Blood cells, Dr Amam
advertisement

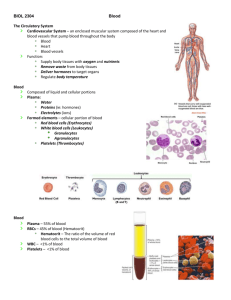
Blood Cells Dr. Amam Ali Amam PhD: Periodontal Disease Blood Cells consists of 1- The cells 2- fluid Blood flow within the closed circulatory system. The blood is a special connective tissue (fluid). ( 5.5 Liter in a man) Different blood cells Fluid medium – Plasma Plasma proteins + inorganic salts Blood Cells, Functions: 1- Transport of Gases (O2, CO2). 2- Transports Nutrients from their site of absorption to various areas of organs 3- Transports cells and hormones 4- Metabolic waste products cells and hormones Blood cell types 1- Red blood cells - ERYTHROCYTES (transport of oxygen and carbon dioxide) 2- White blood cells - LEUKOCYTES: defense and immune systems 3- Platelets - THROMBOCYTES control of bleeding ( haemostasis ) The clot blood contains: 1- Formed Elements 2- Serum clear yellow liquid 1- The lower layer represents 42-47% of the entire volume of blood in the hematocrit tube. (It is Red and is made up of Erythrocytes ) 2- The layer immediately above (1 % of blood volume), which is white or grayish in color, is called buffy coat and consists of Leukocytes. Composition of Plasma 1-Substances of low or high molecular weight that make up 10% of its volume. 2- The main plasma proteins are (7% of the volume): albumin , globulins (α,β,γ), lipoproteins , prothrombin and fibrinogen (that participate in blood coagulation ). Albumin: the most abundant component, has a fundamental role in maintaining the osmotic pressure of the blood. 3- The remainder of the 10% consists of several organic compounds (eg, amino acids, vitamins, hormones, lipoproteins of various origins). Methods of studying & staining - Smear for blood , aspirate for bone marrow. - Giemsa , Wright’s or Leishman’s method. Erythrocytes • biconcave disc shape without nuclei or cytoplasmic organelles • diameter 7.2 µm, 0.8 µm in diameter. • Concen : ♂ 4.1 – 6 million \ mm3 ♀ 3,9 – 5.5 million \ mm3 • lifespan: 120 days . 95% haemoglobin Haemo = porphyrine + Fe Globin : α β γ δ Haemoglobin - ♂ 15 – 18 g\100 ml, ♀ 14,5 g\100 m Leukocytes are divided into 2 groups:s 1- Granulocytes 2- Agranulocytes Polymorphonuclear Leukocytes Mononuclear Leukocytes Neutrophils Lymphocytes Eosinophils Monocytes Basophils Granulocytes • cytoplasmic secretory granules • single multilobed nucleus • polymorphonuclear leukocytes or polymorph Neutrophils (Polymorphonuclear Leukocytes) constitute 60-70% of circulating leukocytes. diameter : 12-15 µm (in blood smears), A nucleus: consisting of 2 to 5 (usually three) lobes linked by fine threads of chromatin . Function: Phagocytosis of bacteria. short-lived cells with a half-life of 6-7 h in blood and a life span of 1-4 days in connective tissues Barr body ,visible in 3% of neutrophils of females Eosinophils (Polymorphonuclear Leukocytes) Constituting only 2-4 % of leukocytes in normal blood. Size: the same size of a neutrophil diameter : 12-15 µm (in blood smears), A nucleus: contains a characteristic bilobed nucleus. a crystalline core. Function: Defense against parasitic helminths, Basophils (Polymorphonuclear Leukocytes) Less than 1 % of leukocytes in normal blood. diameter : 12-15 µm (in blood smears), The nucleus: is divided into irregular lobes. Function: Release of histamine & other inflammation mediators. Main products: specific granules (0.5 µm in diameter) containing histamine and heparin. Lymphocytes Less than 1 % of leukocytes in normal blood. diameter : the small 6-8 µm the large 18 µm the small Lymphocytes has a spherical nucleus The cytoplasma is scanty, it appears as a thin rim around the nucleus.it has mitochondria and a small Golgi complex Function: Generate of antibody Main products:Immunoglobulines. Monocytes Diameter: It’s the largest 12-20 µm 5 % of leukocytes in normal blood. The nucleus is oval, horseshoe or kidney shaped. : The cytoplasm is basophilic , containing very fine azurophilic granules (lysosomes). Golgi complex Function: Generation of mononuclear-phagocyte system cells in tissues, phagocytosis and digestion of protozoa and virus and senescent cells. Main products: Granules with lysosomal enzymes Platelets, (thrombocytes) Diameter: It’s 2-4 µm. platelet counts : 200,000 to 400,000 per microliter of blood. Life span : about 10 days. Function: promote blood clotting and help repair gaps in the walls of blood vessels, preventing loss of blood. Central granular cytoplasm, Peripheral poorly stained cytoplasm . Main products: Blood-clotting factors. Main functions: Clotting of blood.