670-QK and 00670-QZ b. 00670-QK and 00670-QX d. 00670-QY and 00670-QX ANS: D Rationale: In the CPT® Index, look for Anesthesia/Spinal Instrumentation. An anesthesiologist who is medically directing care reports their service separately from the CRNA, depending on the number of concurrent cases. Since there was only one case, the appropriate modifiers to report are QY for the physician and QX for the CRNA. A QZ modifier would indicate the case was performed by a nonmedically directed CRNA. PTS: 1 DIF: Difficult Evaluation & Management 61. Subjective: Six-year-old girl twisted her arm on the play ground. She is seen in the ED complaining of pain in her wrist. Objective: Vital Signs: stable. Wrist: Significant tenderness laterally. X-ray is normal Assessment: Wrist sprain Plan: Over the counter Anaprox. give twice daily with hot packs. Recheck if no improvement. What is the E/M code for this visit? a. 99221 b. 99284 c. 99241 d. 99281 ANS: D Rationale: Emergency Department services must meet or exceed three of the three key components. The physician performed a problem focused history (brief HPI, no ROS, no PFSH), a problem focused exam (one body area is examined), and low MDM (for one new problem to the examiner, one data point for the X-ray, and low level of risk). The problem focused history and exam lead us to select 99281 as the appropriate code. PTS: 1 DIF: Difficult 62. An infant is born six weeks premature in rural Arizona and the pediatrician in attendance intubates the child and administers surfactant in the ET tube while waiting in the ER for the air ambulance. During the 45 minute wait, he continues to bag the critically ill patient on 100 percent oxygen while monitoring VS, ECG, pulse oximetry and temperature. The infant is in a warming unit and an umbilical vein line was placed for fluids and in case of emergent need for medications. How is this coded? a. 99291 c. 99291, 31500, 36510, 94610 b. 99471 d. 99471, 94610, 36510 ANS: C Rationale: When neonatal services are provided in the outpatient setting, Inpatient Neonatal Critical Care guidelines direct the coder to use critical care codes 99291 Critical care, evaluation and management of the critically ill or critically injured patient; first 30-74 minutes and 99292 … each additional 30 minutes (List separately in addition to code for primary service). Care is documented as lasting 45 minutes with the physician in constant attendance. The physician also administered intrapulmonary surfactant (94610), placed an umbilical vein line (36510) and intubated the patient (31500). These services can be separately billed as they are not included in 99291. PTS: 1 DIF: Difficult 63. Mr. Trumph loses his yacht in a poker game and experiences a sudden onset of chest pain which radiates down his left arm. The paramedics are called to the casino he owns in Atlantic City to stabilize him and transport him to the hospital. Dr. H. Art is in the ER to direct the activities of the paramedics. He spends 30 minutes in two-way communication directing the care of Mr. Trumph. When EMS reached the hospital Emergency Department, Mr. Trumph is in full arrest with torsades de pointes (ventricular tachycardia). Dr. H. Art spends another hour stabilizing the patient and performing CPR. What are the appropriate procedure codes for this encounter? a. 99288, 99291, 92950 c. 99288, 99291 b. 99291, 99292 d. 99291, 92950, 92960 ANS: A Rationale: Documentation describes physician direction of the paramedics (99288) In the CPT® Index, look for Physician Services/Direction, Advanced Life Support. He spends another hour stabilizing the patient, reported with critical care code 99291. In the CPT® Index, look for Critical Care Services. CPR is not a service included in the critical care codes and may be reported separately with 92950.In the CPT® Index, look for CPR (Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation). See the CPT® guidelines under Critical Care Services. PTS: 1 DIF: Difficult 64. Patient comes in today at four months of age for a checkup. She is growing and developing well. Her mother is concerned because she seems to cry a lot when lying down but when she is picked up she is fine. She is on breast milk but her mother has returned to work and is using a breast pump, but hasn’t seemed to produce enough milk. PHYSICAL EXAM: Weight 12 lbs 11 oz, Height 25in., OFC 41.5 cm. HEENT: Eye: Red reflex normal. Right eardrum is minimally pink, left eardrum is normal. Nose: slight mucous Throat with slight thrush on the inside of the cheeks and on the tongue. LUNGS: clear. HEART: w/o murmur. ABDOMEN: soft. Hip exam normal. GENITALIA normal although her mother says there was a diaper rash earlier in the week. ASSESSMENT Four month old well check Cold Mild thrush Diaper rash PLAN: Okay to advance to baby foods Okay to supplement with Similac Nystatin suspension for the thrush and creams for the diaper rash if it recurs Mother will bring child back after the cold symptoms resolve for her DPT, HIB and polio What E/M code(s) is/are reported? a. 99212 b. 99391 ANS: B c. 99391, 99212-25 d. 99213 Rationale: Documentation states the encounter is for a “checkup,” which is a Preventive Medicine Service. In the CPT® Index, see Preventive Medicine/Established Patient. Preventive Medicine Service codes are age specific. Although the child has a cold and thrush, additional history and exam elements beyond what is performed in the preventative exam are not documented. It would be inappropriate to bill for an additional E/M service with the modifier 25. See Appendix A description of modifier 25. PTS: 1 DIF: Difficult 65. 28-year-old female patient is returning to her physician’s office with complaints of RLQ pain and heartburn with a temperature of 100.2. The physician performs a detailed history, detailed exam and determines the patient has mild appendicitis. The physician prescribes antibiotics to treat the appendicitis in hopes of avoiding an appendectomy. What are the correct CPT® and ICD-9-CM codes for this encounter? a. 99214, 787.1, 541 c. 99213, 541 b. 99202, 789.03, 541 d. 99203, 780.60, 787.1, 789.03, 541 ANS: A Rationale: This is an established patient E/M level of service due to the indication she returning to her physician for the visit. Code 99214 is appropriate with the key components met or exceeded for this level of service and this is an established patient. According to the ICD-9-CM Official Coding Guidelines Section I.B.6-8, if a definitive diagnosis is established we will code it reporting code 541. Look in the ICD-9-CM Index to Diseases for Appendicitis 541. Any signs or symptoms that would be an integral part of that definitive diagnosis/disease process would not be separately reported. Heartburn is not a symptom commonly seen with appendicitis so we can report this as an additional code. Look in the Index to Diseases for Heartburn 787.1. PTS: 1 DIF: Difficult 66. Dr. Inez discharges Mr. Blancos from the pulmonary service after a bout of pneumococcal pneumonia. She spends 45 minutes at the bedside explaining to Mr. Blancos and his wife the medications and IPPB therapy she ordered. Mr. Blancos is a resident of the Shady Valley Nursing Home due to his advanced Alzheimer’s disease and will return to the nursing home after discharge. On the same day Dr. Inez readmits Mr. Blancos to the nursing facility. She obtains a detailed interval history, does comprehensive examination and the medical decision making is moderate complexity. What is/are the appropriate evaluation and management code(s) for this visit? a. 99238, 99305 c. 99239 b. 99238 d. 99239, 99304 ANS: D Rationale: Hospital discharge is a time-based code. The documentation states that the physician spent 45 minutes discharging the patient. In the CPT® Index, look for Hospital Services/Discharge Services. Code 99239 is for 30 minutes or more. Upon discharge the patient was readmitted to a skilled nursing facility (SNF), where he is a resident. CPT® guidelines preceding the Nursing Facility Services codes state when a patient is discharged from the hospital on the same day and readmitted to a nursing facility both the discharge and readmission should be reported. Initial nursing facility care codes require the three key components to meet or exceed the requirements. Documentation tells us the physician provided a detailed history, comprehensive exam, and medical decision making was of moderate complexity. Code 99304 states the history and exam can be detailed or comprehensive. Our documentation shows it to be of moderate complexity, which meets the requirements. Because our history is only detailed, the requirements are not met for 99305. PTS: 1 DIF: Difficult 67. 37-year-old female is seen in the clinic for follow-up of lower extremity swelling. HPI: Patient is here today for follow-up of bilateral lower extremity swelling. The swelling responded to hydrochlorothiazide. DATA REVIEW: I reviewed her lab and echocardiogram. The patient does have moderate pulmonary hypertension. Exam: Patient is in no acute distress. ASSESSMENT: 1. Bilateral lower extremity swelling. This has resolved with diuretics, it may be secondary to problem #2. 