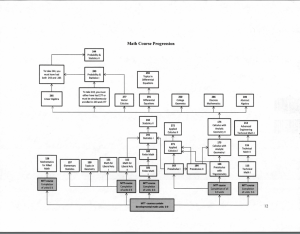
Curriculum table E
advertisement
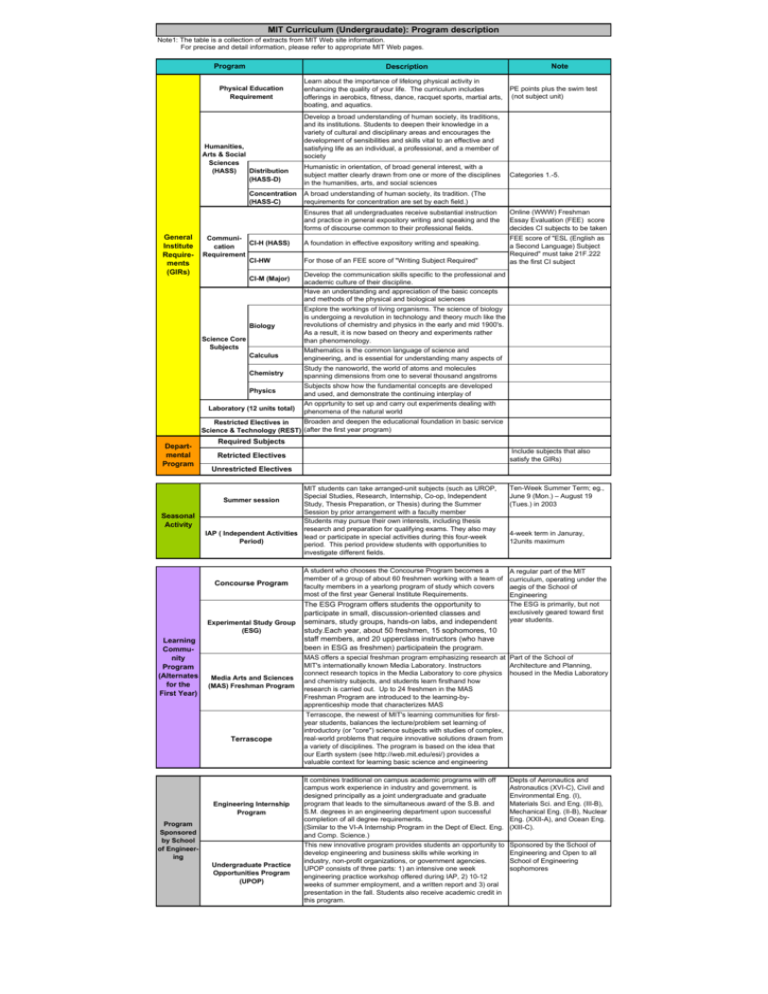
MIT Curriculum (Undergraudate): Program description Note1: The table is a collection of extracts from MIT Web site information. For precise and detail information, please refer to appropriate MIT Web pages. Program Description Physical Education Requirement Humanities, Arts & Social Sciences Distribution (HASS) (HASS-D) Concentration (HASS-C) Learn about the importance of lifelong physical activity in enhancing the quality of your life. The curriculum includes offerings in aerobics, fitness, dance, racquet sports, martial arts, boating, and aquatics. CommuniCI-H (HASS) cation Requirement CI-HW CI-M (Major) Humanistic in orientation, of broad general interest, with a subject matter clearly drawn from one or more of the disciplines in the humanities, arts, and social sciences A foundation in effective expository writing and speaking. For those of an FEE score of "Writing Subject Required" Online (WWW) Freshman Essay Evaluation (FEE) score decides CI subjects to be taken FEE score of "ESL (English as a Second Language) Subject Required" must take 21F.222 as the first CI subject Develop the communication skills specific to the professional and academic culture of their discipline. Have an understanding and appreciation of the basic concepts and methods of the physical and biological sciences Biology Calculus Mathematics is the common language of science and engineering, and is essential for understanding many aspects of Chemistry Study the nanoworld, the world of atoms and molecules spanning dimensions from one to several thousand angstroms Physics Subjects show how the fundamental concepts are developed and used, and demonstrate the continuing interplay of Laboratory (12 units total) Categories 1.-5. A broad understanding of human society, its tradition. (The requirements for concentration are set by each field.) Explore the workings of living organisms. The science of biology is undergoing a revolution in technology and theory much like the revolutions of chemistry and physics in the early and mid 1900's. As a result, it is now based on theory and experiments rather than phenomenology. Science Core Subjects PE points plus the swim test (not subject unit) Develop a broad understanding of human society, its traditions, and its institutions. Students to deepen their knowledge in a variety of cultural and disciplinary areas and encourages the development of sensibilities and skills vital to an effective and satisfying life as an individual, a professional, and a member of society Ensures that all undergraduates receive substantial instruction and practice in general expository writing and speaking and the forms of discourse common to their professional fields. General Institute Requirements (GIRs) Note An opprtunity to set up and carry out experiments dealing with phenomena of the natural world Broaden and deepen the educational foundation in basic service Restricted Electives in Science & Technology (REST) (after the first year program) Departmental Program Seasonal Activity Required Subjects Unrestricted Electives MIT students can take arranged-unit subjects (such as UROP, Special Studies, Research, Internship, Co-op, Independent Summer session Study, Thesis Preparation, or Thesis) during the Summer Session by prior arrangement with a faculty member Students may pursue their own interests, including