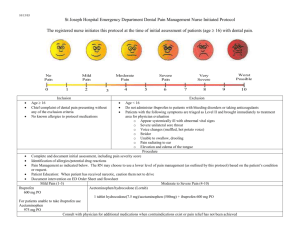
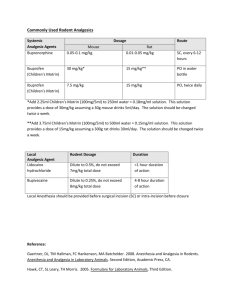
ibuprofen (oral) (eye-byoo-proe-fen) ibuprofen (injection)
advertisement

Name /bks_53161_deglins_md_disk/ibuprofen 03/11/2014 08:20AM Plate # 0-Composite pg 1 # 1 TIME/ACTION PROFILE 1 ROUTE ibuprofen (oral) (eye-byoo-proe-fen) Advil, Advil Migraine Liqui-Gels, Children’s Advil, Children’s Motrin, Excedrin IB, Junior Strength Advil, Medipren, Midol Maximum Strength Cramp Formula, Motrin, Motrin Drops, Motrin IB, Motrin Junior Strength, Motrin Migraine Pain, Nuprin, PediaCare Children’s Fever PEAK DURATION 2–4 hr 1–2 hr 1–2 wk unknown 10–12 hr† 6–8 hr 4–6 hr unknown 6 hr 4–6 hr † With repeated dosing. ibuprofen (injection) Caldolor, NeoProfen (ibuprofen lysine) Classification Therapeutic: antipyretics, antirheumatics, nonopioid analgesics, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agents Pharmacologic: nonopioid analgesics Pregnancy Category C (up to 30 wk gestation), D (starting at 30 wk gestation) Indications PO, IV: Treatment of: Mild to moderate pain, Fever. PO Treatment of: Inflammatory disorders including rheumatoid arthritis (including juvenile) and osteoarthritis, Dysmenorrhea. IV Moderate to severe pain with opioid analgesics. Closure of a clinically significant PDA in neonates weighing 500– 1500 g and ⱕ32 weeks gestational age (ibuprofen lysine only) Action Inhibits prostaglandin synthesis. Therapeutic Effects: Decreased pain and inflammation. Reduction of fever. Pharmacokinetics Absorption: Oral formulation is well absorbed (80%) from the GI tract; IV administration results in complete bioavailability. Distribution: Does not enter breast milk in significant amounts. Protein Binding: 99%. Metabolism and Excretion: Mostly metabolized by the liver; small amounts (1%) excreted unchanged by the kidneys. Half-life: Neonates: 26– 43 hr; Children: 1– 2 hr; Adults: 2– 4 hr. ⫽ Canadian drug name. ONSET PO (antipyretic) 0.5–2.5 hr PO (analgesic) 30 min PO (anti-inflammatory) ⱕ7 days IV (analgesic) unknown IV (antipyretic) within 2 hr ⫽ Genetic Implication. Contraindications/Precautions Contraindicated in: Hypersensitivity (cross-sensitivity may exist with other NSAIDs, including aspirin); Active GI bleeding or ulcer disease; Chewable tablets contain aspartame and should not be used in patients with phenylketonuria; Peri-operative pain from coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) surgery; OB: Avoid after 30 wk gestation (may cause premature closure of fetal ductus arteriosus); Pedi: Ibuprofen lysine: Preterm neonates with untreated infection, congenital heart disease where patency of PDA is necessary for pulmonary or systemic blood flow, bleeding, thrombocytopenia, coagulation defects, necrotizing enterocolitis, significant renal dysfunction. Use Cautiously in: Cardiovascular disease (mayqrisk of cardiovascular events); Renal or hepatic disease, dehydration, or patients on nephrotoxic drugs (mayqrisk of renal toxicity); Aspirin triad patients (asthma, nasal polyps, and aspirin intolerance); can cause fatal anaphylactoid reactions; Geri:qrisk of adverse reactions secondary to age-relatedpin renal and hepatic function, concurrent illnesses, and medications; Chronic alcohol use/abuse; Coagulation disorders; OB: Use cautiously up to 30 wk gestation; avoid after that; Lactation: Use cautiously; Pedi: Safety not established for infants ⬍6 mo (oral) and children ⬍17 yr (IV Caldolor); Ibuprofen lysine: Hyperbilirubinemia in neonates (may displace bilirubin from albumin-binding sites). Exercise Extreme Caution in: History of GI bleeding or GI ulcer disease. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects CNS: headache, dizziness, drowsiness, intraventricular hemorrhage (ibuprofen lysine), psychic disturbances. EENT: amblyopia, blurred vision, tinnitus. CV: arrhythmias, edema, hypertension. GI: GI BLEEDING, HEPATITIS, constipation, dyspepsia, nausea, necrotizing enterocolitis (ibuprofen lysine), vomiting, abdominal discomfort. GU: cystitis, hematuria, renal failure. Derm: EXFOLIATIVE DERMATITIS, CAPITALS indicate life-threatening, underlines indicate most frequent. Strikethrough ⫽ Discontinued. PDF Page #1 Name /bks_53161_deglins_md_disk/ibuprofen 03/11/2014 08:21AM 2 STEVENS-JOHNSON SYNDROME, TOXIC EPIDERMAL NECROLYSIS, rashes, injection site reac- tion. Hemat: anemia, blood dyscrasias, prolonged bleeding time. Misc: allergic reactions including ANAPHYLAXIS. Interactions Drug-Drug: May limit the cardioprotective effects of low-dose aspirin. Concurrent use with aspirin maypeffectiveness of ibuprofen. Additive adverse GI side effects with aspirin, oral potassium, other NSAIDs, corticosteroids, or alcohol. Chronic use with acetaminophen mayqrisk of adverse renal reactions. Maypeffectiveness of diuretics, ACE inhibitors, or other antihypertensives. Mayqhypoglycemic effects of insulin or oral hypoglycemic agents. Mayqserum lithium levels and risk of toxicity.qrisk of toxicity from methotrexate. Probenecidqrisk of toxicity from ibuprofen.qrisk of bleeding with cefotetan, cefoperazone, corticosteroids, valproic acid, thrombolytics, warfarin, and drugs affecting platelet function including clopidogrel, ticlopidine, abciximab, eptifibatide, or tirofiban.qrisk of adverse hematologic reactions with antineoplastics or radiation therapy.qrisk of nephrotoxicity with cyclosporine. Drug-Natural Products:qbleeding risk with, arnica, chamomile, feverfew, garlic, ginger, ginkgo, Panax ginseng, and others. Plate # 0-Composite Pediatric OTC Dosing PO (Children 11 yr/72– 95 lb): 300 mg q 6– 8 hr. PO (Children 9– 10 yr/60– 71 lb): 250 mg q 6– 8 hr. PO (Children 6– 8 yr/48– 59 lb): 200 mg q 6– 8 hr. PO (Children 4– 5 yr/36– 47 lb): 150 mg q 6– 8 hr. PO (Children 2– 3 yr/24– 35 lb): 100 mg q 6– 8 hr. PO (Children 12– 23 mo/18– 23 lb): 75 mg q 6– 8 hr. PO (Infants 6– 11 mo/12– 17 lb): 50 mg q 6– 8 hr. PDA Closure IV (Neonates Gestational age ⱕ32 weeks, 500– 1500 g): 10 mg/kg followed by two doses of 5 mg/kg at 24 and 48 hr after initial dose. NURSING IMPLICATIONS Assessment ● Patients who have asthma, aspirin-induced allergy, and nasal polyps are ● Route/Dosage Analgesia PO (Adults): Anti-inflammatory— 400– 800 mg 3– 4 times daily (not to exceed 3200 mg/day). Analgesic/antidysmenorrheal/antipyretic— 200– 400 mg q 4– 6 hr (not to exceed 1200 mg/day). PO (Children 6 mo– 12 yr): Anti-inflammatory— 30– 50 mg/kg/day in 3– 4 divided doses (maximum dose: 2.4 g/day). Antipyretic— 5 mg/kg for temperature ⬍102.5⬚F (39.17⬚C) or 10 mg/kg for higher temperatures (not to exceed 40 mg/kg/ day); may be repeated q 4– 6 hr. Cystic fibrosis (unlabeled)— 20– 30 mg/kg/day divided twice daily. PO (Infants and Children): Analgesic— 4– 10 mg/kg/dose q 6– 8 hr. IV (Adults): Analgesic— 400– 800 mg q 6 hr as needed (not to exceed 3200 mg/ day); Antipyretic— 400 mg initially, then 400 mg q 4– 6 hr or 100– 200 mg q 4 hr as needed (not to exceed 3200 mg/day). pg 2 # 2 ● ● ● ● ● ● at increased risk for developing hypersensitivity reactions. Assess for rhinitis, asthma, and urticaria. Assess for signs and symptoms of GI bleeding (tarry stools, lightheadedness, hypotension), renal dysfunction (elevated BUN and creatinine levels, decreased urine output), and hepatic impairment (elevated liver enzymes, jaundice). Geri: Higher risk for poor outcomes or death from GI bleeding. Age-related renal impairment increases risk of hepatic and renal toxicity. Assess patient for skin rash frequently during therapy. Discontinue ibuprofen at first sign of rash; may be life-threatening. Stevens-Johnson syndrome or toxic epidermal necrolysis may develop. Treat symptomatically; may recur once treatment is stopped. Pain: Assess pain (note type, location, and intensity) prior to and 1– 2 hr following administration. Arthritis: Assess pain and range of motion prior to and 1– 2 hr following administration. Fever: Monitor temperature; note signs associated with fever (diaphoresis, tachycardia, malaise). PDA Closure: Monitor preterm neonates for signs of bleeding, infection and decreased urine output. Monitor IV site for signs of extravasation. Lab Test Considerations: BUN, serum creatinine, CBC, and liver function tests should be evaluated periodically in patients receiving prolonged therapy. 