2. Pulmonary hypertension: Etiology is not clear at this time, will work up and possibly refer to a pulmonologist. PLAN: Will evaluate the pulmonary hypertension. Patient will be scheduled for a sleep study. a. 99213 c. 99214 b. 99212 d. 99215 ANS: B Rationale: This is a follow up visit indicating an established patient seen in the clinic. In the CPT® Index, look for Established Patient/Office Visit. The code range to select from is 99211-99215. For this code range, two of three key components must be met. History – PF (HPI-Brief, ROS-None, PFSH-Pert), Exam – Problem Focused, MDM – Moderate (Mgmt options - 1 stable problem, one new problem with workup; Data reviewed – lab and EKG; Level of Risk Moderate with unknown cause of pulmonary HTN). 99212 is the level of visit supported. PTS: 1 DIF: Difficult 68. 45-year-old established, female patient is seen today at her doctor’s office. She is complaining of severe dizziness and feels like the room is spinning. She has had palpitations on and off for the past 12 months. For the ROS, she reports chest tightness and dyspnea but denies nausea, edema, or arm pain. She drinks two cups of coffee per day. Her sister has WPW (Wolff-Parkinson-White) syndrome. An extended exam of five organ systems are performed. This is a new problem. An EKG is ordered and labs are drawn, and the physician documents a moderate complexity MDM. What CPT® code should be reported for this visit? a. 99214 c. 99203 b. 99215 d. 99204 ANS: A Rationale: This is a follow up visit indicating an established patient seen in the clinic. In the CPT® Index, look for Established Patient/Office Visit. The code range to select from is 99211-99215. For this code range, two of three key components must be met. History Detailed (HPI-Extended; ROS-Extended, PFSH-Complete), Exam – Detailed, MDM Moderate. 99214 is the level of visit supported. PTS: 1 DIF: Difficult 69. 33 year-old male was admitted to the hospital on 12/17/XX from the ER, following a motor vehicle accident. His spleen was severely damaged and a splenectomy was performed. The patient is being discharged from the hospital on 12/20/XX. During his hospitalization the patient experienced pain and shortness of breath, but with an antibiotic regimen of Levaquin, he improved. The attending physician performed a final examination and reviewed the chest X-ray revealing possible infiltrates and a CT of the abdomen ruled out any abscess. He was given a prescription of Zosyn. The patient was told to follow up with his PCP or return to the ER for any pain or bleeding. The physician spent 20 minutes on the date of discharge. What CPT® code is reported for the 12/20 visit? a. 99221 c. 99238 b. 99231 d. 99283 ANS: C Rationale: The patient is being discharged from the hospital. Hospital discharge codes are determined based on the time documented the physician spent providing services to discharge the patient. The provider documented 20 minutes, which is reported with 99238. PTS: 1 DIF: Difficult 70. 60-year-old woman is seeking help to quit smoking. She makes an appointment to see Dr. Lung for an initial visit. The patient has a constant cough due to smoking and some shortness of breath. No night sweats, weight loss, night fever, CP, headache, or dizziness. She has tried patches and nicotine gum, which has not helped. Patient has been smoking for 40 years and smokes 2 packs per day. She has a family history of emphysema. A limited three system exam was performed. Dr Lung discussed in detail the pros and cons of medications used to quit smoking. Counseling and education was done for 20 minutes of the 30 minute visit. Prescriptions for Chantrix and Tetracylcine were given. The patient to follow up in 1 month. A chest X-ray and cardiac work up was ordered. Select the appropriate CPT code(s) for this visit. a. 99202 c. 99203, 99354 b. 99203 d. 99214, 99354 ANS: B Rationale: Patient is coming to the doctor’s office for help to quit smoking. The patient is new. The physician documents that 20 minutes of the 30 minute visit was spent counseling the patient. E/M Guidelines identify when time is considered the key or controlling factor to qualify for a E/M service. When counseling and/or coordination of care is more than 50% face to face time in the office or other outpatient setting, time may be used to determine the level of E/M. The correct code is 99203 based on the total time of the visit which is 30 minutes. PTS: 1 DIF: Difficult Anesthesia 71. A pre-anesthesia assessment was performed and signed at 10:21 a.m. Anesthesia start time is reported as 12:26 pm, and the surgery began at 12:37 pm. The surgery finished at 15:12 pm and the patient was turned over to PACU at 15:26 pm, which was reported as the ending anesthesia time. What is the anesthesia time reported? a. 10:21 am to 15:12 pm (291 minutes) c. 12:26 am to 15:12 pm (146 minutes) b. 12:26 am to 15:26 pm (180 minutes) d. 12:37 am to 15:26 pm (169 minutes) ANS: B Rationale: Anesthesia time begins when the anesthesiologist begins to prepare the patient for anesthesia in either the operating room or an equivalent area. Pre-anesthesia assessment time is not part of reportable anesthesia time, as it is considered in the base value assigned for the procedure. Anesthesia time ends when the anesthesiologist is no longer in personal attendance. Ending time is generally reported when the patient is safely placed under postoperative supervision, usually in the Post Anesthesia Care Unit (PACU) or equivalent area. Anesthesia start time (12:26) and the anesthesia end time (15:26) calculates as three hours or one hundred eighty (180) minutes of total anesthesia time. PTS: 1 DIF: Difficult 72. Code 00350 Anesthesia for procedures on the major vessels of the neck; not otherwise specified has a base value of ten (10) units. The patient is a P3 status, which allows one (1) extra base unit. Anesthesia start time is reported as 11:02 am, and the surgery began at 11:14 am. The surgery finished at 12:34 am and the patient was turned over to PACU at 12:47 am, which was reported as the ending anesthesia time. Using fifteen-minute time increments and a conversion factor of $100, what is the correct anesthesia charge? a. $1,500.00 c. $1,700.00 b. $1,600.00 d. $1,800.00 ANS: D Rationale: Determining the base value is the first step in calculating anesthesia charges and payment expected. Time reporting is the second step. Anesthesia time begins when the anesthesiologist begins to prepare the patient for anesthesia in either the operating room or an equivalent area. Anesthesia time ends when the anesthesiologist is no longer in personal attendance. Ending time is generally reported when the patient is safely placed under postoperative supervision, usually in the Post Anesthesia Care Unit (PACU) or equivalent area. Physical status modifiers and/or qualifying circumstances may also be added to the charge. In the scenario above, Base units equal ten (10) plus one (1) physical status modifier unit (Base 10 + PS 1 = 11 units). Seven (7) time units, in fifteen minute increments, is calculated by taking the anesthesia start time (11:02) and the anesthesia end time (12:47) and determining one hour 45 minutes (105/15 = 7) of total anesthesia time. Eighteen units (11 + 7 = 18) are then multiplied by the $100 conversion factor (18 X $100 = $1,800.00). PTS: 1 DIF: Difficult 73. Code 00940, anesthesia for vaginal procedures, has a base value of three (3) units. The patient was admitted under emergency circumstances, qualifying circumstance code 99140, which allows two (2) extra base units. A pre-anesthesia assessment was performed and signed at 2:00 a.m. Anesthesia start time is reported as 2:21 am, and the surgery began at 2:28 am. The surgery finished at 3:25 am and the patient was turned over to PACU at 3:36 am, which was reported as the ending anesthesia time. Using fifteen-minute time increments and a conversion factor of $100, what is the correct anesthesia charge? a. $800.00 c. $1,000.00 b. $900.00 d. $1,200.00 ANS: C Rationale: Determining the base value is the first step in calculating anesthesia charges and payment expected. Time reporting is the second step. Anesthesia time begins when the anesthesiologist begins to prepare the patient for anesthesia in either the operating room or an equivalent area. Pre-anesthesia assessment time is not part of reportable anesthesia time, as it is considered in the base value assigned. Anesthesia time ends when the anesthesiologist is no longer in personal attendance. Ending time is generally reported when the patient is safely placed under postoperative supervision, usually in the Post Anesthesia Care Unit (PACU) or equivalent area. Physical status modifiers and/or qualifying circumstances may also be added to the charge. In the scenario above, Base units equal three (3) plus two (2) emergency qualifying circumstances units (Base 3 + QC 2 = 5 units). Five (5) time units, in fifteen minute increments, is calculated by taking the anesthesia start time (2:21) and the anesthesia end time (3:36) and determining one hour 15 minutes (75/15 = 5) of total anesthesia time. Ten units (5 + 5 = 10) are then multiplied by the $100 conversion factor (10 X $100 = $1,000.00). PTS: 1 DIF: Difficult 74. 