thesis research and preparation for qualifying exams. They also may IAP ( Independent Activities lead or participate in special activities during this four-week Period) period. This period providew students with opportunities to investigate different fields. Concourse Program Learning Community Program (Alternates for the First Year) Include subjects that also satisfy the GIRs) Retricted Electives A student who chooses the Concourse Program becomes a member of a group of about 60 freshmen working with a team of faculty members in a yearlong program of study which covers most of the first year General Institute Requirements. Ten-Week Summer Term; eg., June 9 (Mon.) – August 19 (Tues.) in 2003 4-week term in Januray, 12units maximum A regular part of the MIT curriculum, operating under the aegis of the School of Engineering The ESG is primarily, but not exclusively geared toward first year students. Experimental Study Group (ESG) The ESG Program offers students the opportunity to participate in small, discussion-oriented classes and seminars, study groups, hands-on labs, and independent study.Each year, about 50 freshmen, 15 sophomores, 10 staff members, and 20 upperclass instructors (who have been in ESG as freshmen) participatein the program. Media Arts and Sciences (MAS) Freshman Program MAS offers a special freshman program emphasizing research at Part of the School of MIT's internationally known Media Laboratory. Instructors Architecture and Planning, connect research topics in the Media Laboratory to core physics housed in the Media Laboratory and chemistry subjects, and students learn firsthand how research is carried out. Up to 24 freshmen in the MAS Freshman Program are introduced to the learning-byapprenticeship mode that characterizes MAS Terrascope Terrascope, the newest of MIT's learning communities for firstyear students, balances the lecture/problem set learning of introductory (or "core") science subjects with studies of complex, real-world problems that require innovative solutions drawn from a variety of disciplines. The program is based on the idea that our Earth system (see http://web.mit.edu/esi/) provides a valuable context for learning basic science and engineering Engineering Internship Program It combines traditional on campus academic programs with off campus work experience in industry and government. is designed principally as a joint undergraduate and graduate program that leads to the simultaneous award of the S.B. and S.M. degrees in an engineering department upon successful completion of all degree requirements. (Similar to the VI-A Internship Program in the Dept of Elect. Eng. and Comp. Science.) Depts of Aeronautics and Astronautics (XVI-C), Civil and Environmental Eng. (I), Materials Sci. and Eng. (III-B), Mechanical Eng. (II-B), Nuclear Eng. (XXII-A), and Ocean Eng. (XIII-C). Undergraduate Practice Opportunities Program (UPOP) This new innovative program provides students an opportunity to develop engineering and business skills while working in industry, non-profit organizations, or government agencies. UPOP consists of three parts: 1) an intensive one week engineering practice workshop offered during IAP, 2) 10-12 weeks of summer employment, and a written report and 3) oral presentation in the fall. Students also receive academic credit in this program. Sponsored by the School of Engineering and Open to all School of Engineering sophomores Program Sponsored by School