䉷 2015 F.A. Davis Company CONTINUED PDF Page #2 Name /bks_53161_deglins_md_disk/ibuprofen 03/11/2014 08:21AM Plate # 0-Composite pg 3 # 3 3 Patient/Family Teaching CONTINUED ibuprofen (injection) ● Instruct patient to take medication as directed. Take missed doses as soon as re- ● Advise patients to take ibuprofen with a full glass of water and to remain in an up- right position for 15– 30 min after administration. ● Serum potassium, BUN, serum creatinine, alkaline phosphatase, LDH, AST, and ALT may showqlevels. Blood glucose, hemoglobin, and hematocrit concentrations, leukocyte and platelet counts, and CCr may bep. ● May cause prolonged bleeding time; may persist for ⬍1 day following discontinuation. ● Potential Nursing Diagnoses ● Acute pain (Indications) Impaired physical mobility (Indications) Ineffective thermoregulation (Indications) ● Implementation ● Do not confuse Motrin (ibuprofen) with Neurontin (gabapentin). ● Administration of higher than recommended doses does not provide increased pain relief but may increase incidence of side effects. ● ● ● ● Patient should be well hydrated before administration to prevent renal adverse re- actions. Do not give to neonates with urine output ⬍ 0.6 mL/kg/hour. ● Use lowest effective dose for shortest period of time, especially in the elderly. ● Coadministration with opioid analgesics may have additive analgesic effects and may permit lower opioid doses. ● PO: For rapid initial effect, administer 30 min before or 2 hr after meals. May be administered with food, milk, or antacids to decrease GI irritation. Tablets may be crushed and mixed with fluids or food; 800-mg tablet can be dissolved in water. ● Dysmenorrhea: Administer as soon as possible after the onset of menses. Prophylactic treatment has not been shown to be effective. IV Administration ● Intermittent Infusion: Diluent: 0.9% NaCl, D5W, or LR. Concentration: Ibuprofen injection: Dilute the 800 mg dose in at least 200 mL and the 400 mg dose in at least 100 mL for a concentration of 4 mg/mL. Ibuprofen lysine: Dilute in appropriate volume of D5W or 0.9%NaCl and infuse over 15 minutes Do not administer solutions that are discolored or contain particulate matter. Stable for up to 24 hr at room temperature. Rate: Infuse over at least 30 min. ⫽ Canadian drug name. ⫽ Genetic Implication. ● ● membered but not if almost time for next dose. Do not double doses. Pedi: Teach parents and caregivers to calculate and measure doses accurately and to use measuring device supplied with product. May cause drowsiness or dizziness. Advise patient to avoid driving or other activities requiring alertness until response to medication is known. Caution patient to avoid the concurrent use of alcohol, aspirin, acetaminophen, and other OTC or herbal products without consulting health care professional. Advise patient to inform health care professional of medication regimen prior to treatment or surgery. Instruct patients not to take OTC ibuprofen preparations for more than 10 days for pain or more than 3 days for fever, and to consult health care professional if symptoms persist or worsen. Many OTC products contain ibuprofen; avoid duplication. Caution patient that use of ibuprofen with 3 or more glasses of alcohol per day may increase the risk of GI bleeding. Advise patient to consult health care professional if rash, itching, visual disturbances, tinnitus, weight gain, edema, epigastric pain, dyspepsia, black stools, hematemasis, persistent headache, or influenza-like syndrome (chills, fever, muscle aches, pain) occurs. Pedi: Advise parents or caregivers not to administer ibuprofen to children who may be dehydrated (can occur with vomiting, diarrhea, or poor fluid intake); dehydration increases risk of renal dysfuntion. Advise female patients to notify health care professional if pregnancy is planned or suspected. Evaluation/Desired Outcomes ● Decrease in severity of pain. ● Improved joint mobility. Partial arthritic relief is usually seen within 7 days, but maximum effectiveness may require 1– 2 wk of continuous therapy. Patients who do not respond to one NSAID may respond to another. ● Reduction in fever. Why was this drug prescribed for your patient? CAPITALS indicate life-threatening, underlines indicate most frequent. Strikethrough ⫽ Discontinued. PDF Page #3