94-year-old patient is having surgery to remove his parotid gland, with dissection and preservation of the facial nerve. The surgeon has requested the anesthesia department place an arterial line. What CPT® code(s) is/are reported for anesthesia? a. 00300, 36620 c. 00100, 99100 b. 00100, 36620, 99100 d. 00400 ANS: B Rationale: Coder must reference Anesthesia/Salivary Glands in the CPT® Index to determine 00100 is the correct anatomic location. Hint - Coder may need to use the Surgery Section to determine the parotid gland is included in the salivary glands. The arterial line placement is NOT included in the base value and may be reported separately. Due to patient’s advanced age of 94, qualifying circumstance addon code 99100 is also reported. PTS: 1 DIF: Difficult 75. 5- year-old patient is experiencing atrial fibrillation with rapid ventricular rate. The anesthesia department is called to insert a non-tunneled central venous (CV) catheter. What CPT® code is reported? a. 00400 c. 36556 b. 36555 d. 36557 ANS: C Rationale: An anesthesia service was NOT performed; therefore, 00400 is not reported. Look in the CPT® Index for Catheterization/Central Venous and reference is made to See Central Venous Catheter Placement. Many codes are listed. The catheter is non-tunneled; therefore, there are two codes from which to choose; 36555 and 36556, based on patient age. This patient is 5-years-old; therefore, 36556 is correct. PTS: 1 DIF: Difficult 76. 43-year-old patient with a severe systemic disease is having surgery to remove an integumentary mass from his neck. What CPT® code and modifier are reported for the anesthesia service? a. 00300-P2 c. 00322-P3 b. 00300-P3 d. 00350-P3 ANS: B Rationale: Look in the CPT® Index for Anesthesia/Neck, which lists a range of codes or Anesthesia/Integumentary System/Neck which lists one code, 00300. A P3 modifier may be reported for a patient with severe systemic disease. PTS: 1 DIF: Difficult 77. An 11-month-old patient presented for emergency surgery to repair a severely broken arm after falling from a third story window. What qualifying circumstance code(s) may be reported in addition to the anesthesia code? a. 99100 c. 99140 b. 99116 d. 99100, 99140 ANS: D Rationale: Each of the qualifying circumstances codes identifies a different circumstance, and more than one may be appended when applicable, unless the reported anesthesia code already contains the risk factor. In this case, 99100 is assigned for extreme age of one year or younger and 99140 is assigned for emergency conditions. PTS: 1 DIF: Difficult 78. 59-year-old patient is having surgery on the pericardial sac, without use of a pump oxygenator. The perfusionist placed an arterial line. What CPT® code(s) is/are reported for anesthesia? a. 00560 c. 00561 b. 00560, 36620 d. 00562 ANS: A Rationale: Look for Anesthesia/Heart in the CPT® Index or Anesthesia/Intrathoracic System. Check this listing with the Anesthesia Subsection, Intrathoracic to determine 00560 is the correct code reported for patient’s age and without use of a pump oxygenator. The arterial line placement is NOT reported because the perfusionist, not the anesthesia provider, performed it. PTS: 1 DIF: Difficult Radiology 79. 41-year-old male is in his doctor’s office for a follow up of an abnormality, which was noted, on an abdominal CT scan. He is to have a chest X-ray due to chest tightness. He otherwise states he feels well and is here to go over the results of his chest X-ray (PA and Lateral) performed in the office and the CT scan performed at the diagnostic center. The results of the chest X-ray were normal. CT scan was sent to the office and the physician interpreted and documented that the CT scan of the abdomen showed a small mass in his right upper quadrant. What CPT® codes are reported for the doctor’s office radiological services? a. 71020-26, 74150-26 c. 71020-26, 74150 b. 71020, 74150 d. 71020, 74150-26 ANS: D Rationale: The chest X-ray was taken in the doctor’s office and interpreted. This means the doctor’s office can bill for the code without appending a modifier. Modifier 26 is appended to the CT scan code, because, it was performed at another site and the physician only interpreted the image. Look in the CPT® Index for X-ray/Chest directing you to 71010-71035, and CT Scan/without Contrast/Abdomen directing you to 74150, 74176, 74178. PTS: 1 DIF: Difficult 80. A patient has a history of chronic venous embolism in the superior vena cava (SVC) and is having a radiographic study to visualize any abnormalities. In outpatient surgery the physician accesses the subclavian vein and the catheter is advanced to the superior vena cava for injection and imaging. The supervision and interpretation of the images is performed by the physician. What codes are reported for this procedure? a. 36010, 75827-26 c. 36000, 75827-26 b. 36000, 75820-26 d. 36010, 75820-26 ANS: A Rationale: A radiographic study of the superior vena cava is performed to visualize and evaluate any abnormalities. For the insertion of the catheter look in the CPT® Index for Catheterization/Vena Cava referring you to code 36010. For the radiology code look in the CPT® Index for Venography/Vena Cava guiding you to code range 75825-75827. Radiology code 75827 is correct for the superior vena cava. Modifier 26 is appended to the radiology code, because the physician is performing the procedure in an outpatient facility setting. PTS: 1 DIF: Difficult 81. 70-year-old female presents with a complaint of right knee pain with weight bearing activities. She is also developing pain at rest. She denies any recent injury. There is pain with stair climbing and start up pain. An AP, Lateral and Sunrise views of the right knee are ordered and interpreted. They reveal calcification within the vascular structures. There is decreased joint space through the medial compartment where she has near bone-on-bone contact, flattening of the femoral condyles, no fractures noted. The diagnosis is right knee pain secondary to underlying localized degenerative arthritis. What CPT® and ICD-9-CM codes are reported? a. 73560, 715.96 c. 73562, 715.36 b. 73562, 715.96, 719.46 d. 73565, 715.36, 719.46 ANS: C Rationale: Look in the CPT® Index for X-ray/Knee 73560-73564, 73580. Code 73562 reports three views of one knee. The scenario is reported with one ICD-9-CM code. In the ICD-9-CM Index to Diseases (Alphabetical Index) look for Arthritis/degenerative, there is a see also note to go to Osteoarthrosis. Under Osteoarthrosis /localized, guides you to code 715.3 with the fifth digit being six, 715.36. If you look at chapter 13 in your ICD-9-CM codebook, you will see that the fifth digit 6, lower leg, includes the knee joint. Localized osteoarthrosis is appropriate to report, because it is stated as localized.You do not report the ICD-9-CM code for knee pain as this is a symptom of the degenerative arthritis and included in the code. PTS: 1 DIF: Difficult 82. Myocardial Perfusion Imaging—Office Based Test Indications: Chest pain. Procedure: Resting tomographic myocardial perfusion images were obtained following injection of 10 mCi of intravenous cardiolite. At peak exercise, 30 mCi of intravenous cardiolite was injected, and poststress tomographic myocardial perfusion images were obtained. Post stress gated images of the left ventricle were also acquired. Myocardial perfusion images were compared in the standard fashion. Findings: This is a technically fair study. There were no stress induced electrocardiographic changes noted. There are no significant reversible or fixed perfusion defects noted. Gated images of the left ventricle reveal normal left ventricular volumes, normal left ventricular wall motion, and an estimated left ventricular ejection fraction of 50%. Impression: No evidence of myocardial ischemia or infarction. Normal left ventricular ejection fraction. What CPT® code(s) is/are reported? a. 78451 c. 78453 b. 78451, A9500 d. 78451, A9500 x 30 ANS: B Rationale: Tomographic myocardial perfusion imaging was performed. In this procedure the patient receives an intravenous injection of a radionuclide, which localizes in nonischemic tissue. SPECT (single photon emission computed tomographic) images of the heart are taken immediately to identify areas of perfusion vs. infarction. In the CPT® Index, look for Heart/Myocardium/Perfusion Study 78451-78454. A single study SPECT was performed, 78451. This was performed in the office; therefore, report the cardiolite. Using your HCPCS codebook go to the Table of Drugs and Biologicals and look for Cardiolite A9500. The code