of Engineering MIT Curriculum (Undergraudate): Number of Subjects Note1: The table is a collection of extracts from MIT Web site information. For precise and detail information, please refer to appropriate MIT Web pages. Program First Year Physical Education Requirement 2ptsX4classes (1CI in 1stY) Humanities, Arts & Social Sciences (HASS) Second Year Third Year Fourth Year Number of Subjects Subject(s) Unit Value --- --- --- --- 8 PE points plus the swim test 8 9 or 12 for each subject 3 from different HASS-D (Distribution) subjects 3-4 HASS-C (Concentration) subjects Total minimum 8 HASSs General Institute Requirements Communication Requirement (CI) Science Core Subjects CI-H/HW **Note1 CI-H CI-M (Major) CI-M (Major) 4 9 or 12 for each subject Biology *Note2 --- --- --- 1 12 Calculus *Note2 --- --- --- 2 12 for each subject --- --- --- 1 12 --- --- --- 2 12 for each subject --- --- 1 or 2 for a total of 12 units 6 or 12 for each subject --- 2 9 or 12 for each subject Chemistry Physics Laboratory (12 units total) Departmental Program *Note2 12unit-sub X1 or 6unit-sub x2 Restricted Electives in Science & Technology (REST) * Note3 Required Subjects * Note3 Retricted Electives * Note3 Unrestricted Electives * Note3 2 different area REST subjects (inlude subjects that also satisfy the GIRs) * Note 1: Online (WWW) Freshman Essay Evaluation (FEE) test score lets a student select CI subjects to be taken * Note 2: Depending upon the Advanced Placement (AP), GCE "A" Level and International Baccalaureate (IB) Credit * Note 3: Meeting some requrements may let students take departmental subjects. Note 4: Double major cases are not shown. Note 5: Some GIRs selections are connected with or done under the Departmental Program. Note 6: No specific information on Summer Session, IAP (Independent Activities Period) is shown. HASS Subjects (2003-2004) This category consists of subjects devoted to the interpretation of texts, of literary traditions, and of genres. Category 1: Literary and Textual Studies Category 2: Language, Thought, and Value Category 3: Visual and Performing Arts HASS-D (Distribu -tion) Category 4: Cultural and Social Studies Category 5: Historical Studies HASS-C (Concentration) Fields 21F.020J After Columbus: Literature of Exploration, Exile, and Cultural Contact [21L.007J] 21F.022J International Women's Voices [SP.461J] 21F.311 Introduction to French Culture 21F.412 Introduction to German Literature 21F.716 Introduction to Contemporary Hispanic Literature 21L.003 Introduction to Fiction 21L.004 Major Poets 21L.006 American Literature 21L.009 Shakespeare 21L.012 Forms of Western Narrative 21L.421 Comedy 21W.735 Writing and Reading the Essay Subjects in this category focus on the development of fundamental philosophical, conceptual, and moral issues, and stress careful analytical thinking and rigorous argumentation. 21L.001 Foundations of Western Culture I: Homer to Dante 21L.002 Foundations of Western Culture II: Renaissance to Modernity 21L.448J Darwin and Design [21W.739J] 21W.747 Rhetoric 24.00 Problems of Philosophy 24.02 What is the Best Way to Live? 24.03 Relativism, Reason, and Reality 24.04J Justice [17.01J] 24.10J Thinking about Life: Philosophical Problems in Evolution and Development [STS.004J] STS.011 American Science: Ethical Conflicts and Political Choices Subjects in this category are drawn from music, the visual arts, drama, and film. Some are historical and analytical; others are more