A9500 reports the dose per study PTS: 1 DIF: Difficult 83. After intravenous administration of 5.1 millicuries Tc-99m DTPA, flow imaging of the kidneys was performed for approximately 30 minutes. Flow imaging demonstrated markedly reduced flow to both kidneys bilaterally. What CPT® code is reported? a. 78710 c. 78708 b. 78701 d. 78725 ANS: B Rationale: The nuclear imaging test follows the blood as it flows to the kidneys identifying any obstruction and to determine the rate at which the kidneys are filtering. The scenario does not document the function of the tubes and ducts . In the CPT® Index, look for Nuclear Medicine/Diagnostic/Kidney/Vascular Flow directing you to code range 78701-78709. PTS: 1 DIF: Difficult 84. An oncology patient is having weekly radiation treatments with a total of seven conventional fractionated treatments. Two fractionated treatments daily for Monday, Tuesday and Wednesday and one treatment on Thursday. What radiology code(s) is/are appropriate for the clinical management of the radiation treatment? a. 77427 c. 77427 x 2 b. 77427 x 7 d. 77427-22 ANS: A Rationale: There are seven fractions given in this patient’s weekly treatment. According to CPT® guidelines,radiation treatment management is reported in units of five fractions or treatment sessions, regardless of the actual time-period in which the services are furnished. Code 77427 is also reported if there are three or four fractions beyond a multiple of five at the end of a course of treatment, one or two fractions beyond a multiple of five at the end of a course of treatment are not reported separately.” This instruction is found in CPT® under the heading “Radiation Treatment Management” in the Radiology/Radiation Oncology Section of the Radiology Chapter. In the CPT® Index look for Radiation Therapy/Treatment Management/Weekly directing you to 77427. PTS: 1 DIF: Difficult 85. Magnetic resonance imaging of the chest is first done without contrast medium enhancement and then is performed with an injection of contrast. What CPT® code(s) is/are reported for the radiological services? a. 71550, 71551 c. 71555 b. 71552 d. 71275 ANS: B Rationale: The patient is having magnetic resonance imaging in which the images were performed first without contrast and again following the injection of contrast. In the CPT® Index, look for Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)/Chest directing you to 71550-71552. PTS: 1 DIF: Difficult 86. A CT scan confirms improper ossification of cartilages in the upper jawbone and left side of the face area for a patient with facial defects. The CT is performed with contrast material in the hospital. What CPT® code is reported by an independent radiologist contracted by the hospital? a. 70460-26 c. 70487-26 b. 70481-26 d. 70542-26 ANS: C Rationale: The CT scan with contrast is performed on the maxillofacial area. The maxilla is the upper part of the jawbone. In the CPT® Index, look for CT Scan/with Contrast/Maxilla directing you to 70487. Modifier 26 is denotes the professional service. PTS: 1 DIF: Difficult 87. A patient is positioned on the scanning table headfirst with arms at the side for an MRI of the thoracic spine and spinal canal. A contrast agent is used to improve the quality of the images. The scan confirms the size and depth of a previously biopsied leiomyosarcoma metastasized to the thoracic spinal cord. What CPT® and ICD-9-CM codes are reported? a. 72255, 239.7 c. 72070, 192.2 b. 72157, 237.5 d. 72147, 198.3 ANS: D Rationale: In the CPT® Index, look for Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)/Diagnostic/Spine/Thoracic for the code range. Code 72147 describes and MRI of the thoracic spine with contrast. This is a secondary (metastasized) cancer to the thoracic spinal cord. It is indexed in the ICD-9-CM Index to Diseases (Alphabetical Index) under Leiomyosarcoma see Neoplasm, connective tissue, malignant. In the Neoplasm Table look for Neoplasm/connective tissue/cord (true) (vocal)/spinal (thoracic)/Malignant/Secondary (column) you are guided to code 198.3. PTS: 1 DIF: Difficult 88. A young child is taken to the OR to reduce a meconium plug bowel obstruction. A therapeutic enema is performed with fluoroscopy. The patient is in position and barium is instilled into the colon through the anus for the reduction. What CPT® code is reported by the independent radiologist for the radiological service? a. 74270-26 c. 74283-26 b. 74280-26 d. 74246-26 ANS: C Rationale: A therapeutic enema was performed with contrast (barium) to reduce the meconium plug (intraluminal obstruction). In the CPT® Index, look for Enema/Therapeutic/for Intussusception directing you to 74283. The code description includes therapeutic enema with contrast for intraluminal obstruction. PTS: 1 DIF: Difficult Laboratory and Pathology 89. What is/are the code(s) for thawing 4 units of fresh frozen plasma? a. 86927 c. 86931 b. 86927 x 4 d. 86931 x 4 ANS: B Rationale: In the CPT® Index, look for Plasma/Frozen Preparation and you are directed to 86927. Code 86927 is specifically for plasma rather than whole blood. The code is used per unit thawed so the answer is 86927 x 4. PTS: 1 DIF: Difficult 90. The code for sweat collection by iontophoresis can be found in what section of the Pathology Chapter of CPT®? a. Cytopathology c. Hematology b. Chemistry d. Other Procedures ANS: D Rationale: The Other Procedures section includes codes for a number of miscellaneous procedures. Many of them are for analysis of substances found in other body substances and tissues. There are also a number of tests for specific conditions and diseases. In the CPT® Index, look for Iontophoresis/Sweat Collection referring you to 89230. Code 89230 is under the heading, Other Procedures. PTS: 1 DIF: Difficult 91. A patient will be undergoing a transplant and needs HLA tissue typing with DR/DQ multiple antigen and lymphocyte mixed culture. How will these services be coded? a. 86805-26, 86817 b. 86817, 86821 c. 86816-26, 86821 d. 86806-26, 86817 ANS: B Rationale: Code 86817 is the correct code to report for HLA tissue typing with DR/DQ. In the CPT® Index look under Tissue/Typing/Human Leukocyte Antigen (HLA)/Antibodies. Code 86821 is reported for the lymphocyte culture. This is indexed under Tissue/Typing/Lymphocyte Culture. Codes 86805 and 86806 are for lymphocytotoxicity, not lymphocyte mixed culture. PTS: 1 DIF: Difficult 92. A physician orders a quantitative FDP. What CPT® code is reported? a. 85362 c. 85370 b. 85366 d. 85378 ANS: C Rationale: Check for unfamiliar abbreviations in the Index. Read codes closely to identify whether they are quantitative, semi-quantitative, or qualitative. In the CPT® Index, see FDP, you are directed to See Fibrin Degradation Products, this refers you to See Pathology and Laboratory/Fibrin Degradation Products. PTS: 1 DIF: Difficult 93. A patient’s mother and sister have been treated for breast cancer. She has blood drawn for cancer gene analysis with molecular pathology testing. She has previously received genetic counseling. Blood will be tested for full sequence analysis and common duplication or deletion variants (mutations) in BRCA1, BRCA2 (breast cancer 1 and 2). What CPT® code is reported for this molecular pathology procedure? a. 81200 c. 81211 b. 81206 d. 81213 ANS: C Rationale: In the CPT® Index, look for Breast/Cancer Gene Analysis/BRCA1 (breast cancer 1) referring you to 81211-81215. The correct code is 81211. This is a blood test performed to look for any gene mutations affecting the BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes. These human genes are known as tumor suppressors, mutation of these genes has been linked to hereditary breast and/or ovarian cancer. A woman’s risk of developing breast or ovarian cancer is increased if she inherits this harmful mutation. Men with this mutation also have an increased risk of breast cancer. Be sure to read the parenthetical instructions. PTS: 1 DIF: Difficult 94. A patient with AIDS presents for follow up care. An NK (natural killer cell) total count is ordered. What CPT® code(s) is/are reported? a. 86359 c. 86361, 86359 b. 86703 d. 86357 ANS: D Rationale: Although there are a number of cells that attack viruses and other infectious organisms, NK cells are specifically identified by code 86357. In the CPT® Index, see Natural Killer (NK) Cells. PTS: 1 DIF: Difficult 95. A patient has partial removal of his lung. The surgeon also biopsies several lymph nodes in the patient’s chest which are examined intraoperatively by frozen section and sent with the lung tissue for Pathologic examination. The pathologist also performs a trichrome stain. What CPT® codes are reported for the lab tests performed? a. 88309 x 2, 88313 c. 88307, 88305x2, 88332 b. 88309, 88305, 88313, 88331 d. 88309, 88307, 88313 ANS: B Rationale: Separately code for each, the lung examination (all lung specimens are 88309), the lymph node biopsy (88305), the frozen section (first specimen 88331), and for the special trichrome stain (88313). In the CPT® Index, see Pathology/Surgical/Level IV and Level VI. Also, see Surgical Pathology//Consultation/Intraoperative directing you to code range 88329-88334. PTS: 1 DIF: Difficult 96. A couple with inability to conceive has fertility testing. The semen specimen is tested for volume, count, motility and a differential is calculated. The findings indicate infertility due to oligospermia. What CPT® and ICD-9-CM codes are reported? a. 89310, 89320, V26.21 c. 89320, 606.1 b. 89257, 606.9, V26.21 d. 89264, 606.1 ANS: C Rationale: Choose the CPT® code completely identifying the service. Only use multiple codes if there is no code describing everything performed. Only use V codes when there is no final diagnosis. In this case, a very specific diagnosis is known and the code is used. In the CPT® Index, look for Semen Analysis directing you to code range 89300-89322. Code 89320 reports all of the tests performed. For the ICD-9-CM diagnosis, code, look in the Index to Diseases, for Infertility/male/oligospermia leading you to 606.1. PTS: 1 DIF: Difficult 97. In a legal hearing to determine child support there is a dispute about the child’s paternity. The court orders a paternity test, and a nasal smear is taken from the plaintiff and the child. The plaintiff is confirmed as the father of the child. Choose the CPT®, ICD-9-CM codes and modifier for the paternity testing. a. 89190-32, V26.39 c. 86900, V70.4 b. 86910-32, V70.4 d. 86910, V26.39 ANS: B Rationale: Always choose codes identifying the service and reason for the service as specifically as possible. Parenthetic comments in CPT® can sometimes assist in finding a challenging code. Modifier 32 is appropriate when services are mandated by courts or insurers. In the CPT® Index, look for Paternity Testing. For the ICD-9-CM code, look in the Index to Diseases for Paternity testing. PTS: 1 DIF: Difficult 98. A virus is identified by observing growth patterns on cultured media. What is this type of identification is called? a. Definitive c. Quantitative b. Qualitative d. Presumptive ANS: D Rationale: Presumptive identification identifies microorganisms like viruses by observing growth patterns and other characteristics. PTS: 1 DIF: Difficult Medicine 99. A female patient fell on the floor as she got out of bed. She has no known head trauma. She noticed some slight stiffness in her joints and weakness in her lower extremity muscles, with slight stiffness in her arm joints. The physician decided to test for possible multiple sclerosis (MS). She was sent to a clinic providing somatosensory studies. The testing included upper and lower limbs. What CPT® and ICD-9CM codes are reported? a. 95938, 728.87, 719.59 c. 95926, 728.87, 719.59 b. 95925, 95926, 340 d. 95926, 340 ANS: A Rationale: In the CPT® Index, look for Somatosensory Testing. Studies are reported based on location. In this case the upper limbs and lower limbs were performed guiding you to code 95938. Since MS has not been confirmed, the weakness in her muscles (728.87) and stiffness of the joints (719.59) should be reported. In the Index to Diseases, look for Weakness/muscle (generalized). Also, look for Stiffness, joint/multiple sites. PTS: 1 DIF: Difficult 100. 64-year-old patient came to the emergency department complaining of chest pressure. The physician evaluated the patient and ordered a 12 lead EKG. Findings included signs of acute cardiac damage. Appropriate initial management was continued by the ED physician who contacted the cardiologist on call in the hospital. Admission to the cardiac unit was ordered. No beds were available in the cardiac unit and the patient was held in the ED. The cardiologist left the ED after completing the evaluation of the patient. Several hours passed and the patient was still in the ED. During an 80-minute period, the patient experienced acute breathing difficulty, increased chest pain, arrhythmias, and cardiac arrest. The patient was managed by the ED physician during this 80-minute period. Included in the physician management were a new 12 lead EKG, endotracheal intubation and efforts to restore the patient’s breathing and circulation for 20 minutes. CPR was unsuccessful, the patient was pronounced dead after a total of 44 minutes critical care time, exclusive of other separately billable services. What CPT® codes are reported by the physician? a. 99285-25, 93010 x 2, 31500, 92950 b. 99291-25, 31500, 93000, 92950 c. 99291-25, 99292-25, 93005-59 x 2, 31500 d. 99291-25, 31500, 92950 ANS: D Rationale: Only one E&M code is reportable per physician per day. The patient never left the emergency department. The first part of the encounter did not meet critical care, although the second part did meet critical care. In the CPT® Index, see Critical Care Services. Use code 99291 for 44 minutes of critical care. In the CPT® Index, look for Insertion/Endotracheal Tube. Report endotracheal intubation with code 31500. In the CPT® Index, look for CPR. Report cardiopulmonary resuscitation with code 92950. The EKG reading is included in critical care and is not separately billable. PTS: 1 DIF: Difficult 101. A patient with Sickle cell anemia with painful sickle crisis received normal saline IV, 100 cc per hour to run over 5 hours for hydration in the physician’s office. She will be given Morphine & Phenergan, prn (as needed). What codes are reported? a. 96360, 96361 x 4, J7050 x 2, 282.62 c. 96360, 96361 x 3, J7030, 282.62 b. 96360 x 5, J7050, 282.60 d. 96360, J7030, 282.69 ANS: A Rationale: In the CPT® Index, look for Hydration, you are directed to codes 96360-96361. The hydration will run 5 hours at 100 cc per hour. Code the hydration therapy as 96360 for the first hour, then 96361 x 4 to get a total infusion time of 5 hours. Code for the normal saline with J7050 x 2 units for 500 cc (HCPCS Level II). The type of Sickle Cell anemia is not identified, but the patient has painful sickle crisis. In the ICD-9-CM Index to Diseases, look for Crisis/sickle cell. Apply code 282.62. PTS: 1 DIF: Difficult 102. A patient with bilateral sensory hearing loss is fitted with a digital, binaural, behind the ear hearing aid. What HCPCS Level II and ICD-9-CM codes should be reported? a. V5140, 389.11, V53.2 c. V5140, 389.22 b. V5261, V53.2, 389.11 d. V5261, V72.11, 389.11 ANS: B Rationale: The hearing aid is reported with V5261, digital binaural behind the ear appliance. The purpose of the visit is the fitting of the hearing aid. Look in the Index to Disease for Fitting (of)/hearing aid direction you tod V53.2. The condition necessitating the hearing aid is bilateral sensory hearing loss. In the Index to Diseases, look for Loss/hearing/sensory/bilateral. This is reported with 389.11. PTS: 1 103. DIF: Difficult 5-year-old is brought in to see an allergist for generalized urticaria. The family just recently visited a family member that had a cat and dog. The mother wants to know if her son is allergic to cats and dogs. The child’s skin was scratched with two different allergens. The physician waited 15 minutes to check the results. There was a flare up reaction to the cat allergen, but there was no flare up to the dog allergen. The physician included the test interpretation and report in the record. a. 95024 x 2 b. 95027 x 2 c. 95004 x 2 d. 95018 x 2 ANS: C Rationale: Code 95004 describes the scratch test with allergenic extracts. The test is reported twice for the number of substances that were tested on. In the CPT® Index, look for Allergy Tests/Skin Tests/Allergen Extract. PTS: 1 DIF: Difficult 104. 42-year-old patient presented to the urgent care center with complaints of slight dizziness. He had received services at the clinic about 2 years ago. The patient related this episode happened once previously and his 51-year-old brother has a pacemaker. A chest X-ray with 2 views and an EKG with rhythm strip were ordered (equipment owned by the urgent care center). The physician detected no obvious abnormalities, but the patient was advised to see a cardiologist within the next 2 - 3 days. The physician interpreted and provided a report for the rhythm strip and Chest X-ray. What CPT® and ICD9-CM codes are reported for the physician employed by the urgent care center who performed a Level 3 office visit in addition to the ancillary services? a. 99213-25, 71020, 93040, 780.4 c. 99283-25, 71010-26, 93010, 780.5 b. 99213-25, 71020-26, 93042, 780.4 d. 99203-25, 71010, 93000, 786.50 ANS: A Rationale: The patient is an established patient to an urgent care clinic. A code from 99211-99215 is reported. Level three is reported with 99213. Because an EKG was also performed, a modifier 25 is appended to the office visit. The X-ray & EKG equipment are owned by the clinic. The chest X-ray, 2 views, is reported with 71020. In the CPT® Index, look for X-ray/Chest. The EKG and rhythm strip are read, interpreted and a report is written by the physician. Modifiers 26 and TC are not appended to the radiology codes because the urgent care center owns the equipment and the radiologist is an employee of the urgent care center. In the CPT® Index, look for Electrocardiography/Rhythm/Tracing and Evaluation, you are referred to CPT® code 93040. The diagnosis is dizziness (780.4). In the ICD-9-CM Index to Diseases, look for Dizziness. PTS: 1 DIF: Difficult 105. 