directly concerned with the creation of art. 4.301 Introduction to the Visual Arts 4.601 Introduction to Art History 4.602 Modern Art and Mass Culture 4.605 Introduction to the History and Theory of Architecture 4.614 Religious Architecture and Islamic Cultures 21L.005 Introduction to Drama 21L.011 The Film Experience 21M.011 Introduction to Western Music 21M.026 Jazz 21M.030 Introduction to World Music 21M.301 Harmony and Counterpoint I 21M.611 Foundations of Theater Practice 21M.621 Theater and Cultural Diversity in the U.S. 21M.670J Traditions in American Concert Dance: Gender and Autobiography [SP.591J] Subjects in this category study human societies by examining forms of social, cultural, economic, political, and religious organization and behavior. 3.986 The Human Past: Introduction to Archaeology 9.00 Introduction to Psychology 11.002J Fundamentals of Public Policy [17.30J] 11.020 Poverty, Public Policy, and Controversy 14.63 Labor in Industrial Society 14.72 Capitalism and Its Critics 17.20 Introduction to the American Political Process 17.32 Environmental Politics and Policy 17.40 American Foreign Policy: Past, Present, Future 17.53 Democratization in Asia, Africa, and Latin America 17.55J Introduction to Latin American Studies [21A.224J, 21F.084J] 17.57J Soviet Politics and Society, 1917-1991 [21H.467J] 21A.100 Introduction to Anthropology 21A.109 Understanding Culture 21A.230J The Contemporary American Family [SP.456J] 21H.150J Introduction to Asian American Studies: Literature, Culture, and Historical Experience [21F.043J] 21L.015 Introduction to Media Studies SP.401 Introduction to Women's Studies Subjects in this category study the development of peoples, institutions, or countries over time. 21A.220 The Conquest of America 21H.102 The Emergence of Modern America, 1865 to the Present 21H.104J Riots, Strikes, and Conspiracies in American History [11.015J] 21H.105 American Classics 21H.301 The Ancient World: Greece 21H.302 The Ancient World: Rome 21H.416J Medieval Economic History in Comparative Perspective [14.70J] 21H.421 Introduction to Environmental History 21H.433 The Age of Reason: Europe in the18th and 19th Centuries 21H.504 East Asia in the World, 1500-2000 A.D. 21H.523 Emergence of the Modern Japanese State, 1800-1952 21H.601 Islam, the Middle East, and the West 21H.912 The World Since 1492 21W.746 Humanistic Perspectives on Medicine: From Ancient Greece to Modern America STS.001 Technology in American History STS.002 Toward the Scientific Revolution STS.003 The Rise of Modern Science American Studies Ancient and Medieval Studies Anthropology Archaeology and Archaeological Science Black Studies Comparative Media Studies Studies in the Constitutional Tradition East Asian Studies Economics Ethnic Studies Foreign Languages and Literatures Chinese, ESL, French, German, Japanese, Spanish History History of Art and Architecture Labor in Industrial Society Latin American Studies Linguistics Literature Middle Eastern Studies Music Philosophy Political Science Psychology Russian Studies Studies in International Literature and Cultures (SILC) Science, Technology, and Society (STS) Theater Arts Urban Studies Visual Arts and Design Women's Studies Writing CI Subjects (2003-2004) 9.00 Introduction to Psychology 11.002J Fundamentals of Public Policy 11.020 Poverty, Public Policy, and Controversy 17.20 Introduction to the American Political Process 17.31J Science, Technology, and Public Policy 17.40 