55-year-old male has had several episodes of tightness in the chest. His physician ordered a PTCA (percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty) of the left anterior descending coronary artery. The procedure revealed atherosclerosis in the native vessel. It was determined a stent would be required to keep the artery open. The stent was inserted during the procedure. a. 92928-LD, 414.01 c. 92920-LD, 92928, 414.01, 414.06 b. 92920-LD, 92929-59, 414.06 d. 92920-LD, 92928-59, 414.01 ANS: A Rationale: PTCA is a percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty. In the CPT® Index, look for Transcatheter/Placement/Intravascular Stents directing you to 92928-92929. In this case, the angioplasty was followed by stent placement in the LD. Only one procedure can be performed in each of the coronary vessels (LC, LD, and RC). The hierarchy beginning with the lowest is angioplasty, stent, atherectomy, atherectomy & stent placement. Only the stent placement (92928) is reported. Modifier LD indicates the left anterior descending coronary artery. In ICD-9-CM Index to Diseases, look for atherosclerosis and you are directed to see arteriosclerosis. Under Arteriosclerosis/coronary/native artery, you are directed to 414.01. Verification in the Tabular List confirms code selection. PTS: 1 DIF: Difficult 106. A pregnant female is Rh negative and at 28 weeks gestation. The child’s father is Rh positive. The mother is given an injection of a high-titer Rho (D) immune globulin, 300 mcg, IM. What CPT® and ICD-9-CM codes are reported? a. 90384, 96372, 656.13 c. 90384, 90471, 773.0 b. 90386, 96372, 656.13 d. 90386, 90471, 773.0 ANS: A Rationale: When a mother is Rh negative and the father is Rh positive, fetal hemolytic anemia may develop in the fetus. In the CPT® Index, look for Immune Globulins/Rho (D), you are directed to code range 90384-90386. A full dose is 300 mcg. Code 90384 is reported. According to the guidelines for Immune Globulins, an administration code is also reported. In the CPT® Index, look for Immune Globulin Administration/Injection directing you to 96372. The administration code for intramuscular injection is 96372. In the ICD-9-CM Index to Diseases, look for Rh antigen/incompatibility/affecting management of pregnancy, you are directed to 656.1x. A 5th digit of 3 is used to indicate this is an antepartum condition. PTS: 1 DIF: Difficult 107. A patient with hypertensive end stage renal failure, stage V, and secondary hyperparathyroidism is evaluated by the physician and receives peritoneal dialysis. The physician evaluates the patient once before dialysis begins. What CPT® and ICD-9-CM codes are reported? a. 90945, 401.9, 585.5, 588.81 c. 90945, 403.91, 585.6, 588.81 b. 90947, 403.91, 588.81 d. 90947, 403.91, 585.5 ANS: C Rationale: In the CPT® Index, look for Dialysis/Peritoneal, you are directed to codes 90945, 90947 & 4055F (an outcomes measurement code). The peritoneal dialysis with one physician evaluation is reported with 90945. A combination code is reported for a patient with hypertension and renal failure. The two conditions are not reported separately. In the Hypertension Table, look for Hypertension/with/chronic kidney disease/stage V or end stage renal disease/Unspecified column directs you to 403.91. The instructions for category 403 state to use an additional code to identify the stage of CKD. In the ICD-9-CM Index to Diseases, look for Disease/renal/end-stage, directing you to 585.6 for end stage renal disease. The patient also has secondary hyperparathyroidism reported with 588.81, found in the Index to Diseases under Hyperparathyroidism. PTS: 1 DIF: Difficult 108. A patient with congestive heart failure and chronic respiratory failure is placed on home oxygen. Prescribed treatment is 2 L nasal cannula oxygen at all times. A home care nurse visited the patient to assist with his oxygen management. What CPT® and ICD-9-CM codes are reported? a. 99503, 428.0, 518.83 c. 99504, 428.40, 518.83 b. 99503, 428.9, 518.82 d. 99503, 428.0, 518.82 ANS: A Rationale: In the CPT® Index, look for Home Services/Respiratory Management, you are directed to code 99503. In the ICD-9-CM Index to Diseases, look for Failure/heart/congestive and you are directed to 428.0. Then look for Failure/respiration/chronic, you are directed to 518.83. Confirmation in the Tabular List confirms code selection. PTS: 1 DIF: Difficult Medical Terminology 109. The meaning of the root “blephar/o” is: a. Choroid b. Sclera ANS: C PTS: 1 c. Eyelid d. Uvea DIF: Moderate 110. The meaning of heteropsia (or anisometropia) is: a. Blindness in half the visual field c. Unequal vision in the two eyes b. Double vision d. Blindness in both eyes ANS: C PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate 111. The radiology term “fluoroscopy” is described as: a. Technique using magnetism, radio waves and a computer to produce images b. An X-ray procedure allowing the visualization of internal organs in motion c. A scan using an X-ray beam rotating around the patient d. Use of high-frequency sound waves to image anatomic structures ANS: B PTS: 1 112. Sialography is an X-ray of : a. Sinuses b. Liver ANS: C PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate c. Salivary glands d. Ventricles of the brain DIF: Moderate 113. A projection is the path of the X-ray beam. If the projection is front to back it would be: a. Lateral c. Decubitis b. Recumbent d. Anteroposterior ANS: D PTS: 1 114. Cytopathology is the study of: a. Tissue b. Cells ANS: B PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate c. Blood d. Organs DIF: Moderate 115. The process of preserving cells or whole tissues at extremely low temperatures is known as: a. Cryotherapy c. Cryalgesia b. Cryopexy d. Cryopreservation ANS: D PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate 116. A gonioscopy is an examination of what part of the eye: a. Anterior chamber of the eye c. Lacrimal duct b. Interior surface of the eye d. Posterior segment ANS: A PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate Anatomy 117. Which cells produce hormones to regulate blood sugar? a. Eosinophils c. Hemoglobin b. Pancreatic islets d. Target cells ANS: B PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate 118. Which part of the brain controls blood pressure, heart rate and respiration? a. Cortex c. Cerebellum b. Cerebrum d. Medulla ANS: D PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate 119. What are chemicals which relay, amplify and modulate signals between a neuron and another cell? a. Neurotransmitters c. Interneurons b. Hormones d. Myelin ANS: A PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate 120. Which of the following conditions results from an injury to the head? The symptoms include headache, dizziness and vomiting. a. Meningitis c. Concussion b. Parkinson’s disease d. Epilepsy ANS: C PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate 121. Lacrimal glands are responsible for which of the following? a. Production of tears c. Production of vitreous b. Production of zonules d. Production of mydriatic agents ANS: A PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate 122. Which of the following does NOT contribute to refraction in the eye? a. Aqueous c. Cornea b. Macula d. Lens ANS: B PTS: 1 123. A patient diagnosed with glaucoma has: a. A lens that is no longer clear b. Bleeding vessels on the retina ANS: C PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate c. Abnormally high intraocular pressure d. Corneal neovascularization DIF: Moderate 124. Which of the following is true about the tympanic membrane? a. It separates the middle ear from the inner ear b. It separates the external ear from the middle ear c. It sits within the middle ear d. It sits within the inner ear ANS: B PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate ICD-9-CM 125. Use both ____ and ____ when locating and assigning a diagnosis code. a. Alphabetic Index and Appendix C c. ICD-9-CM code book and Dictionary b. Alphabetic Index and Tabular List d. Tabular List and Index to Procedures ANS: B Rationale: According to the ICD-9-CM guidelines Section 1.B.1 both Alphabetical Index and Tabular List are used to locate and assign a code. Reliance on only using the Alphabetic Index or the Tabular List will lead to errors and less specificity in reporting codes. PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate 126. When a patient has a condition that is both acute and chronic and there are separate entries for both, how is it reported? a. Code only the acute code c. Code both sequencing the acute first b. Code both sequencing the chronic first d. Code only the chronic code ANS: C Rationale: According to the ICD-9-CM Section 1.B.10 coding guidelines, if the same condition is described as both acute (subacute) and chronic, and separate entries exist in the Alphabetic Index at the same indentation level, code both and sequence the acute (subacute) first. PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate 127. A patient with chronic back and neck pain developed a drug dependency on oxycodone (opoid). After being taken off the drug, he was seen in the clinic for withdrawal symptoms. What ICD-9-CM codes are reported? a. 305.50, 292.0, E935.2 c. 292.0, 304.00, E935.2 b. 292.0, 305.50, E935.2 d. 304.00, 292.0, E935.2 ANS: C Rationale: Withdrawal symptoms are a result of unpleasant effects upon the body when there is a sudden discontinuation/separation of drugs and/or alcohol. In the Index to Diseases (Alphabetic Index) locate Withdrawal symptoms, syndrome/drug or narcotic. You are directed to code 292.0. In the Tabular List code 292.0 identifies Drug withdrawal. In the Tabular List there is a note under category code 292 stating to use an additional code for drug dependence and an E code to identify the drug. In the Index to Diseases (Alphabetic Index) locate Dependence/oxycodone. You’re directed to 304.0. In the Tabular List, use 5th digit ‘0’ for unspecified use. The patient took the medication for therapeutic reasons which had lead to a drug dependency. Look in the Table of Drugs for Opiates, opioids, opium. Use the code from the Therapeutic column (E935.2). PTS: 1 DIF: Difficult 128. A patient with metastatic bone cancer (primary site unknown) presents to the oncologist’s office for a chemotherapy treatment. On examination, the oncologist finds the patient to be severely dehydrated and cancels the chemotherapy. The patient will receive intravenous hydration in the office and reschedule the chemotherapy treatment. What ICD-9-CM codes are reported? a. 170.9, 276.51, 199.1 c. 198.5, 276.51 b. 276.51, 198.5, 199.1 d. 276.51, 199.1, 198.5 ANS: B Rationale: Per ICD-9-CM Guidelines, Section I.C.2.c.3, when the admission/encounter is for management of dehydration due to the malignancy or therapy, or a combination of both, and only the dehydration is being treated (intravenous hydration); the dehydration is sequenced first, followed by the code(s) for the malignancy. When information is not available about the primary site of the cancer, the secondary site is coded first followed by code 199.1. In the Index to Diseases (Alphabetic Index), look for Dehydration 276.51. Look in the Index to Diseases (Alphabetic Index), in the Neoplasm Table for Neoplasm, neoplastic/bone. Use the code from the secondary column (198.5). Then look in the Neoplasm Table for unknown or unspecified site and use the code from the primary column (199.1). PTS: 1 DIF: Difficult 129. 22-year-old developed gas gangrene (gas bacillus infection) and went into septic shock after a surgical procedure. What ICD-9-CM codes should be reported? a. 995.92, 998.02, 040.0 c. 785.52, 995.92 b. 785.52, 040.0 d. 040.0, 998.02, 995.92 ANS: D Rationale: Per ICD-9-CM Guidelines, Section I.C.1.b.6.(a), for cases of septic shock, the code for the systemic infection should be sequenced first, followed by codes 995.92, Severe sepsis and 785.52, Septic shock or 998.02, Postoperative septic shock. For the systemic infection, look in the Index to Diseases (Alphabetic Index) for Gangrene, gangrenous/gas (bacillus) 040.0. Look in the Index to Diseases (Alphabetic Index) for Shock/septic/due to surgical procedure 998.02. In the Tabular List, there is an instruction to code first the underlying infection (040.0) and to use an additional code to identify the severe sepsis (995.92). PTS: 1 DIF: Difficult 130. A patient with hypertensive heart disease is now experiencing accelerated hypertension due to papillary muscle dysfunction. What ICD-9-CM code(s) should be reported? a. 402.00 c. 401.0, 429.81 b. 402.00, 429.81 d. 404.00, 429.81 ANS: A Rationale: Per ICD-9-CM guidelines, Section I.C.7.a.2, Heart conditions (425.8, 429.0-429.3, 429.8, 429.9) are assigned from category 402 when a casual relationship is stated (due to hypertension or implied (hypertensive). The same heart conditions with hypertension, but without a stated causal relationship, are coded separately. In the Index to Diseases (Alphabetic Index), look for Hypertension/accelerated (See also Hypertension, by type, malignant); Hypertension/heart/malignant guides you to code 402.00. This will be the only code to report since there is a casual relationship between the hypertension and the heart disease. PTS: 1 DIF: Difficult 131. A three-year-old is brought to the burn unit after pulling a pot of hot soup off the stove spilling onto to her body. She sustained 18% second degree burns on her legs and 20% third degree burns on her chest and arms. Total body surface area burned is 38%. What ICD-9-CM codes should be reported for the burns (do not include E codes for the accident)? a. 945.20, 943.30, 945.20, 948.33 c. 942.32, 943.30, 945.20, 948.32 b. 942.32, 943.30, 945.20, 948.33 d. 945.20, 943.30, 945.20, 948.12 ANS: C Rationale: ICD-9-CM Coding guideline I.C.17.c.1.a states to sequence first the code that reflects the highest degree of burn when more than one burn is present. In this case, the burns on her chest and arms are third degree and should be reported first. In the Index to Diseases, look for Burn/chest wall (anterior)/third degree referring you to code 942.32; Burn/arm(s)/ third degree guiding you to code 943.30; Burn/legs/second degree guiding you to code 945.20. Refer to ICD-9-CM guideline Section I.C.17.c.6 for instructions on assigning a code from category 948. The fourth digit represents the total body surface area (all degrees) that was burned. The fifth digit represents the percentage of third degree burns to the body. In the scenario 38% is documented as the TBSA, making 3 as the fourth digit; 20% is third degree burns making 2 as the fifth digit. E codes would also be reported for the accident. PTS: 1 DIF: Difficult 132. Newborn twin girls delivered at 27 weeks, weighing 850 grams for twin A and 900 grams for twin B. Both were diagnosed with extreme immaturity. What ICD-9-CM codes should be reported for both twins? a. 765.03, V32.00 c. 765.13, 765.24, V31.00 b. V31.00, 765.03, 765.24 d. V32.00, 765.13, 765.24 ANS: B Rationale: ICD-9-CM Guidelines I.C.15.b Use of codes V30-V39: When coding the birth of an infant, assign a code from categories V30-V39, according to the type of birth. A code from this series is assigned as a principal diagnosis, and assigned only once to a newborn at the time of birth. V31.00 is assigned to indicate twin with live born mate, indicating the two babies were live born. The V code is indexed under Newborn/twin NEC/mate liveborn/born in the hospital. Code 765.03 is assigned for extreme immaturity with weight between 750-999 grams. This code is indexed under Immaturity/extreme referring you to subcategory code 765.0x; fifth digit 3 to indicate both babies being between 750-999 grams. In the Tabular List, there is an instructional note under subcategory code 765.0x to use an additional code for weeks of gestation (765.20-765.29). Code 765.24 indicates 27 weeks gestation. PTS: 1 DIF: Difficult 133. Baby boy is born by cesarean section in the hospital. The mother has a history of diabetes mellitus, which complicated the management of her pregnancy. In addition, the mother abused cocaine throughout her pregnancy. The newborn was monitored for drug withdrawal, however no symptoms were noted and the toxicology report came back negative. ABO incompatibility was documented, but the Coomb's test was negative. What ICD-9-CM codes should be reported for the newborn’s record? a. 648.03, 250.00, 648.43, 305.60. V30.01 c. V30.01, 775.0, V29.8 b. V30.01, V29.8 d. 779.5, 773.1, V30.01 ANS: B Rationale: According to ICD-9-CM Guidelines 1.C.11.a.2, Chapter 11 codes (630-679) are only used on the maternal record. Code V30.X is coded as a principal/first listed code to report the type of birth. This is found in the Index to Diseases by looking for Newborn/single/born in hospital/with cesarean delivery or section. Because the newborn was observed for effects of the maternal drug use, look in the Index to Diseases for Observation/suspected/condition/newborn/specified NEC. Report codes V30.01 and V29.8 since the other conditions were not present or treated. PTS: 1 DIF: Difficult 134. The diagnostic statement indicates respiratory failure due to administering incorrect medication. Valium was administered instead of Xanax. What ICD-9-CM codes should be reported? a. 969.4, 518.81, E962.0 c. 969.4, 518.81, E853.2 b. 518.81, 969.4, E939.4 d. E939.4, 969.4, 518.81 ANS: C Rationale: Poisoning codes are sequenced by 1) poison code, 2) the condition or manifestation and 3) the E code to describe the external cause. ICD-9-CM guideline Section I.C.17.e.2.