American Foreign Policy: Past, Present, and Future 17.471 American National Security Policy 17.55J Introduction to Latin American Studies 21A.219J Law and Society 21F.020J After Columbus: Literature of Exploration, Exile and Cultural Contact 21F.035 Topics in Culture and Globalization 21F.041 Topics in South Asian Literature 21F.056 Visual Histories: German Cinema 1945 to Present 21F.059 Paradigms of European Thought and Culture 21F.222 Expository Writing for Bilingual Students 21F.226 Advanced Workshop in Writing for Science and Engineering: CI-H/ CI-HW CI-M HASS-D [17.30J] HASS-D HASS-D HASS-D [STS.082J] HASS-D [21A.430J, 21F.084J] HASS-D [11.163J, 17.249J] [21L.007J] HASS-D HASS-D CI-HW ESL 21H.104J Riots, Strikes, and Conspiracies in American History [11.015J] HASS-D 21H.105 American Classics 21L.001 Foundations of Western Culture I: Homer to Dante 21L.003 Introduction to Fiction 21L.004 Major Poets 21L.005 Introduction to Drama 21L.006 American Literature 21L.009 Shakespeare 21L.010J Writing About Literature 21L.011 The Film Experience 21L.421 Comedy 21L.015 Introduction to Media Studies 21L.421 Comedy 21L.448J Darwin and Design 21L.455 Classical Literature 21L.472 Major European Novels 21L.501 The American Novel 21M.030 Introduction to World Music 21M.230 Vivaldi, Bach, and Handel 21M.710 Script Analysis 21W.730 Expository Writing 21W.731 Writing and Experience 21W.732 Introduction to Technical Communication 21W.735 Writing and Reading the Essay 21W.747 Rhetoric 21W.778 Science Journalism 24.00 Problems of Philosophy 24.04J Justice 24.900 Introduction to Linguistics SP.401 Introduction to Women's Studies STS.002 Toward the Scientific Revolution HASS-D HASS-D HASS-D HASS-D HASS-D HASS-D HASS-D [21W.734J] CI-HW HASS-D HASS-D HASS-D HASS-D [21W.739J] HASS-D HASS-D CI-HW CI-HW CI-HW HASS-D HASS-D HASS-D [17.01J] HASS-D HASS-D HASS-D HASS-D Shown in the respective departmental subject lists REST Subjects (2003-2004) Restricted Electives in Science & Technology (REST) 1.00 Introduction to Computers and Engineering Problem Solving 1.018J Fundamentals of Ecology [7.30J] 1.034 Introduction to Engineering Geology 1.050 Solid Mechanics 2.001 Mechanics and Materials I 2.003 Modeling Dynamics and Control 2.005 Thermal-Fluids Engineering I 3.00 Thermodynamics of Materials 3.10 Chemical Physics of Materials 3.13 Structure of Materials 4.42J Fundamentals of Energy in Buildings [1.044J, 2.66J] 4.440 Basic Structural Theory 5.07 Biological Chemistry I 5.12 Organic Chemistry I 5.60 Thermodynamics and Kinetics 5.61 Physical Chemistry 6.001 Structure and Interpretation of Computer Programs 6.002 Circuits and Electronics 6.041 Probabilistic Systems Analysis 6.071 Introduction to Electronics 7.03 Genetics 7.05 General Biochemistry 8.03 Physics III 8.04 Quantum Physics I 8.20 Introduction to Special Relativity 8.282J Introduction to Astronomy [12.402J] 8.286 The Early Universe 9.01 Neuroscience and Behavior 10.301 Fluid Mechanics 12.001 Introduction to Geology 12.002 Physics and Chemistry of the Solid Earth 12.003 Physics of the Atmosphere and Ocean 12.004 Introduction to Planetary Science 12.102 Environmental Earth Science 12.400 The Solar System 13.00 Introduction to Ocean Science and Technology 14.30 Introduction to Statistical Method in Economics 16.010 Unified Engineering I 18.03 Differential Equations 18.034 Differential Equations 18.05 Introduction to Probability and Statistics 18.06 Linear Algebra 18.700 Linear Algebra 22.01 Introduction to Ionizing Radiation 22.02 Introduction to Applied Nuclear Physics Science Core and Laboratory Requirement Subjects (2003-2004) Biology 1 Biology 2 Calculus 1 Calculus 2 Calculus 3 Calculus 4 Science Calculus 5 Core Calculus 6 Subjects Chemistry 1 Chemistry 2 Chemistry 3 Physics 1 Physics 2 Physics 3 Physics 4 Laboratory Requirement 7.012&7.013 Introductory Biology Core material to exploring current areas 7.014 Introductory Biology Basic biochemistry and geneteics 18.01 Calculus I single variable calculus: 18.02 Calculus II multivariable calculus: 18.022 Calculus II multivariable calculus: 18.023 Calculus II multivariable calculus with applications: 18.01A-18.02A Calculus I and II sequence 18.013A-18.023A Calculus I and II with applications 5.111 Principles of Chemical Science 5.112 Principles of Chemical Science (a minimum of two years of high school chemistry) 3.091 Introduction to Solid State Chemistry 8.01-8.02 Physics I and II I classical mechanics & II basic phenomena 8.01L Physics I: Same as 8.01, but will finish during IAP (L = long) 8.01X- 8.02X Physics I and II Emphasizes measurement and data analysis 8.012-8.022 Physics I and II deeper level and with a more free use of mathematics 1.103 Civil Engineering Materials Laboratory (1-2-3) 1.105 Solid Mechanics Laboratory (0-3-3) 1.106 Environmental Fluid Transport Processes and Hydrology Laboratory (0-4-2) 1.107 Environmental Chemistry and Biology Laboratoy (0-4-2) 2.008 Design and Manufacturing II (3-5-4) [gives six units of laboratory credit] 2.671 Measurement and Instrumentation (2-3-7) [gives six units of laboratory credit] 2.672 Project Laboratory (1-3-2) 3.081 Materials Laboratory (2-6-7) [gives 12 units of laboratory credit] 4.411 Building Technology Laboratory (2-4-6) 5.310 Laboratory Chemistry (2-8-2 5.311 Introductory Chemical Experimentation (2-8-2) 6.101 Introductory Analog Electronics Laboratory (2-9-1) 6.111 Introductory Digital Systems Laboratory (3-7-2) 6.115 Microcomputer Project Laboratory (3-6-3) 6.121J Bioelectronics Project Laboratory (2-8-2) [HST.575J] 6.151 Semiconductor Devices Project Laboratory (0-12-0) 6.161 Modern Optics Project Laboratory (3-6-3 6.163 Strobe Project Laboratory (2-8-2) 6.182 Psychoacoustics Project Laboratory (3-6-3) 7.02 Introduction to Experimental Biology (2-8-2) [gives 12 units of laboratory credit] 8.13 Experimental Physics I (0-6-12) [gives 12 units of laboratory credit] 8.14 Experimental Physics II (0-6-12) [gives 12 units of laboratory credit] 9.02 Brain Laboratory (1-5-6) 9.50 Research in Brain and Cognitive Sciences (2-8-2) 9.63 Laboratory in Cognitive Science (3-6-3) 10.467 Polymer Science Laboratory (1-7-4) 11.188 Urban Planning and Social Science Laborator (3-6-3) 12.115 Field Geology II (0-18-0) [gives 12 units of laboratory credit] 12.119 Analytical Techniques for Studying Environmental and Geologic Samples (2-6-4 12.307 Weather and Climate Laboratory (1-4-7) 12.410J Observational Techniques of Optical Astronom [8.287J] (4-3-8) 13.017 Design of Ocean Systems I (2-4-6) [gives six units of laboratory credit] 13.018 Design of Ocean Systems II (2-4-6) [gives six units of laboratory credit] 14.33 Economic Research and Communication (3-4-5) 15.301 Managerial Psychology Laboratory (2-4-9) 16.622 Experimental Projects II (1-7-4) 17.871 Political Science Laboratory (3-6-6) 22.09 Principles of Nuclear Radiation Measurement an Protection (2-6-4) MAS.450 Holographic Imaging (3-5-4)