(a), states, “Errors made in drug prescription or in the administration of the drug by provider, nurse, patient, or other person, use the appropriate poisoning code from the 960-979 series.” In the Table of Drugs and Chemicals find Valium and use the code from the poisoning column which is 969.4. The manifestation is respiratory failure; in the Index to Diseases find Failure/respiration, respiratory which refers you to 518.81. The E code is found the Table of Drugs and Chemicals by finding Valium and using the code from the Accident column; E853.2. PTS: 1 DIF: Difficult HCPCS 135. How many days does it take for CMS to implement HCPCS Level II Temporary Codes that have been reported as added, changed, or deleted? a. 365 b. 90 c. 30 d. 60 ANS: B Rationale: Per CMS Temporary codes can be added, changed, or deleted on a quarterly basis. Once established, temporary codes are usually implemented within 90 days, the time needed to prepare and issue implementation instructions and to enter the new code into CMS's and the contractors' computer systems and initiate user education. This time is needed to allow for instructions such as bulletins and newsletters to be sent out to suppliers to provide them with information and assistance regarding the implementation of temporary CMS codes. http://www.cms.hhs.gov/MedHCPCSGenInfo/Downloads/LevelIICodingProcedures.pdf PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate 136. What temporary HCPCS Level II codes are required for use by Outpatient Prospective Payment System (OPPS) Hospitals? a. C codes c. H codes b. G codes d. Q codes ANS: A Rationale: Outpatient PPS (C1300-C9899) Guideline explains C codes are required for use by Outpatient Prospective Payment System (OPPS) Hospitals to report new technology procedures, medical devices, drugs, biologicals, and radiopharmaceuticals; that do not have other HCPCS codes assigned. Other facilities may report C-codes at their discretion. PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate 137. What agency maintains and distributes HCPCS Level II codes? a. AMA c. HIPAA b. CMS d. CPT® Assistant ANS: B Rationale: CMS has been delegated to maintain and distribute HCPCS Level II codes. PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate 138. HCPCS Level II includes code ranges which consist of what type of codes? a. Category II codes, temporary national codes, and miscellaneous codes. b. Dental codes, morphology codes, miscellaneous codes, and permanent national codes. c. Permanent national codes, dental codes, category II codes. d. Permanent national codes, miscellaneous codes, and temporary national codes. ANS: D Rationale: HCPCS Level II codes consist of permanent national codes, miscellaneous codes, and temporary national codes. PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate 139. How often is HCPCS Level II permanent national codes updated? a. annually c. bi-annually b. quarterly d. three times a year ANS: A Rationale: Permanent national codes are updated once a year in January. PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate Coding Guidelines 140. What does “non-facility” describe when calculating Physician Fee Schedule payments? a. hospitals b. nursing homes c. non-hospital owned physician practices d. hospital owned physician practices ANS: C Rationale: “Non-facility” location calculations are for private practices or non-hospital-owned physician practices. Reimbursement is higher for private practices because the practice incurs the full expense of providing the service. PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate 141 . What three components are considered when Relative Value Units are established? a. Physician work, Practice expense, Malpractice Insurance b. Geographic region, Practice expense, Malpractice Insurance c. Geographic region, Conversion factor, Physician fee schedule d. Physician work, Physician fee schedule, Conversion factor ANS: A Rationale: Per CMS - Relative value units (RVUs) – RVUs capture the three following components of patient care: Physician work RVU, Practice Expense RVU, and Malpractice RVUs. PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate 142. CPT® Category III codes are reimbursable at what level of reimbursement? a. 10 percent b. 100 percent c. 85 percent d. Reimbursement, if any, is determined by the payer ANS: D Rationale: Per AMA, no relative value units (RVUs) are assigned to these codes. Payment for these services or procedures is based on the policies of payers. PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate 143. The Surgical Global Package applies to services performed in what setting? a. Hospitals c. Physician’s offices b. Ambulatory Surgical Centers d. All of the above ANS: D Rationale: The Medicare approved amount for surgery includes the following services when furnished by the physician who performs the surgery. The services included in the global surgical package may be furnished in any setting, eg, in hospitals, ASCs, and physicians' offices. Visits to a patient in an intensive or critical care unit are also included if made by the surgeon. PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate 144. What surgical status indicator represents the Surgical Global Package for endoscopic procedures (without an incision)? a. XXX c. 000 b. 010 d. 090 ANS: C Rationale: Per CMS Internet-only manuals (IOM) Medicare Claims Processing Manual – surgical status indicator 000 = Endoscopic or minor procedure with related preoperative and postoperative relative values on the day of the procedure only included in the fee schedule payment amount; evaluation and management services on the day of the procedure generally not payable. PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate 145. Which statement is TRUE regarding the Instruction for use of the CPT® codebook? a. Use an unlisted code when a procedure is modified. b. Parenthetical instructions define each code listed in the codebook. c. Select the name of the procedure or service that most closely approximates the procedure or service performed. d. Select the name of the procedure or service that accurately identifies the service performed. ANS: D Rationale: CPT® Instructions for the use of the CPT® codebook include “select the name of the procedure or service that accurately identifies the service performed.” PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate Practice Management 146. The Medicare program is made up of several parts. Which part is most significant to coders working in physician offices and covers physician fees without the use of a private insurer? a. Part A c. Part C b. Part B d. Part D ANS: B Rationale: Medicare Part B helps to cover medically-necessary doctors’ services, outpatient care, and other medical services (including some preventive services) not covered under Medicare Part A. Medicare Part B is an optional benefit for which the patient must pay a premium, and which requires a yearly copay. Medicare Part B is the most significant portion of the Medicare program for coders working in physician offices. PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate 147. If an NCD doesn’t exist for a particular service/procedure performed on a Medicare patient, who determines coverage? a. To determine new codes under Current Procedural Terminology (CPT) b. Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) c. Medicare Administrative Contractor (MAC) d. The patient ANS: C Rationale: If an NCD doesn’t exist for a particular item, it’s up to the MAC to determine coverage. According to CMS guidelines (www.cms.gov/transmittals/downloads/R2NCD1.pdf), “Where coverage of an item or service is provided for specified indications or circumstances but is not explicitly excluded for others, or where the item or service is not mentioned at all in the CMS Manual System, the Medicare contractor is to make the coverage decision, in consultation with its medical staff, and with CMS when appropriate, based on the law, regulations, rulings and general program instructions.” PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate 148. Local Coverage Determinations are administered by ____? a. Each regional MAC c. LMRP’s b. NCD’s d. State Law ANS: A Rationale: Each Medicare Administrative Contractor (MAC) is then responsible for interpreting national policies into regional policies PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate 149. When are providers responsible for obtaining an ABN for a service not considered medically necessary? a. After providing a service or item to a beneficiary b. Prior to providing a service or item to a beneficiary c. During a procedure or service d. After a denial has been received from Medicare ANS: B Rationale: Providers are responsible for obtaining an ABN prior to providing the service or item to a beneficiary. PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate 150. HIPAA was made into law in what year? a. 1992 b. 1995 c. 1997 d. 1996 ANS: D Rationale: HIPAA was adopted into law in 1996 PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate